Global Animal Feed Plant Based Protein Isolate Market By Source (Sunflower Protein, Soybean Protein, Pea Protein, Canola Protein, Potato Protein, Others), By Form (Powder, Liquid), By Application (Poultry Feed, Aquaculture Feed, Livestock Feed, Pet Food, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Sep 2025
- Report ID: 158935
- Number of Pages: 318
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
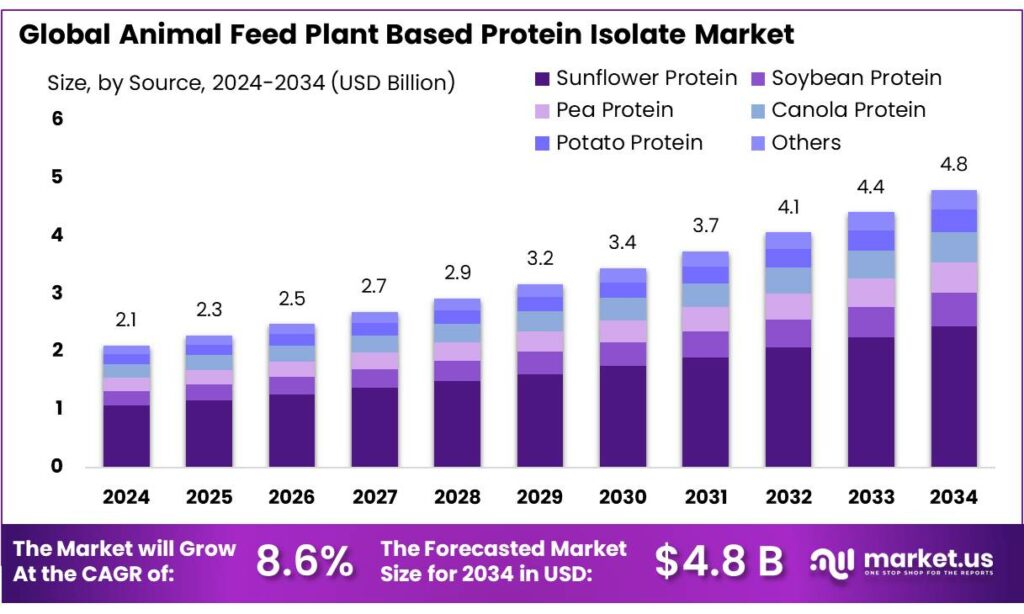
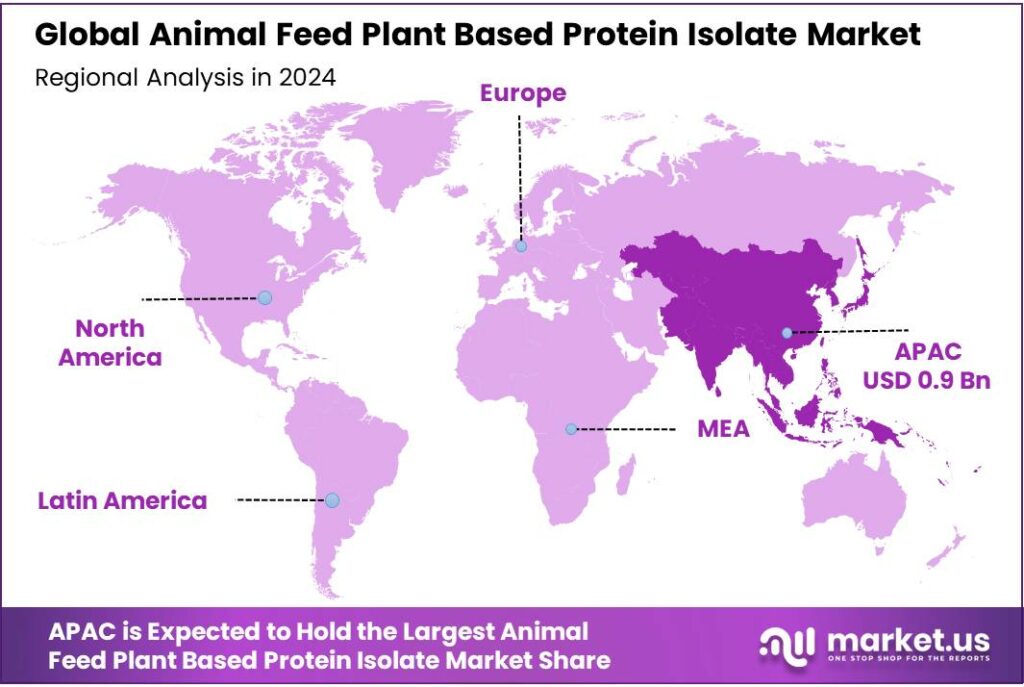
The Global Animal Feed Plant Based Protein Isolate Market size is expected to be worth around USD 4.8 Billion by 2034, from USD 2.1 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 8.6% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024 Asia Pacific held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.8% share, holding USD 0.9 Billion in revenue.
Animal‐feed plant‐based protein isolates are concentrated protein ingredients derived from plants, processed to remove much of the non-protein material, used in formulated feeds for livestock, poultry, aquaculture, etc. Compared to conventional protein sources such as fishmeal, animal by-products, or full meals/cakes, isolates offer advantages including higher purity, more consistent nutritional profiles, potential reductions in anti-nutritional factors, and often lower environmental impacts. They are especially relevant in regions facing feed protein deficits, high costs of animal proteins, or regulatory / sustainability pressures.
In terms of Animal‐feed plant‐based protein isolates, a number of global agricultural, fisheries, and food-nutritional bodies have observed mounting demand for alternatives to fishmeal and conventional protein sources, particularly in aquaculture and poultry feed.
- For example, FAO has documented that fishmeal production is under pressure globally, while demand from livestock and aquaculture is growing, making the substitution by plant-derived proteins technically viable and increasingly necessary. Studies show that in Asia, fishmeal consumption for Nile tilapia grew from about 0.8 million tonnes to 1.7 million tonnes over a period, while fish feed output increased from 40% to 60% from 2000 to 2008.
On the policy and government initiative front, multiple governments are taking steps that indirectly (or directly) support the growth of plant-based protein isolates in feed. In India, the Department of Animal Husbandry & Dairying instituted the Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF) in 2020, with a corpus of Rs. 15,000 crore, aimed at increasing private sector investment in infrastructure including animal feed plants among its eligible sectors.
The European Union has made plant protein production a policy focus: in 2023-24, EU arable crop sector produced 64 million tonnes crude protein, and EU imports of plant-based protein products amounting to 19 million tonnes crude protein signal significant external dependency.
- Additionally, data from modeling feed dry matter availability in India shows total current dry matter availability ~510.6 million tonnes, of which ~47.2 million tonnes are from concentrates (which tend to include higher protein fractions), ~319.6 million from crop residues, ~143.8 million from greens.
Key Takeaways
- Animal Feed Plant Based Protein Isolate Market size is expected to be worth around USD 4.8 Billion by 2034, from USD 2.1 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 8.6%.
- Sunflower Protein Plant Based Protein Isolate Extract held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 51.2% share.
- Powder held a dominant market position in the Animal Feed Plant Based Protein Isolate market, capturing more than an 88.1% share.
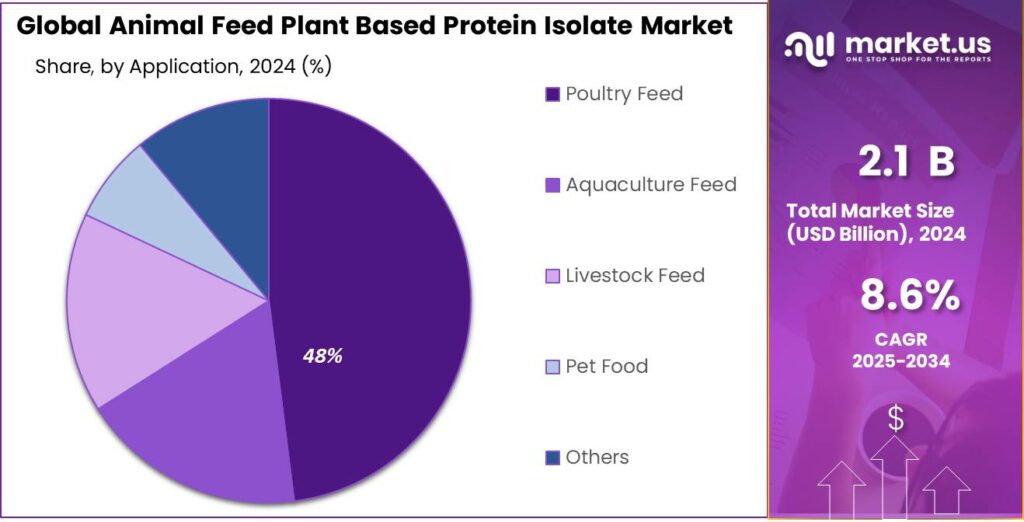
- Poultry Feed held a dominant market position in the Animal Feed Plant Based Protein Isolate market, capturing more than a 48.9% share.
- Asia Pacific region dominated the animal feed plant-based protein isolate market, holding a 43.8% share, equivalent to approximately USD 0.9 billion.
By Source Analysis
Sunflower Protein dominates with 51.2% share due to high nutritional value and digestibility
In 2024, Sunflower Protein Plant Based Protein Isolate Extract held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 51.2% share in the animal feed protein isolate segment. This leadership is attributed to its rich amino acid profile, high digestibility, and growing preference among feed manufacturers seeking sustainable and non-GMO protein sources. Sunflower protein is increasingly preferred for poultry, swine, and aquaculture feed formulations, offering both cost efficiency and nutritional benefits.
Its adoption is supported by government programs promoting sustainable agriculture and feed efficiency, encouraging the use of high-quality plant protein sources. The sector is witnessing increased processing capacity, better extraction technologies, and greater awareness of the benefits of sunflower protein in animal nutrition.
By Form Analysis
Powder form dominates with 88.1% share due to ease of handling and high shelf life
In 2024, Powder held a dominant market position in the Animal Feed Plant Based Protein Isolate market, capturing more than an 88.1% share. The widespread preference for powder form is driven by its convenience in storage, ease of blending into feed formulations, and longer shelf life compared to other forms. Powdered protein isolates offer uniformity in nutrient content, making them ideal for precise feed formulation across poultry, swine, and aquaculture industries.
Government initiatives promoting sustainable livestock feed practices and high-quality protein usage further encourage the adoption of powder isolates. Additionally, technological advancements in spray drying and micronization processes are enhancing the quality and solubility of powdered plant-based proteins, reinforcing their dominant position in the market.
By Application Analysis
Poultry Feed dominates with 48.9% share due to high protein demand and growth in poultry sector
In 2024, Poultry Feed held a dominant market position in the Animal Feed Plant Based Protein Isolate market, capturing more than a 48.9% share. The strong demand is driven by the rapid expansion of the poultry industry and the increasing need for high-quality, digestible protein to support growth, egg production, and overall poultry health. Plant-based protein isolates provide a sustainable and efficient alternative to traditional animal-based proteins, making them highly preferred in poultry nutrition.
Government programs supporting sustainable livestock practices and feed fortification further encourage the use of plant-based protein isolates in poultry diets. With advancements in protein extraction technologies and better integration into feed formulations, poultry feed applications remain a key driver for the growth of plant-based protein isolates in the animal feed sector.
Key Market Segments
By Source
- Sunflower Protein
- Soybean Protein
- Pea Protein
- Canola Protein
- Potato Protein
- Others
By Form
- Powder
- Liquid
By Application
- Poultry Feed
- Broilers
- Layers
- Turkey
- Aquaculture Feed
- Fish
- Crustaceans
- Mollusks
- Livestock Feed
- Swine
- Cattle (Beef & Dairy)
- Sheep & Goats
- Pet Food
- Dogs
- Cats
- Others
Emerging Trends
Growing Shift from Fishmeal to Plant Protein in Aquafeeds
One of the strongest trends right now is that aquaculture (fish farming) is increasingly replacing fishmeal and other marine protein sources with plant-based protein isolates or concentrates. This shift is being driven by sustainability concerns, rising costs of fishmeal, and improvement in plant protein quality (better digestibility, fewer antinutritional factors). It is a trend with big implications for how feed is produced, how animals are fed, and for the people who depend on aquaculture for income and food.
- Recent scientific reviews show what kind of replacement is technically viable. For example, a 2024 review found that soybean meal can replace about 25 percent of fishmeal in certain fish diets without severely harming growth or feed conversion performance; seaweeds about 10 percent, insect-based ingredients around 50 percent in controlled studies.
In India, government and regulatory bodies are responding to this trend. The “Smart Protein in India” report notes that states like Maharashtra aim to build “smart protein” hubs: manufacturing, farmer linkages, and processing facilities that support plant-based protein value chains. Such hubs are meant to ensure that raw materials (legumes, pulses, other protein crops) are processed locally into isolates or concentrates, so that feed makers can obtain better quality plant protein more reliably, reducing dependency on imported fishmeal or high cost marine proteins.
Drivers
Rising Feed & Fodder Deficit Pressures Farmers Toward Better Protein Inputs
One of the strongest forces pushing plant-based protein isolates into animal feed is the growing shortage of quality feed and fodder—green fodder, dry fodder, and concentrate (protein) feeds—in many livestock-producing regions. When farmers cannot reliably get enough conventional feed, they look for alternative protein sources that can help maintain animal growth, health, and productivity. This deficit makes plant protein isolates attractive.
- As of 2024/25, India suffers shortages of 11.24% for green fodder, 23.4% for dry fodder, and 28.9% for concentrate feed ingredients. Because concentrates are typically the richest in protein, such a large gap pushes the feed industry to explore more concentrated protein options, especially from plants.
- Another study by the Indian government (“Assessment of Livestock Feed and Fodder: An All India Study”) reports that cooperatives produce about 2.5 million tonnes per year of feed, but this amount is far below what is needed, and the deficit has resulted in steep feed prices in many parts of the country.
These feed deficits aren’t restricted just to India. Globally, animal protein demand is rising fast. Meat production worldwide has more than tripled in the last fifty years, exceeding 350 million tonnes each year in recent times. (OurWorldinData, based on FAO data). Coupled with increasing demand from aquaculture, poultry, and dairy sectors, this growth amplifies pressure on feed resources. When conventional protein sources become scarce or expensive, plant isolates become more viable.
Restraints
Anti-Nutritional Factors & Digestibility Limitations
One of the biggest barriers holding back greater use of plant protein isolates in animal feed is the presence of anti-nutritional factors (ANFs) in many plant sources, and how they lower digestibility & animal performance unless properly processed. Because animals—especially non-ruminants like poultry and fish—depend heavily on efficient digestion and absorption of amino acids, minerals, and other nutrients, even small amounts of ANFs can create large losses in growth, health, feed conversion, or increase costs due to added processing or supplementation.
Plants naturally contain compounds such as phytic acid, tannins, protease inhibitors, lectins, saponins, amylase inhibitors etc., which interfere with nutrient absorption in various ways. For instance, phytic acid binds minerals like zinc, iron or calcium, making them unavailable; trypsin inhibitors reduce the activity of digestive enzymes; lectins may irritate gut lining or reduce nutrient uptake.
- An example comes from pea protein isolates. In a GRAS notification by the FDA for “Roquette’s Pea Protein Isolate”, regular unselected peas have phytates in the range 0.72-1.23% (of dry weight) and trypsin inhibitor activity of 6-15 TIU/mg sample. After processing (cultivar selection + extraction + heat), the pea protein isolate reduces trypsin inhibitor activity to <2.5 TIU/mg, and lower phytate levels, plus lower tannin content.
Governments and regulatory bodies are aware of these issues. For instance, in India the FSSAI (Food Safety and Standards Authority of India) has a draft regulation that requires legumes, pulses, oil seed flours / protein products (including isolates) to be processed “to reduce, as much as possible, the anti-nutritional factors normally present such as phytates, lectins (haemagglutinins), trypsin and chymotrypsin inhibitors”.
Opportunity
Expanding Pulses Production & Self-Reliance Opens Path for More Plant-Based Protein Isolates
A big growth opportunity for plant-based protein isolates in animal feed lies in the expanding pulses production in countries like India, under strong government support, with the goal of reducing import dependence and boosting domestic supply. Pulses (legumes) are naturally rich in protein; greater pulse production means more raw material available for processing into isolates. This raw material availability can lower costs, improve supply stability, and allow feed producers to scale up plant‐based protein isolates.
- In India, pulses production has been growing steadily. In 2022-23, pulse output reached 26.06 million tonnes (MT). Recognizing that this still does not completely meet domestic consumption and feed needs, the government has set a roadmap via NITI Aayog to increase pulses supply. Under business-as-usual conditions, supply is projected to reach 30.59 MT by 2030, rising to 45.79 MT by 2047. With strategic interventions, the target is even higher: approximately 48.44 MT by 2030 and 63.64 MT by 2047.
For animal feed processors aiming to use plant protein isolates, this ramp-up in pulses production is significant. More pulses means more raw protein material (for example, from crops like pigeon pea, black gram, lentils etc.). It reduces reliance on imports and raises opportunities to develop milled, concentrated protein isolates domestically. When supply is reliable, processors can invest in infrastructure (mills, extractors, purification units) with more confidence.
Another government initiative that supports this opportunity is the Production-Linked Incentive Scheme for Food Processing Industry (PLISFPI) in India. This scheme offers incentives to food processors to increase value addition, improve supply chains, and processing capacities. Under PLISFPI, an outgo on incentive is estimated at ₹10,790 crore, with projected increase in food processing sales of ₹1,20,267 crore over six years.
Regional Insights
Asia Pacific leads with 43.8% share, valued at USD 0.9 billion in 2024, driven by rising demand for sustainable animal feed solutions
In 2024, the Asia Pacific region dominated the animal feed plant-based protein isolate market, holding a 43.8% share, equivalent to approximately USD 0.9 billion. This leadership is attributed to the region’s robust agricultural infrastructure, increasing livestock production, and a growing shift towards plant-based protein sources in animal nutrition. Countries like China, India, Japan, and South Korea are at the forefront, driven by both domestic consumption and export opportunities.
For instance, China’s “Green Agriculture” policy encourages the adoption of environmentally friendly farming practices, including the use of plant-based feed ingredients. Similarly, India’s National Livestock Mission aims to enhance livestock productivity through improved feeding practices, indirectly boosting the demand for plant-based protein isolates.
Technological advancements in protein extraction and processing are also contributing to the market’s expansion. Innovations in enzyme technology and fermentation processes are improving the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of producing plant-based protein isolates, making them more accessible to feed manufacturers.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Scoular, founded in 1892 and headquartered in Omaha, Nebraska, is a major agriculture supply chain and ingredient company. It trades over one billion bushels of grain annually and has more than 100 storage, handling, and processing facilities. Scoular offers customized soy protein isolates for animal feed and pet‐food applications, with features like ≥ 90 % nutritional protein content, non-GMO sourcing, gluten-free, plus good functional properties (e.g. water‐holding, emulsification). Their vertically integrated supply chain helps ensure consistent quality and supply.
Cargill is a global agribusiness giant with a broad portfolio including plant proteins. In its plant proteins offering, Cargill supplies pea protein, wheat protein, soy, etc., with protein contents often in the 50-80 % range for some functional isolates. Their proteins are used in everything from beverages, bakery, plant-based dairy alternatives, to hybrid dairy/animal protein blend products. Cargill operates globally and emphasizes label-friendly, non-GMO options, mild flavors, emulsification, solubility, and texture.
Glanbia PLC, headquartered in Ireland, is a global nutrition company with strong capabilities in both dairy-based and plant-based proteins. Their plant-based protein range includes pea, flaxseed, chia, and others, functionally optimized for texture, flavour, solubility, and nutrition. On the dairy side, they also produce whey protein isolates with around 90 % protein content, used in supplements, infant nutrition, and performance nutrition. Glanbia serves over 130 countries, employs ~5,500 people and generates multi-billion dollar revenues.
Top Key Players Outlook
- The Scoular Company
- Cargill, Incorporated
- Hamlet Protein
- Glanbia PLC
- Ingredion
- A&B Ingredients Inc.
- HL Agro Products Pvt. Ltd.
- Roquette Freres
- ADM
- Emsland Group
Recent Industry Developments
In FY2024-25, The Scoular Company achieved about US$7.3 billion in total sales, of which around US$1.6 billion came from its feed ingredients & proteins business, which includes plant-based protein meals and plant-derived feed inputs.
In late 2024, Ingredion entered into a strategic partnership with Lantmännen (Europe) involving an investment of over €100 million to build a state-of-the-art factory in Sweden for yellow pea protein isolates.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 2.1 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 4.8 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 8.6% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Source (Sunflower Protein, Soybean Protein, Pea Protein, Canola Protein, Potato Protein, Others), By Form (Powder, Liquid), By Application (Poultry Feed, Aquaculture Feed, Livestock Feed, Pet Food, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape The Scoular Company, Cargill, Incorporated, Hamlet Protein, Glanbia PLC, Ingredion, A&B Ingredients Inc., HL Agro Products Pvt. Ltd., Roquette Freres, ADM, Emsland Group Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Animal Feed Plant Based Protein Isolate MarketPublished date: Sep 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Animal Feed Plant Based Protein Isolate MarketPublished date: Sep 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- The Scoular Company
- Cargill, Incorporated
- Hamlet Protein
- Glanbia PLC
- Ingredion
- A&B Ingredients Inc.
- HL Agro Products Pvt. Ltd.
- Roquette Freres
- ADM
- Emsland Group










