Global Ammonia Market By Form (Aqueous, Anhydrous), By Type (Grey/Brown, Blue, Green, Turquoise), By Feedstock (Natural Gas, Coal, Oil, Hydrogen, Others), By Application(Fertilizers, Refrigerants, Transportation, Textile, Power Generation, Others), By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends, and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Jan 2025
- Report ID: 18440
- Number of Pages: 223
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
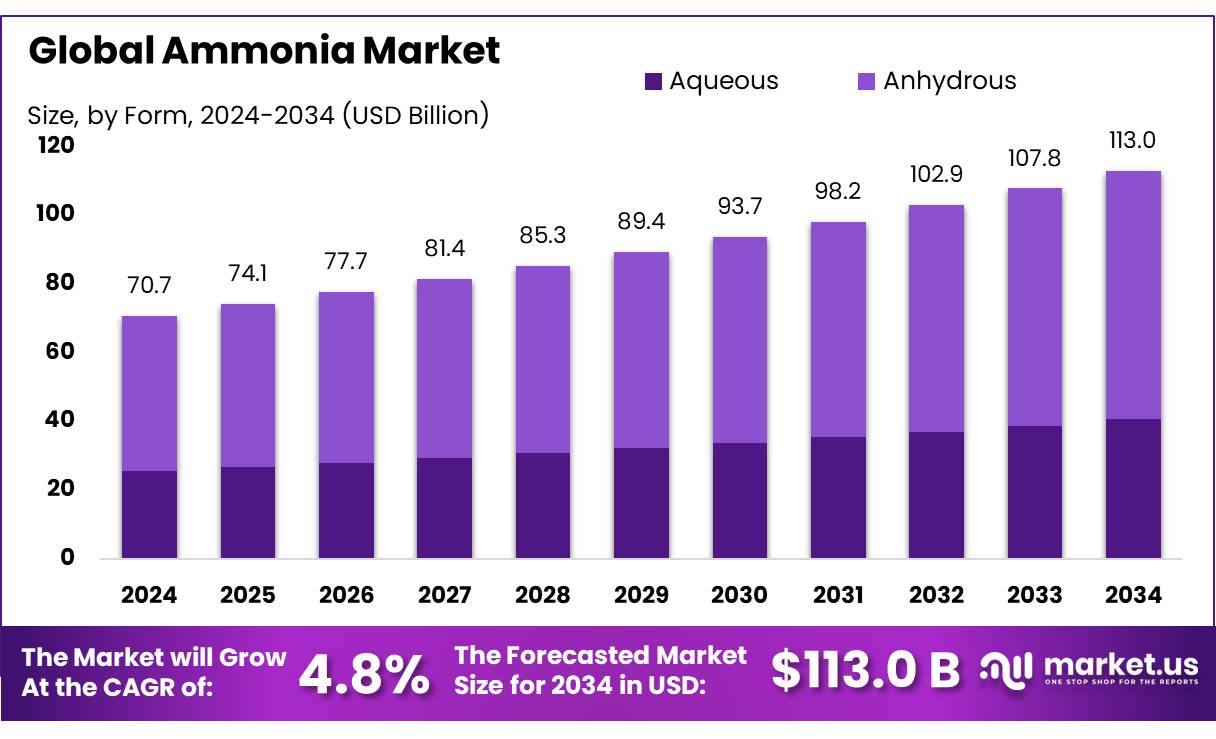
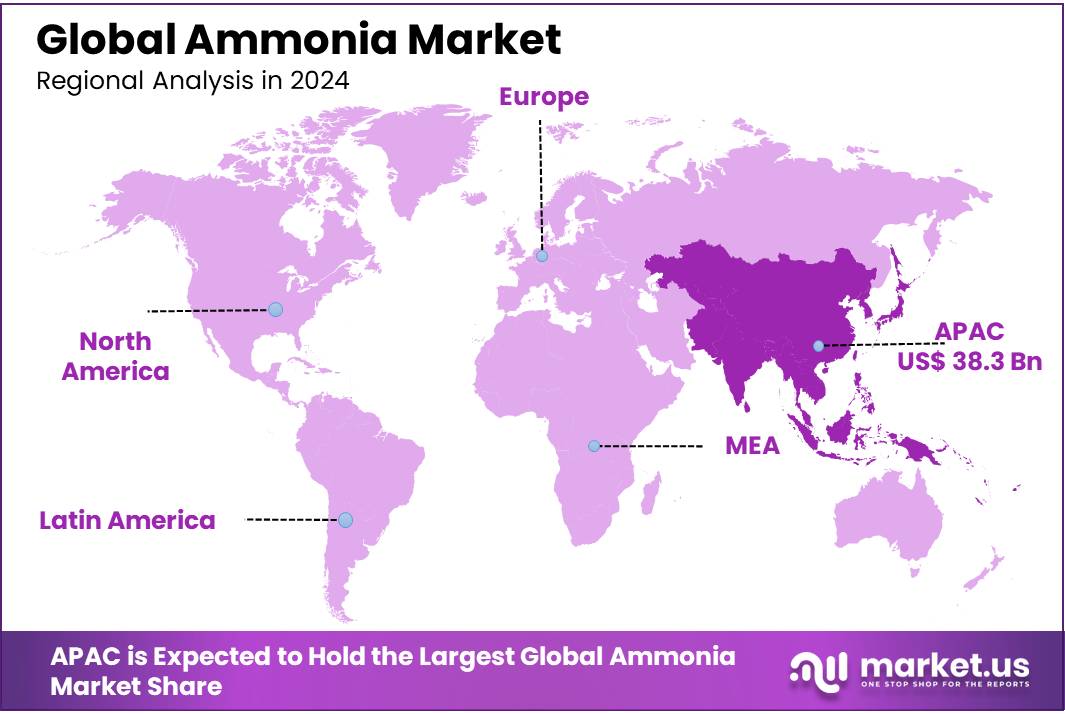
The Global Ammonia Market size is expected to be worth around USD 113.0 Billion by 2034, from USD 70.7 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 4.8% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. Asia Pacific dominated a 54.20% market share in 2024 and held USD 38.3 Billion in revenue from the Ammonia Market.
The global ammonia market is a crucial component of the chemical industry, primarily driven by its extensive applications in fertilizers, industrial chemicals, refrigeration, and emerging clean energy solutions. Ammonia (NH₃), a colorless gas with a pungent odor, serves as a primary nitrogen source in fertilizers, accounting for nearly 80% of global ammonia consumption. This demand is fueled by the need for higher agricultural productivity to support a growing global population, increasing investments in sustainable farming, and the expansion of ammonia’s role in alternative energy applications.
The ammonia industry operates under a dynamic demand-supply balance, dictated by agricultural requirements, industrial chemical production, and new energy applications. Fertilizer production, especially urea, ammonium nitrate, and ammonium sulfate, dominates the ammonia market. Key production hubs are concentrated in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific, with China leading as the largest producer, contributing nearly 30% of global ammonia output.
Several factors are driving the ammonia market’s expansion, including rising global food demand and the corresponding need for increased agricultural efficiency. As the world’s population is projected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, the demand for high-yield fertilizers continues to rise, solidifying ammonia’s essential role in the agricultural sector. Additionally, ammonia is emerging as a clean energy carrier, particularly in hydrogen storage and transportation.
Beyond agriculture and energy, ammonia finds widespread industrial use in plastics, pharmaceuticals, textiles, and explosives, contributing to stable demand across multiple sectors. market growth is expected to be driven by the advancement of green ammonia, which eliminates carbon emissions through renewable energy-powered electrolysis. Governments and private enterprises are investing over USD 50 billion in sustainable ammonia projects, supporting large-scale green ammonia production facilities.
The maritime sector is also exploring ammonia as a zero-carbon alternative fuel for ships, expanding its market potential in global decarbonization efforts. Innovations in ammonia cracking and hydrogen conversion technology are expected to accelerate adoption in the clean energy transition. Additionally, stricter environmental regulations and increasing consumer awareness of sustainable agricultural and industrial practices are pushing companies toward greener solutions.
Key Takeaways
- Ammonia Market size is expected to be worth around USD 113.0 Billion by 2034, from USD 70.7 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 4.8%.
- Anhydrous ammonia held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 64.50% share of the ammonia market.
- Grey/Brown ammonia held a dominant market position, capturing more than 72.20% of the overall market share.
- Natural Gas held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 65.50% share of the ammonia market.
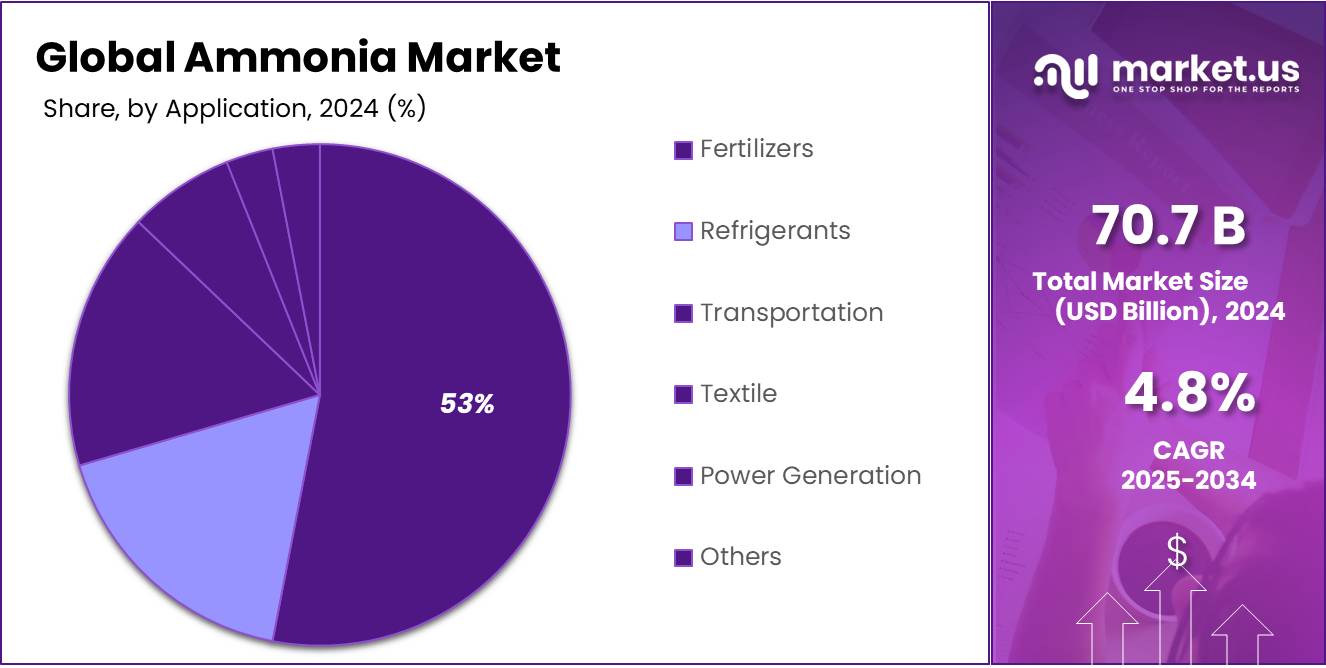
- Fertilizers held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 53.40% share of the ammonia market.
- APAC held a commanding share of 54.20%, valued at approximately USD 38.3 billion.
By Form Analysis
In 2024, Anhydrous ammonia held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 64.50% share of the ammonia market. This segment’s growth is driven primarily by its widespread use in agricultural applications, particularly in fertilizer production. Anhydrous ammonia is a preferred choice due to its high nitrogen content, which makes it highly effective as a fertilizer. The increasing demand for agricultural products, coupled with the need to enhance soil productivity, continues to fuel the growth of this segment.
aqueous ammonia, although growing, occupies a smaller share of the market. In 2024, aqueous ammonia contributed significantly to the industrial sector, particularly in applications such as water treatment, refrigeration, and certain chemical processes. Its use in these areas has seen gradual growth, driven by stricter environmental regulations and the push for more sustainable practices in various industries.
By Type
In 2024, Grey/Brown ammonia held a dominant market position, capturing more than 72.20% of the overall market share. This segment’s stronghold is largely attributed to its widespread use in industrial applications, particularly in agriculture and manufacturing, where it is primarily utilized as a refrigerant and fertilizer. Grey/Brown ammonia is produced using conventional methods, relying on fossil fuels, which makes it the most cost-effective option compared to newer, more environmentally focused alternatives.
The Blue ammonia segment is expected to see significant growth. Blue ammonia, which is produced through a process that includes carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies, is becoming more attractive as industries and governments alike strive to reduce carbon footprints. While still a small segment in 2024, Blue ammonia is projected to capture an increasing share in the coming years, driven by stricter environmental regulations and rising sustainability initiatives across various industries.
Green ammonia, produced using renewable energy sources like wind or solar to power the electrolysis of water for hydrogen production, is still in the early stages of commercialization but is expected to gain traction by 2025. Although its market share remains limited in 2024, it has garnered considerable attention as a potential game-changer in sustainable ammonia production.
Turquoise ammonia, which is generated through the pyrolysis of methane to produce hydrogen, is a newer entrant in the market. While still in the research and development phase, it shows promise as a cleaner alternative to Grey/Brown ammonia with lower carbon emissions.
By Feedstock
In 2024, Natural Gas held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 65.50% share of the ammonia market. This feedstock is the most widely used in ammonia production due to its efficiency and lower carbon footprint compared to other sources. The process of producing ammonia from natural gas, primarily through the Haber-Bosch method, is well-established, cost-effective, and energy-efficient. With the growing demand for fertilizers and other ammonia-based products, the natural gas feedstock segment is expected to continue its growth trajectory, particularly as the global agricultural industry expands.
Coal, while not as dominant as natural gas, contributes a notable portion of ammonia production. This feedstock accounts for a smaller share of the market but is still used in regions where natural gas supply is limited or expensive. In 2024, the coal segment is projected to maintain a steady, though slightly declining, share as companies move toward more sustainable production methods.
Oil, another traditional feedstock, has seen a slight decrease in its role in ammonia production over the years. In 2024, the oil-based ammonia segment is expected to maintain a minor share, primarily in areas where oil is more readily available or economically viable. However, as natural gas and hydrogen become more attractive options, the reliance on oil is expected to decrease further in the coming years.
Hydrogen, while still a small player in the market, is expected to see growth in ammonia production, especially with the increasing focus on clean and sustainable production methods.
By Application Analysis
In 2024, Fertilizers held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 53.40% share of the ammonia market. Ammonia is a key component in nitrogen-based fertilizers, which are essential for global food production. The growing demand for food, driven by population growth and increasing agricultural productivity needs, continues to be the primary factor driving the dominance of ammonia in the fertilizer segment.
Refrigerants, while a smaller market segment, are steadily growing due to ammonia’s use in industrial refrigeration systems. In 2024, the refrigerant segment is projected to contribute a significant share to the ammonia market. Ammonia is a natural refrigerant, which is gaining favor due to its low environmental impact compared to synthetic refrigerants.
The transportation sector accounts for a smaller portion of the ammonia market, but it is gradually expanding. Ammonia is used in certain transportation systems, particularly in the form of compressed or liquid ammonia, as an alternative fuel. This sector is projected to see moderate growth in 2024 and 2025, driven by the push for cleaner and more sustainable fuel alternatives in the transport industry. However, the share of ammonia in transportation will remain limited compared to fertilizers and refrigerants.
The textile industry, which uses ammonia in dyeing processes, also contributes to the ammonia market. In 2024, the textile segment is expected to hold a modest share, with steady growth anticipated as ammonia’s role in textile manufacturing remains vital. The global demand for textiles continues to rise, and as the industry becomes more focused on efficiency and sustainability, ammonia will continue to play a significant role in this sector’s operations.
Power generation remains a niche application for ammonia, with limited but steady demand in specific sectors. Ammonia is used in certain power plants for NOx control and is being explored as part of clean energy solutions like ammonia-based fuel cells. This segment is expected to grow slowly but steadily in 2024 and beyond, as renewable energy solutions gain more traction and power generation systems become more eco-friendly.
Key Market Segments
By Form
- Aqueous
- Anhydrous
By Type
- Grey/Brown
- Blue
- Green
- Turquoise
By Feedstock
- Natural Gas
- Coal
- Oil
- Hydrogen
- Others
By Application
- Fertilizers
- Refrigerants
- Transportation
- Textile
- Power Generation
- Others
Driving Factors
Growing Global Demand for Food and Agricultural Products
As the world’s population continues to grow, there is an ever-increasing need to produce more food to meet the demands of consumers. According to the United Nations, the global population is expected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, which means agricultural production must increase by approximately 70% to feed everyone adequately. This increase in food demand is one of the primary reasons ammonia, especially in the form of nitrogen-based fertilizers, plays such a critical role in modern agriculture.
Ammonia-based fertilizers, particularly nitrogen fertilizers, are vital to improving crop yields. Nitrogen is one of the essential nutrients that plants need to grow, and ammonia is one of the most efficient ways to provide this nutrient. It helps plants grow quickly and strongly, making it one of the most widely used fertilizers in the world. The need for increased agricultural productivity is becoming even more pressing as arable land per person decreases due to urbanization and environmental changes.
According to the International Fertilizer Association (IFA), nitrogen fertilizers, including ammonia, account for around 50-60% of the world’s total fertilizer consumption. In 2024, this proportion is expected to remain significant as the agricultural sector continues to rely heavily on these fertilizers to increase crop production and ensure food security. With the demand for food expected to rise by 70% by 2050, ammonia production will be closely tied to these needs. The IFA also reports that in 2020, global nitrogen fertilizer consumption reached approximately 116 million metric tons, highlighting the critical role that ammonia plays in global food production
In the United States, ammonia production and consumption are also integral to maintaining agricultural output. The U.S. is one of the largest producers of ammonia in the world, and much of the ammonia produced is used for fertilizers that support its robust agricultural industry. According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), in 2023, over 13 million tons of ammonia were applied to crops, mainly for corn, wheat, and soybean production, underscoring the crucial role ammonia plays in ensuring crop health and yield.
This rising global demand for food and the increasing need for efficient fertilizers are compounded by changing climate conditions, which make farming more challenging. Droughts, floods, and unpredictable weather patterns are affecting crop yields, and farmers are turning to ammonia-based fertilizers as one of the most reliable solutions to boost productivity. As global temperatures rise, these weather patterns are only expected to become more erratic, further driving the need for fertilizers that enhance crop resilience.
Restraining Factors
Environmental Concerns and Emission Regulations
The ammonia production process accounts for roughly 1-2% of global CO₂ emissions, which is a considerable environmental impact. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), ammonia production alone emits approximately 450 million tons of CO₂ annually. This makes it one of the top industrial sources of carbon emissions. As the world continues to prioritize sustainability, industries like ammonia production are under increasing scrutiny. Governments worldwide have introduced stricter environmental regulations, such as carbon taxes and emission reduction targets, which add to the operational costs of ammonia producers.
The European Union (EU), for example, has set ambitious goals under its Green Deal, aiming to cut net greenhouse gas emissions by at least 55% by 2030 compared to 1990 levels. The ammonia industry, like many other heavy industries, faces significant challenges in meeting these targets. The EU is also implementing a carbon border adjustment mechanism that could impose tariffs on carbon-intensive products, including ammonia, which could increase the cost of ammonia production and make it less competitive compared to cleaner alternatives. These regulatory pressures are pushing ammonia producers to invest in technologies that can reduce emissions or even completely decarbonize their production processes.
According to the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), nitrogen fertilizers, including ammonia, contribute to around 3-4% of global greenhouse gas emissions, with much of this coming from agricultural practices. For instance, the global use of fertilizers has increased by about 4% per year, according to the FAO, with nitrogen fertilizers, including ammonia, making up the majority of this increase.
As environmental regulations tighten and sustainability becomes a central focus of policy, ammonia producers will need to adapt by investing in greener technologies. This includes innovations in carbon capture and storage (CCS), green ammonia production using renewable energy, and alternative fertilizers with lower environmental impacts. However, the transition to more sustainable practices is costly and technologically challenging, which could slow the growth of the ammonia market in the short to medium term.
Growth Opportunity
Green Ammonia Production and Sustainable Agriculture
Green ammonia is produced by using renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, or hydropower to power the electrolysis of water to produce hydrogen, which is then combined with nitrogen to form ammonia. Unlike conventional ammonia production, which relies on fossil fuels like natural gas, green ammonia offers a much lower carbon footprint. As environmental concerns and sustainability goals become increasingly urgent, this shift toward green ammonia represents a significant opportunity for the market’s growth.
The global demand for green ammonia is projected to rise as both governments and industries prioritize sustainable agricultural practices and aim to meet ambitious climate targets. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the production of green ammonia could reduce CO₂ emissions by as much as 1.8 gigatons annually by 2050 if adopted at a large scale. In 2024, several countries, including the United States, Australia, and countries within the European Union, have launched pilot projects focused on green ammonia production, and this trend is expected to gain momentum over the next decade.
For example, in 2023, the European Union invested more than €150 million in green ammonia research and development projects under the Horizon Europe program. This investment is aimed at advancing the technology and scaling up the production of green ammonia, making it more commercially viable. Similarly, the U.S. Department of Energy has committed to funding green ammonia projects as part of its efforts to decarbonize heavy industries, with a focus on improving the sustainability of the agriculture sector. The U.S. government has earmarked over $500 million to support low-carbon technologies, including green ammonia, as part of its broader goal to reduce carbon emissions across industrial sectors.
The rise of green ammonia is closely tied to the increasing demand for sustainable agriculture, which is a key factor driving the growth of ammonia. Fertilizer use is essential to meet the global food demand, and ammonia is a key component of nitrogen fertilizers. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), global fertilizer use must increase by around 30% to meet the growing demand for food by 2050, as the world’s population continues to rise. This increasing demand for fertilizers presents an opportunity for green ammonia to replace conventional ammonia in fertilizer production, thereby supporting both food security and environmental sustainability. In 2024, the global fertilizer industry is expected to consume around 190 million metric tons of nitrogen fertilizers, with a growing share coming from greener, more sustainable sources.
Latest Trends
The Shift Towards Carbon-Free and Green Ammonia
Green ammonia is produced using renewable hydrogen, generated from water electrolysis powered by renewable energy sources like wind, solar, or hydropower. This process avoids the carbon emissions associated with conventional ammonia production, which typically relies on natural gas through the Haber-Bosch process. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), ammonia production accounts for about 1-2% of global CO₂ emissions, making it one of the key industrial sectors targeted for decarbonization.
The U.S. government has also been proactive in encouraging green ammonia production. In 2023, the Department of Energy (DOE) awarded $100 million in funding to several green ammonia projects, focusing on hydrogen production technologies that will enable low-carbon ammonia synthesis. The U.S. is particularly focused on supporting the agricultural industry, which remains one of the largest users of ammonia fertilizers. With sustainable ammonia production methods in the pipeline, the U.S. aims to make its agriculture sector more sustainable while contributing to broader climate goals.
In addition to government support, the trend towards green ammonia is also being fueled by increasing private sector involvement. Leading ammonia producers are investing heavily in research and development to improve the efficiency and scalability of green ammonia production. For example, companies like Yara International and CF Industries have launched pilot projects for green ammonia production, with Yara investing approximately $1.2 billion in a green ammonia facility in Norway. This facility, expected to start production in 2025, will help meet the growing demand for sustainable fertilizers in Europe, demonstrating the significant commercial potential of green ammonia.
The agricultural sector, which is responsible for a large portion of global ammonia consumption, is particularly keen on adopting green ammonia. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) has reported that ammonia-based fertilizers account for around 60% of the world’s nitrogen fertilizer use. As governments and private companies invest in cleaner production methods, green ammonia is becoming increasingly viable as a sustainable alternative. According to the International Fertilizer Association (IFA), the global demand for ammonia is projected to grow by about 2% annually over the next decade, with green ammonia expected to make up a larger portion of this demand.
Regional Analysis
The ammonia market is significantly influenced by regional dynamics, with the Asia Pacific (APAC) region dominating the market. In 2024, APAC held a commanding share of 54.20%, valued at approximately USD 38.3 billion. This dominance is primarily driven by the high demand for ammonia in agriculture, particularly in countries like China, India, and Japan, which are among the largest producers and consumers of fertilizers. The region’s agricultural sector is heavily reliant on ammonia-based nitrogen fertilizers to support its growing food production needs, contributing to APAC’s strong market presence.
In Europe, ammonia consumption is also robust, though the market share is comparatively smaller. Europe accounts for around 20% of global ammonia consumption. The region’s ammonia market is supported by its strict environmental regulations, which are driving the adoption of cleaner technologies such as green ammonia production. The European Union’s green deal and focus on sustainability are likely to spur innovation and increase the adoption of low-carbon ammonia technologies in the coming years.
North America holds a smaller but significant share, making up roughly 15% of the global market. The United States, in particular, is a key player in ammonia production, driven by the demand for fertilizers and industrial chemicals. Furthermore, North America is seeing growing investments in sustainable ammonia production methods, driven by government incentives for clean energy technologies.
In the Middle East & Africa (MEA) and Latin America, ammonia consumption is more focused on industrial applications, including refrigeration and power generation. These regions contribute to a smaller portion of the global market but are projected to see gradual growth due to emerging industrialization and agricultural needs.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Key Player Analysis
The ammonia market is dominated by several key players with a significant global presence. CF Industries Holdings, Inc., BASF SE, Yara International ASA, and Nutrien Ltd. are some of the leading companies in the sector. CF Industries and Nutrien are major ammonia producers in North America, with a strong focus on fertilizers, which make up the largest share of ammonia consumption.
BASF and Yara International, based in Europe, have expanded their market reach through technological advancements in sustainable ammonia production, aligning with global shifts toward environmentally-friendly practices. Qatar Fertiliser Company (QAFCO) is another major player, contributing to the Middle East’s growing ammonia output, driven by the region’s abundant natural gas resources.
Other notable players include Togliattiazot and SABIC, which have strong positions in Russia and the Middle East, respectively. These companies cater to the significant demand for ammonia in agricultural, industrial, and chemical applications.
Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd. and EuroChem Group are also key contributors, with Sumitomo focusing on innovative ammonia production technologies and EuroChem expanding its presence in both Europe and the CIS regions. In the technology space, companies like Nel Hydrogen, Siemens AG, and ThyssenKrupp AG are advancing ammonia production through sustainable, green methods, particularly hydrogen-based ammonia.
Key Players
- Yara International ASA
- CF Industries Holdings, Inc.
- BASF SE
- Nutrien Ltd.
- QATAR FERTILISER COMPANY
- Togliattiazot
- SABIC
- Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd.
- CSBP
- EuroChem Group
- Group DF
- ThyssenKrupp AG
- Nel Hydrogen
- Sinopec
- Rashtriya Chemicals and Fertilizers Limited
- Siemens AG
- Other Key Players
Recent Developments
- In 2024, CF Industries reported revenues exceeding $10 billion, with ammonia contributing to around 70% of this total. The company’s operations are strongly aligned with global agricultural needs, as ammonia is a key ingredient in fertilizers used to improve crop yields.
- In 2024, BASF’s ammonia-related revenues are estimated to exceed €4.5 billion, with fertilizers being the largest segment, contributing roughly 60% of this total.
- In 2024 Yara International ASA, the company expanded its green ammonia production by 15%, aligning with global efforts to decarbonize the agricultural sector.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 70.7 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 113.0 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 4.8% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, COVID-19 Impact, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Form (Aqueous, Anhydrous), By Type (Grey/Brown, Blue, Green, Turquoise), By Feedstock (Natural Gas, Coal, Oil, Hydrogen, Others), By Application(Fertilizers, Refrigerants, Transportation, Textile, Power Generation, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Yara International ASA, CF Industries Holdings, Inc., BASF SE, Nutrien Ltd., QATAR FERTILISER COMPANY, Togliattiazot , SABIC, Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd., CSBP , EuroChem Group, Group DF, ThyssenKrupp AG, Nel Hydrogen, Sinopec, Rashtriya Chemicals and Fertilizers Limited, Siemens AG, Other Key Players Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three license to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Yara International ASA
- CF Industries Holdings, Inc.
- BASF SE
- Nutrien Ltd.
- QATAR FERTILISER COMPANY
- Togliattiazot
- SABIC
- Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd.
- CSBP
- EuroChem Group
- Group DF
- ThyssenKrupp AG
- Nel Hydrogen
- Sinopec
- Rashtriya Chemicals and Fertilizers Limited
- Siemens AG
- Other Key Players









