Global AI-Powered Recycling Robot Market By Type of Robot (Autonomous Robots, Teleoperated Robots), By Application Area (Industrial Waste Management, Municipal Waste Management), By Material Stream Sorted (Plastics, Paper and Cardboard, Metals, E-Waste, Others), By Technology (Machine Learning Algorithms, Computer Vision, Others), By Size of Operation (Small Scale Operations, Medium Scale Operations), By End-User (Recycling Facilities, Waste Management Companies, Municipalities, Others), By Regional Analysis, Global Trends and Opportunity, Future Outlook By 2025-2035
- Published date: Jan. 2026
- Report ID: 173641
- Number of Pages: 270
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
- Report Overview
- Top Market Takeaways
- Key Insights Summary
- Drivers Impact Analysis
- Risk Impact Analysis
- Restraint Impact Analysis
- Type of Robot Analysis
- Application Area Analysis
- Material Stream Sorted Analysis
- Technology Analysis
- Size of Operation Analysis
- End-User Analysis
- Investor Type Impact Matrix
- Technology Enablement Analysis
- Emerging Trends
- Growth Factors
- Key Market Segments
- Regional Analysis
- Driver Analysis
- Restraint Analysis
- Opportunity Analysis
- Challenge Analysis
- Competitive Analysis
- Future Outlook
- Recent Developments
- Report Scope
Report Overview
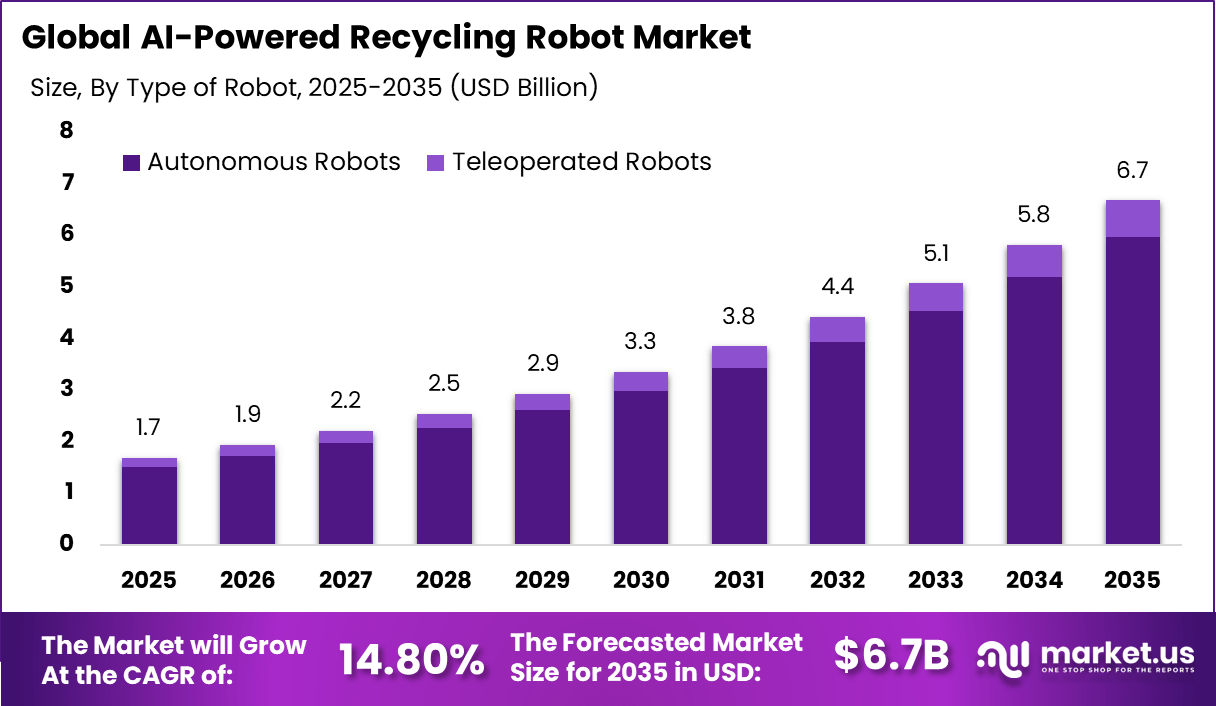
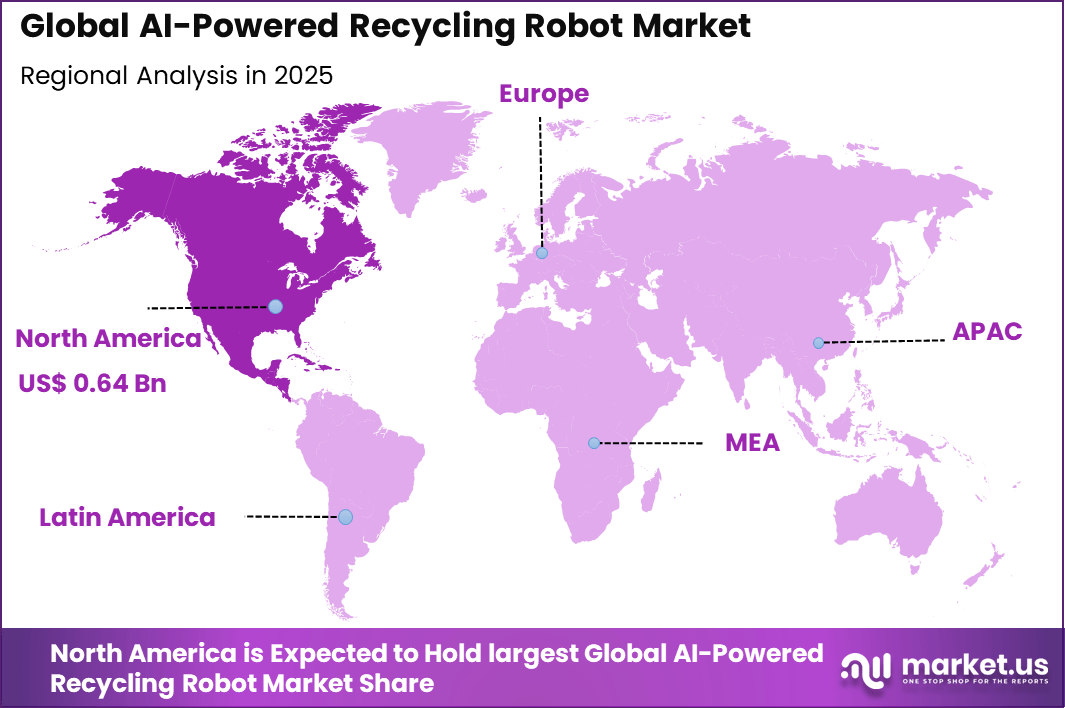
The Global AI-Powered Recycling Robot Market generated USD 1.7 billion in 2025 and is predicted to register growth from USD 1.9 billion in 2026 to about USD 6.7 billion by 2034, recording a CAGR of 14.80% throughout the forecast span. In 2025, North America held a dominan market position, capturing more than a 38.6% share, holding USD 0.64 Billion revenue.
The AI powered recycling robot market refers to robotic systems that use artificial intelligence to identify, sort, and separate recyclable materials from waste streams. These robots use sensors, cameras, and machine learning models to recognize different materials such as plastics, metals, paper, and glass. AI powered recycling robots are deployed in recycling facilities, waste management centers, and material recovery plants.
They aim to improve sorting accuracy and processing speed. Adoption supports more efficient and consistent recycling operations. Market development has been influenced by rising waste generation and the need to improve recycling efficiency. Manual sorting is labor intensive and prone to errors. Traditional mechanical systems lack flexibility in handling mixed waste streams. AI powered robots introduce adaptive sorting capabilities.
One major driving factor of the AI powered recycling robot market is the need to improve recycling rates. Governments and organizations aim to reduce landfill waste. Accurate material separation is critical for effective recycling. AI powered robots improve purity levels of sorted materials. Higher recovery rates drive adoption. Another key driver is labor shortage and workplace safety concerns. Recycling facilities often face challenges in hiring and retaining workers.
Sorting tasks can be repetitive and hazardous. Robots reduce reliance on manual labor. Improved safety and workforce stability support market growth. Demand for AI powered recycling robots is influenced by expansion of recycling infrastructure. Municipalities and private operators invest in modern material recovery facilities. Automation helps handle higher waste volumes efficiently. Robots support consistent performance at scale. Infrastructure growth increases demand.
Top Market Takeaways
- By type of robot, autonomous robots took 89.3% of the AI-powered recycling robot market, operating without human input for 24/7 sorting efficiency.
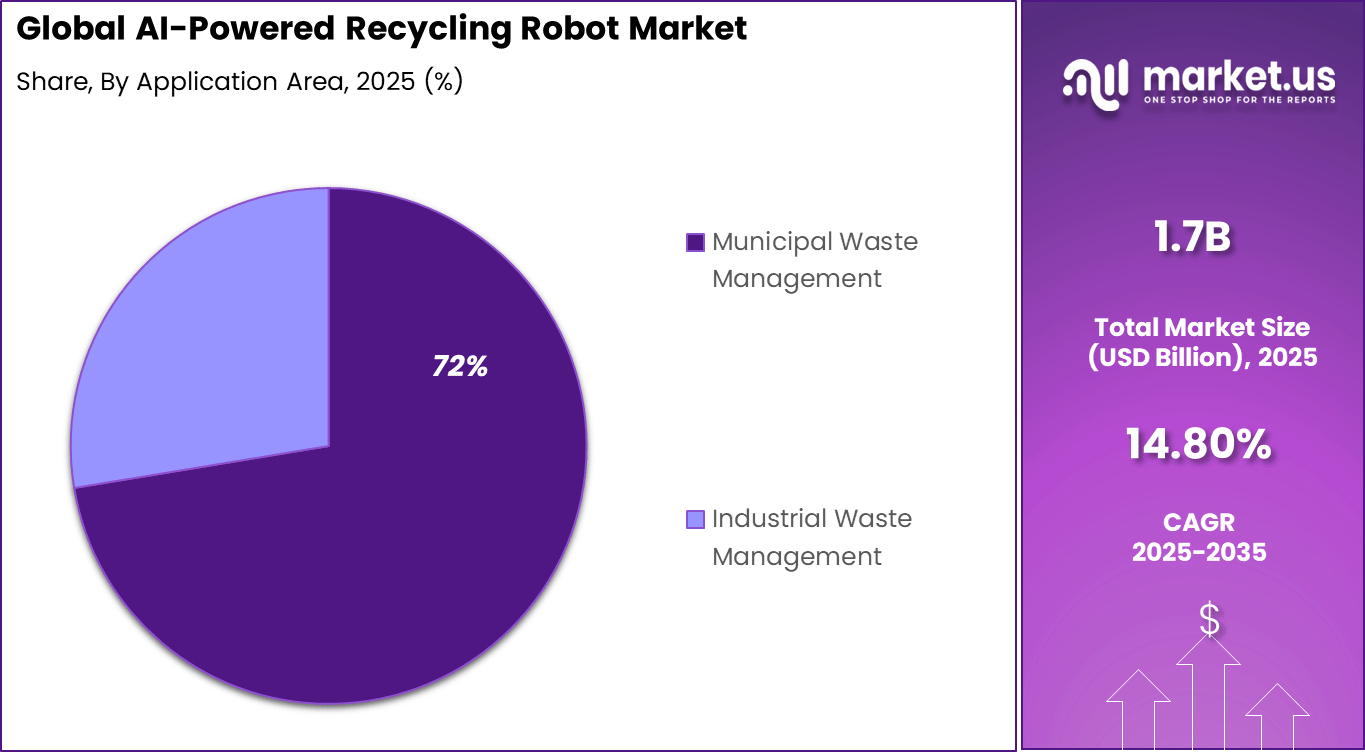
- By application area, municipal waste management held 72.4% share, processing large volumes from cities and landfills.
- By material stream sorted, plastic captured 47.8%, targeting high-value recyclables with AI precision separation.
- By technology, computer vision led with 60.2%, using cameras to identify materials by shape, color, and texture.
- By size of operation, medium scale operations accounted for 62.5%, balancing cost with automation benefits.
- By end-user, waste management companies took 51.4%, deploying robots to cut labor costs and boost recovery rates.
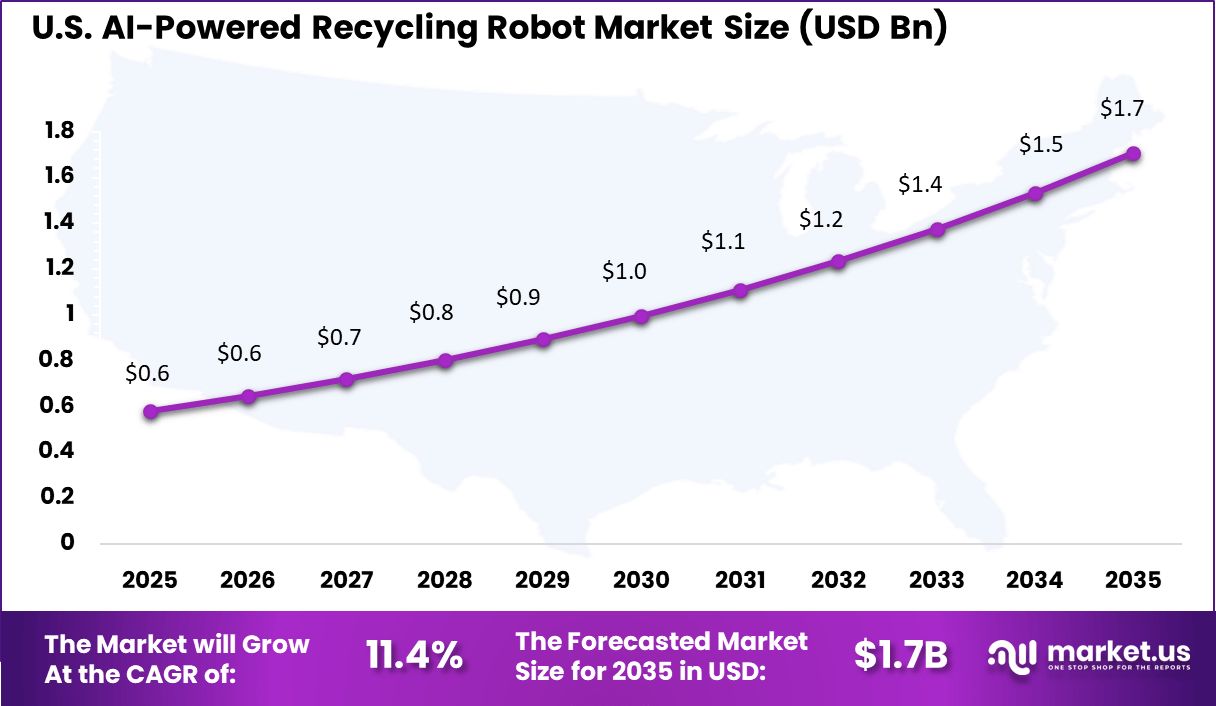
- North America had 38.6% of the global market, with the U.S. at USD 0.58 billion in 2025 and growing at a CAGR of 11.4%.
Key Insights Summary
Operational Performance
- AI-powered sorting robots achieve 80+ picks per minute, compared with 30-40 picks per minute by human workers.
- Facilities using AI robotics report around 60% improvement in overall operational efficiency.
- Material identification accuracy reaches 99%, supporting consistent and reliable sorting outcomes.
- Bale purity improves by 8% to 12% after AI robot deployment.
- Installing a robot at the last sorting stage increases total resource recovery by 40% to 70%.
Economic and Labor Impact
- Manual labor costs decline by 59% to 60% following AI robotics integration.
- Robots operate continuously with over 99% uptime, supporting round-the-clock processing.
- Large recovery facilities generate up to USD 400,000 in additional annual revenue by capturing missed recyclables.
- Worker injuries decrease by about 35%, improving safety conditions in waste facilities.
Environmental Impact
- AI-driven sorting and inventory systems reduce carbon emissions by more than 26,000 tons of CO₂ annually in large deployments.
- Contamination in recycled material streams falls by nearly 40%, lowering rejection and landfill rates.
- Growth in AI infrastructure may increase global e-waste by 3% to 12% by 2030, highlighting the need for sustainable system design.
Drivers Impact Analysis
Driver Category Key Driver Description Estimated Impact on CAGR (%) Geographic Relevance Impact Timeline Rising waste generation Need for faster and accurate sorting ~4.1% Global Short Term Labor shortages in recycling facilities Automation of manual sorting tasks ~3.6% North America, Europe Short Term Increasing recycling efficiency targets Higher material recovery rates ~3.0% North America, Europe Mid Term Adoption of AI and computer vision Improved material identification ~2.5% Global Mid Term Sustainability and circular economy goals Reduction of landfill dependency ~1.6% Global Long Term Risk Impact Analysis
Risk Category Risk Description Estimated Negative Impact on CAGR (%) Geographic Exposure Risk Timeline High capital investment Cost of robotic systems and integration ~4.3% Emerging Markets Short Term Technology accuracy limitations Misclassification of complex materials ~3.5% Global Short Term Maintenance and downtime risks Specialized servicing requirements ~2.9% Global Mid Term Integration challenges Compatibility with existing MRF lines ~2.3% Global Mid Term Regulatory uncertainty Changing recycling standards ~1.8% Global Long Term Restraint Impact Analysis
Restraint Factor Restraint Description Impact on Market Expansion (%) Most Affected Regions Duration of Impact High upfront system cost Budget constraints for smaller operators ~4.9% Emerging Markets Short to Mid Term Limited skilled operators Need for AI and robotics expertise ~3.8% Global Mid Term Facility retrofit complexity Physical space and line redesign ~3.1% Global Mid Term Uncertain ROI timelines Gradual payback from efficiency gains ~2.4% Global Long Term Vendor ecosystem dependency Limited supplier options ~1.9% Global Long Term Type of Robot Analysis
Autonomous robots account for 89.3%, showing their dominant role in recycling operations. These robots operate with minimal human intervention and perform continuous sorting tasks. Automation improves processing speed and accuracy in waste facilities. Autonomous systems adapt to changing material streams effectively. Reliability is essential for uninterrupted operations.
The dominance of autonomous robots is driven by labor efficiency needs. Waste facilities seek to reduce manual handling. Autonomous robots support consistent sorting quality. They also operate in demanding environments safely. This sustains strong adoption of autonomous systems.
Application Area Analysis
Municipal waste management represents 72.4%, making it the leading application area. Cities manage large volumes of mixed waste daily. AI-powered robots support efficient sorting at scale. Improved sorting reduces landfill dependency. Operational efficiency remains a priority.
Growth in municipal applications is driven by urban population growth. Municipalities invest in automated waste processing. Robotics improve recycling rates and consistency. Data-driven operations support planning. This keeps municipal waste management central to adoption.
Material Stream Sorted Analysis
Plastic sorting accounts for 47.8%, making it the most common material stream. Plastics vary in shape, color, and composition. AI-powered robots identify plastics accurately. Effective sorting improves recycling value. Consistency reduces contamination.
The focus on plastic is driven by environmental concerns. Plastic waste volumes remain high globally. Accurate sorting supports reuse and recycling goals. Robotics reduce manual errors. This sustains strong demand for plastic sorting solutions.
Technology Analysis
Computer vision holds 60.2%, making it the leading technology. Vision systems analyze materials based on shape and color. Real-time image processing improves sorting accuracy. Computer vision supports adaptive learning. Precision is critical for effective sorting.
Adoption of computer vision is driven by material complexity. Waste streams are diverse and unpredictable. Visual analysis handles variation efficiently. Continuous learning improves performance. This keeps computer vision widely adopted.
Size of Operation Analysis
Medium scale operations account for 62.5%, highlighting their strong adoption. These facilities balance volume and investment capacity. AI-powered robots fit operational needs effectively. Automation improves throughput without excessive cost. Flexibility remains important.
Growth in medium scale operations is driven by regional facilities. These sites modernize to improve efficiency. Robotics support incremental upgrades. Performance gains justify investment. This sustains strong adoption among medium scale operations.
End-User Analysis
Waste management companies represent 51.4%, making them the largest end-user group. These companies manage collection, sorting, and recycling processes. AI-powered robots improve operational efficiency. Automation supports consistent service delivery. Cost control remains essential.
Adoption among waste management companies is driven by regulatory pressure. Companies aim to improve recycling rates. Robotics reduce operational risk. Data insights support optimization. This sustains strong end-user demand.
Investor Type Impact Matrix
Investor Type Adoption Level Contribution to Market Growth (%) Key Motivation Investment Behavior Waste management companies Very High ~51.4% Operational efficiency and cost reduction Facility wide deployment Municipal authorities High ~24% Recycling targets and compliance Program based investment Industrial recyclers Moderate ~14% Material recovery optimization Selective adoption Environmental service providers Moderate ~7% Technology differentiation Pilot projects SMEs Low ~4% Cost sensitive automation Limited usage Technology Enablement Analysis
Technology Layer Enablement Role Impact on Market Growth (%) Adoption Status Computer vision systems Material recognition and sorting ~4.5% Mature Machine learning algorithms Continuous accuracy improvement ~3.8% Growing Robotic arms and actuators High speed material handling ~3.1% Mature Sensor fusion technologies Multi material detection ~2.3% Developing Cloud based analytics Performance monitoring and optimization ~1.6% Developing Emerging Trends
Key Trend Description Hyperspectral imaging for sorting Advanced sensors identify materials that standard cameras cannot detect, enabling precise material separation. Autonomous robotic arms Robotic systems pick and sort materials at high speeds with minimal human oversight. IoT real-time monitoring Connected systems track operational performance continuously and optimize processes dynamically. Predictive analytics for maintenance AI forecasts equipment issues in advance to reduce downtime and maintenance costs. Blockchain material traceability Blockchain ensures authenticity and traceability of recycled materials from sorting to reuse. Growth Factors
Key Factors Description Stringent environmental regulations Policies mandate higher recycling rates and reduced landfill waste. Labor shortages in waste handling Robotics replace hazardous and labor-intensive manual sorting tasks. Rising waste volumes globally Urbanization and consumption growth require scalable automated waste solutions. Circular economy initiatives Focus on material recovery and reuse accelerates adoption of robotic sorting systems. Cost declines in AI and robotics Falling technology costs make advanced sorting solutions accessible to more facilities. Key Market Segments
By Type of Robot
- Autonomous Robots
- Teleoperated Robots
By Application Area
- Industrial Waste Management
- Municipal Waste Management
By Material Stream Sorted
- Plastics
- Paper & Cardboard
- Metals
- E-Waste
- Others
By Technology
- Machine Learning Algorithms
- Computer Vision
- Others
By Size of Operation
- Small Scale Operations
- Medium Scale Operations
By End-User
- Recycling Facilities
- Waste Management Companies
- Municipalities
- Others
Regional Analysis
North America accounted for 38.6% share, supported by growing focus on waste management efficiency and sustainability initiatives across municipalities and industrial facilities. AI powered recycling robots have been adopted to automate material sorting and improve recovery rates in recycling plants.
Demand has been driven by stricter environmental regulations, rising waste volumes, and the need to reduce reliance on manual labor. Advanced vision systems and machine learning algorithms have enabled more accurate identification of recyclable materials, strengthening adoption across the region.
The U.S. market reached USD 0.58 Bn and is projected to grow at an 11.4% CAGR, reflecting steady adoption across municipal recycling centers and private waste management companies. AI powered recycling robots have helped U.S. operators address labor shortages and improve consistency in material sorting. Adoption has been particularly strong in facilities handling mixed waste streams, where automated systems deliver higher accuracy than manual processes.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherlands
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Driver Analysis
The AI-powered recycling robot market is being driven by increasing emphasis on efficient waste sorting and resource recovery within sustainability and circular economy initiatives. Traditional recycling facilities often rely on manual labour and mechanical sorting methods that are time consuming and prone to error.
AI-enabled robots equipped with computer vision and machine learning algorithms can identify, classify, and separate a wide variety of materials such as plastics, metals, paper, and glass with higher speed and precision.
These automated systems reduce contamination rates in recycling streams, improve throughput, and enhance operational efficiency. Growing regulatory pressure to meet waste reduction targets and rising material processing costs further encourage adoption of intelligent robotic sorting solutions.
Restraint Analysis
A significant restraint facing the AI-powered recycling robot market arises from the high initial investment and technical complexity associated with deployment. Advanced robots require sophisticated sensors, AI models trained on diverse material datasets, and integration with existing conveyor and sorting infrastructure.
Many recycling facilities operate legacy systems with limited automated capability, making retrofit projects complex and costly. Smaller waste processing operators may lack the capital, technical expertise, or operational scale to justify such investments, which can slow wider market adoption.
Opportunity Analysis
Emerging opportunities in the AI-powered recycling robot market are linked to expanding applications beyond traditional municipal waste management into industrial, commercial, and specialised material recovery streams. Robots capable of sorting e-waste, construction and demolition debris, or high-value recyclables present new avenues for efficiency and revenue generation.
Integration with data analytics and cloud-based optimisation tools can enable predictive maintenance and performance benchmarking for robotic fleets across multiple facilities. Partnerships between technology providers and waste management organisations to co-develop tailored solutions also open pathways for broader deployment and service-oriented business models that reduce barriers to entry for smaller operators.
Challenge Analysis
A central challenge confronting this market relates to achieving reliable performance across highly variable waste streams and evolving material compositions. Waste sorting environments are inherently unstructured, with items of diverse shapes, sizes, and contamination levels.
AI models must be trained on extensive and representative datasets to accurately recognise and classify materials, and continuous learning mechanisms are required to adapt to new waste profiles. Ensuring system robustness, minimising downtime, and maintaining safety in dynamic industrial environments demand ongoing refinement of both hardware and software components.
Competitive Analysis
Key players such as ZenRobotics, AMP Robotics, and Sadako Technologies focus on AI-based vision and robotic arms for automated material sorting. Their solutions improve sorting accuracy and processing speed in recycling facilities. Machine learning models are used to identify plastics, metals, and paper in mixed waste streams. Adoption is driven by labor shortages and the need for higher recycling purity.
Established equipment providers such as Machinex Industries Inc., Bulk Handling Systems, and Tomra Systems ASA integrate AI robotics into end-to-end recycling lines. General Kinematics Corporation strengthens the market with mechanical handling and system integration. These players benefit from long-term relationships with recycling plants.
Emerging and niche players such as Pellenc ST, MSS Inc., and Optical Sorting Systems support specialized sorting needs. Eagle Vizion and Waste Robotics focus on flexible AI vision platforms. Other regional vendors expand adoption across smaller facilities. This competitive landscape supports steady innovation and wider use of AI-powered recycling automation.
Top Key Players in the Market
- ZenRobotics
- AMP Robotics
- Sadako Technologies
- Waste Robotics
- Machinex Industries Inc.
- Bulk Handling Systems (BHS)
- Tomra Systems ASA
- General Kinematics Corporation
- Greeen Creative
- Pellenc ST
- Recycling Equipment Inc.
- MSS Inc.
- Optical Sorting Systems (OSS)
- Eagle Vizion
- Others
Future Outlook
Growth in the AI-Powered Recycling Robot market is expected to remain strong as waste management systems focus on efficiency and sustainability. These robots are being used to identify, sort, and separate recyclable materials with higher accuracy than manual processes.
Rising waste volumes and stricter environmental regulations are supporting wider adoption across recycling facilities. Over time, improvements in AI vision, robotic speed, and system integration are likely to reduce operating costs and improve recycling rates.
Recent Developments
- Sadako Technologies advanced its AI platforms for construction waste in 2025, with pilots boosting recovery rates by 20% in European sites.
- Machinex Industries Inc. launched enhanced SamurAI with MACH Vision 3.0 in mid-2025, cutting sort times by 30% for fiber recovery.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2025) USD 1.7 Bn Forecast Revenue (2035) USD 1.9 Bn CAGR(2025-2035) 14.80% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2024 Forecast Period 2025-2035 Report Coverage Revenue forecast, AI impact on Market trends, Share Insights, Company ranking, competitive landscape, Recent Developments, Market Dynamics and Emerging Trends Segments Covered By Type of Robot (Autonomous Robots,Teleoperated Robots), By Application Area (Industrial Waste Management,Municipal Waste Management), By Material Stream Sorted (Plastics,Paper and Cardboard,Metals,E-Waste,Others), By Technology (Machine Learning Algorithms,Computer Vision,Others), By Size of Operation (Small Scale Operations,Medium Scale Operations), By End-User (Recycling Facilities,Waste Management Companies,Municipalities,Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of Latin America; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape ZenRobotics, AMP Robotics, Sadako Technologies, Waste Robotics, Machinex Industries Inc., Bulk Handling Systems (BHS), Tomra Systems ASA, General Kinematics Corporation, Greeen Creative, Pellenc ST, Recycling Equipment Inc., MSS Inc., Optical Sorting Systems (OSS), Eagle Vizion, Others Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three license to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  AI-Powered Recycling Robot MarketPublished date: Jan. 2026add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
AI-Powered Recycling Robot MarketPublished date: Jan. 2026add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- ZenRobotics
- AMP Robotics
- Sadako Technologies
- Waste Robotics
- Machinex Industries Inc.
- Bulk Handling Systems (BHS)
- Tomra Systems ASA
- General Kinematics Corporation
- Greeen Creative
- Pellenc ST
- Recycling Equipment Inc.
- MSS Inc.
- Optical Sorting Systems (OSS)
- Eagle Vizion
- Others










