Global AI-based Surgical Robots Market Analysis By Product Type (Hardware, Services), By Level of Automation (Semi-Autonomous Systems, Autonomous Systems, Telerobotic Systems), By Application (General Surgery, Orthopedic Surgery, Neurological Surgery, Urological Surgery, Gynecological Surgery, Others), By End-User (Hospitals, Ambulatory Surgical Centers) By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Oct 2025
- Report ID: 163512
- Number of Pages: 281
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
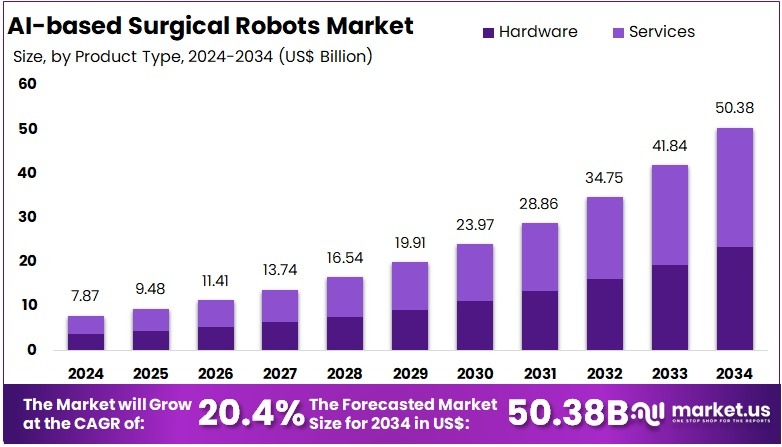
The Global AI-based Surgical Robots Market size is expected to be worth around US$ 50.38 Billion by 2034, from US$ 7.87 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 20.4% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 42.2% share and holds US$ 3.32 Billion market value for the year.
AI-based surgical robots are advanced robotic systems designed to assist surgeons in performing minimally invasive and complex procedures with high precision. The systems use machine learning, computer vision, and real-time data analysis. Enhanced dexterity and visualization improve surgical accuracy. Better outcomes, shorter hospital stays, and fewer complications are enabled. According to industry observations, demand has increased as hospitals seek reliable automation and consistent surgical performance across specialties.
Substantial growth has been driven by rising chronic-disease cases and growing surgical volumes. The market has benefited from increasing healthcare expenditure and the global shift toward minimally invasive surgeries. For instance, the growing use of automated suturing and robotic navigation based on patient-specific anatomical data supports advanced clinical adoption. Training programs for surgeons and supportive reimbursement pathways further strengthen hospital confidence in adopting robotic systems.
Supportive regulatory actions continue to accelerate deployment. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration issued final guidance on Predetermined Change Control Plans, enabling safe iterative software updates. As of 31 August 2024, the FDA listed 903 AI-enabled devices, and as of 25 March 2025, this number had risen to 1,016 authorised AI or ML-enabled medical devices. In 2024 alone, 253 devices were approved, signaling strong regulatory maturity and advancement of clinical AI tools.
Global sustainability programs reinforce digital readiness. WHO’s Global strategy on digital health reported that 40 Member States participate in the Global Digital Health Partnership. According to the WHO, a health-workforce shortfall of 11 million workers is expected by 2030, supporting the need for automation. Study by international researchers in 2025 showed improved healthcare-worker performance (β = 0.452, p < 0.001) and reduced workload (β = 0.594, p < 0.001) with digital health-technology adoption, emphasizing greater reliance on intelligent surgical systems.
Policy Drivers and Market Expansion
Policy clarity has improved confidence in robotic surgery programs. FDA guidance on cybersecurity rules requires proactive vulnerability monitoring, timely patches, and software bills of materials in premarket submissions. These updates strengthen safety for networked robotic platforms and enhance procurement trust. For example, section 524B of the Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act provides explicit expectations for cyber-device compliance, reducing security-related adoption barriers and enabling hospitals to deploy AI-guided systems confidently.
Interoperability advancements support data-driven surgery. The United States introduced the Trusted Exchange Framework and Common Agreement with multiple Qualified Health Information Networks. Under ONC’s HTI-2 proposals, certification and data exchange requirements link participation to standardized information-sharing rules. Access to perioperative data improves AI model training and real-time decision support. For example, better data pipelines elevate robotic navigation accuracy and quality assurance, strengthening benefits for both surgeons and patients.
International initiatives demonstrate government commitment. NHS England introduced a plan in June 2025 to expand robot-assisted surgeries to approximately 500,000 procedures annually by 2035. National programs guide workforce planning, technology integration, and multi-specialty deployment. Global bodies, including WHO, ITU, and WIPO, launched the Global Initiative on AI for Health to standardize evaluation frameworks. In March 2025, WHO issued governance guidance for multimodal AI in health, promoting transparency and safe human oversight in robotic systems.
National digital-health strategies improve system readiness. For example, Indonesia launched its 2024 Digital Health Transformation Strategy to modernize e-health infrastructure. Such policies help hospitals integrate robotic platforms with imaging systems, electronic health records, and analytics tools. According to the FDA, more than 1,000 AI-enabled devices have already been authorised under established pathways, confirming accelerating innovation. Together, collaborative standards, workforce programs, and digital reforms are setting strong foundations for long-term AI-based surgical-robot expansion.
Key Takeaways
- The global AI-based surgical robots market is projected to rise from US$ 7.87 billion in 2024 to nearly US$ 50.38 billion by 2034, registering 20.4% CAGR.
- Services accounted for more than 53.7% share in 2024 within product type segmentation, supported by growing needs for maintenance, software updates, and technical training.
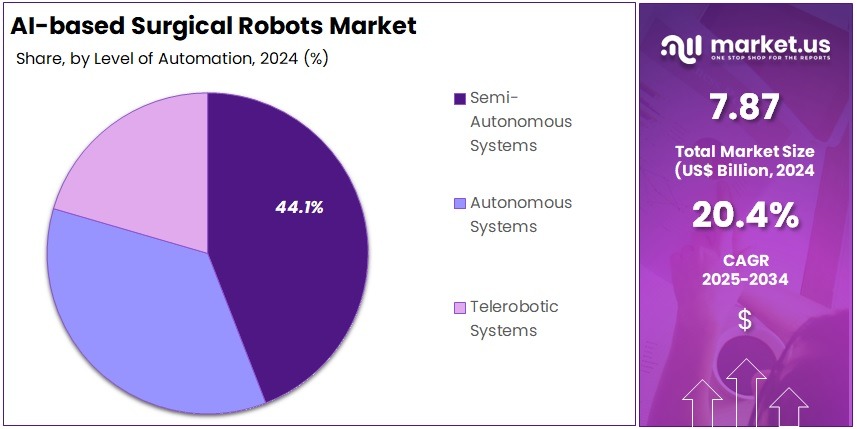
- Semi-autonomous systems captured over 44.1% market share in 2024, reflecting strong adoption of platforms combining automated capabilities with surgeon oversight for enhanced precision.
- General surgery held above 29.7% application share in 2024, indicating extensive deployment of AI-driven robotic systems across multiple surgical specialties and procedures.
- Hospitals represented more than 73.9% end-user share in 2024, driven by increased robotic system integration in large healthcare facilities and advanced surgical centers.
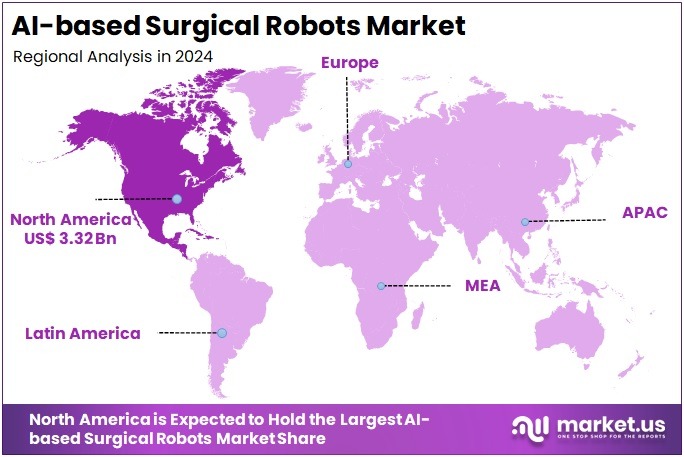
- North America accounted for over 42.2% market share in 2024, representing approximately US$ 3.32 billion, supported by strong technological adoption and healthcare investment.
Product Type Analysis
In 2024, the Services Section held a dominant market position in the Product Type Segment of AI-based Surgical Robots Market, and captured more than a 53.7% share. Strong demand for installation, maintenance, training, and software support services contributed to this leadership.
The rising use of AI-enabled systems in hospitals enhanced the need for technical assistance. Service programs were preferred to ensure accuracy, performance, and minimal downtime. The focus on continuous AI algorithm upgrades and remote monitoring strengthened this segment further. Long-term service contracts and subscription-based support models also expanded adoption. Growth of robotic surgery ecosystems increased reliance on clinical support and system integration solutions.
The Hardware segment accounted for a notable share in 2024. Hardware demand was driven by robotic arms, imaging modules, sensors, and navigation platforms. High capital investment was recorded due to advanced mechanical systems and precision tools. Surgical robot installations across tertiary care hospitals and specialized surgical centers accelerated hardware uptake. Improvements in AI-integrated robotics parts created efficiency and reliability in surgical procedures. Hardware adoption benefited from the shift toward minimally invasive surgeries. Continuous technological upgrades and rising replacement cycles contributed to growth.
Level of Automation Analysis
In 2024, the Semi-Autonomous Systems Section held a dominant market position in the Level of Automation Segment of the AI-based Surgical Robots Market, and captured more than a 44.1% share. The strong demand for semi-autonomous systems was driven by higher surgeon control, reduced procedural risk, and improved surgical precision. These systems were adopted in complex procedures where complete automation remained limited due to clinical safety considerations and regulatory frameworks. Their ability to enhance decision support, accuracy, and intraoperative efficiency contributed to significant penetration in high-value hospital settings.
Autonomous Systems accounted for a notable share and are expected to experience accelerated growth over the forecast period. Advancements in machine learning, imaging algorithms, and robotic navigation are driving greater autonomy in surgical execution. Adoption has been supported by increased confidence in AI-driven surgical planning and execution. However, regulatory approvals, ethical considerations, and the need for extensive clinical validation have been acting as key restraints. Despite this, procedural accuracy improvements and reduced surgeon fatigue are anticipated to propel adoption.
Telerobotic Systems demonstrated a growing adoption rate, supported by advancements in telepresence and remote surgical platforms. Growth has been influenced by the rising focus on expanding access to specialized surgical care in remote and underserved locations. Improved connectivity technologies and high-precision robotic systems have enabled surgeons to perform operations at long distances. The segment is expected to gain momentum as 5G networks, real-time data transfer capabilities, and AI-enabled remote surgical assistance expand globally. However, cybersecurity risks and infrastructure requirements have remained barriers in some regions.
The Level of Automation landscape is expected to transition steadily. Increased integration of real-time analytics, autonomous decision support, and augmented control mechanisms will drive stronger adoption across segments. Semi-autonomous platforms will continue to dominate in the near term. Autonomous and telerobotic systems will gain market share as regulatory clarity, data security infrastructure, and surgeon trust improve. The long-term outlook remains optimistic, supported by continuous AI innovation and a rising need for precision surgical solutions.
Application Analysis
In 2024, the General Surgery Section held a dominant market position in the Application Segment of AI-based Surgical Robots Market, and captured more than a 29.7% share. This leadership was supported by rapid adoption of robotic systems across hernia repair, bariatric surgery, and colorectal procedures. Higher accuracy and reduced post-operative recovery time were key factors. Growing hospital investments strengthened installation rates. Surgeons increasingly preferred intelligent assistance for complex tasks. Training programs expanded. Improved clinical safety and consistency reinforced acceptance.
Orthopedic applications followed with a strong presence. Demand was driven by rising joint replacement and spine procedures. AI-powered robotic systems enabled precise bone alignment and better implant positioning. Reduced revision rates and shorter rehabilitation periods encouraged use. Adoption was fueled by aging populations and trauma cases. Hospitals adopted advanced platforms to improve surgical precision. Consistent improvement in patient outcomes supported wider integration. Surgeons leveraged real-time guidance for critical decisions.
Neurological, urological, and gynecological surgeries showed steady growth. Neurosurgery adoption increased due to high accuracy needs for brain and spine operations. Urology procedures such as prostatectomy and nephrectomy benefitted from robotic precision and tissue mapping. Gynecological surgeries adopted robots for hysterectomy and myomectomy with improved suturing and visualization. Minimally invasive trends boosted demand across these segments. Other areas, including pediatric and ENT surgeries, gradually expanded. Continuous development and clinical approvals strengthened future growth potential.
End-User Analysis
In 2024, the Hospitals Section held a dominant market position in the End-User Segment of AI-based Surgical Robots Market, and captured more than a 73.9% share. This lead was linked to advanced medical infrastructure and higher adoption of robotic-assisted systems for complex surgeries. Hospitals supported greater investment in AI-based platforms due to large patient volumes and specialized departments. Dedicated training programs and established reimbursement systems also played key roles. This segment benefitted from trust in hospital-based robotic procedures and strong capital spending.
Ambulatory Surgical Centers were observed gaining rising attention as a secondary end-user segment. Their growth was supported by increasing demand for minimally invasive procedures in outpatient settings. Cost-efficient treatment models, shorter stays, and faster recovery attracted both patients and providers. Technology suppliers launched compact and cost-friendly robotic platforms for ASCs. Regulatory clarity and private healthcare investment also assisted adoption. This category is expected to gain traction as day-care surgeries become more common globally.
Market observers noted continued preference toward hospitals, while ASCs showed strong future promise. Technological advancements, AI-powered decision support, and automation in surgical workflows are expected to accelerate adoption across both end-user groups. Declining system costs and better surgical outcomes also encouraged wider acceptance. As awareness increases and system efficiency improves, AI-based surgical robots are projected to move beyond large hospital networks. Overall, steady market growth is anticipated as healthcare providers prioritize precision, efficiency, and patient safety.
Key Market Segments
By Product Type
- Hardware
- Services
By Level of Automation
- Semi-Autonomous Systems
- Autonomous Systems
- Telerobotic Systems
By Application
- General Surgery
- Orthopedic Surgery
- Neurological Surgery
- Urological Surgery
- Gynecological Surgery
- Others
By End-User
- Hospitals
- Ambulatory Surgical Centers
Drivers
National Scaling Initiatives and Procurement Frameworks
According to national health authorities, large-scale implementation programs and structured procurement frameworks are key drivers of AI-based surgical robot adoption. Health-system mandates, such as those issued by NHS England, have accelerated this trend. For instance, NHS England plans to expand robot-assisted surgeries to approximately 500,000 procedures annually by 2035. Additionally, the release of a detailed implementation guide addressing standards, workforce development, and performance evaluation is strengthening the foundation for consistent adoption across hospitals and surgical networks.
Furthermore, these initiatives reflect a broader policy commitment to digital transformation in healthcare. Study by government agencies and professional bodies has emphasized the importance of integrating robotics to enhance surgical precision and patient outcomes. As procurement frameworks mature, hospitals gain easier access to approved technologies. This structured approach ensures cost efficiency and compliance with safety standards. Consequently, AI-based surgical robotics are expected to become integral to national surgical strategies in the coming decade.
Surgical Workforce Constraints and Rising Unmet Need
A growing shortage of trained surgeons and an expanding backlog of surgical cases are major drivers of AI-enabled robotics in surgery. According to recent policy analyses, the global unmet need for essential operations exceeds 160 million procedures annually. This shortage has placed significant pressure on healthcare systems to adopt productivity-enhancing technologies. For example, AI-assisted robots can reduce procedure times and enable less experienced clinicians to perform complex operations with greater precision and consistency.
Moreover, workforce constraints are creating an urgent need for automation and decision-support tools. Studies highlight that aging populations and increasing demand for surgical care are intensifying the gap between available professionals and patient needs. As a result, health systems are increasingly turning to robotic platforms integrated with AI to optimize surgical throughput and standardize outcomes. Therefore, the growing imbalance between workforce capacity and patient demand is directly influencing the accelerated deployment of AI-based surgical robots.
Restraints
Heightened Cybersecurity Obligations
AI-based surgical robots face growing regulatory pressure related to cybersecurity compliance. The U.S. FDA has introduced strengthened premarket cybersecurity guidance for all connected medical devices. As a result, manufacturers must now incorporate advanced security designs, detailed documentation, and lifecycle risk-management strategies during product development. These additional requirements have increased the time and cost of obtaining market approval. Consequently, compliance with these cybersecurity obligations has become a significant restraint on the rapid commercialization of AI-driven surgical systems.
The inclusion of continuous monitoring, secure software updates, and post-market vulnerability management has added further complexity. Each system must demonstrate resilience against potential cyberattacks that could compromise patient safety or data integrity. This obligation demands higher investment in cybersecurity testing and skilled personnel. These efforts, while essential for safety, extend development timelines and regulatory review processes. Thus, stringent cybersecurity standards are slowing the adoption pace of AI-based robotic surgery technologies in healthcare facilities.
Network Dependence for Advanced and Remote Functions
AI-based surgical robots rely heavily on network connectivity for advanced and remote-assisted surgical functions. Features such as telesurgery and cloud-based data processing demand ultra-low latency and uninterrupted connectivity. However, the current real-world network infrastructure often lacks the reliability and speed required for such precision-dependent operations. Inconsistent performance, bandwidth limitations, and connection drops present significant barriers to ensuring stable, real-time control during procedures. These challenges have restricted the widespread deployment of connected robotic surgical systems.
Moreover, the dependence on robust digital networks introduces medico-legal and operational uncertainties. Liability concerns arise if surgery outcomes are affected by network disruptions or cyber incidents. Healthcare institutions must also address infrastructure costs to meet the performance standards required for safe operation. Without guaranteed stability, the full potential of remote or AI-assisted surgical systems remains unrealized. Therefore, network dependence continues to be a key technical and regulatory restraint on the expansion of AI-based surgical robots.
Opportunities
Expansion of Tele-Mentoring and Telesurgery through 5G and Edge Technologies
The integration of 5G and edge computing is creating strong opportunities for AI-based surgical robots. These technologies enable real-time data transmission with minimal latency, making remote robotic surgeries more reliable and secure. Clinical studies are exploring robotic-assisted procedures performed remotely, which can extend surgical expertise to underserved or rural areas. This technological shift supports new service models such as remote proctoring, cross-site collaboration, and virtual training, enhancing accessibility and improving the overall quality of surgical care.
Furthermore, the use of AI algorithms allows surgical robots to adapt dynamically during remote operations. Predictive analytics and real-time monitoring help in anticipating procedural challenges and maintaining precision. As 5G networks expand globally, AI-based robotic systems can perform complex surgeries across long distances with improved accuracy. This evolution in tele-mentoring and telesurgery is expected to create significant commercial opportunities, allowing healthcare systems to offer specialized care without geographical barriers and reducing healthcare disparities.
Regulatory Support Expanding Indications and Clinical Applications
The regulatory landscape for AI-based surgical robots is becoming more favorable, supporting their adoption across multiple specialties. Regulatory bodies and Health Technology Assessment (HTA) agencies are introducing structured pathways for evidence generation and early value guidance. For instance, programs like the NICE evidence-generation framework are listing advanced robotic systems for soft-tissue surgeries. These initiatives validate safety and clinical effectiveness, thereby accelerating approval timelines and increasing confidence among healthcare providers and patients.
This progressive regulatory environment enables surgical robots to enter broader indications and clinical settings. It encourages hospitals and surgical centers to invest in AI-driven platforms for diverse procedures, from general surgery to urology and gynecology. As clearances expand, manufacturers can strategically position their technologies across multiple markets. This shift is expected to drive widespread adoption, create new revenue streams, and strengthen market penetration, marking a pivotal step in the commercialization and global acceptance of AI-based surgical robots.
Trends
System-Level Standardization and Structured Training
Health systems are moving toward standardized and coordinated adoption of AI-based surgical robots. The deployment of robotics is being aligned with unified clinical protocols, credentialing requirements, and consistent safety benchmarks. This approach ensures predictable performance and safer implementation across multiple hospital sites. The shift supports centralized procurement and structured workflows. It also reduces variability across surgeons and facilities, allowing large-scale data generation for outcome assessment, cost control, and evidence-based improvements in robotic surgery programs.
This trend is strengthened by structured training pathways. Hospitals are designing programs that integrate simulation, competency-based evaluations, and continuous learning modules. These initiatives ensure that surgeons and support teams gain uniform proficiency, while ongoing performance reviews support quality assurance. Certification standards are becoming more formalized, improving patient safety and institutional accountability. The adoption of robotics is increasingly linked to broader service redesign goals, rather than isolated use cases, supporting long-term scaling and consistent clinical value.
Real-Time Surgical Video Understanding
Significant advances in artificial intelligence are improving real-time analysis of surgical video feeds. Machine-learning models are enabling real-time recognition of surgical stages, instrument usage, and tissue structures within endoscopic and robotic procedures. This capability supports context-aware alerts and decision assistance inside the operating room. The technology ensures timely guidance for surgeons, reducing risk and enhancing precision. Increased accuracy of video-based predictions is contributing to safer robotic workflows and improving intraoperative visibility.
Real-time AI assistance is moving toward on-device deployment. Edge computing is enabling faster processing without dependency on external networks, improving reliability during surgery. This shift supports instant feedback and enhances robotic autonomy. Integrating predictive analytics and workflow monitoring is expected to optimize procedure flow and surgeon performance. The growing maturity of real-time surgical video understanding indicates an evolution toward intelligent robotic systems that can support surgeons proactively while strengthening quality outcomes and procedural consistency.
Regional Analysis
In 2024, North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 42.2% share and holds US$ 3.32 Billion market value for the year. The region benefited from early and large-scale adoption of robotic and AI-enabled surgical platforms in U.S. hospitals and federal health networks. According to AHRQ’s HCUP analyses, steady growth was recorded in robotic-assisted procedures across inpatient and ambulatory settings, indicating a shift from niche applications toward routine clinical use across major surgical service lines.
The United States regulatory environment further accelerated adoption. According to FDA data, surgical robots and AI/ML-enabled medical devices continued to be approved through 510(k), De Novo, and PMA pathways. The presence of a dedicated FDA program with public listings for AI-enabled devices built trust in technology standards and safety. For instance, this structured clearance system gave hospitals confidence to integrate AI-assisted capabilities such as imaging guidance and workflow analytics into operating rooms at scale.
Federal system participation strengthened market maturity. Study by the Veterans Health Administration showed increasing robotic surgery utilization across its network, signifying both institutional confidence and operational capacity. Although earlier datasets undercounted cases, subsequent studies confirmed rising adoption across multiple VA centers. Moreover, CMS coverage frameworks supported selected robotic orthopedic indications, indicating how robotic systems can support implant positioning, bone resection, and soft-tissue assessment. This clear reimbursement landscape guided capital planning and service-line expansion among U.S. facilities.
Academic research and innovation capacity also played a critical role. Studies highlighted rapid diffusion of robotic techniques across general surgery and subspecialties. A 2024–2025 bibliometric review identified the United States as the leading contributor by publications and citations in robotic surgery research. For example, a strong research base supported faster technique iteration and clinical evidence generation for AI-enhanced platforms. High digital maturity complemented this progress, as near-universal EHR adoption reported by OECD since 2017 enabled consistent data capture, algorithm evaluation, and perioperative AI support.
Canada further reinforced regional leadership. According to CIHI coding standards, robotic-assisted procedures were consistently documented across provinces, allowing unified benchmarking and clinical planning. This harmonized data environment, alongside U.S. volume scale, created a positive feedback loop that accelerated vendor innovation, clinician training, and real-world validation. As a result, North America remained the leading hub for AI-based surgical robots, backed by strong regulatory clarity, healthcare infrastructure, and evidence-driven adoption.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherland
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- New Zealand
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
The AI-based surgical robots market is led by companies with strong technological capabilities and established clinical networks. Intuitive Surgical, Medtronic, and Johnson & Johnson (Auris Health) dominate due to extensive installed bases, surgeon training programs, and AI-enabled vision and workflow tools. Their focus remains on precision, safety, and reduced variability in operating rooms. Integrated imaging, advanced automation, and recurring revenue from instruments and services strengthen their competitive positions. Long-term clinical evidence and enterprise procurement agreements support sustained adoption across major global healthcare systems.
Orthopedic-focused players also hold a significant position in this market. Stryker and Zimmer Biomet drive growth through AI-enabled planning, navigation, and data-driven alignment systems used in joint replacement surgeries. Their platforms create integrated implant-robot ecosystems, strengthening clinical value and customer retention. Continuous data feedback improves surgical accuracy and patient outcomes. These companies benefit from rising orthopedic procedure volumes and demand for minimally invasive precision. They also maintain strong hospital relationships and specialized surgeon training programs to support high utilization rates.
Emerging innovators enhance competitive intensity by offering differentiated solutions and cost-efficient platforms. CMR Surgical, Asensus Surgical, and Vicarious Surgical focus on accessible robotic systems with AI-powered intraoperative guidance, digital laparoscopy, and compact architectures. Titan Medical and Activ Surgical emphasize advanced visualization and navigation. These players aim to improve workflow efficiency and lower system costs. They also target secondary hospitals and ambulatory centers. Their partnerships with healthcare institutions and technology providers help speed adoption and clinical validation in growing regional markets.
Additional companies strengthen the technological depth of the industry. Accuray and Renishaw apply AI in radiosurgery and neurosurgical guidance. Medrobotics and Smith & Nephew develop flexible and orthopedic-focused robotic tools. These firms advance niche applications in oncology, spine, and sports medicine. Innovation emphasizes computer vision, robotics software, and image-guided safety systems. Expanding procedure coverage and regulatory approvals remain critical factors. Competitive progress relies on clinical outcomes, cost advantages, and scalable platform design to meet the rising demand for AI-supported surgical automation worldwide.
Market Key Players
- Intuitive Surgical Inc.
- Medtronic plc
- Johnson & Johnson (Auris Health)
- Stryker Corporation
- Zimmer Biomet Holdings Inc.
- Accuray Incorporated
- CMR Surgical Ltd.
- Asensus Surgical Inc.
- Activ Surgical Inc.
- Titan Medical Inc.
- Medrobotics Corporation
- Smith & Nephew plc
- Renishaw plc
- Vicarious Surgical Inc.
- Othe key players
Recent Developments
- In Aug 2024: CE Mark for Accuray Helix™ helical radiation delivery system. Regulatory clearance was received in the EU for a new platform positioned to enhance treatment efficiency and precision within Accuray’s portfolio (CyberKnife®/Radixact®). The development strengthens the company’s advanced, robotics-enabled radiosurgery offering.
- In April 2024: Medtronic introduced a digital platform enhancement: the Touch Surgery™ Ecosystem was upgraded to include a Live Stream capability and 14 newly developed AI-driven algorithms covering surgical workflow, instrument and anatomy detection in laparoscopic and robotic-assisted procedures. This development advances the company’s ambition to integrate AI analytics and video-based insights into robot-assisted and minimally invasive surgery, enabling hospitals and surgical teams to gain actionable post-procedure performance insights and to support remote observation/training.
- In April 2024: The company announced the successful completion of the world’s first robotic-assisted shoulder replacement surgery using its ROSA® Shoulder System. The system had received U.S. FDA 510(k) clearance in February 2024. The platform integrates pre-operative 3D imaging (via the Signature™ ONE 2.0 Surgical Planning System) with intra-operative robotic assistance to execute anatomical or reverse shoulder arthroplasty with data-driven precision.
- In March 2024: The company announced that its next-generation multi-port robotic system, the da Vinci 5, received clearance from the U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA) for use in all surgical specialties and procedures indicated for its predecessor (da Vinci Xi), excluding cardiac and pediatric indications. This marks a major product-launch milestone for the company’s robotic surgical portfolio, providing a broader platform for automation, advanced visualization and future integration of AI-based tools.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) US$ 7.87 Billion Forecast Revenue (2034) US$ 50.38 Billion CAGR (2025-2034) 20.4% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, COVID-19 Impact, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Product Type (Hardware, Services), By Level of Automation (Semi-Autonomous Systems, Autonomous Systems, Telerobotic Systems), By Application (General Surgery, Orthopedic Surgery, Neurological Surgery, Urological Surgery, Gynecological Surgery, Others), By End-User (Hospitals, Ambulatory Surgical Centers) Regional Analysis North America – The US, Canada, & Mexico; Western Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Portugal, Ireland, Austria, Switzerland, Benelux, Nordic, & Rest of Western Europe; Eastern Europe – Russia, Poland, The Czech Republic, Greece, & Rest of Eastern Europe; APAC – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia & New Zealand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, & Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Colombia, Chile, Argentina, Costa Rica, & Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – Algeria, Egypt, Israel, Kuwait, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, & Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Intuitive Surgical Inc., Medtronic plc, Johnson & Johnson (Auris Health), Stryker Corporation, Zimmer Biomet Holdings Inc., Accuray Incorporated, CMR Surgical Ltd., Asensus Surgical Inc., Activ Surgical Inc., Titan Medical Inc., Medrobotics Corporation, Smith & Nephew plc, Renishaw plc, Vicarious Surgical Inc., Othe key players Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  AI-based Surgical Robots MarketPublished date: Oct 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
AI-based Surgical Robots MarketPublished date: Oct 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Intuitive Surgical Inc.
- Medtronic plc
- Johnson & Johnson (Auris Health)
- Stryker Corporation
- Zimmer Biomet Holdings Inc.
- Accuray Incorporated
- CMR Surgical Ltd.
- Asensus Surgical Inc.
- Activ Surgical Inc.
- Titan Medical Inc.
- Medrobotics Corporation
- Smith & Nephew plc
- Renishaw plc
- Vicarious Surgical Inc.
- Othe key players










