Global 5G Market Size, Share and Growth By Component (Hardware, Software, Services), By Network Architecture (Standalone (SA) 5G, Non-Standalone (NSA) 5G), By Application (Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), Massive Machine-Type Communications (mMTC), Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communications (URLLLC), Fixed Wireless Access (FWA)), By End-User (Consumers, Enterprises, Industrial Verticals), By End-User Industry (Manufacturing (Industry 4.0), Automotive & Transportation, Healthcare, Media & Entertainment, Energy & Utilities, Others), By Regional Analysis, Global Trends and Opportunity, Future Outlook By 2025-2035
- Published date: Dec. 2025
- Report ID: 171375
- Number of Pages: 341
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
- Report Overview
- Top Market Takeaways
- Quick Market Facts
- Increasing Adoption of Technologies
- Investment Opportunities
- AI-Led Growth Outlook
- US Market Size
- Key Insights
- By Component
- By Network Architecture
- By Application
- By End User
- By End-User Industry
- Strategic Snapshot
- Value Chain Overview
- Emerging Trends
- Growth Factors
- Key Market Segments
- Driver
- Restraint
- Opportunity
- Challenge
- Competitive Analysis
- Recent Developments
- Report Scope
Report Overview
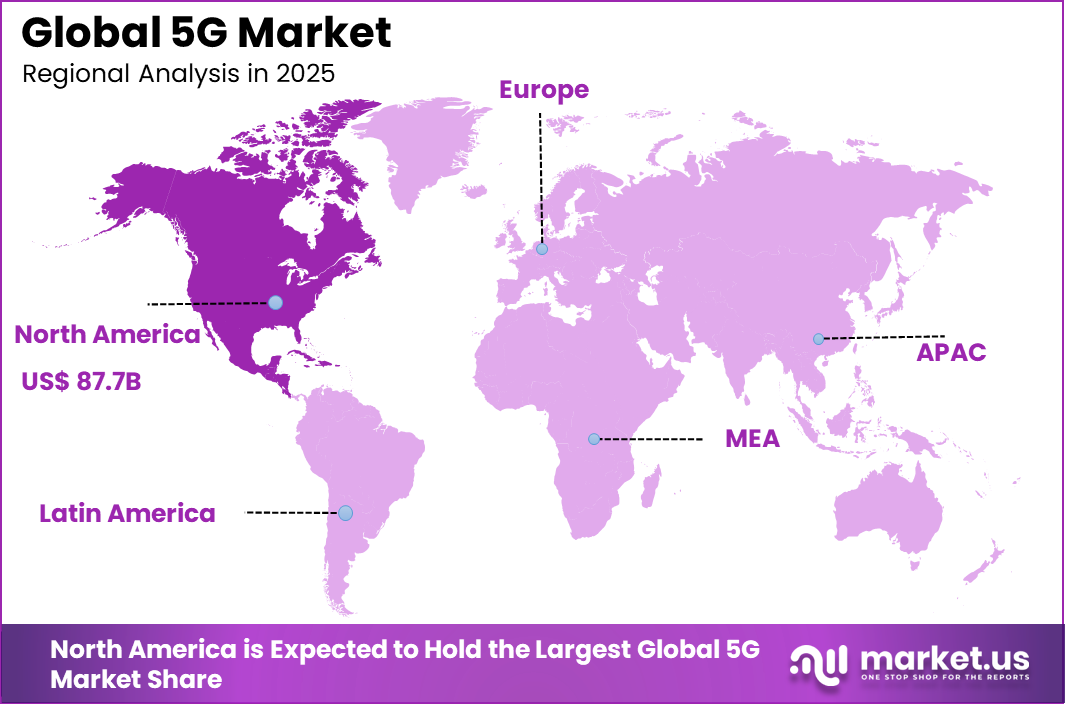
The Global 5G Market size is expected to be worth around USD 2,156 Billion By 2035, from USD 261.2 billion in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 23.5% during the forecast period from 2026 to 2035. In 2025, North America held a dominan Market position, capturing more than a 33.6% share, holding USD 87.6 Billion revenue.
The 5G market represents the next phase of mobile network development, designed to deliver faster data speeds, lower latency, and higher network reliability. It supports advanced digital services across industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, transportation, and media. Unlike earlier generations, 5G is built to handle large volumes of connected devices at the same time. This makes it a core foundation for digital infrastructure development.
By late 2024, global 5G connections hit 2.25 billion, growing four times faster than 4G at the same point, and reached 2.4 billion by Q1 2025. Over 600 operators in 184 countries now invest in these networks, shifting from tests to full operations. The market includes network equipment, software platforms, core networks, and end-user devices that support 5G connectivity. Telecom operators are upgrading existing infrastructure while also building new standalone 5G networks.
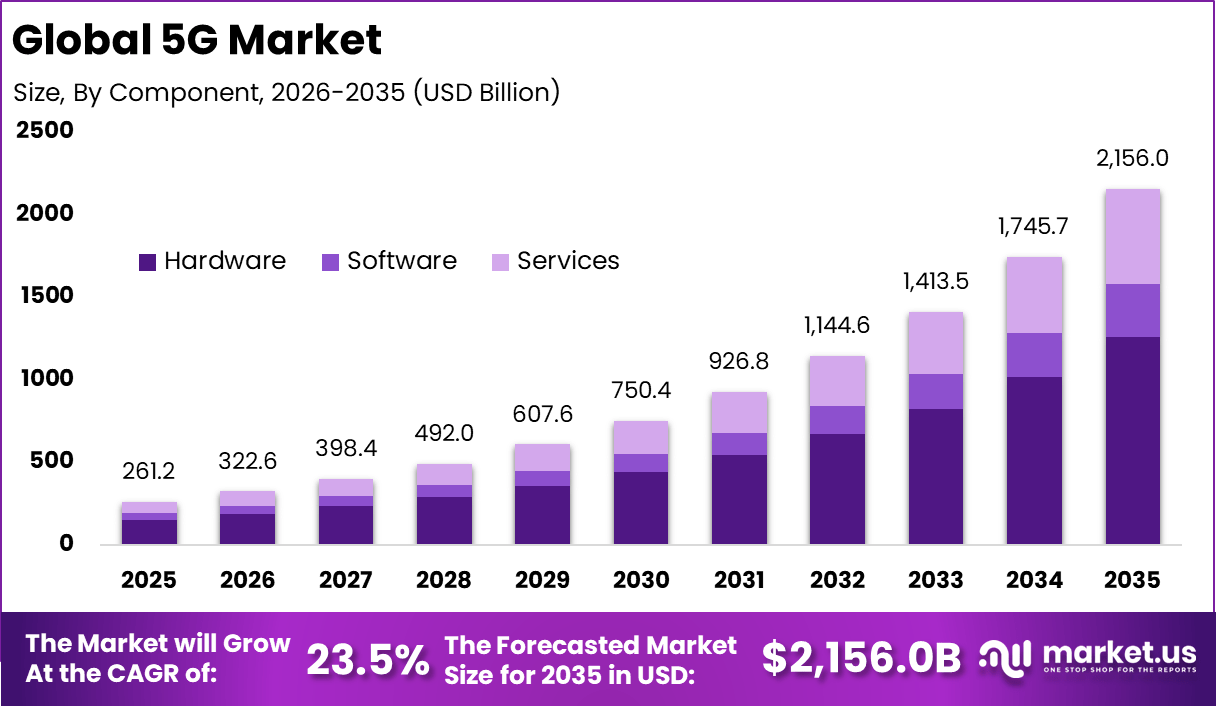
Demand for 5G services is rising across both consumer and enterprise segments. Consumers are adopting 5G-enabled smartphones to access faster downloads, smoother video streaming, and improved gaming experiences. In dense urban areas, network congestion on older technologies has further increased the need for 5G capacity. This steady consumer pull is supporting early revenue generation.
Top Market Takeaways
- Hardware dominated the 5G market with a 58.4% share, as radios, antennas, and core network equipment remain critical for large-scale deployment.
- Non-Standalone 5G accounted for 62.7%, reflecting faster rollout strategies that build on existing 4G infrastructure.
- Enhanced Mobile Broadband led applications with 71.5%, supported by rising demand for high-speed data, streaming, and low-latency services.
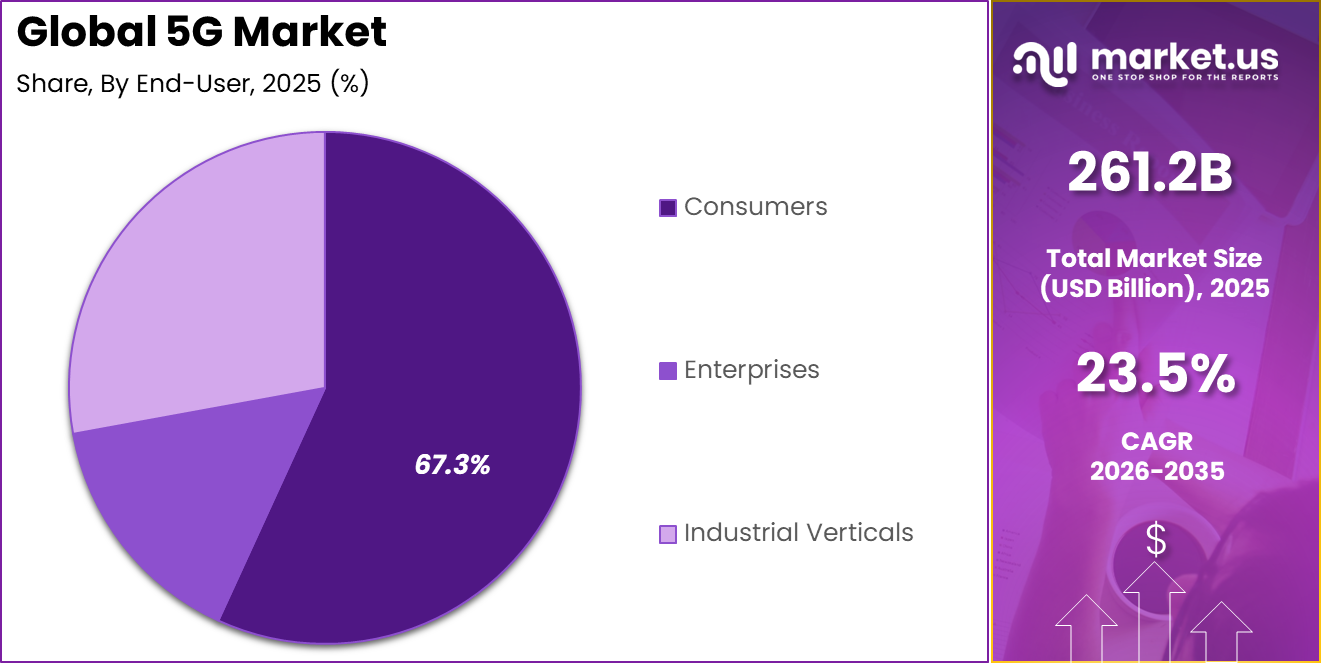
- Consumers represented 67.3% of end-user adoption, driven by widespread use of 5G-enabled smartphones and data-intensive applications.
- Manufacturing captured 28.9% among end-user industries, showing increasing use of 5G in automation, robotics, and smart factory environments.
- North America held a 33.6% share, supported by early spectrum allocation, strong operator investments, and advanced digital ecosystems.
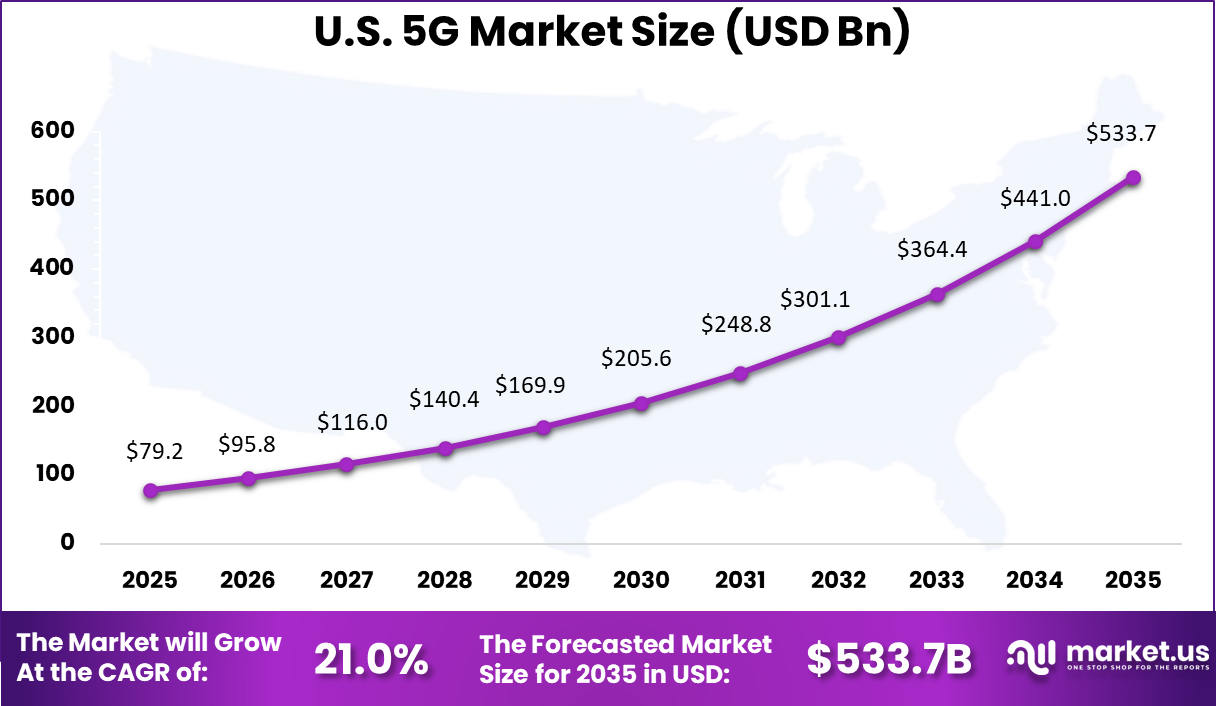
- The U.S. market reached USD 79.2 billion in 2024 and is expanding at a 21.02% CAGR, driven by nationwide network expansion, enterprise adoption, and rising mobile data consumption.
Quick Market Facts
Global 5G adoption continues to accelerate, with subscriptions expected to reach 2.9 bn by late 2025, representing nearly one third of all mobile subscriptions worldwide. Connections had already reached close to 2 bn by the first quarter of 2024, supported by the addition of 185 mn new users. North America leads adoption with 32% of cellular connections on 5G, followed by Northeast Asia with 1.4 bn connections and strong uptake across GCC countries.
India has emerged as a key growth market, reaching 365 mn 5G subscribers within three years of launch, equal to 35% penetration. By 2025, the country had deployed over 486,000 5G base transceiver stations, supporting wide coverage and high performance. India ranked among the top 10 countries globally for 5G speeds in 2023, with median speeds exceeding 300 Mbps, and 5G is expected to contribute around ₹36.4 trillion or USD 455 billion to the economy by 2040.
From a performance and technology perspective, high median speeds are driving increased data usage, with monthly consumption ranging between 18 GB and 55 GB in India. Population coverage outside China is projected to reach 60% by the end of 2025. In enterprise environments, around 75% of data is expected to be processed at the edge by 2025, enabled by low latency and high capacity 5G networks that support advanced digital and industrial use cases.
Increasing Adoption of Technologies
The adoption of 5G is closely linked with technologies such as edge computing, cloud platforms, and Internet of Things systems. Edge computing reduces data processing delays by placing compute resources closer to users and devices. When combined with 5G, this setup enables real-time analytics and faster decision-making. This integration is particularly important for industrial automation and smart infrastructure.
Another area of adoption is network virtualization and software-defined networking. These technologies allow operators to manage networks more efficiently and scale services based on demand. Network slicing enables multiple use cases to operate on the same physical infrastructure without interference. This flexibility improves service quality while lowering operational complexity.
A major reason for adopting 5G is its ability to support applications that require real-time responsiveness. Ultra-low latency makes it suitable for autonomous systems, remote operations, and interactive digital services. These capabilities are not reliably achievable with previous mobile generations. As a result, 5G is seen as essential for next-generation digital applications.
Another reason is long-term cost efficiency for network operators and enterprises. Although initial investments are high, 5G networks are more energy-efficient per unit of data transmitted. Improved spectral efficiency also allows better use of limited frequency resources. Over time, these benefits help reduce total cost of ownership.
Investment Opportunities
Investment opportunities in the 5G market extend beyond telecom operators. Equipment manufacturing, semiconductor design, and network software development are key areas attracting capital. Companies involved in radio access networks, core network software, and testing tools are positioned for sustained demand. These segments benefit directly from ongoing rollout and upgrade cycles.
There is also growing investor interest in enterprise-focused 5G solutions. Private networks, edge platforms, and industry-specific applications offer recurring revenue potential. Startups and system integrators are playing a role in tailoring 5G deployments for specific use cases. This diversification broadens the investment landscape across the value chain.
AI-Led Growth Outlook
Artificial intelligence is becoming a central element in the evolution of 5G networks. AI is used to optimize network performance, predict traffic patterns, and automate maintenance tasks. These capabilities improve service reliability and reduce downtime. As networks grow more complex, AI-driven management becomes increasingly important.
AI-enabled applications are also driving traffic and service demand on 5G networks. Real-time analytics, intelligent video processing, and autonomous systems rely on both AI and low-latency connectivity. The combination of AI and 5G creates a reinforcing growth cycle. This interaction is expected to shape the next phase of network monetization.
US Market Size
The United States reached USD 79.2 Billion with a CAGR of 21.02%, reflecting rapid market expansion. Growth is driven by consumer demand and industrial adoption. Ongoing network upgrades continue across urban and rural areas. 5G remains a core technology for digital development. By late 2025, the U.S. 5G market shows near full population coverage, with most Americans able to access 5G services from major carriers, according to 5G Americas.
The country recorded over 340 million 5G connections by Q3 2025, reflecting strong nationwide adoption. Device penetration has also advanced, with 5G enabled devices accounting for nearly 50% of all wireless connections, underscoring the transition toward next generation mobile networks.
North America accounts for 33.6%, supported by early 5G rollout and strong telecom infrastructure. The region shows high adoption across consumer and enterprise segments. Investments focus on expanding coverage and improving capacity. Digital readiness supports steady growth.
Key Insights
Adoption and Coverage Insights
- The U.S. has achieved over 99% 5G penetration in 2025, far exceeding the global average of 36%.
- Around 93.2% of the U.S. population is covered by at least one 5G network as of late 2025.
- North America, led by the U.S., reached 339 million 5G connections by Q2 2025 and is on track to exceed 100% population coverage by year-end.
- T-Mobile shows the highest availability, with about 89.4% of users accessing 5G most of the time.
- AT&T delivers roughly 90% availability across major urban areas.
- Verizon is recognized for strong reliability and speed in urban markets, supported by mmWave and C-band deployments.
Data Usage and Performance Insights
- North American users consume an average of 111 GB per month in 2025, the highest globally.
- Median U.S. download speeds reached 155 Mbps in 2025, up from 128 Mbps in 2022.
- T-Mobile leads average 5G download performance at around 150 Mbps.
- 5G now carries about 43% of all mobile data traffic, rising from 34% at the end of 2024.
Economic and Infrastructure Insights
- Over 95% of net new broadband additions in the U.S. over the past two years came from 5G fixed wireless access services.
- U.S. 5G FWA connections are expected to exceed 13 million by the end of 2025.
- Total U.S. wireless investment has reached $734 billion, with $219 billion dedicated to 5G since 2018.
- The U.S. 5G technology market is expected to expand from $4.08 billion in 2024 to nearly $23.3 billion by 2032.
- As of late 2025, North America operates 18 commercial 5G networks, reflecting a mature and competitive infrastructure landscape.
By Component
Hardware accounts for 58.4%, showing that physical infrastructure remains the foundation of 5G deployment. This includes base stations, antennas, routers, and network equipment required to support high-speed connectivity. Strong investment in hardware is essential to enable wide network coverage. Reliable hardware supports consistent network performance.
The dominance of hardware is driven by ongoing network expansion and capacity upgrades. Telecom operators continue to invest in advanced equipment to support higher data volumes. Hardware improvements also help reduce latency and improve signal stability. These factors sustain demand across regions.
By Network Architecture
Non-Standalone 5G holds 62.7%, reflecting its role as the primary architecture during early and mid-stage deployments. This architecture builds on existing 4G infrastructure while adding 5G radio capabilities. It allows faster rollout with lower initial investment. Operators use this model to accelerate service availability.
Adoption of Non-Standalone 5G is supported by cost efficiency and deployment speed. Network providers can upgrade existing systems instead of replacing them completely. This approach reduces operational risk during transition. It also supports gradual migration to full 5G networks.
By Application
Enhanced Mobile Broadband represents 71.5%, making it the leading application of 5G technology. This application focuses on delivering higher data speeds and improved network capacity. Consumers benefit from better video streaming, gaming, and mobile internet services. Network performance improves significantly under heavy data usage.
Growth in this segment is driven by rising demand for data-intensive applications. Increased smartphone usage and digital content consumption support adoption. Enhanced broadband improves user experience across urban and high-density areas. This continues to drive network investment.
By End User
Consumers account for 67.3%, highlighting their central role in 5G adoption. Consumer use cases include mobile internet access, entertainment, and smart device connectivity. High smartphone penetration supports strong demand. Consumers expect faster and more reliable connectivity.
Adoption among consumers is driven by improved service quality and new digital experiences. 5G enables smoother streaming and lower latency applications. Telecom providers focus heavily on consumer offerings. This segment remains the largest source of network traffic.
By End-User Industry
Manufacturing holds 28.9%, making it the leading industrial end-user segment. Manufacturers use 5G to support automation, connected machinery, and real-time monitoring. Reliable connectivity improves production efficiency. It also supports advanced industrial communication.
Growth in manufacturing adoption is driven by digital transformation initiatives. 5G enables faster data exchange between machines and systems. This improves operational visibility and control. Manufacturers continue to invest in connected production environments.
Strategic Snapshot
From a strategic perspective, 5G is viewed as a long-term infrastructure platform rather than a short-term revenue upgrade. Operators are focusing on coverage expansion, service quality, and enterprise partnerships. Collaboration with cloud providers and technology firms is becoming common. These strategies aim to build ecosystems instead of isolated services.
At the national level, 5G strategy is closely tied to digital sovereignty and economic development. Countries are aligning spectrum policy, security frameworks, and innovation programs around 5G deployment. This coordinated approach supports large-scale adoption across industries. Strategic alignment is expected to remain a defining feature of the market.
Value Chain Overview
The 5G value chain begins with research, standards development, and semiconductor manufacturing. Chipsets, radio components, and network processors form the foundation of all 5G equipment. These components are integrated into base stations, core networks, and user devices. Strong coordination across suppliers is required to ensure interoperability.
Further along the chain, telecom operators deploy and operate the networks. Software providers, cloud platforms, and system integrators add service layers on top of connectivity. Enterprises and consumers represent the final demand side of the value chain. Value creation increasingly occurs at the application and service level rather than basic connectivity.
Emerging Trends
Aspect Details Private 5G Networks Expansion Private 5G grows fast in factories for secure control. Over 70% of 2025 investments target standalone networks. They offer dedicated coverage public 5G cannot match. Standalone 5G Deployments Operators shift to standalone cores for low latency. Eight new launches in Asia Pacific in 1H 2025. Standalone holds 48% share for critical uses. Edge Computing Integration Edge pairs with 5G for AR, VR, and AI near devices. New networks boosted edge use cases in 1H 2025. Latency drops under 10 ms. Network Slicing Maturity Slicing creates tailored virtual networks securely. Europe had six new launches in
1H 2025. It aids video and control efficiency.Growth Factors
Aspect Details Rising Mobile Data Demand Data surges from video drive 5G uptake. Connections hit 2.6 billion by end Q2 2025, up 37% year over year. Faster speeds help manage crowded areas. Enterprise Digitalization Factories are adopting 5G to support automation. India shipments rose 16% year over year in Q3 2025. This improves real time productivity. Spectrum Availability Auctions are releasing new spectrum, including India’s Rs 96,000 crore auction in 2024. Bids reached Rs 11,000 crore on day one. This supports wider 5G coverage. Device Ecosystem Growth Affordable 5G smartphones are expanding rapidly. India reached 87% 5G phone share in Q2 2025 with a sharp rise in low cost models. Global adoption reached 20.1%. Key Market Segments
By Component
- Hardware
- Software
- Services
By Network Architecture
- Standalone (SA) 5G
- Non-Standalone (NSA) 5G
By Application
- Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB)
- Massive Machine-Type Communications (mMTC)
- Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communications (URLLC)
- Fixed Wireless Access (FWA)
By End-User
- Consumers
- Enterprises
- Industrial Verticals
By End-User Industry
- Manufacturing (Industry 4.0)
- Automotive & Transportation
- Healthcare
- Media & Entertainment
- Energy & Utilities
- Others
Regional Analysis and Coverage
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherlands
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of Latin America
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Driver
The primary driver of the 5G market is the sharp rise in mobile data consumption across consumer and enterprise users. High-definition video, cloud-based services, and real-time applications are increasing pressure on existing network capacity. 5G networks are designed to deliver higher speeds and lower latency to address these performance gaps. This technical advantage is pushing telecom operators to accelerate network upgrades.
Another important driver is the growing demand for digital infrastructure in industrial sectors. Manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and utilities rely on stable and low-latency connectivity for automation and remote operations. Governments also view 5G as a strategic asset for economic growth and digital inclusion. Policy support and spectrum allocation initiatives further strengthen deployment momentum.
Restraint
High infrastructure deployment costs remain a major restraint for the 5G market. Network rollout requires significant investment in base stations, fiber backhaul, and advanced core networks. In many regions, returns on investment take time to materialize due to pricing pressures. This slows adoption, especially in low-density and rural areas.
Another restraint is the complexity of spectrum availability and regulation. Spectrum allocation differs across countries and often involves lengthy auction processes. Delays in licensing can push back commercial rollout timelines. These regulatory challenges add uncertainty to long-term planning for network operators.
Opportunity
The expansion of private 5G networks presents a strong growth opportunity. Enterprises are exploring dedicated networks to support secure and controlled environments such as factories, ports, and campuses. Private deployments allow customization based on performance and security needs. This creates new revenue streams beyond traditional consumer services.
Another major opportunity lies in the integration of 5G with edge computing and cloud platforms. These combinations support real-time analytics and low-latency applications. Industries such as smart transportation and digital healthcare benefit directly from this setup. As use cases mature, demand for specialized 5G solutions is expected to rise.
Challenge
Network security is one of the most critical challenges facing the 5G market. The expanded attack surface created by virtualized networks and connected devices increases security risks. Operators must manage data protection while maintaining service performance. Addressing these concerns requires continuous investment in security frameworks.
Another challenge is ensuring consistent coverage and service quality. Urban deployments progress faster than rural rollouts due to economic viability. This creates uneven access to 5G benefits across regions. Bridging this gap remains a long-term challenge for both operators and policymakers.
Competitive Analysis
The competitive landscape of the 5G market is shaped by global telecom equipment providers, network software developers, and service operators. Competition is focused on network performance, energy efficiency, and software capabilities. Vendors are increasingly differentiating through cloud-native cores and network automation tools. Strategic partnerships are common to accelerate innovation and reduce deployment risk.
Telecom operators compete on coverage quality, pricing models, and enterprise service offerings. Collaboration with cloud providers and system integrators is becoming a key competitive strategy. Smaller technology firms compete by offering niche solutions for private networks and industry-specific use cases. Overall competition is shifting from hardware dominance to service and solution differentiation.
Top Key Players in the Market
- Ericsson
- Nokia Corporation
- Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
- ZTE Corporation
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Qualcomm Incorporated
- Intel Corporation
- NEC Corporation
- Fujitsu, Ltd.
- Ciena Corporation
- Mavenir Systems, Inc.
- Affirmed Networks
- CommScope Holding Company, Inc.
- Amdocs, Ltd.
- Others
Recent Developments
- December, 2025 – Ericsson and Orange deployed a next-generation 5G mission-critical network in Madrid for public safety, using Ericsson’s private 5G portfolio to deliver low-latency push-to-talk and video for first responders across urban sites.
- December, 2025 – Nokia signed a 5-year RAN deal with Telefónica Germany to modernize its 5G network using AirScale portfolio, Habrok Massive MIMO, Cloud RAN and AI-driven MantaRay management for capacity and sustainability.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2025) USD 261.2 Bn Forecast Revenue (2035) USD 2,156 Bn CAGR(2026-2035) 23.5% Base Year for Estimation 2025 Historic Period 2020-2024 Forecast Period 2026-2035 Report Coverage Revenue forecast, AI impact on Market trends, Share Insights, Company ranking, competitive landscape, Recent Developments, Market Dynamics and Emerging Trends Segments Covered By Component (Hardware, Software, Services), By Network Architecture (Standalone (SA) 5G, Non-Standalone (NSA) 5G), By Application (Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), Massive Machine-Type Communications (mMTC), Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communications (URLLLC), Fixed Wireless Access (FWA)), By End-User (Consumers, Enterprises, Industrial Verticals), By End-User Industry (Manufacturing (Industry 4.0), Automotive & Transportation, Healthcare, Media & Entertainment, Energy & Utilities, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of Latin America; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Ericsson, Nokia Corporation, Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., ZTE Corporation, Cisco Systems, Inc., Qualcomm Incorporated, Intel Corporation, NEC Corporation, Fujitsu, Ltd., Ciena Corporation, Mavenir Systems, Inc., Affirmed Networks, CommScope Holding Company, Inc., Amdocs, Ltd., Others Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three license to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Ericsson
- Nokia Corporation
- Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
- ZTE Corporation
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Qualcomm Incorporated
- Intel Corporation
- NEC Corporation
- Fujitsu, Ltd.
- Ciena Corporation
- Mavenir Systems, Inc.
- Affirmed Networks
- CommScope Holding Company, Inc.
- Amdocs, Ltd.
- Others












