Introduction
Cybersecurity statistics underscore the rapidly intensifying landscape of digital threats as cloud adoption, remote operations, and device interconnectivity continue to surge. Organisations across various industries are facing increased exposure as cyberattacks become more advanced, automated, and financially disruptive. The steady rise in data breaches, ransomware attacks, identity theft, and assaults on critical infrastructure signals an urgent need for more resilient security measures.
In response, governments, regulators, and enterprises are prioritizing investments in modern defenses. Including zero-trust architectures, AI-enabled threat detection, and multi-factor authentication. With cybersecurity spending increasing and global compliance requirements strengthening. Current statistics provide essential visibility into evolving threat dynamics, organizational readiness, and the strategies needed to protect digital environments.
Editor’s Choice
- The global average cost of a data breach in 2025 reached $4.44 million, showing a slight decline from $4.88 million in 2024.
- In the United States, the average cost of a data breach increased to $10.22 million in 2025, marking the highest globally.
- Around 88% of cybersecurity breaches are attributed to human error.
- The average time to identify a breach in 2025 was 181 days, continuing a trend of improvement since 2021.
- The average lifecycle of a breach decreased to 241 days in 2025, down from 258 days in 2024.
- The likelihood of detecting and prosecuting a cybercrime entity in the U.S. remains extremely low at 05%.
- About 68% of breaches in 2025 involved a human element.
- The Federal Trade Commission received over 2 million reports of identity theft in 2024.
- Security breaches in 2024 increased by 75% year-over-year, with organizations experiencing an average of 1,876 cyberattacks per quarter.
- Cyber fatigue affected 46% of organizations in 2025.
- Around 64% of Americans have never checked if a data breach impacted them.
- Nearly 56% of Americans are unaware of the steps to take if they are affected by a cyberattack.
- Only 4% of organizations feel fully confident in their security for connected devices.
- The global cybersecurity workforce was estimated at 7 million professionals in 2025.
- The median annual salary for information security analysts was $102,600 in 2021, with the lowest 10% earning less than $61,520 and the highest 10% earning more than $165,920.
Moreover
- Chief Information Security Officers earned an average salary of $170,980 as of July 2022.
- Employment for information security analysts is projected to grow by 35% from 2021 to 2031.
- Approximately 56,500 new cybersecurity jobs are expected to be created between 2021 and 2031.
- By 2025, there are projected to be 5 million unfilled cybersecurity positions globally.
- An estimated 93% of organizations plan to increase cybersecurity spending over the next year.
- Approximately 600 million cyberattacks occur daily, underscoring the massive scale and frequency of global cyber threats.
- Nearly 54 people per second fall victim to a cyberattack, revealing the rapid and continuous nature of digital exploitation.
- Nearly 6 in 10 businesses have experienced a ransomware attack this year, highlighting the growing vulnerability of organizations worldwide.
- North America recorded an 8% increase in ransomware incidents this year, reflecting a regional surge in targeted cybercrime.
- The average cost of an effective attack on an Internet of Things (IoT) device tops $330,000, highlighting the high cost of breaches in connected ecosystems.
- Over $6.3 billion was lost through business email compromise scams in the past year, underscoring the significant financial risks associated with social engineering attacks.
Further
- The largest known data breach exposed more than 3 billion user accounts, marking one of the most severe security incidents in digital history.
- Global cybercrime losses are projected to hit 63 trillion by 2029, rising from 10.5 trillion in 2025.
- Around 71% of chief risk officers expect severe operational disruption due to cyber risks in the coming year.
- The United States was the most targeted country in 2025, accounting for 8% of all cyberattacks.
- Nearly 98 % of security professionals have adopted or plan to adopt AI-based technologies within 12
- Third-party involvement in data breaches doubled to 30%, highlighting the growing vulnerability of supply chains.
- Exploitation of vulnerabilities surged by 34%, driven largely by zero-day attacks on perimeter devices and VPNs.
- Ransomware appeared in 44% of breaches, up 37% year-over-year, despite a drop in median ransom payments.
- Data exfiltration was present in 80% of cyberattacks, confirming that data theft is the primary motive behind most breaches.
- 100% of companies now use AI-generated code, yet 81% of security teams lack visibility into its deployment, indicating a growing concern about shadow AI.
- The average annual cost of insider incidents reached $ 17.4 million per organization, with non-malicious insiders responsible for the majority of Cases.
Historic Data Breaches Statistics
- Over 560 million Ticketmaster customers had their personal data stolen in a 2024 cyber breach.
- The 2021 LinkedIn breach exposed the personal information of 700 million users, representing approximately 93% of all LinkedIn members.
- In March 2021, an attack on Microsoft compromised more than 30,000 organizations across the U.S.
- A two-year-old vulnerability, discovered in April 2021, exposed the personal data of over 533 million
- In 2021, hackers infiltrated the Colonial Pipeline Company by exploiting a single password, triggering a ransomware attack that led to nationwide fuel shortages.
- Meat producer JBS suffered a ransomware attack that shut down processing plants on four
- In 2023, T-Mobile confirmed two data breaches: the first affected 37 million customers, and the second compromised an additional 836 customers.
- In September 2021, Neiman Marcus discovered an 18-month-old breach that exposed the data of 6 million shoppers.
- A 2021 data leak exposed information of more than 100 million Android users due to misconfigured cloud services.
Further
- Robinhood suffered a social engineering attack that compromised the personal data of 5 million
- AT&T experienced 2 major breaches in 2024, exposing nearly 200 million phone numbers and passwords.
- In 2023, a hacker leaked over 220 million user email addresses from X (formerly Twitter).
- The Marriott-Starwood breach, made public in 2018, compromised data on 500 million guests, dating back to 2014.
- The 2019 MGM data breach exposed records of 142 million hotel guests.
- The 2017 Wanna Cry virus infected approximately 100,000 groups and 400,000 servers in at least 150 countries, resulting in a cost of around $4 billion.
- Uber tried to conceal a breach involving the data of 57 million users by paying off the hackers.
- The 2013 Yahoo breach remains one of the largest data breaches ever, compromising approximately 3 billion
- In 2023, AT&T suffered another breach, exposing the personal details of approximately 9 million
(Source: Statista, Bizzabo, Markletic, EventMB, Exhibitor Online, LAI Live, Eventtus, 99Firms.com, BBC, RestorePrivacy, Microsoft, Auth0, Bloomberg, Wall Street Journal, IT Governance, Neiman Marcus, Check Point, Robinhood, CSO Online, CPO Magazine, Technology Inquirer, New York Times)
Cybercrime Statistics By Attack Type
Ransomware and Malware Attack Statistics
- The average ransomware payout increased from $812,380 in 2022 to nearly $1,000,000 in 2025, indicating escalating ransom demands and growing sophistication of attacks.
- The average ransomware recovery cost reached $1.5 million in 2025, reflecting growing remediation expenses for affected organizations.
- Roughly 24,000 malicious mobile applications are blocked daily, underscoring the persistent threat of malware targeting mobile users.
- In 2025, automated traffic (bots) accounted for 51% of total web activity, with 37% of these bots being malicious, attempting to steal credentials or send spam.
- Between November 2021 and October 2022, Microsoft Office applications represented 70% of the most exploited software vulnerabilities worldwide.
- Approximately 94% of malware infections are delivered via email, making phishing campaigns a primary vector for infection.
- Only 8% of organizations that pay ransoms fully recover their data, highlighting the unreliability of negotiating with attackers.
- During the first half of 2022, nearly 79 million domains were flagged as malicious, indicating a rise in automated domain-based attacks.
- Around 75% of organizations experienced at least one ransomware incident in the previous year, highlighting a widespread vulnerability.
Moreover
- Approximately 20% of all newly observed domains in early 2022 were classified as malicious.
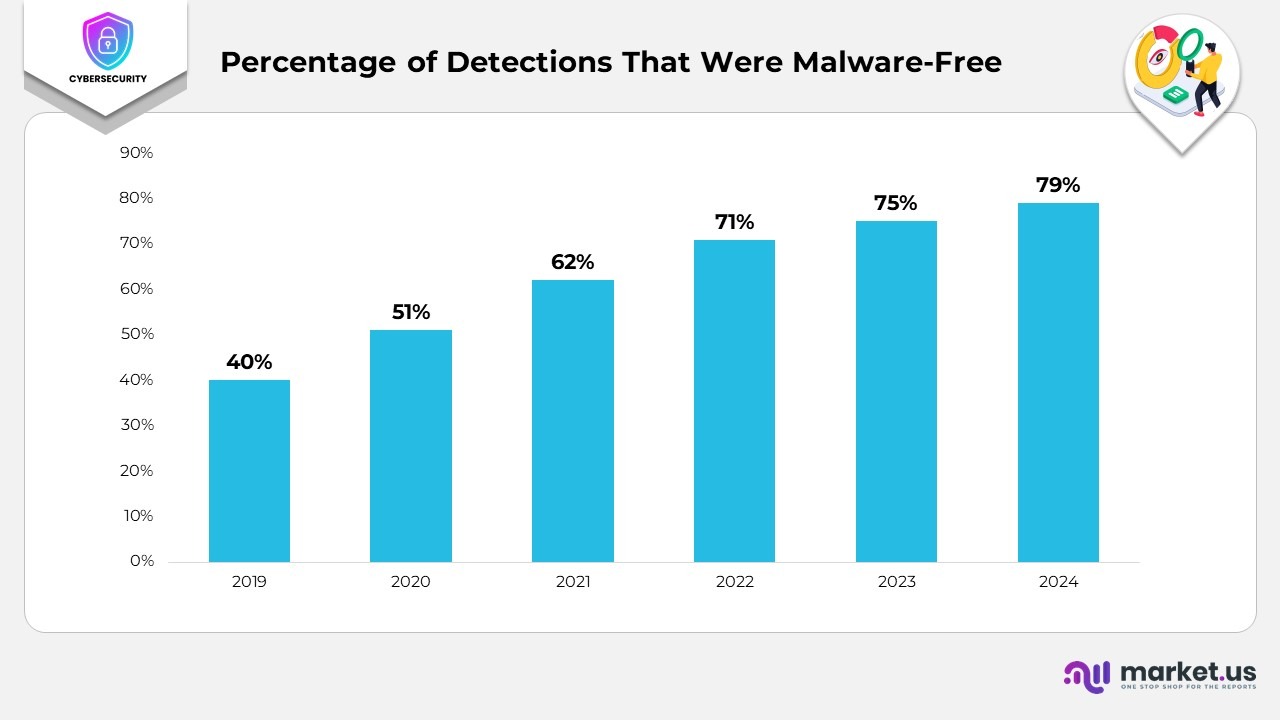
- The percentage of malware-free detections has increased steadily from 2019 to 2024, signalling a significant shift in cyber threats.
- In 2019, only 40% of detections were malware-free, indicating that most attacks still relied on traditional malware payloads.
- By 2020, this figure had risen to 51%, reflecting the early emergence of fileless and non-malware attack techniques.
- In 2021, 62% of detections were identified as malware-free, indicating a growing reliance by attackers on legitimate tools and living-off-the-land (LotL) methods.
- The upward trend continued in 2022, reaching 71%, as adversaries increasingly adopted stealthier techniques that evade signature-based defenses.
- By 2023, 75% of detections no longer contained malware, marking a clear shift towards non-malware attacks, such as credential theft and script-based exploits.
- In 2024, malware-free detections reached a peak of 79%, indicating that cybercriminals are increasingly focusing on exploiting trusted applications and user privileges to bypass traditional security controls, rather than deploying malicious files.
(Source: Sophos, Tech Jury, Imperva, Statista, Verizon, Akamai, Infosecurity Magazine, Global Threat Report 2025)
Phishing Attack Statistics
- Approximately 57% of organizations experience phishing attempts on a weekly or daily basis, highlighting the persistent nature of social engineering attacks.
- Phishing served as the initial vector in 16% of all data breaches in 2025, making it the most common method of compromise.
- Nearly 1 in 6 attacks originated from vulnerable public-facing applications or APIs, pointing to weak digital perimeter defenses.
- Phishing attacks account for over 80% of all reported cybersecurity incidents globally.
- An estimated $17,700 is lost every minute due to phishing-related cybercrimes.
(Source: GreatHorn, IBM, CSO Online)
DDoS, IoT, and Other Cyberattack Statistics
- Stolen card usage remains the most prevalent cyber threat, followed by ransomware and phishing schemes.
- The number of DDoS attacks increased by 46% in 2024 compared to 2023, reflecting a rise in botnet activity.
- Application-layer DDoS attacks increased by 15% in the second quarter of 2023, highlighting the growing complexity of attack strategies.
- Cryptocurrency-targeted crimes spiked by 600% in early 2023, before slightly easing in 2024.
- Around 35% of data breaches in 2023 involved insider threats, including both malicious and accidental incidents.
- On average, 820,000 IoT attacks occurred daily in 2025, highlighting the massive scale of exploitation of connected devices.
- Nearly 58% of IoT-related attacks targeted cryptocurrency mining, indicating a trend of financially motivated targeting.
- The average smart home faces over 12,000 hacking attempts per week, highlighting the critical risk posed by unsecured IoT devices.
- In 2022, hackers leaked more than 24 billion passwords, with 64% containing only 8–11 characters, making them easily crackable.
(Source: Verizon, Cloudflare, Chainalysis, Deepstrike, Purplesec, Norton)
Regional Confidence Levels in Cyber Resilience
- Latin America reported the lowest preparedness, with 42% of respondents not confident in their ability to handle major cyber incidents targeting critical infrastructure.
- Africa followed closely, with 38% expressing low confidence, while 27% remained neutral and 9% expressed high confidence in their national readiness.
- Asia displayed moderate confidence, with only 20% lacking faith in readiness and a combined 40% expressing confidence or higher assurance levels.
- The Middle East demonstrated strong optimism, with 36% of respondents expressing very high confidence, one of the highest rates globally.
- Europe reflected a balanced outlook, with 15% lacking confidence but over 50% reporting confidence or very high confidence in national cyber resilience.
- North America demonstrated robust confidence, with 65% of respondents feeling confident or very confident in their ability to respond effectively.
- Oceania ranked among the most optimistic regions, with 50% neutral, 25% confident, and 25% very confident, signaling widespread assurance in cyber readiness.

(Source: Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025, World Economic Forum)
Cybersecurity Concerns Amid Rising Geopolitical Tensions
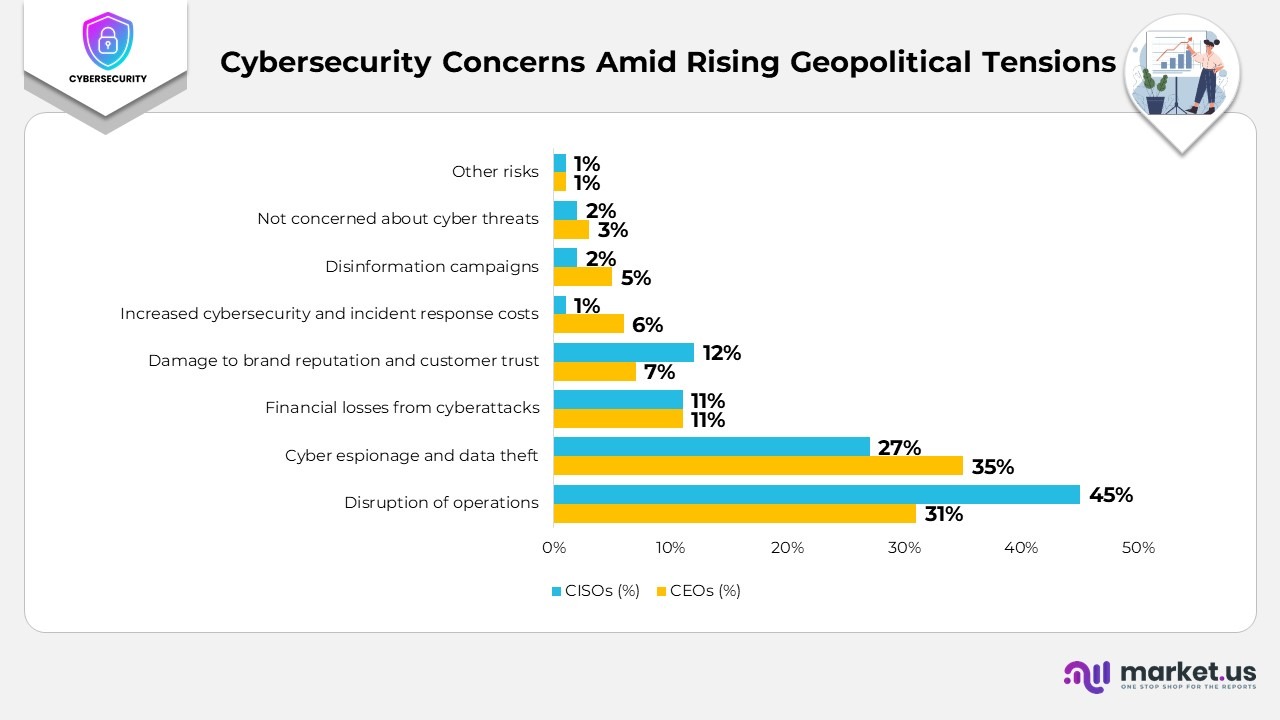
- Disruption of operations stands as the most pressing issue, with 45% of CISOs and 31% of CEOs identifying it as their top cyber risk amid geopolitical uncertainty.
- Cyber espionage and data theft closely follow, concerning 35% of CEOs and 27% of CISOs, reflecting growing fears over intellectual property exposure.
- Financial losses from cyberattacks were reported by 11% of both CEOs and CISOs, indicating a consistent concern about the direct economic repercussions.
- Damage to brand reputation and customer trust was highlighted by 12% of CISOs and 7% of CEOs, pointing to shared anxiety over public perception following breaches.
- Increased cybersecurity and incident response costs were cited by 6% of CEOs but only 1% of CISOs, suggesting differing viewpoints on financial preparedness.
- Disinformation campaigns emerged as a concern for 5% of CEOs and 2% of CISOs, indicating an emerging but secondary focus on this threat.
- Only 3% of CEOs and 2% of CISOs claimed they were not concerned about cyber threats related to geopolitical tensions, underscoring the industry’s overall vigilance.
- A minimal 1% mentioned “other” risks, reaffirming that operational disruption and cyber espionage dominate current security priorities
(Source: Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025, World Economic Forum)
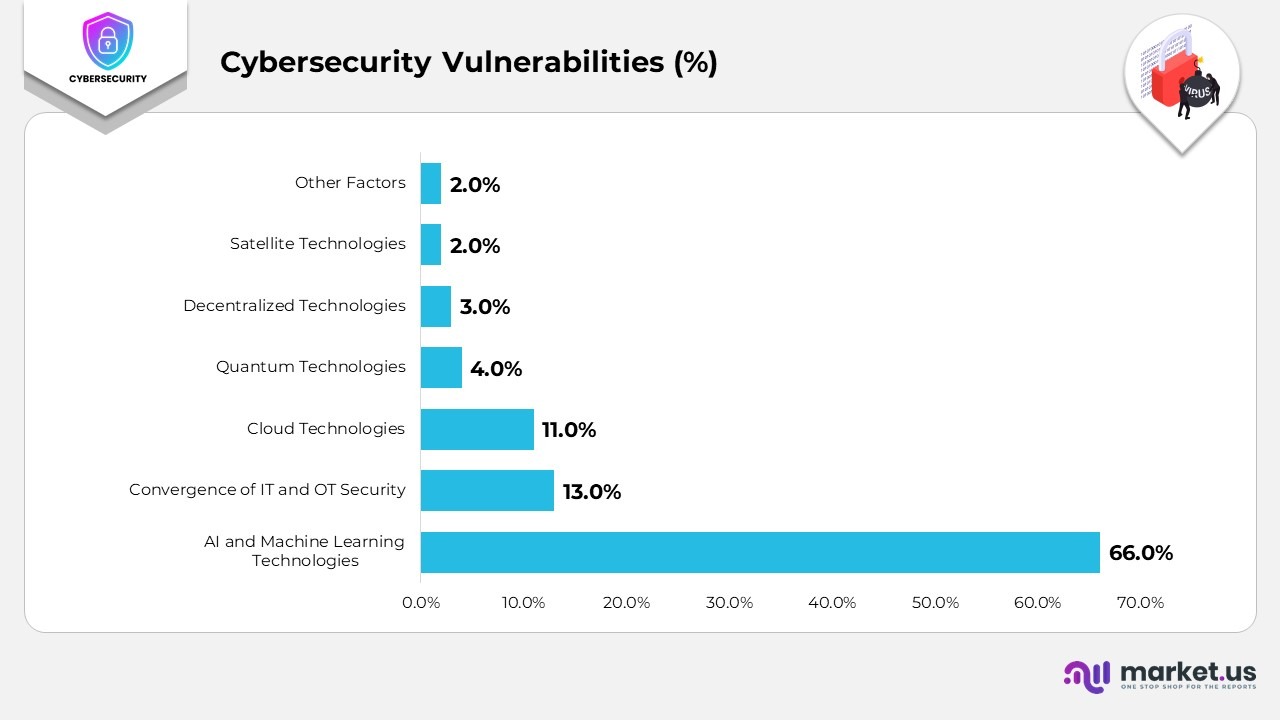
Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities
- AI and machine learning technologies are anticipated to have the most significant impact on cybersecurity, cited by 66% of respondents, due to the rise of generative AI misuse, malicious automation, and challenges in AI-driven threat detection.
- Convergence of IT and OT security is a growing concern for 13%, reflecting the increasing integration of operational systems with traditional IT infrastructure.
- Cloud technologies are seen as a critical factor by 11%, driven by the wider adoption of cloud services and evolving data protection requirements.
- Quantum technologies are expected to influence cybersecurity by 4%, as advances in quantum computing raise new challenges for encryption and data security.
- Decentralized technologies, including multi-party computation and blockchain, are mentioned by 3% as emerging sources of potential vulnerability.
- Satellite technologies, covering communication and GPS infrastructure, are highlighted by 2% of respondents as areas needing stronger security oversight.
- Other factors account for 2%, encompassing miscellaneous risks linked to evolving digital ecosystems.
(Source: Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025, World Economic Forum)
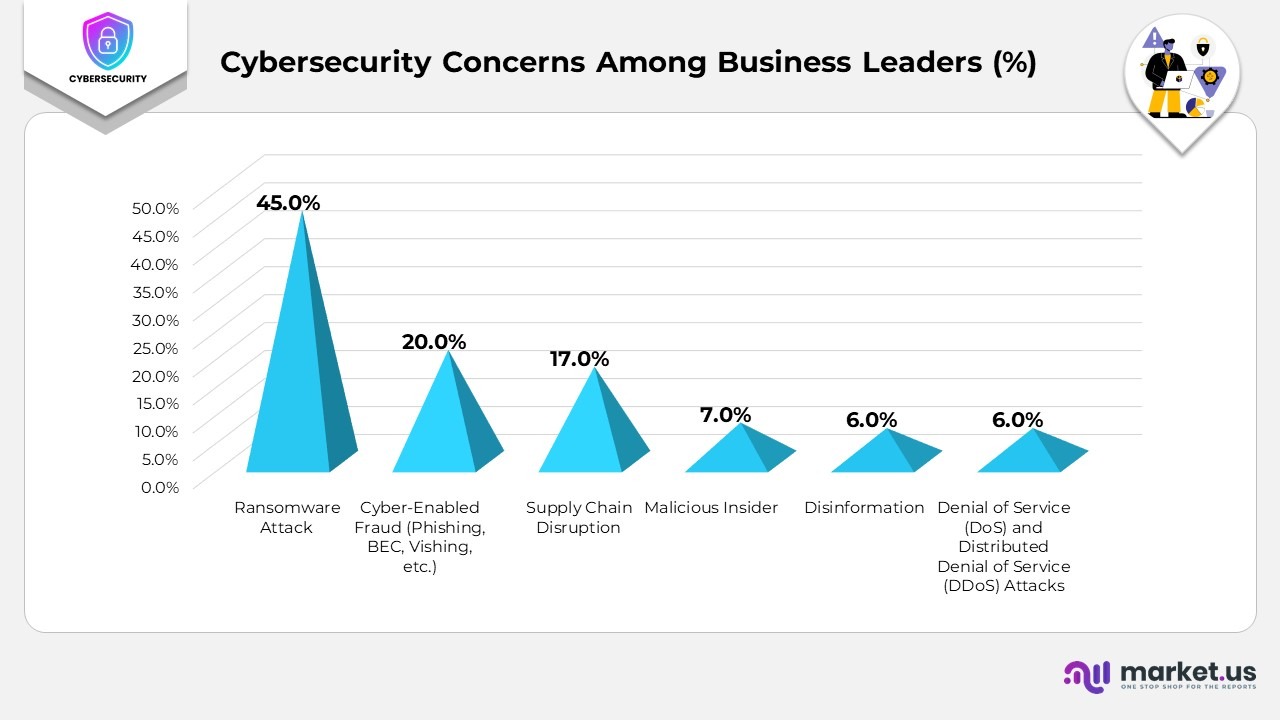
Cybersecurity Concerns Among Business Leaders
- Ransomware attacks remain the leading concern for organizations, with 45% identifying them as the most significant cyber risk.
- Cyber-enabled fraud, including phishing and business email compromise, worries 20% of respondents, underscoring the continued threat of social engineering.
- Supply chain disruption is a major issue for 17%, reflecting vulnerabilities across vendor and logistics networks.
- Malicious insiders are cited by 7% as a growing challenge, emphasizing the need for stronger internal monitoring and access management.
- Disinformation is a concern for 6% of organizations, primarily due to its potential to erode trust and damage brand reputation.
- Denial-of-service (DoS) and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks also trouble 6%, as these can disrupt business operations and online availability.
(Source: Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025, World Economic Forum)
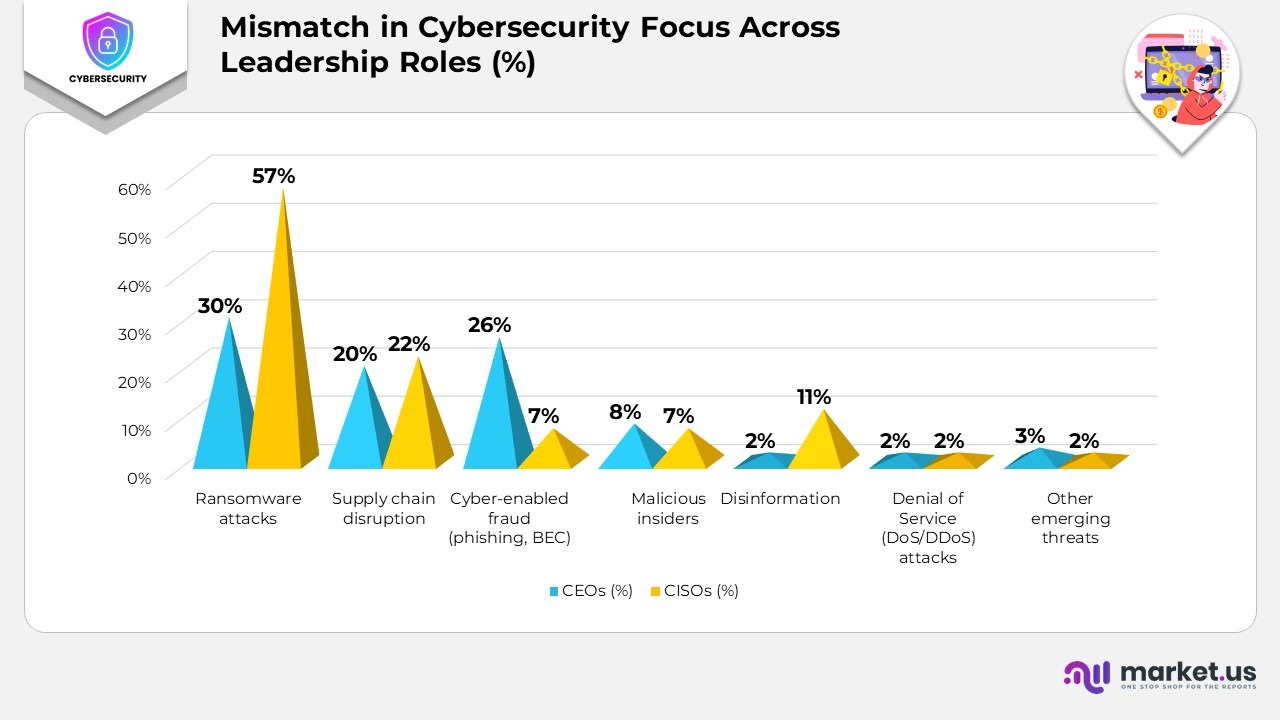
Mismatch in Cybersecurity Focus Across Leadership Roles
- Ransomware attacks remain the most pressing cyber risk, with 30% of CEOs and 57% of CISOs identifying it as their top concern, underscoring its critical impact on operations and reputation.
- Supply chain disruption ranks high, cited by 20% of CEOs and 22% of CISOs, reflecting continued worries over third-party dependencies and systemic vulnerabilities.
- Cyber-enabled fraud, including phishing and business email compromise, is prioritized by 26% of CEOs and 7% of CISOs, showing differing levels of concern about human-driven threats.
- Malicious insiders are a shared concern for 8% of CEOs and 7% of CISOs, highlighting the importance of robust internal access and monitoring policies.
- Disinformation is viewed as a risk by 2% of CEOs but draws significantly more attention from 11% of CISOs due to its potential to influence brand credibility and stakeholder trust.
- Denial of Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks are seen as a threat by 2% of both CEOs and CISOs, indicating consistent awareness of network disruption risks.
- Other emerging threats were mentioned by 3% of CEOs and 2% of CISOs, suggesting niche but notable risks beyond the traditional attack surface.
(Source: Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025, World Economic Forum)
Personal Cybersecurity Concerns
- In 2025, identity theft emerged as the top personal cyber concern, cited by 37% of respondents, reflecting rising anxieties over data misuse and impersonation.
- Loss of access to utilities was highlighted by 24%, indicating growing concerns about infrastructure-linked cyber disruptions.
- Compromised personal data and cyber extortion each concerned 20% of respondents, pointing to the persistent threat of data breaches and ransomware targeting individuals.
- By contrast, in 2024, 46% were primarily worried about cyber extortion, while only 11% cited identity theft, showing a significant shift in public perception within a year.
- Concerns over compromised data increased sharply from 9% in 2024 to 20% in 2025, indicating a growing awareness of privacy risks in digital ecosystems.
(Source: Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025, World Economic Forum)
Cybersecurity Concerns Emerging from Generative AI Adoption
- The advance of adversarial capabilities, including phishing, malware creation, and deepfakes, is the leading concern, reported by 47% of respondents.
- Data leaks involving exposure of personal or sensitive information through GenAI platforms concern 22% of participants.
- Other issues, such as AI supply chain risks, system vulnerabilities, and intellectual property disputes, were mentioned by 17% of respondents.
- The increased complexity of security governance, due to evolving compliance and oversight challenges, worries 14% of organizations.
(Source: Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025, World Economic Forum)
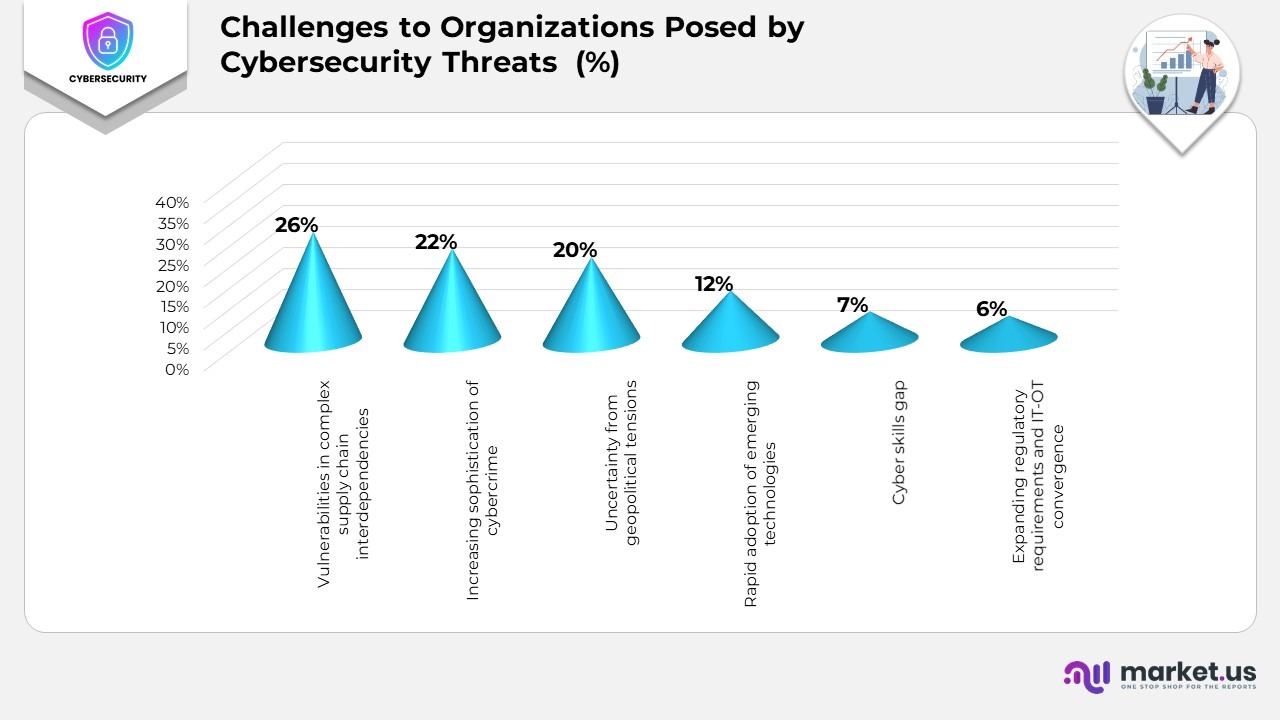
Challenges to Organizations Posed by Cybersecurity Threats
- 26% of organizations identify vulnerabilities in complex supply chain interdependencies as their biggest cybersecurity challenge, highlighting risks linked to third-party systems and cross-industry dependencies.
- 22% cite the increasing sophistication of cybercrime, underscoring how advanced tactics, such as AI-driven attacks, are intensifying security demands.
- 20% of respondents point to uncertainty from geopolitical tensions as a major factor impacting cybersecurity planning and operational stability.
- The rapid adoption of emerging technologies concerns 12%, reflecting difficulties in integrating innovation without exposing new vulnerabilities.
- 7% see the cyber skills gap as a key challenge, emphasizing the shortage of skilled professionals in defending against evolving threats.
- Both expanding regulatory requirements and IT-OT convergence are mentioned by 6% of organizations. Revealing the strain of aligning compliance and technology integration efforts within complex digital environments.
(Source: Statista, Bizzabo, Markletic, EventMB, LAI Live)
Impact of Geopolitical Tensions on Cybersecurity Strategies
- 59% of organizations report that geopolitical tensions have influenced their cybersecurity strategies, leading to noticeable operational and policy shifts.
- In response, several organizations have modified their insurance policies to adapt coverage and reflect heightened geopolitical and cyber risk exposure.
- Many have changed or are in the process of changing vendors. Prioritizing supply chain resilience and reducing dependence on high-risk regions.
- A segment of organizations has stopped conducting business in certain countries. Illustrating the tangible economic impact of rising geopolitical instability.
- Others have revised their trading or operating policies to ensure compliance with emerging global regulations and cross-border data restrictions.
- Meanwhile, 41% of organizations report that geopolitical tensions have not influenced their cybersecurity strategy. Reflecting varying levels of regional exposure and preparedness.
(Source: Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025, World Economic Forum)
Key Approaches to Closing the Global Cybersecurity Skills Gap (2025)
- 76% of organizations are focusing on upskilling their current employees, highlighting a strong commitment to developing in-house cybersecurity capabilities.
- 54% are choosing to recruit experienced cyber professionals, addressing immediate gaps by bringing in external expertise.
- 24% expect employees to independently upskill themselves, showing a shift toward personal responsibility in continuous learning.
- Another 24% are promoting apprenticeship programs, fostering a pipeline of skilled cybersecurity talent through practical training.
- 23% are recruiting candidates without traditional cybersecurity degrees, emphasizing skills-based hiring over formal education credentials.
- 7% of organizations are pursuing other innovative approaches to address workforce shortages and strengthen overall cyber resilience.
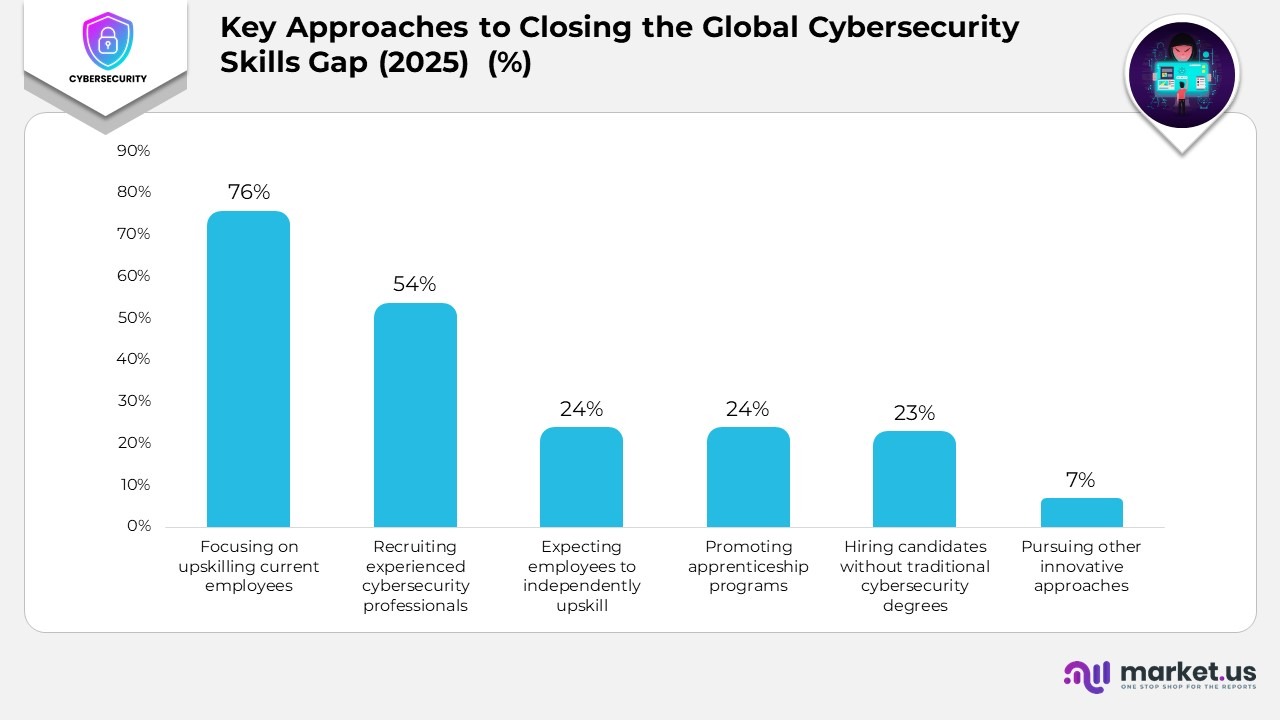
(Source: Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025, World Economic Forum)
Governance And Compliance In Cybersecurity
- 66% of organizations report that compliance mandates are a key factor influencing their cybersecurity spending decisions.
- 78% of companies anticipate an annual rise in regulatory compliance obligations, highlighting growing pressure to meet evolving global standards.
- For larger enterprises, the cost of compliance can reach up to $10,000 per employee. Underscoring the financial burden of maintaining regulatory alignment.
- In 2024, total U.S. HIPAA fines and settlements amounted to $9.16 million, more than double the previous year’s total. Reflecting stricter enforcement of data privacy laws.
- During the first half of 2024, data breaches exposed approximately 7 billion records. Demonstrating the continuing escalation of global data vulnerabilities.
- Each employee, on average, has access to approximately 25,000 sensitive folders. Posing a significant risk of internal data exposure.
- Around 90% of organizations have sensitive files openly accessible to all employees via M365 Copilot. Highlighting the risks associated with improper permission settings.
- Nearly 98% of organizations have staff using unsanctioned or “Shadow AI” applications. Raising serious concerns about data governance and visibility.
- Approximately 60% of companies maintain more than 500 accounts with passwords that never expire. Leaving their critical systems vulnerable to potential breaches.
- Over 77% of organizations lack a formal incident response plan, revealing significant preparedness gaps in the face of increasing cyber threats.
(Source: CSO Online, Thomson Reuters, Forbes, Compliance Group, IT Governance, Varonis, Cybint)
Conclusion
The cybersecurity landscape reflects a decisive transition from reactive defense to proactive resilience. Across industries, organizations are strengthening their digital ecosystems against increasingly complex threats ranging from AI-driven attacks and ransomware to geopolitical risks. Investments in automation, real-time threat detection, and zero-trust architecture have become central to modern defense frameworks. Simultaneously, rising regulatory pressures and cross-border data privacy requirements are pushing cybersecurity to the forefront of strategic business planning. Transforming it from a technical necessity into a core pillar of organizational sustainability.
However, technology alone is insufficient to secure the digital frontier. The persistent shortage of skilled cybersecurity professionals continues to challenge enterprises, prompting global efforts to upskill existing workforces, expand partnerships, and integrate intelligent, AI-assisted security tools. Moreover, as digital interconnectivity deepens, cybersecurity is no longer viewed merely as protection; it has evolved into a culture of continuous adaptation, vigilance, and innovation essential for safeguarding the world’s critical infrastructure.