Global Virtualized 5G RAN (vRAN) Market Size, Share, Industry Analysis Report By Component (Radio Unit, Distributed Unit, Central Unit, Others), By Communication Infrastructure (Small Cell, Macro Cell), By End User (Telecommunication, Government & Defense, Commercial, Others), By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: August 2025
- Report ID: 156391
- Number of Pages: 238
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
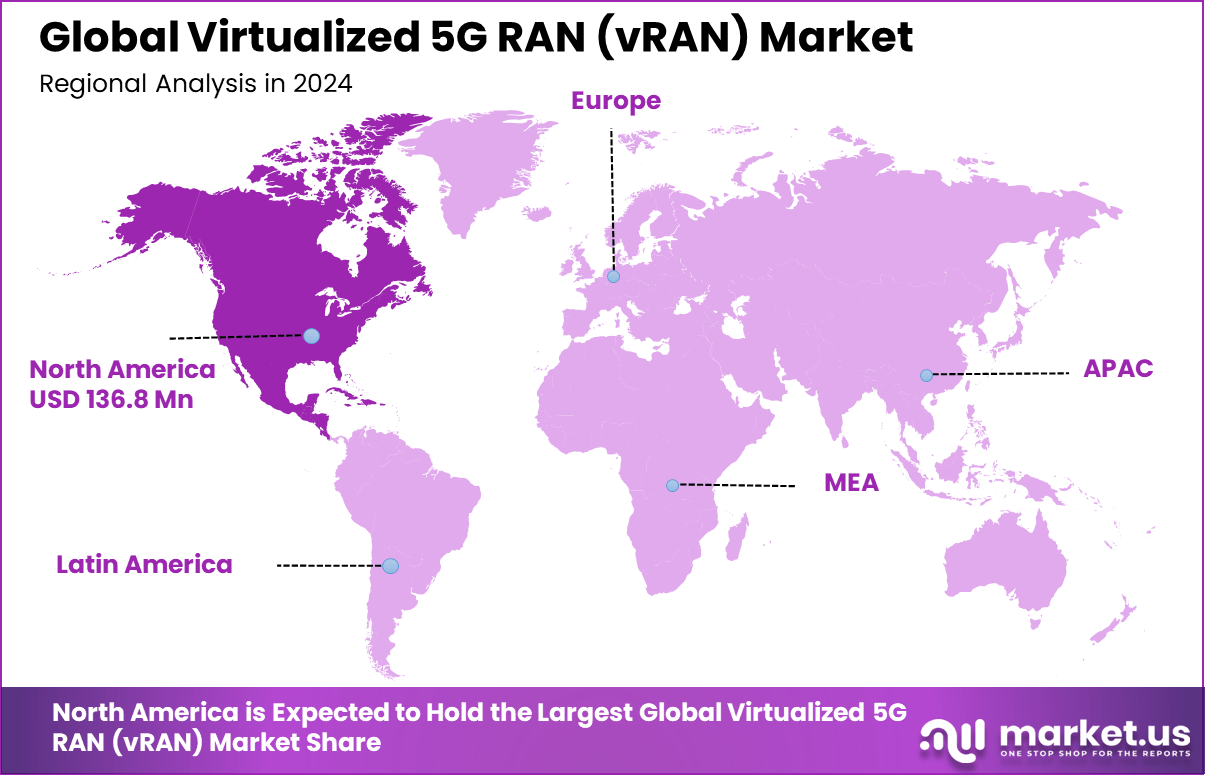
The Global Virtualized 5G RAN (vRAN) Market size is expected to be worth around USD 9,287.6 million by 2034, from USD 360.2 million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 38.4% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38% share, holding USD 136.8 million in revenue.
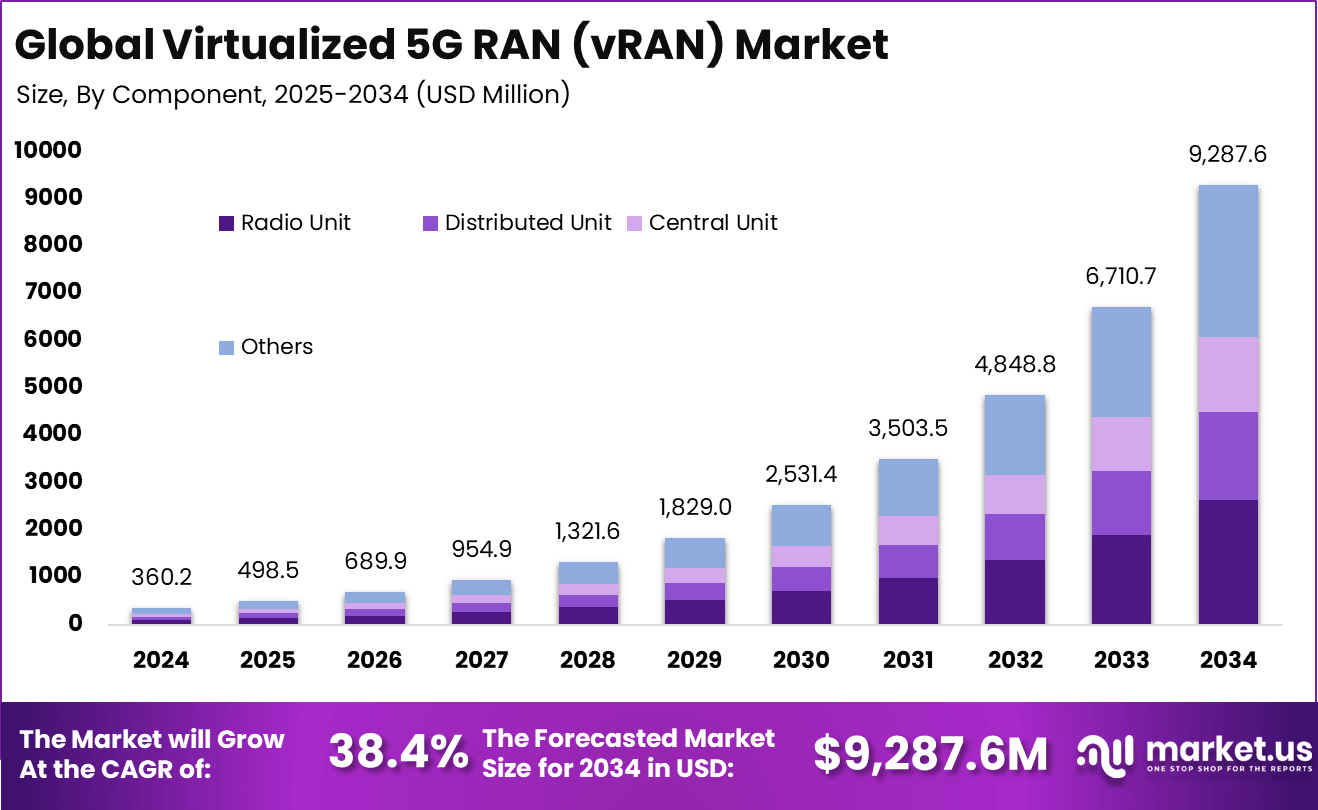
The global Virtualized 5G RAN (vRAN) market is experiencing rapid growth, fueled by the surge in mobile data consumption and accelerated 5G deployments. The main driving forces include increasing smartphone penetration, expanding IoT applications, and the need for scalable, flexible, and cost-effective network architectures.
vRAN technologies enable operators to decouple hardware from software, streamline network management, and support dynamic resource allocation, making them highly attractive for dense urban regions and enterprises seeking private 5G networks.
For instance, in July 2025, Orange conducted a field trial in southwest France featuring Samsung’s Open vRAN solution, deployed with multi-band radios and virtualized components on Wind River’s cloud platform and Dell servers. This collaboration marks a critical step in validating vRAN technology in a live environment.
Demand for vRAN solutions is notably strong in areas experiencing dense mobile traffic, such as urban centers and enterprise deployment scenarios. The flexibility of virtualized infrastructure is particularly valued where rapidly changing network demands require swift adjustments in resource allocation. As network complexity grows, vRAN adoption is increasingly driven by the imperative to manage infrastructure more dynamically and efficiently
Key Takeaway
- In 2024, the Radio Unit segment led with a 28.4% share, reflecting its critical role in enabling flexible, software-driven network functions.
- The Macro Cell segment dominated with a 68.3% share, highlighting its importance in large-scale 5G deployments.
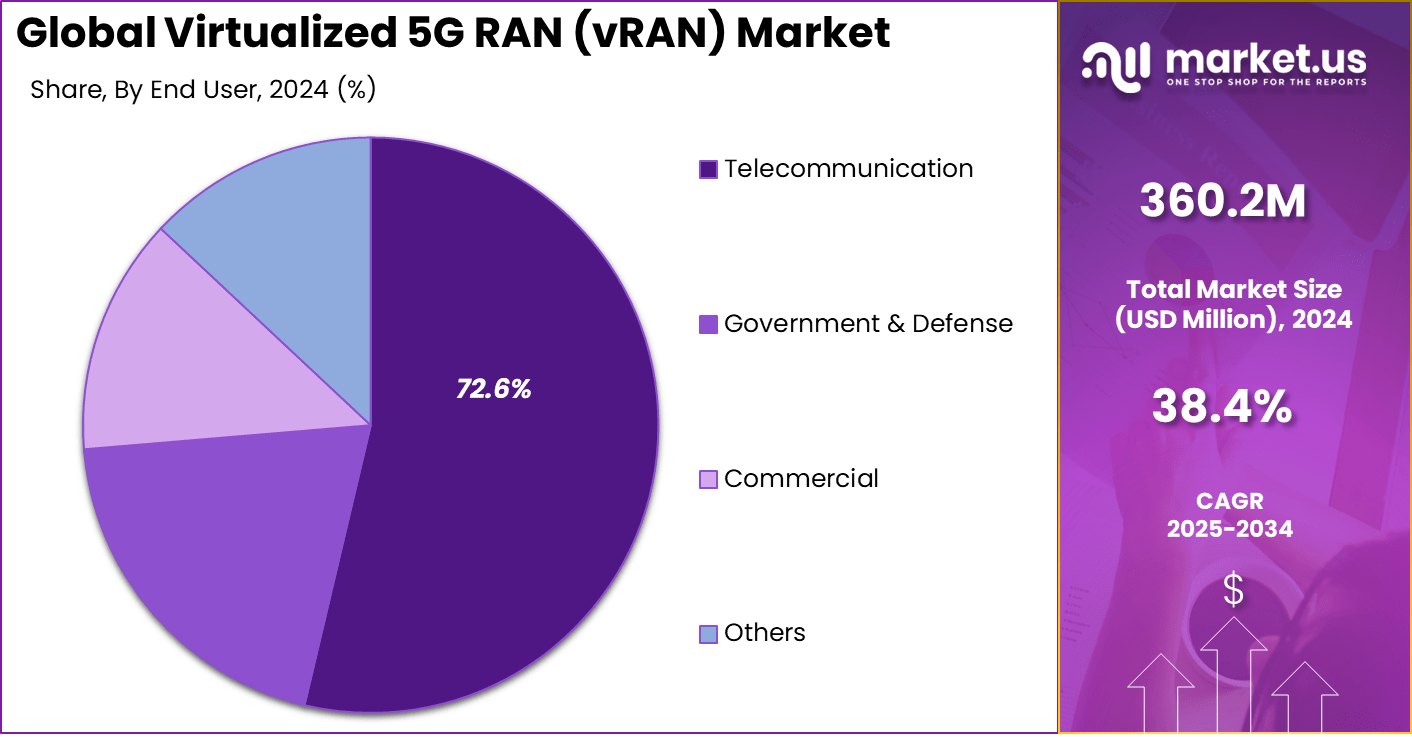
- By end-use, the Telecommunication sector captured a 72.6% share, driven by operators modernizing networks for efficiency and scalability.
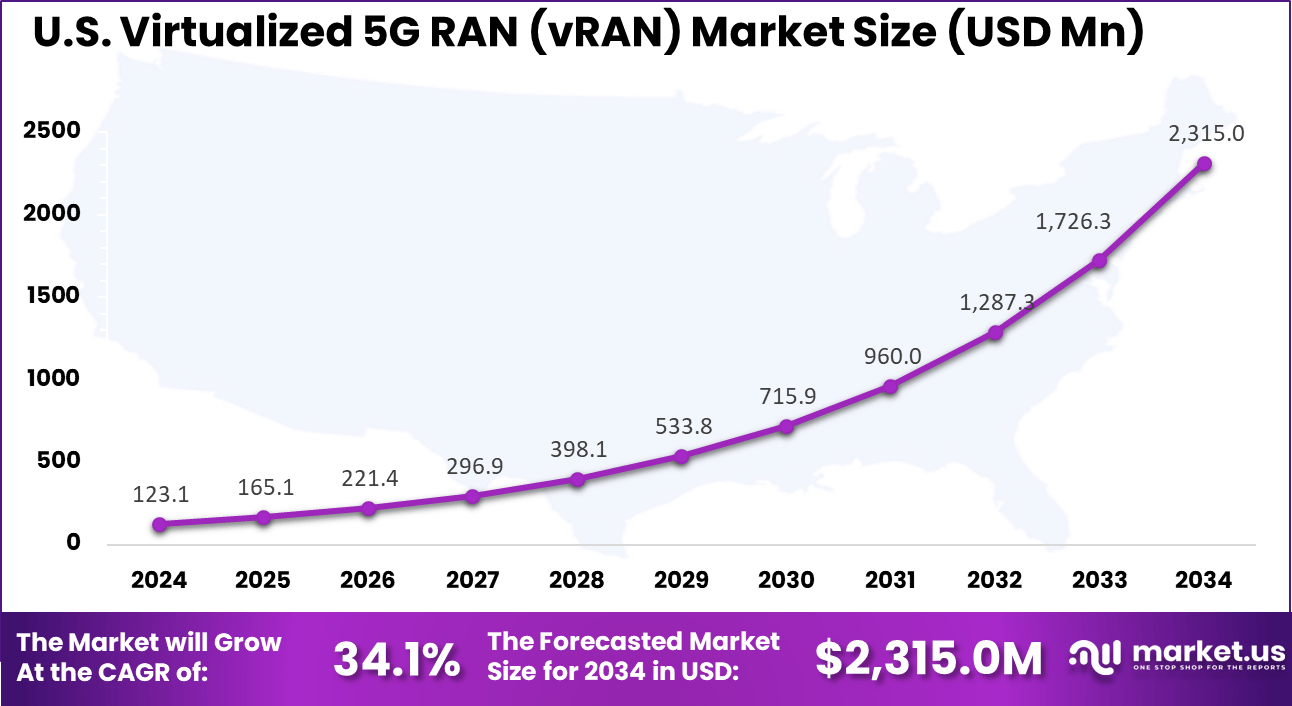
- The U.S. vRAN market was valued at USD 123.1 Million in 2024, with a strong projected CAGR of 34.1%.
- North America held a dominant position globally, accounting for more than 38% share in 2024, supported by early adoption and large-scale 5G rollouts.
U.S. vRAN Market Size
The market for Virtualized 5G RAN (vRAN) within the U.S. is growing tremendously and is currently valued at USD 123.1 million, the market has a projected CAGR of 34.1%. The market is growing tremendously due to aggressive 5G rollout strategies, strong investments in Open RAN initiatives, and federal backing for telecom innovation.
The demand for faster, more reliable connectivity from both consumers and enterprises is accelerating 5G adoption. Additionally, rising enterprise demand for private 5G networks and edge computing is fueling vRAN adoption. The presence of leading technology vendors and hyperscalers also accelerates innovation, making the U.S. a critical growth hub for vRAN deployment.
For instance, in February 2023, DISH Network began deploying Samsung’s Open RAN radios and 5G vRAN software across its cloud-native network, reinforcing the United States’ leadership in vRAN innovation. This deployment exemplifies how U.S. operators are driving next-generation architecture adoption through partnerships with global technology vendors.
In 2024, North America held a dominant market position in the Global Virtualized 5G RAN (vRAN) Market, capturing more than a 38% share, holding USD 136.8 million in revenue. The dominance is due to the early 5G adoption, robust investment in telecom infrastructure, and proactive support for Open RAN initiatives.
Major U.S. carriers accelerated vRAN deployments to enhance network agility, reduce costs, and meet surging data demands. The region also benefited from strong collaboration between telecom operators, cloud providers, and technology vendors, positioning North America at the forefront of innovation in virtualized, software-defined network architectures.
For instance, in February 2024, Samsung and AWS advanced vRAN innovation by deploying virtualized RAN solutions on the public cloud, reinforcing North America’s leadership in telecom modernization. Leveraging AWS’s robust U.S. cloud infrastructure, this collaboration enabled scalable, software-based RAN deployments for mobile operators.
Top Use Cases for vRAN
Sectors Description Telecom Flexible, scalable network architecture for rapid 5G deployment Private 5G Custom, secure connectivity for manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics Edge Computing Low-latency apps (AR/VR, autonomous vehicles, IoT) leveraging distributed RAN Network Slicing Dynamic allocation for enterprise and public safety needs Public Safety High-assurance emergency communications Emerging Trends in vRAN
Trends Details Cloud-Native Architectures Containerized, microservices-based deployments AI & Machine Learning Predictive analytics for network optimization, anomaly detection Open RAN Initiatives Vendor interoperability, supply chain resilience Edge Computing Real-time, distributed resource scaling Energy Efficiency Dynamic power management and green features Component Analysis
Radio units account for 28.4% of the vRAN market, playing a crucial role in connecting mobile devices to the telco network. As carriers upgrade to virtualized infrastructure, dedicated radio units enable efficient signal transmission, handle increased traffic loads, and support newly deployed 5G frequencies. The shift towards software-driven networks has not reduced the significance of hardware; rather, modern radio units are becoming more scalable and energy-efficient.
Demand for advanced radio units is rising in tandem with 5G adoption, as they allow operators to adapt quickly to changing spectrum requirements and user demands. Vendors are developing next-generation radio hardware that supports multi-band operation, massive MIMO, and flexible deployment models, helping carriers optimize network coverage and performance in dense urban and rural settings.
For Instance, in February 2022, KDDI activated the world’s first 5G standalone Open RAN site powered by vRAN, highlighting the pivotal role of Radio Units in disaggregated architectures. This milestone demonstrated the feasibility of integrating RU with virtualized DU/CU components in a real-world deployment.
Communication Infrastructure Analysis
Macro cells comprise a dominant 68.3% of vRAN deployments, underlining their importance for wide-area network coverage in the first phase of 5G rollout. Macro cells provide robust, high-capacity connectivity for large geographic areas, making them the backbone for nationwide coverage. Most telecom operators initially prioritize macro cell upgrades when transitioning to virtualized radio access networks, as these sites deliver optimal capacity and coverage while unlocking key efficiencies.
As more traffic shifts to mobile networks, the use of macro cells simplifies operations, reduces costs, and makes it easier to scale capacity. With vRAN, macro cells allow operators to separate hardware from software, increasing flexibility and accelerating network upgrades. Modern macro cells are also integral to supporting high-bandwidth and low-latency applications, ensuring the reliability of services for consumers and enterprise users alike.
For instance, in February 2025, UScellular partnered with Samsung to enhance its 5G network using vRAN technology, with macro cells playing a central role in the deployment. Macro cells provide the broad coverage and high capacity needed for large-scale 5G rollouts, making them ideal for integrating virtualized RAN components.
End User Analysis
Telecommunication service providers represent 72.6% of vRAN market adoption. These organizations are leading the charge in implementing virtualized 5G networks to deliver enhanced connectivity, reduce costs, and improve operational agility. The shift to vRAN allows telecom companies to move functions previously tied to specialized hardware onto general-purpose servers, making networks easier to maintain and upgrade.
By utilizing vRAN, telecom operators can rapidly launch new services and respond to evolving customer and enterprise demands. These deployments support advanced features such as edge computing, network slicing, and private 5G networks, all of which are central to modern telecom offerings. The push from telecom organizations will continue to drive innovation and broad adoption of vRAN across the industry.
For Instance, in July 2024, Vodafone Idea initiated discussions with Samsung to adopt vRAN technology for its 4G and 5G network rollouts, emphasizing the telecom sector’s role in driving vRAN adoption. As operators seek to modernize infrastructure and improve cost efficiency, virtualized RAN offers a scalable, software-driven solution.
Key Market Segments
By Component
- Radio Unit
- Distributed Unit
- Central Unit
- Others
By Communication Infrastructure
- Small Cell
- Macro Cell
By End User
- Telecommunication
- Government & Defense
- Commercial
- Others
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherlands
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Drivers
5G Network Deployment Acceleration
The global rollout of 5G is accelerating, and virtualized RAN (vRAN) offers a scalable, software-centric alternative to traditional RAN systems. With vRAN, it separates hardware from software, enabling faster and more flexible network deployment, particularly in high-density urban areas and enterprise environments.
vRAN is based on a cloud-native architecture capable of rapid provisioning and resource efficiency, allowing operators to meet customer data demands faster and with reduced time-to-market. As operators race to deliver next-gen connectivity, vRAN serves as a critical enabler of efficient, future-proof network deployment strategies.
For instance, in August 2025, Cellwize announced a strategic collaboration focused on expediting the rollout of 5G vRAN networks through advanced AI integration. The initiative leverages automation and machine learning to streamline deployment, enhance real-time decision-making, and improve network performance.
Restraint
High Initial Investment for Transition
Moving from legacy RAN to virtualized 5G RAN involves very high upfront costs, which include initially modernizing some infrastructure, embedding new hardware and software stacks, and retraining staff. Operators will need to invest capital in cloud-native platforms, orchestration, and analytic capability if they want to leverage vRAN to its full potential.
For smaller telcos and in emerging markets, the capital cost can be an impediment. The return on investment, while promising long-term, may deter rapid adoption without strong business cases or supportive policy frameworks.
For instance, in May 2024, Samsung and O2 Telefónica initiated a vRAN and Open RAN deployment in Germany, underscoring the scale of investment needed for next-generation network transformation. These implementations demand upgrades to cloud-native infrastructure, integration with legacy systems, and workforce reskilling.
Opportunities
AI and Automation Integration
vRAN’s software-defined nature offers a robust foundation for AI and automation integration. Intelligent algorithms can dynamically allocate resources, predict network congestion, and automate fault detection and resolution, enhancing both performance and cost-efficiency.
With AI, operators can deliver superior Quality of Service (QoS), reduce manual intervention, and support complex 5G use cases like autonomous systems and immersive applications. This represents a major opportunity to operationalize data-driven, adaptive networks at scale.
For instance, in June 2025, Samsung Networks advanced this trajectory by pioneering AI-powered telecom infrastructure to enhance automation and performance in vRAN environments. Their solution emphasizes intelligent resource management, predictive analytics, and self-healing capabilities.
Challenges
Cybersecurity Risks
The virtualization of RAN and adoption of cloud-native architectures significantly expand the network’s attack surface, making cybersecurity a critical concern. Distributed architectures, multi-vendor environments, and open interfaces introduce vulnerabilities that require comprehensive, adaptive security frameworks.
Operators must implement robust measures, including zero-trust principles, real-time threat detection, and secure orchestration layers, to safeguard data integrity and service availability. Failure to address these risks could compromise network resilience and affect customer trust in 5G services.
For instance, in February 2025, NEC unveiled advanced security enhancements for virtualized 5G infrastructure, aiming to fortify network integrity across distributed architectures. Their approach addresses the expanding attack surface through AI-powered threat detection and secure orchestration.
Key Players Analysis
In the Virtualized 5G RAN (vRAN) market, network hardware and semiconductor specialists such as Intel Corporation, Qualcomm Technologies, Inc., Microchip Technology Inc., and Qorvo, Inc. play a central role. Their focus is on delivering processors, chipsets, and radio frequency components optimized for virtualization. These companies are enabling low-latency communication and high throughput, which are essential for advanced 5G use cases.
Telecom equipment providers including Ericsson Inc., Nokia Corporation, Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., ZTE Corporation, Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd., Fujitsu Limited, and NEC Corporation dominate the deployment side. They offer end-to-end solutions covering virtualized base stations, cloud-native software, and integration support. Their global scale and long-standing operator relationships allow them to accelerate commercial rollouts of vRAN.
The ecosystem is further strengthened by software and platform innovators such as Mavenir Systems, Radisys Corporation, Quortus Limited, Juniper Networks Inc., Red Hat, Inc., Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP, and Cisco Systems, Inc.. These companies provide virtualization platforms, orchestration layers, and cloud infrastructure support. Their expertise ensures seamless management of disaggregated RAN components.
Top Key Players in the Market
- Juniper Networks Inc.
- Microchip Technology Inc.
- MTI Mobile
- Qorvo, Inc.
- Mavenir Systems
- Qualcomm Technologies, Inc.
- Quortus Limited
- Radisys Corporation
- ZTE Corporation
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Fujitsu Limited
- Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd
- NEC Corporation
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
- Verizon Communications
- Ericsson Inc.
- Nokia Corporation
- Red Hat, Inc
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP
- Intel Corporation
- Others
Recent Developments
- In February 2024, Mavenir and Parallel Wireless announced a strategic collaboration to advance next-generation 5G Non-Standalone (NSA) Open RAN solutions. The partnership completed interoperability testing between Parallel Wireless’s GreenRAN platform and Mavenir’s cloud-native 5G converged packet core.
- In November 2024, Aramco Digital entered advanced discussions to invest US$1 billion in Mavenir, signaling strong confidence in the future of Open RAN and virtualized 5G RAN (vRAN) technologies. This strategic move aims to accelerate telecom innovation in Saudi Arabia, including the establishment of a dedicated Open RAN development center.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 360.2 Mn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 9,287.6 Mn CAGR(2025-2034) 38.4% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue forecast, AI impact on Market trends, Share Insights, Company ranking, competitive landscape, Recent Developments, Market Dynamics and Emerging Trends Segments Covered By Component (Radio Unit, Distributed Unit, Central Unit, Others), By Communication Infrastructure (Small Cell, Macro Cell), By End User (Telecommunication, Government & Defense, Commercial, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of Latin America; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Juniper Networks Inc., Microchip Technology Inc., MTI Mobile, Qorvo, Inc., Mavenir Systems, Qualcomm Technologies, Inc., Quortus Limited, Radisys Corporation, ZTE Corporation, Cisco Systems, Inc., Fujitsu Limited, Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd, NEC Corporation, Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., Verizon Communications, Ericsson Inc., Nokia Corporation, Red Hat, Inc., Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP, Intel Corporation, Others Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three license to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Virtualized 5G RAN (vRAN) MarketPublished date: August 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Virtualized 5G RAN (vRAN) MarketPublished date: August 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Juniper Networks Inc.
- Microchip Technology Inc.
- MTI Mobile
- Qorvo, Inc.
- Mavenir Systems
- Qualcomm Technologies, Inc.
- Quortus Limited
- Radisys Corporation
- ZTE Corporation
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Fujitsu Limited
- Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd
- NEC Corporation
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
- Verizon Communications
- Ericsson Inc.
- Nokia Corporation
- Red Hat, Inc
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP
- Intel Corporation
- Others













