Global Tertiary Butyl Alcohol Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Application (Fuel Additives, Solvents, Chemical Intermediates, Pharmaceuticals, Others), By End-User (Automotive, Chemical Manufacturing, Pharmaceuticals, Paints and Coatings, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Nov 2025
- Report ID: 164238
- Number of Pages: 377
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
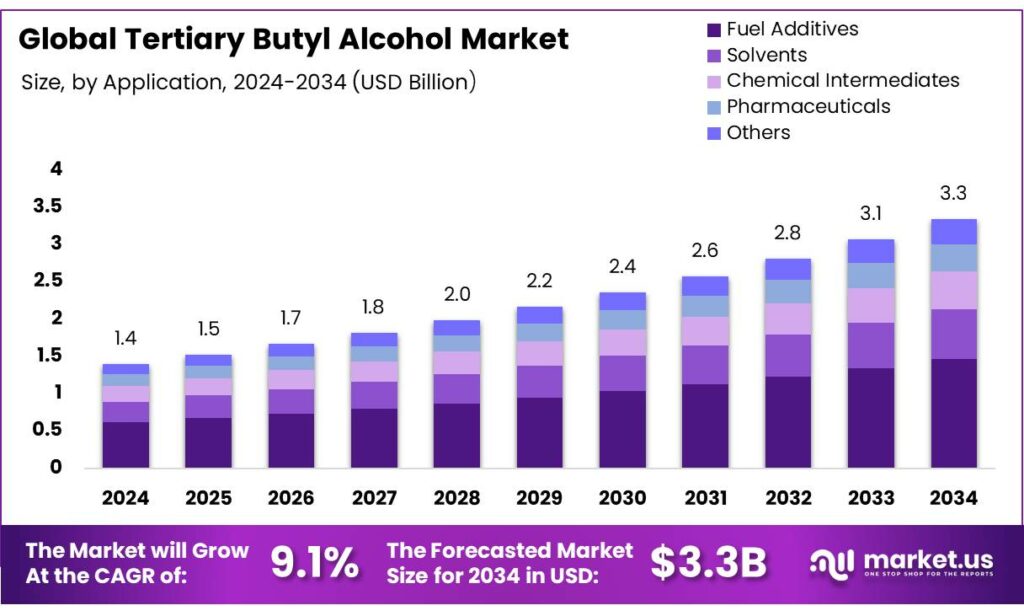
The Global Tertiary Butyl Alcohol Market size is expected to be worth around USD 3.3 Billion by 2034, from USD 1.4 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 9.1% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024 North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.80% share, holding USD 0.6 Billion in revenue.
Tertiary butyl alcohol (TBA) is a versatile C4 solvent and intermediate produced mainly as a co-product in the propylene oxide (PO)/TBA process. Its downstream value lies in high-octane oxyfuels—methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) and ethyl tert-butyl ether (ETBE)—as well as in chemical dehydration to isobutylene for polyisobutylene and other derivatives. LyondellBasell started up the world’s largest PO/TBA complex on the U.S. Gulf Coast in March 2023, designed for 470,000 metric tons/year of PO and 1,000,000 metric tons/year of TBA and derivatives, underlining structural capacity for oxyfuels and C4 derivatives demand.
The industrial backdrop is shaped by liquid-fuel demand and gasoline-pool quality requirements. The International Energy Agency reports global oil consumption rose 0.8% to 193 EJ in 2024, slowing from 2023 but remaining structurally high, underpinning oxygenate and octane needs in many markets. In the United States, finished motor gasoline consumption averaged 8.94 million b/d in 2023, keeping the U.S. the single largest gasoline market—relevant for oxygenates derived from TBA’s isobutylene pathway.
Policy remains a key driver. In Europe, the Renewable Energy Directive sets an at least 42.5% overall renewables share by 2030 and embeds transport targets that sustain oxygenate routes in specific markets. Earlier RED II framing included a 14% renewable energy sub-target for transport by 2030 with a 3.5% advanced-biofuels sub-target, supporting oxygenate pathways compatible with refinery systems. These measures keep ETBE relevant in blends where ethanol logistics or volatility constraints favor etherized bio-components.
Japan provides a concrete, long-running example: under the Act on Sophisticated Methods of Energy Supply Structures, the national target has been 1.94 million kL of bio-ETBE per year, with 500,000 kL of bioethanol input; trade statistics show ~57,825 kL of ethanol imported in FY2022 for ETBE, and USDA estimates 811 million liters of bio-ETBE-equivalent ethanol used on-road in 2023, delivering about a 1.8% ethanol blend rate.
On the supply side, PO capacity expansion trends implicitly add TBA molecules when the PO/TBA route is selected. Industry and consultancy estimates point to steady PO growth through the decade, reinforcing co-product TBA availability and enabling downstream investments in ETBE/MTBE, peroxides, and solvent segments. Occupational and product-stewardship frameworks also influence TBA handling. U.S. OSHA’s permissible exposure limit is 100 ppm (300 mg/m³) TWA, with 150 ppm (450 mg/m³) STEL cited by NIOSH/ACGIH, guiding plant design, monitoring, and PPE standards across TBA manufacturing and use sites.
Key Takeaways
- Tertiary Butyl Alcohol Market size is expected to be worth around USD 3.3 Billion by 2034, from USD 1.4 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 9.1%
- Fuel Additives held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.80% share of the global tertiary butyl alcohol (TBA) market.
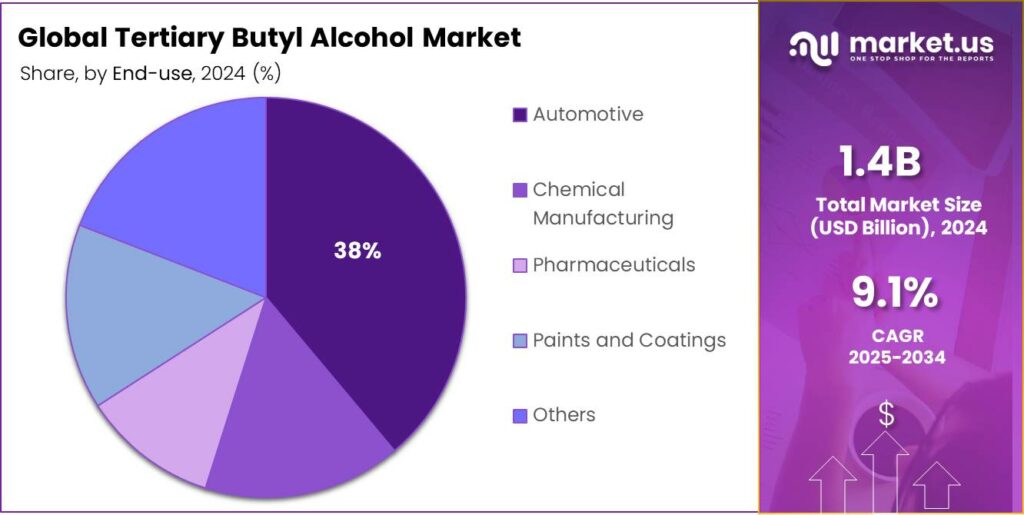
- Automotive held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.9% share of the global tertiary butyl alcohol (TBA) market.
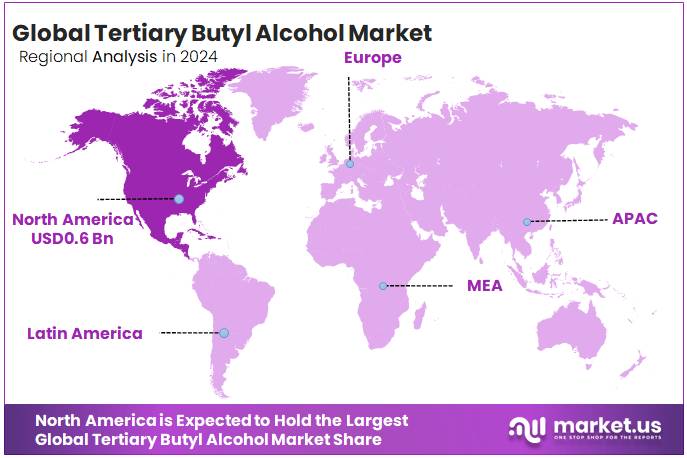
- North America held a dominant position in the global tertiary butyl alcohol (TBA) market, capturing approximately 43.80% share, with an estimated market value of USD 0.6 billion.
By Application Analysis
Fuel Additives lead the market with 43.80% share in 2024 due to rising demand for cleaner combustion solutions
In 2024, Fuel Additives held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.80% share of the global tertiary butyl alcohol (TBA) market. This dominance was mainly supported by its widespread application as an oxygenate and octane booster in gasoline blending. The compound’s ability to enhance combustion efficiency and reduce vehicular emissions has made it a preferred additive, especially in regions with strict emission standards such as North America and parts of Asia-Pacific. Rising urbanization and the continued reliance on internal combustion engines, despite the growing shift toward electric mobility, have sustained the industrial demand for fuel-grade alcohols.
During 2024, production levels of TBA used for fuel additive formulations were observed to rise steadily, reflecting increased consumption in gasoline blending operations. The market saw continued utilization of TBA as a feedstock for methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) and ethyl tert-butyl ether (ETBE), which are blended into fuels to improve air quality by reducing carbon monoxide and hydrocarbon emissions. Additionally, government initiatives promoting cleaner fuels and the adoption of oxygenates under environmental compliance programs further strengthened this segment’s growth outlook.
By End-User Analysis
Automotive dominates with 38.9% share in 2024 driven by strong demand for fuel additives and performance enhancers
In 2024, Automotive held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.9% share of the global tertiary butyl alcohol (TBA) market. The segment’s leadership was driven by the extensive use of TBA-derived compounds in gasoline blending and fuel performance enhancement. The growing focus on improving fuel efficiency, reducing emissions, and complying with environmental standards such as Euro 6 and EPA Tier 3 has significantly boosted the consumption of TBA within the automotive value chain. Automakers and fuel producers have increasingly adopted TBA-based additives to optimize combustion characteristics and meet regulatory limits for particulate and carbon monoxide emissions.
The sector benefited from the steady recovery in vehicle production and rising fuel demand, particularly across Asia-Pacific and North America. The increasing use of passenger and commercial vehicles in developing economies further elevated the need for high-quality fuels and performance chemicals, reinforcing TBA’s industrial significance. Additionally, the expansion of refineries and blending facilities capable of producing oxygenated fuels supported the segment’s continued dominance during the year.
Key Market Segments
By Application
- Fuel Additives
- Solvents
- Chemical Intermediates
- Pharmaceuticals
- Others
By End-User
- Automotive
- Chemical Manufacturing
- Pharmaceuticals
- Paints and Coatings
- Others
Emerging Trends
Agri-ethanol supply chaining into TBA via bio-ETBE
A clear, recent trend is the tighter coupling of agricultural ethanol supply chains with refinery oxygenate systems, using bio-ETBE as the bridge—and that pull runs straight through tertiary butyl alcohol (TBA). Policymakers are locking in ethanol volumes, and refiners are choosing ETBE where it fits logistics, volatility limits, or infrastructure better than neat ethanol. Japan is the most consistent signal: since 2017 it has kept a de-facto biofuel mandate of 500 million liters (crude-oil-equivalent)—about 824 million liters of bioethanol—largely supplied as bio-ETBE blended nationwide.
The scale and direction of global ethanol trade further support this ETBE-centric integration. The latest OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2025–2034 projects world ethanol trade rising from 11.0 billion L to 11.9 billion L by 2034, with the U.S. and Brazil lifting their combined export share from 75% to 79%. That matters because dependable, competitively priced ethanol exports keep bio-ETBE programs running and, by extension, keep demand flowing into TBA-to-isobutylene chains.
Behind these national moves sits a structural energy-materials backdrop: even as EVs chip away at gasoline demand, petrochemicals keep growing, preserving the relevance of C4 streams that feed TBA and its derivatives. The International Energy Agency underscores that petrochemicals account for over one-third of oil-demand growth to 2030 and nearly half to 2050. For TBA, this means integrated PO/TBA and C4 systems can serve both chemical derivatives and bio-ETBE oxygenates—diversifying margins across cycles.
Drivers
Fuel-Blending Policies and Oxygenate Mandates
One of the strongest forces propelling demand for tertiary butyl alcohol (TBA) is the regulatory requirement for oxygenate additives in gasoline, which helps improve combustion, reduce emissions, and meet fuel-quality mandates. For instance, in Japan the national policy under the Act on Sophisticated Methods of Energy Supply Structures mandates the supply of 1.94 million kL of bio-ETBE (ethyl tertiary-butyl ether) each year, equivalent to roughly 127,900 kL of ETBE derived from imported ethanol in fiscal year 2022.
This policy-driven demand also aligns with global clean-air and fuel-quality drivers: in the U.S., the regulatory mandate for oxygenated gasoline under the Clean Air Act Amendments of 1990 contributed to the rise of fuel‐oxygenate use – for example, the use of MTBE (methyl tertiary-butyl ether) increased from 83,000 barrels per day in 1990 to 269,000 barrels per day by 1997, as a direct result of that oxygenate requirement. Although these figures are for MTBE rather than TBA, they illustrate how regulatory mandates for oxygenates can sharply increase demand for tert-butyl derivatives.
What this means for TBA is that when government policies call for higher renewable-oriented oxygenates, refiners and fuel producers turn to ETBE or other tert-butyl ethers, thereby increasing demand for TBA feedstock. In Japan’s example, while the ethanol blend rate stood at only 1.9% in 2022, the fixed target volume of bio-ETBE (1.94 million kL) ensures a steady baseline demand—even in the face of declining total gasoline consumption.
From a humane angle: because these policies are designed to reduce vehicle emissions, improve air quality, and transition toward cleaner fuel mixes, TBA’s role becomes not just chemical or commercial—but also environmental and societal. Local refining industries must adapt to these policy shifts, and TBA producers are increasingly linked to the energy-transition narrative. For example, Japan’s refineries blend bio-ETBE to satisfy a mandated volume, not purely to chase profit margins—so TBA becomes a component of the national clean-fuel strategy.
Restraints
Environmental Liability and Regulatory Backlash
One of the key obstacles facing the growth of tertiary-butyl alcohol (TBA) and its derivatives springs from the environmental and regulatory baggage attached to its historic cousins. To put it plainly: when a chemical product or its derivatives create contamination concerns, producers and markets feel the ripples, sometimes for years. A telling example lies in how methyl tertiary-butyl ether (MTBE), a cousin in the ether/oxygenate family, became a cautionary tale. In the U.S., blending of MTBE into motor gasoline peaked at around 260,000 barrels per day in 1999, before a combination of groundwater contamination concerns and regulatory action forced a dramatic decline.
Since TBA is used to make ether additives (such as ETBE, MTBE) and is integrated into gasoline-oxygenate regimes, any regulatory blowback or liability environment for oxygenates bleeds into the broader tert-butyl ecosystem. When several U.S. states began banning MTBE (for example, complete or partial bans across more than 20 states by mid-2000s) because of its groundwater contamination profile, the market for ethers changed.
That scenario triggered lawsuits, remediation efforts and public mistrust. For example, the agency report notes that MTBE has been identified in at least 45 hazardous waste sites on the U.S. National Priorities List. Producers of TBA derivatives cannot entirely shield themselves from the reputational and regulatory aftershock of oxygenate-related contamination concerns—even if TBA itself is not always the culprit.
In the U.S., the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) published a “Chapter 13” report on MTBE which shows that policy decisions, liability exposure and groundwater risk together pushed refiners to pivot to ethanol instead. And in Europe, the very detailed monitoring of gasoline ethers in 30 countries revealed that the production capacity of gasoline ether oxygenates (GEO) rose from 4,108 ktonnes in 2002 to 6,049 ktonnes in 2010, but data also underscore that no production records of TBA for gasoline blending existed in Europe, reflecting regulatory and market constraints.
Opportunity
Bio-ETBE demand riding farm-fuel policies
A clear growth opening for tertiary butyl alcohol (TBA) is the steady rise of ethanol-based gasoline blending—especially where governments prefer bio-ETBE (made from ethanol and isobutylene from TBA) to meet transport decarbonization goals. Japan keeps a mandated annual supply of 1.94 million kilolitres of bio-ETBE, anchoring oxygenate demand even as total gasoline falls. In practice, refiners convert imported ethanol into ETBE to hit this fixed volume; recent U.S. Department of Agriculture reporting shows Japan’s program continues at scale, with hundreds of millions of liters of ethanol channeled into ETBE each year. This policy gives TBA a durable offtake route via ETBE production.
India adds powerful momentum. New Delhi advanced its 20% ethanol-in-petrol target to ESY 2025-26, and blending has climbed stepwise—10% in 2021-22, 12.06% in 2022-23, 14.60% in 2023-24, and 17.98% by Feb 28, 2025. Those hard numbers matter because every percent of blending raises oxygenate logistics, co-processing, and refinery optimization needs—spaces where ETBE can complement direct ethanol blending and where TBA-to-isobutylene integration brings cost and operability benefits.
Global agricultural supply capacity is also supportive. The joint OECD-FAO outlook projects world ethanol trade rising from 11.0 billion L to 11.9 billion L by 2034, with the U.S. and Brazil together lifting their export share from 75% to 79%—a sign that dependable ethanol flows will remain available to feed ETBE programs and, in turn, TBA demand for tert-butyl chemistry. This is not market chatter; it is a baseline from two of the world’s leading agricultural institutions, tying farm output to transport fuels over a full decade.
Europe’s rules extend the runway. Under the recast Renewable Energy Directive, EU countries must either reach 29% renewables in transport by 2030 or cut transport-fuel GHG intensity by 14.5%, alongside a combined 5.5% sub-target for advanced biofuels and renewable hydrogen. Earlier RED II architecture also embedded an advanced-biofuels share rising to 3.5% by 2030. These legally binding targets keep oxygenate solutions like ETBE in the toolkit—especially where volatility constraints, logistics, or refinery configurations favor ethers over neat ethanol. For TBA suppliers, this sustains a policy-backed outlet for isobutylene and ETBE chains.
Regional Insights
North America leads the global market with 43.80% share, valued at USD 0.6 billion in 2024
In 2024, North America held a dominant position in the global tertiary butyl alcohol (TBA) market, capturing approximately 43.80% share, with an estimated market value of USD 0.6 billion. The region’s leadership is attributed to its well-established petroleum refining industry, strong demand for high-performance fuel additives, and robust manufacturing infrastructure for specialty chemicals.
The United States represents the largest contributor to the regional market, supported by the extensive use of TBA as an intermediate for methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) and other oxygenates that improve fuel combustion efficiency and reduce vehicular emissions. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), total motor gasoline consumption in the U.S. reached 8.8 million barrels per day in 2024, reflecting steady demand for fuel blending components like TBA.
The regional growth has also been driven by increased automotive production and rising fuel efficiency mandates under the Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) standards, which encourage cleaner fuel formulations. Canada and Mexico contribute to regional expansion through refining investments and chemical manufacturing capacity enhancements. North America’s strong regulatory framework for cleaner fuels and emission reductions, combined with ongoing research into renewable and bio-based alcohol production routes, continues to reinforce the strategic role of TBA in the regional market.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Exxon Mobil is a major global integrated oil & gas and chemicals firm with broad downstream and upstream operations. While its publicly-listed product portfolio emphasises Exxon™ Butyl rubber and other butyl-related derivatives, public documentation does not highlight TBA individually. This suggests Exxon Mobil participates in related C4 feedstocks but may not treat TBA as a flagship standalone product line. Their chemicals segment focuses on resilience and integration across refining, petrochemicals and performance materials.
BASF is the largest chemical company in the world (revenue €59.3 billion in 2019). In the TBA context, BASF supports the PO/TBA (propylene oxide / tertiary butyl alcohol) process route—its catalyst portfolio notes the PO/TBA technology among commercially available processes. Thus BASF plays a role in enabling TBA-linked production even if it does not themselves emphasise TBA as a primary standalone product. They offer integrated chemical, plastics and catalyst offerings globally.
LyondellBasell is explicitly referenced in its chemicals portfolio as producing “tertiary butyl alcohol” alongside other basic chemicals such as propylene oxide, methanol and acetic acid. The company is reported to have built a major PO/TBA plant in Channelview, Texas, reportedly producing 2.2 billion pounds of TBA per year. This makes LyondellBasell a key direct producer of TBA and derivatives, with scale and global reach.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Exxon Mobil Corporation
- BASF SE
- LyondellBasell Industries NV
- SABIC
- Formosa Plastics Corporation
- Reliance Industries Limited
- Braskem S.A.
- LOTTE Chemical Corporation
- Ineos Group Ltd
- Gazprom Neft PJSC
- ENEOS Corporation
- Valero Energy Corporation
- Petronas
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024, BASF SE recorded sales revenue of €21,791 million for BASF SE itself, down from €22,832 million in 2023. In its Chemicals segment, sales rose by 4.5% to €10,838 million in 2024.
In 2024, LyondellBasell reported revenue of US$ 40,302 million, down from US$ 41,107 million in 2023. The company also announced that it generated US$ 3,800 million in cash from operating activities in 2024, with capital expenditures of approximately US$ 1,800 million and shareholder returns of about US$ 1,900 million.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 1.4 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 3.3 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 9.1% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Application (Fuel Additives, Solvents, Chemical Intermediates, Pharmaceuticals, Others), By End-User (Automotive, Chemical Manufacturing, Pharmaceuticals, Paints and Coatings, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Exxon Mobil Corporation, BASF SE, LyondellBasell Industries NV, SABIC, Formosa Plastics Corporation, Reliance Industries Limited, Braskem S.A., LOTTE Chemical Corporation, Ineos Group Ltd, Gazprom Neft PJSC, ENEOS Corporation, Valero Energy Corporation, Petronas Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Tertiary Butyl Alcohol MarketPublished date: Nov 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Tertiary Butyl Alcohol MarketPublished date: Nov 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Exxon Mobil Corporation
- BASF SE
- LyondellBasell Industries NV
- SABIC
- Formosa Plastics Corporation
- Reliance Industries Limited
- Braskem S.A.
- LOTTE Chemical Corporation
- Ineos Group Ltd
- Gazprom Neft PJSC
- ENEOS Corporation
- Valero Energy Corporation
- Petronas










