Global Space Insurance Market Size, Share, Industry Analysis Report By Coverage Type (Launch Insurance, In-Orbit Insurance, Third-Party Liability Insurance, Spacecraft Recovery Insurance), By End-User (Commercial, Government and Civil, Defense), By Distribution Channel (Direct Sales, Brokers and Agents), By Regional Analysis, Global Trends and Opportunity, Future Outlook By 2025-2034
- Published date: Oct. 2025
- Report ID: 160921
- Number of Pages: 269
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
- Report Overview
- Top Market Takeaway
- Analysts’ Viewpoint
- Role of Generative AI
- Regional Insights: North America
- Coverage Type Analysis
- End-User Analysis
- Distribution Channel Analysis
- Emerging Trends
- Growth Factors
- Key Market Segments
- Drivers
- Restraint
- Opportunities
- Challenges
- Key Players Analysis
- Recent Developments
- Report Scope
Report Overview
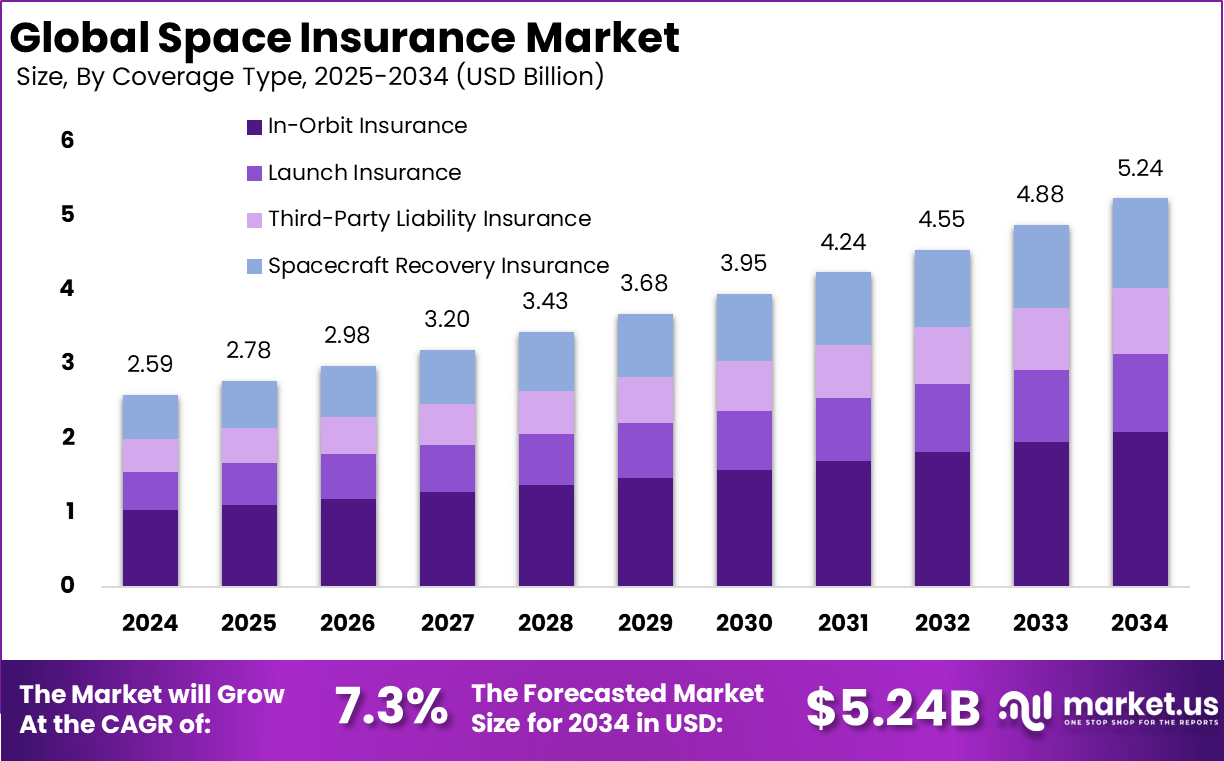
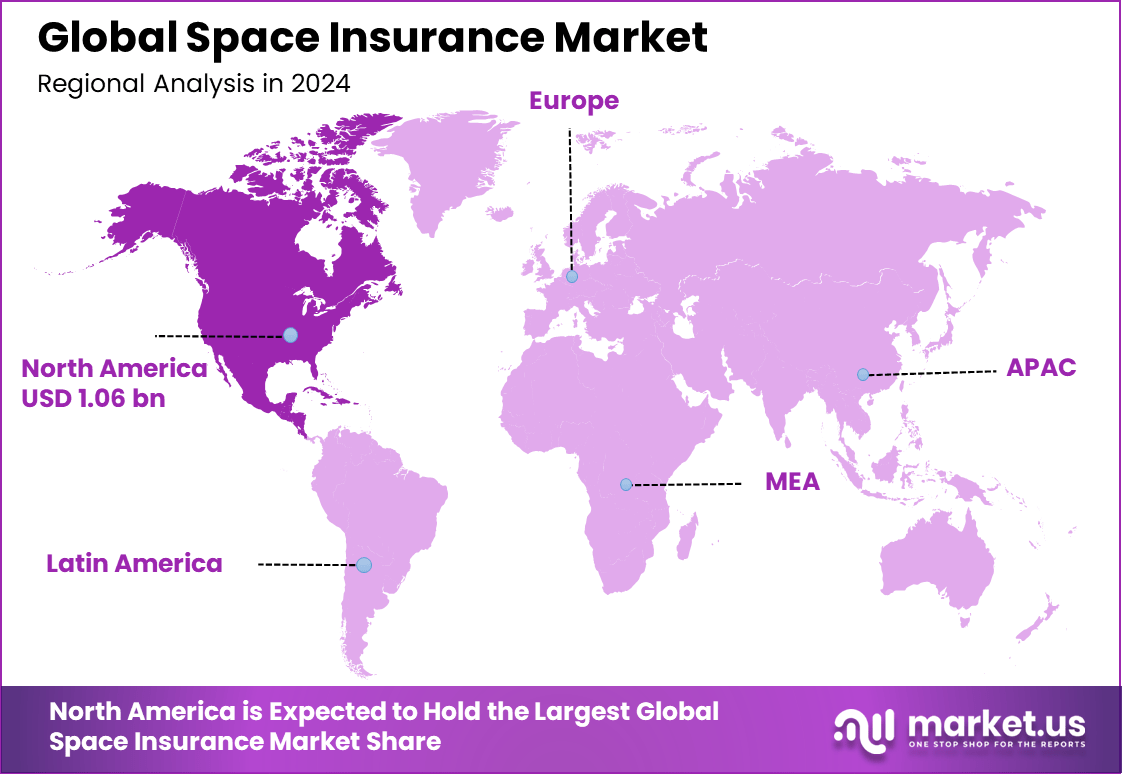
The Global Space Insurance Market size is expected to be worth around USD 5.24 billion by 2034, from USD 2.59 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 7.3% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 41% share, holding USD 1.06 billion in revenue.
The Space Insurance Market is an important part of the growing space industry. It provides financial protection against risks faced during satellite launches, space missions, and operations in orbit. This market covers losses from launch failures, satellite malfunctions, and damage caused by space debris. The rising number of satellites and renewed interest in space exploration by governments and commercial players continues to boost demand for space insurance.
The main driving factors for space insurance include the surge in satellite deployments for communication, weather monitoring, and navigation. Companies and governments are launching more satellites to meet the need for global connectivity. Another key driver is the growing involvement of military and government agencies in space programs, which require secure insurance for valuable assets.
Demand is growing as companies develop new types of satellite constellations and space technologies become more advanced but complex. The lower cost of access to space has encouraged private ventures and startups to participate, creating a diverse customer base for insurance providers. New space activities like space tourism and lunar missions are also increasing the coverage options required.
According to Gitnux, more than 6,000 satellites are currently orbiting the Earth. The commercial space sector generates approximately USD 160 billion each year. SpaceX has launched over 2,600 Starlink satellites as part of its satellite internet network. On average, launching a single satellite costs around USD 62 million. Globally, the number of private companies engaged in space activities has grown to over 2,500.
For instance, in July 2025, Angel One entered the life insurance space through a joint venture with Singapore’s LivWell. The partnership aims to provide innovative life insurance products in India, combining Angel One’s extensive customer base with LivWell’s expertise in insurance services. This move marks a significant expansion for Angel One, diversifying its portfolio beyond trading and investment services.
Top Market Takeaway
- In 2024, the In-Orbit Insurance segment led with a 40% share, reflecting the growing need to protect satellites during their operational life cycle.
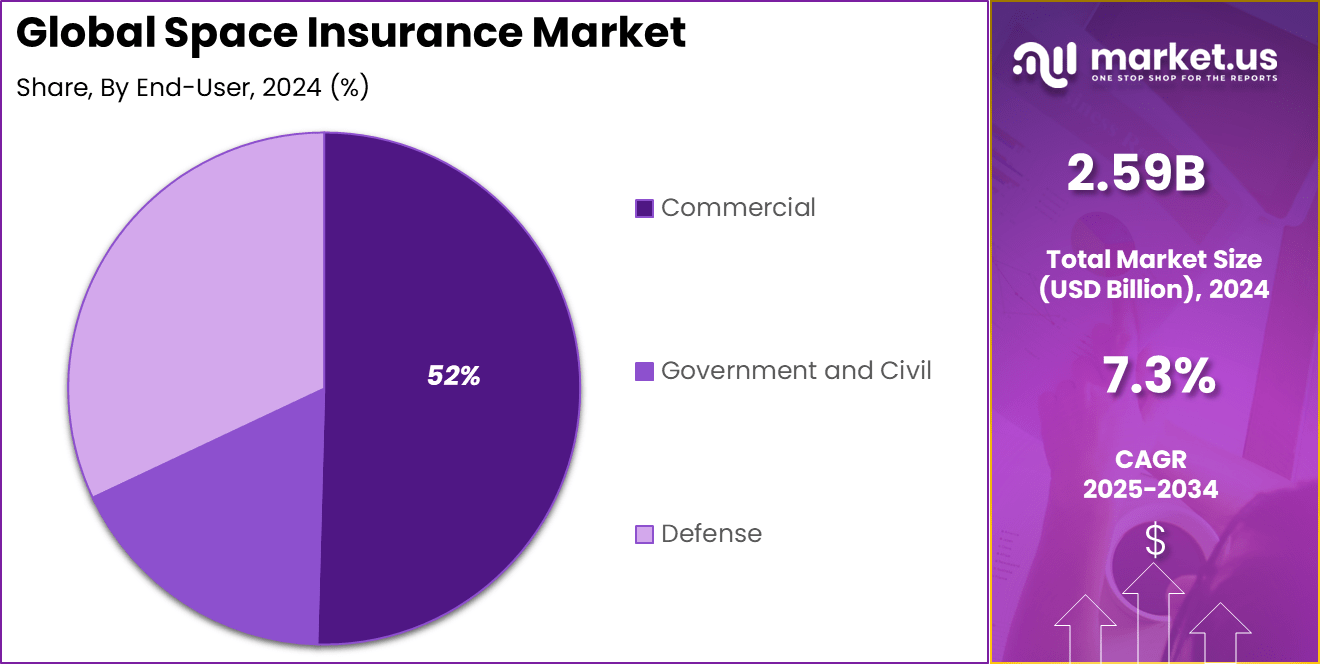
- The Commercial segment dominated with 52%, highlighting rising private sector participation in space missions.
- Brokers and agents held a strong 71% share, emphasizing their central role in connecting insurers with satellite operators and space companies.
- North America accounted for more than 41%, supported by advanced space infrastructure, frequent satellite launches, and growing investments from both government and private space entities.
Analysts’ Viewpoint
Investors are showing interest in space insurance due to its expanding role in reducing financial risks in an unpredictable industry. Public and private partnerships, technological advances in satellite monitoring, and artificial intelligence help insurers better assess risks and price their policies. There are opportunities for innovation in products that cover newer challenges like space debris impact and environmental risks.
The business benefits of space insurance include giving space operators confidence to pursue ambitious projects knowing their investments are covered. Insurance helps them manage the high costs and risks of space missions by transferring some financial burden to insurers. It supports the stable growth of the space economy by allowing companies to focus on innovation. Comprehensive insurance products tailored to operator needs improve the sustainability and attractiveness of space ventures.
The regulatory environment for space insurance is shaped by national and international rules. Many countries require that satellite operators and launch providers hold third-party liability insurance before receiving licenses. These regulations set minimum coverage levels and protect governments and third parties from losses related to space missions. Policies vary by region but emphasize accountability and risk management in space activities.
Role of Generative AI
Generative AI is playing a transformative role in space insurance by automating complex tasks like risk assessment and claims processing. It allows underwriters to review large volumes of data efficiently, producing detailed reports faster and with more precision. Studies indicate that about 40% of an underwriter’s time, often spent on administrative tasks, can be saved through AI automation.
Using generative AI, insurers can also simulate different catastrophe scenarios to better anticipate potential losses and reduce fraud by analyzing complex patterns unseen by traditional methods. These capabilities improve both operational efficiency and customer service, helping insurers manage the increasing complexity of space-related risks.
Regional Insights: North America
In 2024, North America held a dominant market position in the Global Space Insurance Market, capturing more than a 41% share, holding USD 1.06 billion in revenue. This dominance is due to the strong presence of leading space companies like SpaceX and government agencies such as NASA.
The region’s extensive investments in space exploration, satellite deployments, and commercial space ventures significantly contribute to the demand for specialized insurance coverage. Additionally, North America’s advanced technological infrastructure, regulatory support, and strategic focus on space sustainability further solidify its leadership.
For instance, In May 2025, SpaceX received FAA approval for Starship Flight 9, conditional on obtaining $500 million in liability insurance. This highlights the importance of insurance in North America’s leadership in space exploration. The high coverage requirement reflects growing risks in missions using reusable launch vehicles like Starship.
Coverage Type Analysis
In 2024, In-orbit insurance represents a significant 40% of the space insurance market, covering risks encountered once satellites and space assets are operational in orbit. This coverage protects against technical failures, collisions with space debris, and loss of signal, all of which are growing concerns as the number of active satellites increases in orbit.
It is a crucial element for satellite operators who depend on continuous and reliable satellite function to support telecommunications, earth observations, and navigation services. The increasing deployment of both large satellites and growing constellations of smaller satellites elevates the demand for in-orbit insurance. This trend reflects the industry’s recognition of operational risks beyond launch, emphasizing the need to limit financial losses during a satellite’s active phase.
For Instance, in May 2024, Tata AIG launched a specialized insurance product for in-orbit satellites, marking a significant step in expanding the scope of space insurance offerings. This new coverage is designed to protect satellites during their operational phase in orbit, addressing risks such as malfunctions, collisions, or damage caused by space debris.
End-User Analysis
In 2024, the Commercial enterprises dominate as end-users, accounting for more than 52% of space insurance demand. This market growth is largely driven by private companies investing heavily in satellite technology, space exploration projects, and related infrastructure. These enterprises require comprehensive coverage because their financial investments and operational continuity depend on mitigating high risks unique to space activities.
The commercial sector includes satellite operators, launch service providers, and emerging private space ventures. These companies increasingly prioritize insurance coverage as they participate in competitive satellite deployments and new space missions, which push the boundaries of technology and market demands. Their strong presence underscores the commercial space industry’s central role in shaping insurance needs.
For instance, in March 2025, Axiom Space announced plans to send more passengers to orbit, expanding its commercial spaceflight operations. The company secured significant new investments, which valued it at $2 billion, to help fund the development of its commercial space station and other space exploration projects.
Distribution Channel Analysis
In 2024, Brokers and agents lead distribution channels with a commanding 71% share. This dominance is due to the specialized knowledge required to assess space-related risks and tailor insurance policies to the unique requirements of satellite launches, operating risks, and liability. These intermediaries facilitate access to a variety of insurance products from different providers, offering clients a broad selection and expert guidance.
Because space insurance involves complex and high-value assets, brokers and agents play a vital role in negotiating terms and advising clients on coverage specifics. Their expertise also helps clients navigate the evolving regulatory landscape and emerging risks such as space debris or cyber threats. This channel remains critical to ensuring tailored and effective insurance solutions in a highly specialized market.
For Instance, In September 2025, the UK Space Agency supported a partnership between insurance broker Eco Monitoring and space insurers to provide specialized coverage for satellites and space assets. Using advanced data analytics, the collaboration aims to assess risks more accurately, emphasizing the rising role of brokers in space insurance.
Emerging Trends
Emerging trends in space insurance include the use of AI-powered data analytics to enhance risk modeling and the development of policies for new space activities, such as commercial space tourism and mega satellite constellations. In 2024, the number of active satellites reached over 6,700, up by nearly 2,000 compared to the previous year, driving demand for more detailed and dynamic insurance solutions.
Another trend is the growing attention to space debris, which poses collision risks to valuable spacecraft, prompting insurers to offer new coverage addressing debris-related damages. The convergence of aviation, aerospace, and insurance sectors is also reshaping product offerings, extending traditional aviation insurance into space flight.
Growth Factors
Key factors driving growth in space insurance include the rising number of commercial satellite launches, reduced launch costs, and increasing government investments in space exploration. More countries and private companies are deploying satellites for communication, navigation, and earth observation, fueling demand for insurance that covers launch failures, in-orbit malfunctions, and liability issues.
Technology advancements also enable insurers to use predictive models, boosting accuracy in pricing and risk management. Additionally, growing awareness of the impact of space debris on operational satellites has led to specialized policies, expanding market scope and complexity. Government spending continues to dominate space activities, significantly impacting the space insurance market.
In 2024, global government funding for space programs was around $135 billion, with over half allocated to defense-related purposes. This large investment highlights the strategic importance of space for national security and exploration. Civil spending focuses on human spaceflight, satellite manufacturing, space launch, and research and development, creating complex insurance needs to protect costly assets.
Key Market Segments
By Coverage Type
- Launch Insurance
- In-Orbit Insurance
- Third-Party Liability Insurance
- Spacecraft Recovery Insurance
By End-User
- Commercial
- Government and Civil
- Defense
By Distribution Channel
- Direct Sales
- Brokers and Agents
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
Drivers
Increasing Satellite Launches and Space Exploration Activities
The space insurance market is driven strongly by the rising number of satellite launches worldwide. Commercial enterprises and governments are launching satellites for communication, navigation, earth observation, and scientific research at an unprecedented scale. This surge in launches raises financial risks related to failures, damage, or mission loss, making insurance essential for risk management.
As more missions are planned, including space tourism and planetary exploration, demand for insurance products tailored to launch, in-orbit, and liability risks continues to grow. This trend is fundamental in making space ventures financially viable and supporting market expansion.
For instance, In October 2025, SpaceX launched new Starlink satellites aboard Falcon 9, expanding its global broadband network. This reflects the rising number of space missions and satellite deployments, increasing the demand for specialized space insurance to protect assets during launch, in-orbit operations, and potential collisions.
Restraint
High Costs and Limited Coverage Options
One major restraint for the space insurance market is the high premium costs paired with limited coverage variety. Space missions involve uncertain and complex risks, which make underwriting challenging and costly for insurance providers.
The high premiums can be a barrier especially for smaller companies or new entrants in the space sector. Additionally, standardized insurance options are scarce due to the unique nature of each mission, limiting flexibility. This results in affordability issues that may slow down market growth and adoption of insurance solutions.
For instance, In September 2024, Data Center Dynamics reported that rising premiums made 2023 a challenging year for space insurance. Increased costs were driven by more complex and frequent space missions, along with higher risks from satellite launches and in-orbit operations. Insurers’ concerns over failures, collisions, and space debris made coverage more expensive for both private companies and government agencies.
Opportunities
New Insurance Models for Mega-Constellations
The growth of mega-constellations, with hundreds to thousands of small satellites deployed for global coverage, offers a significant opportunity for space insurers. Traditional single-satellite policies are being complemented by parametric insurance models that cover clusters of satellites under one contract.
This approach simplifies risk management and provides more efficient, cost-effective coverage options for operators of large satellite fleets. The shift to parametric and bulk insurance products unlocks a new market segment and promotes innovation in insurance offerings to meet emerging commercial space needs.
For instance, in August 2025, India selected Pixxel, a Google-backed company, to build its largest-ever homegrown satellite constellation. This partnership marks a significant step in India’s space capabilities, with Pixxel set to deploy a series of Earth-observing satellites. As satellite constellations expand globally, the demand for specialized space insurance to cover these large-scale networks increases.
Challenges
Navigating Multinational Regulatory Frameworks and Political Risks
The global nature of space missions introduces complexities related to multinational regulatory frameworks and political risks. International space missions often involve multiple countries with differing legal systems and regulatory environments, making compliance challenging.
Political risks, such as sanctions, conflicts, or shifting national policies, can also impact space operations and insurance coverage. Insurers must navigate this intricate legal landscape to provide effective coverage, managing geopolitical uncertainties that could potentially disrupt space missions and complicate risk assessment.
For instance, in September 2025, Clyde & Co. highlighted the evolving regulatory frameworks in space insurance, emphasizing how the growing frequency and complexity of space missions are testing existing legal and insurance structures. The firm discussed the challenges of managing liability, especially as private companies increasingly participate in space exploration.
Key Players Analysis
The Space Insurance Market is dominated by leading global insurers such as AXA XL, Munich Re, Swiss Re, and Lloyd’s of London. These companies provide coverage for satellite launches, in-orbit operations, and spacecraft payloads. Their expertise in risk assessment, premium structuring, and claims management ensures protection against technical failures, collisions, and launch delays, making them key stakeholders for private and government space missions.
Specialized aerospace and underwriting firms including Global Aerospace, Atrium Underwriters, AIG (American International Group), and Allianz Global Corporate & Specialty (AGCS) offer tailored policies for satellite operators and commercial space ventures. Their offerings focus on mitigating orbital debris risks, liability coverage, and loss-of-revenue protection, supporting both emerging and established space enterprises.
Insurance brokers and market facilitators such as Marsh McLennan, Willis Towers Watson (WTW), and BRIT Insurance play a critical role in connecting clients with underwriters, negotiating terms, and structuring multi-layered coverage. A growing number of other players continue to expand the market by offering innovative policy solutions for space tourism, commercial launch services, and interplanetary exploration.
Top Key Players in the Market
- AXA XL
- Munich Re
- Swiss Re
- Lloyd’s of London
- Global Aerospace
- Atrium Underwriters
- AIG (American International Group)
- Allianz Global Corporate & Specialty (AGCS)
- Marsh McLennan (Insurance Broker)
- Willis Towers Watson (WTW)
- BRIT Insurance
- Others
Recent Developments
- In August 2025, AXA XL expanded its space insurance portfolio to address the evolving needs of the space industry. The company introduced comprehensive coverage options that include pre-launch, launch, in-orbit, and third-party liability protection. This expansion is part of AXA XL’s efforts to adapt to the growing complexity of space missions and the increasing demand for specialized insurance solutions, driven by the rise in commercial space activities and satellite deployment.
- In July 2025, Atrium Underwriting Group Ltd. announced a definitive agreement with CRC Group for the acquisition of Atrium’s managing agency. This strategic move aims to enhance Atrium’s capabilities in underwriting space insurance risks. The partnership with CRC Group will provide Atrium with increased resources and expertise, enabling the company to better address the growing complexities and demand within the space insurance market.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 2.59 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 5.24 Bn CAGR(2025-2034) 7.3% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue forecast, AI impact on Market trends, Share Insights, Company ranking, competitive landscape, Recent Developments, Market Dynamics and Emerging Trends Segments Covered By Coverage Type (Launch Insurance, In-Orbit Insurance, Third-Party Liability Insurance, Spacecraft Recovery Insurance), By End-User (Commercial, Government and Civil, Defense), By Distribution Channel (Direct Sales, Brokers and Agents) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of Latin America; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape AXA XL, Munich Re, Swiss Re, Lloyd’s of London, Global Aerospace, Atrium Underwriters, AIG (American International Group), Allianz Global Corporate & Specialty (AGCS), Marsh McLennan (Insurance Broker), Willis Towers Watson (WTW), BRIT Insurance, Others Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three license to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- AXA XL
- Munich Re
- Swiss Re
- Lloyd’s of London
- Global Aerospace
- Atrium Underwriters
- AIG (American International Group)
- Allianz Global Corporate & Specialty (AGCS)
- Marsh McLennan (Insurance Broker)
- Willis Towers Watson (WTW)
- BRIT Insurance
- Others










