Global RoCE for AI Workloads Market Size, Share, Industry Analysis Report By Product Type (Hardware, Software, Services), By Application (Model Training, High-Performance Computing, Hyperconverged Infrastructure, Cloud Renting), By End-User (Cloud Service Providers, Enterprises, Data Centers, Others), By Regional Analysis, Global Trends and Opportunity, Future Outlook By 2025-2034
- Published date: Dec. 2025
- Report ID: 168435
- Number of Pages: 392
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
- Report Overview
- Key Takeaway
- Key Performance and Metrics
- Role of Generative AI
- Investment and Business Benefits
- U.S. Market Size
- Product Type Analysis
- Application Analysis
- End-User Analysis
- Emerging Trends
- Growth Factors
- Key Market Segments
- Drivers
- Restraint
- Opportunities
- Challenges
- Key Players Analysis
- Recent Developments
- Report Scope
Report Overview
The Global RoCE for AI Workloads Market size is expected to be worth around USD 6.82 billion by 2034, from USD 1.26 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 18.4% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 52.6% share, holding USD 0.66 billion in revenue.
The RoCE for AI workloads market has expanded as data centers adopt high performance networking technologies to support rapid model training and large scale inference. Growth reflects increasing demand for low latency communication between accelerators, rising cluster sizes and the need for networking that can handle massive parallel workloads. RoCE is now widely used in AI optimized data centers, cloud computing clusters and enterprise supercomputing environments.
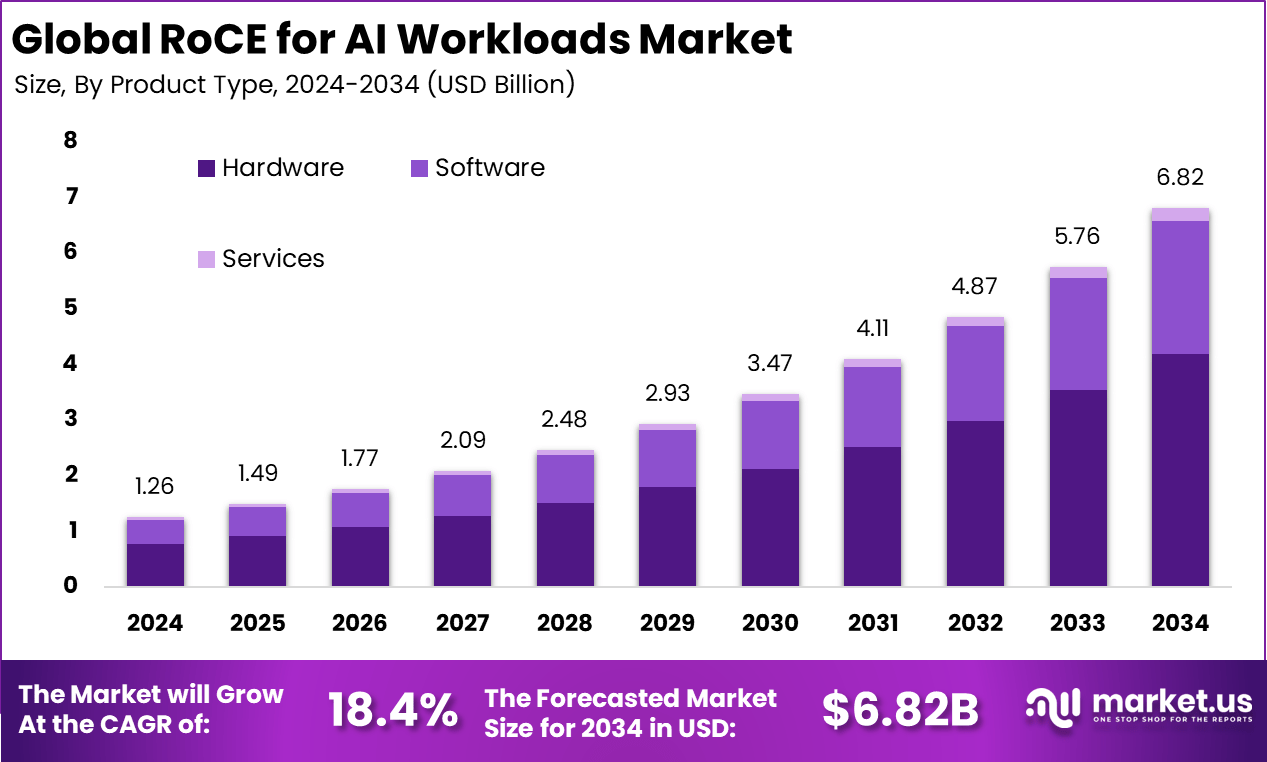
Top driving factors for RoCE adoption in AI workloads include the growing demand for low-latency networking and high bandwidth to handle expansive datasets. AI models and training environments often require synchronous data exchange, where even minor delays can slow down the entire system. RoCE’s capacity to reduce data transfer latency to microseconds and support multi-gigabit speeds ensures that AI clusters operate efficiently and reliably.
The market for RoCE for AI workloads is driven by the surging need for ultra-low latency and high-bandwidth data transfers in training massive models. RoCE skips CPU involvement for direct memory access over Ethernet, slashing delays to microseconds and freeing processors for core AI tasks. This fits perfectly with hyperscale data centers handling huge datasets, boosting speed and efficiency without pricey new cables.
For instance, in November 2025, Broadcom joined the Ethernet Scale-Up Networking push at OCP Summit, advancing RoCE for massive AI fabrics alongside partners. This targets congestion-free paths vital for GPU-heavy workloads.
Key Takeaway
- In 2024, the Hardware segment accounted for 61.4% of the Global RoCE for AI Workloads Market, indicating its strong role in enabling RDMA-based acceleration.
- In 2024, the Model Training segment captured 71.6%, showing that RoCE adoption was mainly driven by high-intensity AI training workloads.
- In 2024, the Cloud Service Providers segment reached 78.3%, reflecting strong reliance on RDMA-enabled Ethernet fabrics within large cloud environments.
- The US market generated USD 0.60 Billion in 2024 with a CAGR of 16.8%, highlighting stable demand for RoCE-based performance optimization.
- In 2024, North America held 52.6%, confirming the region’s leadership in deploying advanced Ethernet-based RDMA solutions for AI workloads.
Key Performance and Metrics
- Latency is reduced to microseconds because data is moved directly between servers without routing through the CPU, which supports faster response for real-time AI tasks.
- Bandwidth reaches extremely high rates as the technology utilizes advanced Ethernet speeds, ensuring that data flow remains steady during heavy deep learning workloads.
- CPU usage decreases sharply as network processing is handled by dedicated hardware, allowing the CPU to focus on core computational work.
- Throughput approaches nearly 400 Gbps in optimized configurations, revealing a strong performance gap compared to traditional virtual machine networking.
- Scaling efficiency remains near linear across distributed nodes, demonstrating that RDMA-based Ethernet fabrics support growth for demanding AI training clusters.
- Operational cost can fall by up to 55% over multi-year periods when high-performance Ethernet fabrics are used instead of proprietary interconnect systems.
- Performance remains sensitive to packet loss which requires careful use of flow control and congestion management to preserve stability during peak traffic.
Role of Generative AI
Generative AI plays a significant role in driving the demand for faster and more efficient AI workload processing. In sectors like computer science and mathematics, workers spent nearly 12% of their work hours using generative AI, reporting an average of 5.4% time savings in their tasks. This boosts productivity by about 33% for each hour generative AI is used.
These productivity gains create a pressing need for infrastructures that can keep up with the rapid data processing and low-latency requirements of generative AI models. By enabling rapid training and inference processes, generative AI increases the complexity of workload demands.
This fuels the adoption of advanced networking protocols like RoCE, which provide the necessary low latency and high bandwidth to support large-scale, distributed AI training and real-time AI applications. The improved network performance directly contributes to quicker AI insights and enhanced operational efficiencies.
Investment and Business Benefits
Investment opportunities focus on the modernization of data center networking to support AI, cloud infrastructure, enhancing distributed AI training, and emerging technologies such as silicon photonics and data processing units (DPUs) that complement RoCE.
Edge AI infrastructure is also gaining attention due to its ability to bring processing closer to data sources, significantly reducing latency in real-time inference applications. Investments targeting these network infrastructure components tend to benefit from increased AI workload density and the growing need for energy efficiency in large-scale AI operations.
Business benefits of RoCE include faster AI model training cycles, higher resource utilization, and reduced operational costs by minimizing CPU overhead and lowering the number of required servers. The protocol’s compatibility with existing Ethernet systems also leads to cost savings and energy efficiency, decreasing the environmental footprint of AI data centers.
U.S. Market Size
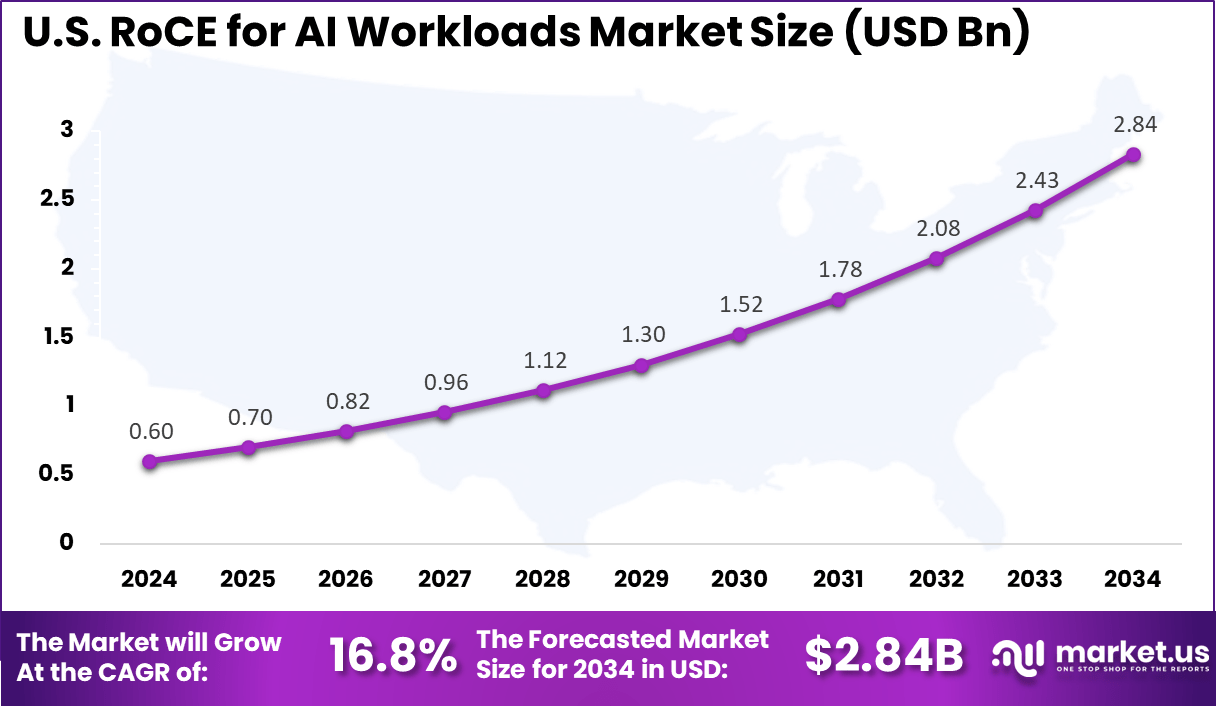
The market for RoCE for AI Workloads within the U.S. is growing tremendously and is currently valued at USD 0.60 billion, the market has a projected CAGR of 16.8%. This growth stems largely from the rapid adoption of AI across industries, which demands high-performance, low-latency networking to support increasing data center workloads. As AI models grow more complex, efficient data transfer through RoCE becomes critical for speeding up model training and inference.
Additionally, investments in cloud infrastructure and data centers are driving this market. The rise of hyperscale cloud providers and enterprise adoption has intensified demand for RoCE-enabled hardware, capable of handling massive AI workloads efficiently. Energy demands and infrastructure upgrades in U.S. data centers also support this growth trajectory, reflecting the broad impact of AI on technology and energy sectors.
For instance, In October 2025, Arista Networks introduced its R4 Series platforms designed for high-density AI workloads in modern data centers. The systems support 800 Gbps connectivity and integrate 3.2 Tbps HyperPorts to strengthen RoCE-based networking. Their low-latency and lossless architecture improves distributed AI training efficiency, with job completion times reduced by up to 44%.
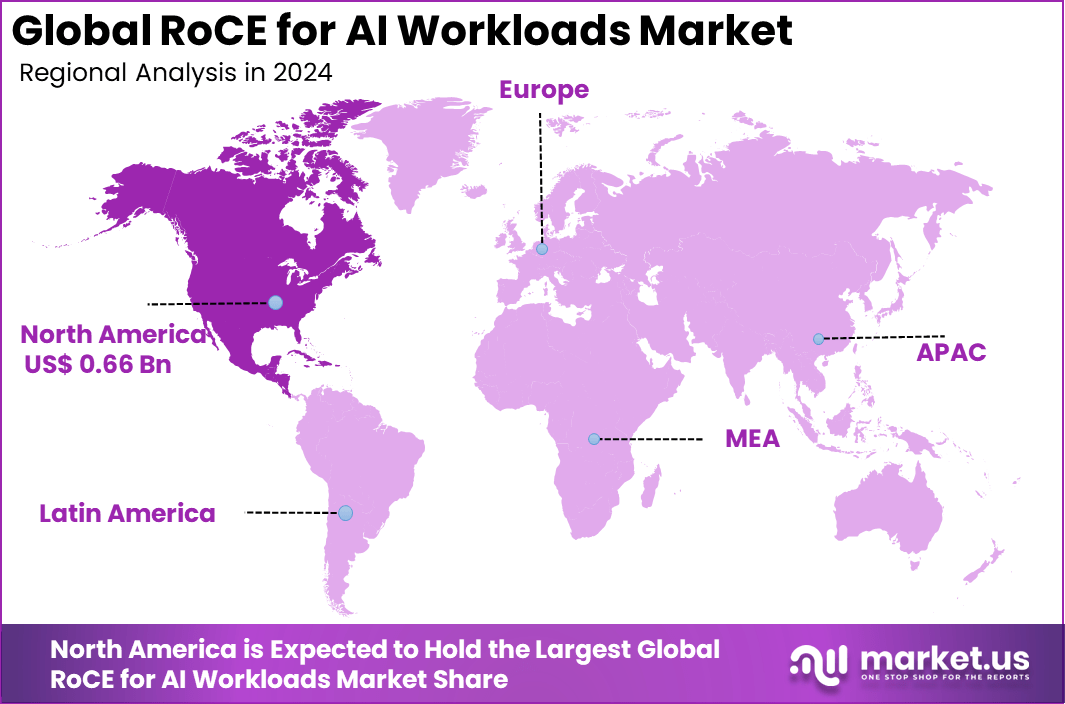
In 2024, North America held a dominant market position in the Global RoCE for AI Workloads Market, capturing more than a 52.6% share, holding USD 0.66 billion in revenue. This dominance stems from the region’s advanced data center infrastructure, strong presence of major technology companies, and leadership in cloud computing. These factors create an environment ripe for the rapid adoption of RoCE technology to support high-performance AI workloads.
Furthermore, significant investments in AI research, development, and deployment by both private and government sectors fuel this growth. The presence of hyperscale cloud providers and cutting-edge semiconductor manufacturers enhances market expansion, allowing North America to meet increasing demand for efficient AI workload management and networking solutions.
For instance, In February 2025, NVIDIA expanded RoCE capabilities through its Spectrum-X platform, which improved AI storage performance by up to 48% in collaboration with major OEM partners. The platform has been deployed across large Ethernet and RoCE fabrics scaled toward 129K-GPU environments, enabling faster RDMA-based data movement with lower latency.
Product Type Analysis
In 2024, The Hardware segment held a dominant market position, capturing a 61.4% share of the Global RoCE for AI Workloads Market. Specialized network cards and Ethernet adapters make up this segment by enabling direct memory access that cuts down wait times for data movement in AI setups. These components handle the heavy lifting of shifting large data batches between servers and processors without slowing things down.
The focus on hardware comes from its proven track record in boosting speed and handling the constant data flow needed for AI tasks. Teams building AI systems pick these parts because they free up main processors for actual computing work instead of network chores. This keeps everything running smoothly in busy data centers.
For Instance, in October 2025, NVIDIA announced the deployment of its BlueField-4 Data Processing Units (DPUs) alongside Oracle’s AI infrastructure, optimizing large-scale AI workloads by offloading key infrastructure services. This collaboration exemplifies the growing reliance on specialized hardware components like DPUs and RoCE-compatible network devices to meet demanding AI workload needs.
Application Analysis
In 2024, the Model Training segment held a dominant market position, capturing a 71.6% share of the Global RoCE for AI Workloads Market. Training complex AI models requires efficient handling of massive datasets and high-throughput data transfer between computing nodes. RoCE’s ability to provide low-latency, reliable communication between GPUs and servers accelerates the training process significantly. This efficiency is crucial for reducing time-to-insight and expediting the development of AI solutions.
Investment focusing on model training uses RoCE’s direct memory access capabilities to optimize distributed training workflows, which are becoming increasingly common in AI research and development. The dominance of model training reflects the need for superior network fabrics that support growing AI workloads and enhance the scalability of machine learning infrastructures.
For instance, in July 2025, AMD showcased enhanced AI compute capabilities during its Advancing AI event, emphasizing generational leaps in inferencing and training speeds facilitated by its latest GPUs combined with efficient memory subsystems. This highlights the significant role of RoCE-enabled infrastructure in supporting intensive model training.
End-User Analysis
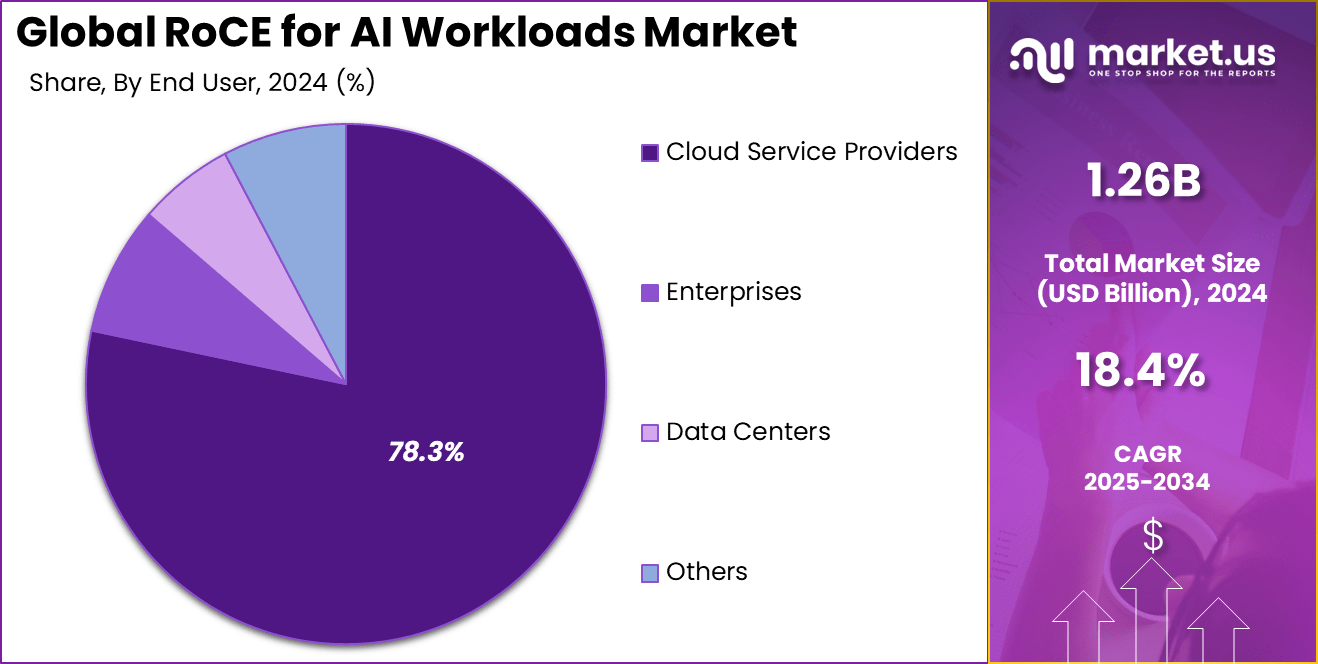
In 2024, The Cloud Service Providers segment held a dominant market position, capturing a 78.3% share of the Global RoCE for AI Workloads Market. These providers integrate RoCE technology within their data centers to deliver scalable, high-performance AI compute services to a variety of clients ranging from enterprises to startups.
The adoption of RoCE enables cloud providers to improve network efficiency, reduce latency, and deliver better cost performance to their customers. As AI applications proliferate across industries, cloud providers invest heavily in optimizing their infrastructure with RoCE-enabled Ethernet fabrics. This results in greater flexibility, improved hardware utilization, and the ability to meet the increasing demand for AI processing power.
For Instance, in November 2025, Dell Technologies launched new AI factory solutions combining automated infrastructure with high-performance PowerEdge servers, enabling cloud providers to deploy scalable AI training and inference workloads efficiently. Networking innovations in Dell’s portfolio support large-scale AI deployments for cloud environments.
Emerging Trends
One emerging trend is the enhanced implementation of queue pair scaling and advanced routing techniques in RoCE networks, achieving performance improvements up to 40% in collective AI operations like AllReduce. This trend helps accommodate the bursty and high-throughput nature of AI workloads by optimizing message distribution and balancing traffic flows efficiently across the network.
Another trend is the integration of Priority Flow Control (PFC) mechanisms, which manage congestion and prioritize critical RDMA traffic in RoCE networks. This ensures deterministic and consistent performance, which is crucial for safety-critical AI deployments such as autonomous vehicles and medical diagnostics, where predictable latency is essential.
Growth Factors
Low latency and high bandwidth are core growth factors for RoCE in AI workloads. RoCE cuts latency to microseconds by allowing direct memory access between servers, bypassing CPUs and traditional networking stacks. This accelerates neural network training and inference, enabling AI solutions to scale effectively across large datasets while maintaining responsiveness.
Scalability is another driving element. RoCE facilitates efficient communication between growing numbers of distributed compute and storage nodes. Its ability to support tens or hundreds of gigabits per second ensures AI infrastructures can expand horizontally without compromising data flow speeds, meeting the surging data demands of AI and machine learning models.
Key Market Segments
By Product Type
- Hardware
- Software
- Services
By Application
- Model Training
- High-Performance Computing
- Hyperconverged Infrastructure
- Cloud Renting
By End-User
- Cloud Service Providers
- Enterprises
- Data Centers
- Others
Regional Analysis and Coverage
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherlands
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of Latin America
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Drivers
Ultra-Low Latency and High Bandwidth for AI
RoCE enables direct memory-to-memory data transfers between servers without relying on CPU or operating system processes, allowing latency to fall to microseconds. This improvement supports faster model training and real-time inference by reducing delays during data movement. Its ability to run on standard Ethernet infrastructure while delivering performance similar to InfiniBand makes it valuable for data centers seeking higher throughput and responsiveness.
The technology provides high bandwidth for handling large datasets and distributed AI workloads. By shifting data transfer tasks to specialized network cards, RoCE frees CPU resources for core AI computation. This approach reduces operational time and cost for organizations working with intensive AI applications, creating a more efficient path to performance gains in data-heavy environments.
In September 2025, NVIDIA introduced Spectrum-X, an Ethernet-based solution for generative AI that applies GPU Direct RDMA to reduce training latency by up to 90%. This capability allows GPUs to communicate directly across RoCE networks without CPU involvement, enabling faster execution of large-scale AI models and improving overall data center efficiency.
Restraint
Complex Integration and Infrastructure Challenges
RoCE adoption remains constrained by the need for precise network tuning to prevent packet loss and congestion, which depends on mechanisms such as Priority Flow Control and Explicit Congestion Notification. These requirements make integration difficult in data centers built without support for specialized traffic patterns. Many organizations struggle to upgrade older systems or lack the expertise needed to design and maintain RoCE-optimized environments.
Interoperability across mixed IT infrastructures creates further complexity. RoCE deployments must align with traditional Ethernet operations while relying on specialized hardware and software adjustments. Smaller enterprises often face cost and skill limitations, which slows uptake even when performance benefits are clear. These compatibility and resource challenges continue to delay broader standardization of RoCE for AI workloads.
In July 2025, Arista Networks detailed its Etherlink systems with RDMA-Aware QoS to improve RoCE performance inside AI clusters, while acknowledging persistent difficulties in performing dynamic load balancing at scale. Many existing facilities require custom configuration for each switch and network interface card, and workforce shortages make full deployment slower in operationally demanding environments.
Opportunities
Expanding AI and Cloud Computing Demand
The rapid growth of AI applications, especially in hyperscale data centers, fuels increasing demand for RoCE’s high-performance networking. As organizations scale their AI infrastructure, the need for efficient data movement protocols like RoCE becomes critical. The rise of cloud and hybrid cloud architectures also opens opportunities for RoCE adoption, as it supports fast, scalable data access across distributed systems and multiple geographic locations.
Enterprises prioritizing digital transformation and real-time AI insights stand to benefit from RoCE’s capabilities. Vendors offering interoperable, secure, and scalable RoCE solutions can capture a significant share of the evolving market. Geographic markets such as North America and rapidly digitizing Asia Pacific are expected to drive substantial growth opportunities in RoCE deployment for AI workloads over the next several years.
For instance, in June 2025, AMD teamed with Oracle Cloud for zettascale clusters using Pensando Pollara NICs with RoCE for up to 131,072 Instinct MI355X GPUs in AI supercomputing. The low-jitter RDMA networking meets surging demand for distributed inference across clouds. Hyperscalers see big chances to build out AI factories with this efficient setup.
Challenges
Security and Data Privacy Concerns
As RoCE networks handle sensitive AI data transfers with direct memory access, protecting data from unauthorized access or breaches is a major concern. The bypassing of traditional CPU processing layers can expose networks to new vulnerabilities, requiring robust encryption and security protocols tailored to RDMA traffic. Ensuring secure data flows without compromising RoCE’s performance advantages poses a complex challenge for network architects.
Moreover, compliance with data privacy regulations adds another layer of difficulty in deploying RoCE widely in industries like healthcare and finance, where AI is increasingly used. Addressing these security issues demands ongoing innovation and investment in security features integrated with RoCE solutions, without adding significant overhead that could erode latency and bandwidth benefits.
For instance, in February 2025, Juniper partnered with IBM to blend Mist AI and watsonx for safer network ops, tackling RoCE vulnerabilities in AI data flows through better diagnostics. Privacy rules demand tight controls on RDMA traffic in finance and health AI apps. Balancing security with performance remains a key hurdle for broad use.
Key Players Analysis
One of the leading players in the market, in September 2025, NVIDIA teamed up with Intel to build custom data center CPUs using NVLink for smoother AI processing, plus NVIDIA put $5 billion into Intel stock to push joint AI setups. This move helps RoCE handle heavy AI traffic better by linking chips faster. It opens doors for mixed CPU-GPU systems in big AI clusters.
Top Key Players in the Market
- NVIDIA
- AMD
- Intel
- Cisco
- Arista Networks
- Broadcom
- Marvell
- Dell Technologies
- HPE
- Juniper Networks
- IBM
- Fujitsu
- Lenovo
- Supermicro
- Inspur
- Others
Recent Developments
- In January 2025, Intel debuted Core Ultra processors at CES with built-in AI Boost for edge inferencing, tying into RoCE ecosystems via partnerships like NVIDIA NVLink. These handle video and real-time AI with lower power draw.
- In October 2025, HPE finalized its takeover of Juniper Networks, boosting AI-native networking with RoCE-ready fabrics for high-speed AI clusters. The deal doubles down on handling trillion-parameter models in government and enterprise data centers.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 1.26 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 6.82 Bn CAGR(2025-2034) 18.4% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue forecast, AI impact on Market trends, Share Insights, Company ranking, competitive landscape, Recent Developments, Market Dynamics and Emerging Trends Segments Covered By Product Type (Hardware, Software, Services), By Application (Model Training, High-Performance Computing, Hyperconverged Infrastructure, Cloud Renting), By End-User (Cloud Service Providers, Enterprises, Data Centers, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of Latin America; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape NVIDIA, AMD, Intel, Cisco, Arista Networks, Broadcom, Marvell, Dell Technologies, HPE, Juniper Networks, IBM, Fujitsu, Lenovo, Supermicro, Inspur, Others Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three license to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  RoCE for AI Workloads MarketPublished date: Dec. 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
RoCE for AI Workloads MarketPublished date: Dec. 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- NVIDIA
- AMD
- Intel
- Cisco
- Arista Networks
- Broadcom
- Marvell
- Dell Technologies
- HPE
- Juniper Networks
- IBM
- Fujitsu
- Lenovo
- Supermicro
- Inspur
- Others













