Global Robotic Fashion Inductor Market Size, Share Report Analysis By Component (Hardware, Software, Services), By Application (Smart Tag & RFID Inlay Manufacturing, Precision Embroidery & Circuit Printing, Automated Garment Assembly with Integrated Electronics, Others), By End-User (Smart Apparel Manufacturers, Luxury & High-Tech Fashion Houses, Technical Sportswear Brands, Others), By Regional Analysis, Global Trends and Opportunity, Future Outlook By 2025-2034
- Published date: Dec. 2025
- Report ID: 170709
- Number of Pages: 220
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
- Report Overview
- Top Market Takeaways
- Performance Statistics
- Quick Market Facts
- Investment and Business Benefits
- By Component
- By Application
- By End User
- By Region
- Emerging Trends
- Growth Factors
- Key Market Segments
- Driver Analysis
- Restraint Analysis
- Opportunity Analysis
- Challenge Analysis
- Competitive Analysis
- Recent Developments
- Future Outlook and Opportunities
- Report Scope
Report Overview
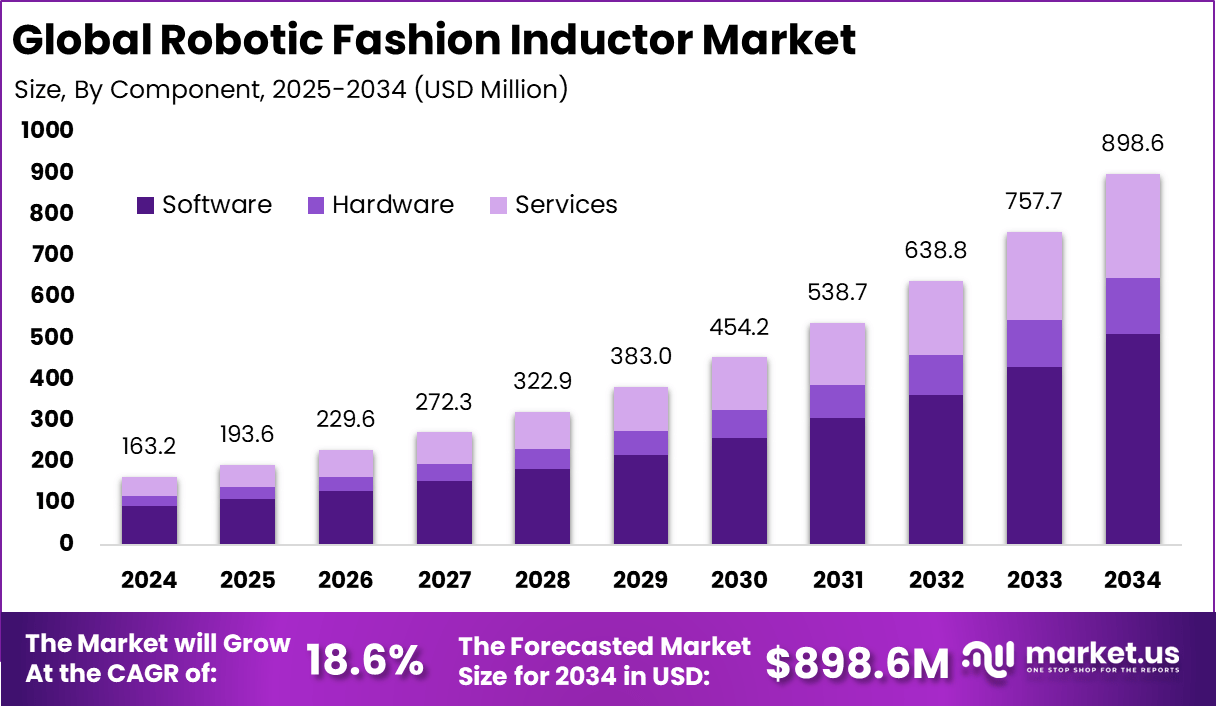
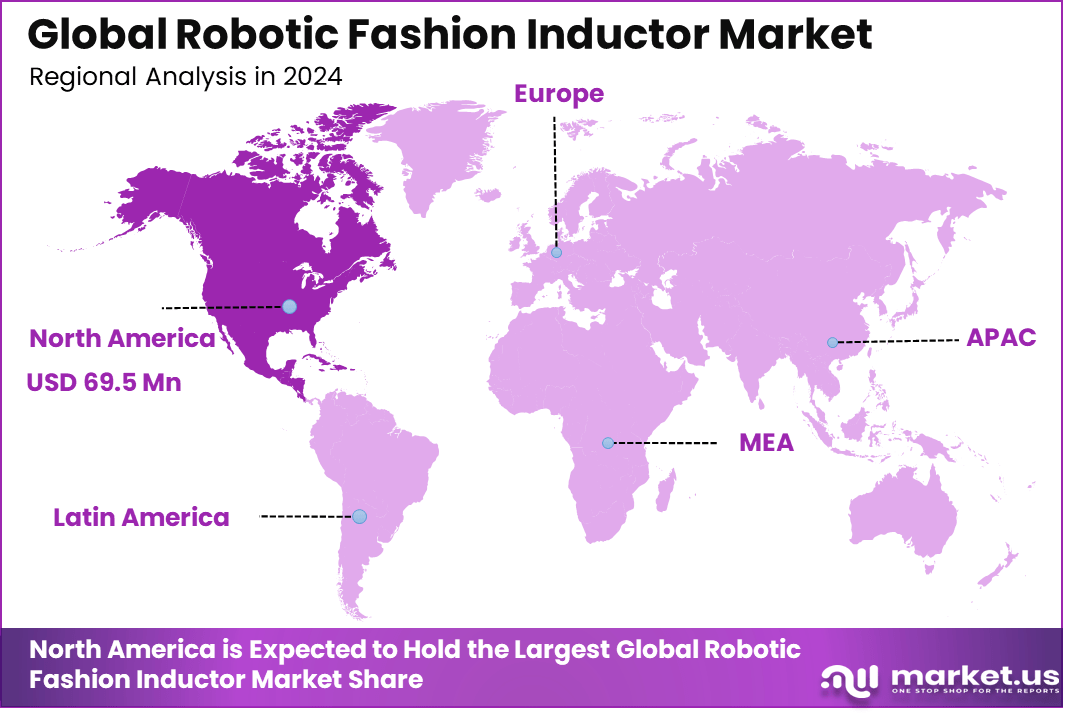
The Global Robotic Fashion Inductor Market generated USD 163.2 Million in 2024 and is predicted to register growth from USD 193.6 Million in 2025 to about USD 898.6 Million by 2034, recording a CAGR of 18.6% throughout the forecast span. In 2024, North America held a dominan market position, capturing more than a 42.6% share, holding USD 69.5 Million revenue.
The robotic fashion inductor market includes systems that guide and prepare materials, garments, and components during fashion production processes. These robots perform tasks such as material positioning, fabric handling, folding alignment, and feed preparation for sewing and finishing operations. As fashion manufacturers seek higher productivity and consistent quality, robotic inductors have become more relevant.
This market plays a crucial role in improving efficiency and consistency in fashion manufacturing. Robotic fashion inductors ensure that materials are accurately positioned and aligned before processing, reducing errors and rework. In complex fashion products with multiple panels and fabric types, robots help maintain uniform feed conditions for downstream sewing or cutting machines.
In automated fashion production suggest that material handling tasks such as feeding and alignment represent over 30% of total manual effort, making induction automation impactful for operations. Growth is driven by rising labor costs, skilled labor shortages, and the push for faster turnaround times in fashion production. The fashion industry has long faced difficulty in maintaining quality while meeting short lead times.
Robotics offer solutions that reduce repetitive strain on workers and improve consistency. Advances in machine vision, soft material handling, and adaptive gripping technologies have made robotic inductors more capable of handling delicate fabrics. Industry observations indicate that garment production facilities using automation report productivity gains of over 25% compared to fully manual operations.
Top Market Takeaways
- Software components led with a 56.9% share, as automation platforms and control systems play a central role in managing precision-driven fashion manufacturing workflows.
- Smart tag and RFID inlay manufacturing accounted for 36.41%, driven by rising demand for item-level tracking, inventory visibility, and smart apparel integration.
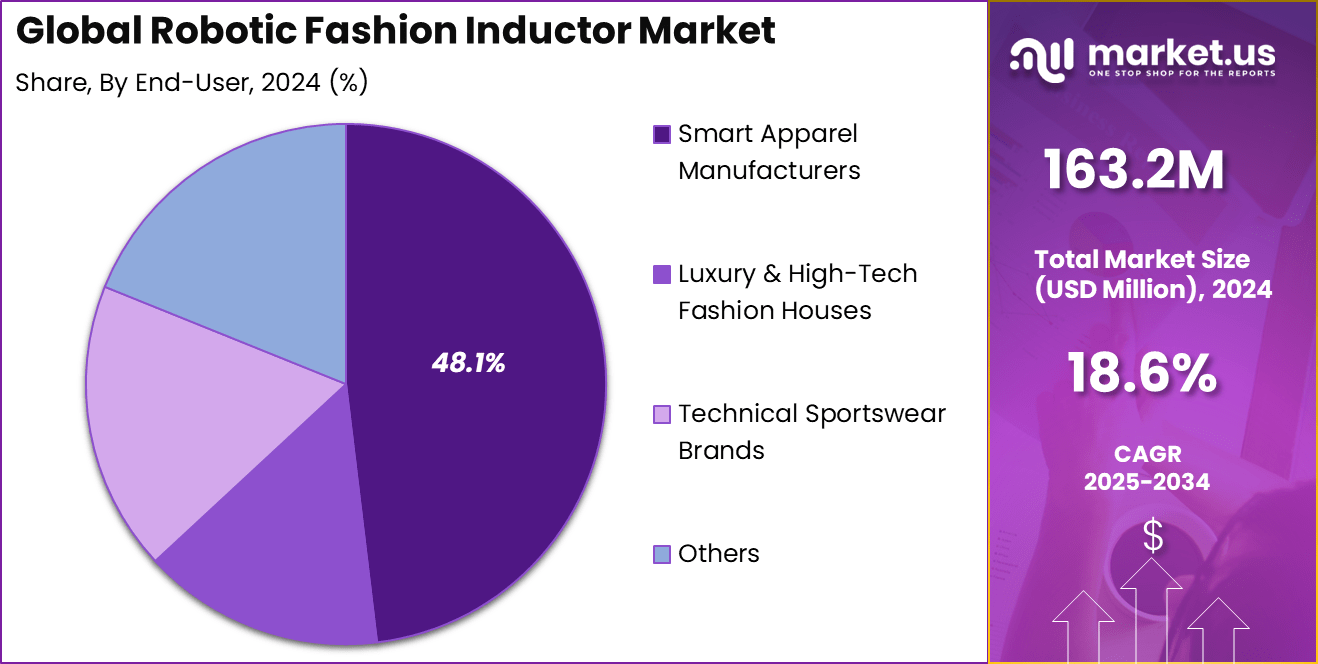
- Smart apparel manufacturers dominated end-user adoption with 48.1%, reflecting strong uptake of robotic inductors in connected and wearable fashion production.
- North America held a leading 42.6% share, supported by advanced manufacturing capabilities and early adoption of fashion automation technologies.
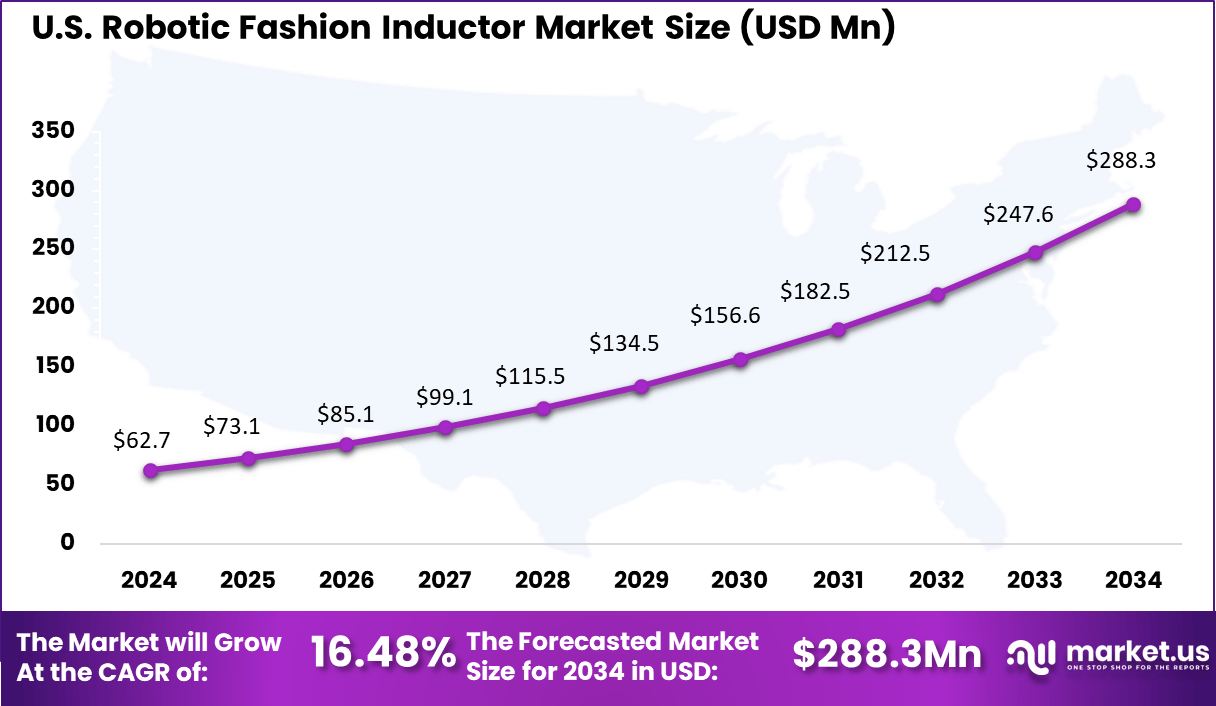
- The U.S. market reached USD 62.72 million, expanding at a robust 16.48% CAGR due to investments in smart textiles and RFID-enabled apparel.
- The global market generated USD 163.2 million in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 193.6 million in 2025 to USD 898.6 million by 2034.
- A strong 18.6% CAGR highlights rapid expansion, driven by automation needs, rising smart apparel demand, and digital transformation across the fashion supply chain.
Performance Statistics
- High picking speed: Capable of processing up to 1,300 picks per hour, supporting fast-moving fashion and apparel logistics operations.
- Very high accuracy: Delivers over 99.5% picking accuracy, even with soft, flexible, and deformable items such as polybags and fabric pouches.
- Fully autonomous operation: Designed to run continuously without human supervision, helping lower cost per pick and increase overall throughput.
- Advanced AI vision: Uses AI-driven vision with pre-trained models to identify stable grasp points in cluttered, unstructured environments like bins and conveyors.
- Built for fashion logistics: Optimized specifically for apparel and accessories, where product variability and handling complexity are high.
Quick Market Facts
Demand for robotic fashion inductors is increasing among apparel manufacturers, textile converters, and specialized garment processors. High volume producers and fast fashion brands are early adopters due to their need for rapid throughput. Demand is also emerging in technical textiles and performance wear sectors where precise material handling is required.
Surveys of manufacturing operations show that automation projects focusing on material handling receive strong internal support due to measurable returns in quality and cycle time. Key technologies supporting adoption include advanced vision systems for fabric detection, force sensitive grippers for soft material handling, and AI driven motion planning.
Pattern recognition and real time adjustment help robots adapt to varying fabric conditions. Cloud connected production monitoring systems allow performance tracking and fleet coordination across multiple induction stations. Research indicates that over 60% of recent robotic material handling pilots incorporate vision guided systems for improved accuracy.
Organizations adopt robotic fashion inductors to reduce manual labor, improve quality consistency, and accelerate production. Robots help minimize human error in material staging, leading to less waste and fewer defects. Reduction in worker fatigue and repetitive strain injuries is another motivator. Many manufacturers also view automation as a way to maintain competitiveness in markets with short lead times and high customization demands.
Investment and Business Benefits
Investment opportunities exist in robotic gripping technologies, machine vision solutions tailored to textile materials, and integrated control systems for fashion production lines. Customized solutions for delicate fabric handling and mixed material types are areas of growing interest.
Services such as deployment consulting, training, and maintenance support for robotic induction systems are also in demand. Automation investment trends in manufacturing show that material handling and preparation systems often receive priority due to their impact on overall line efficiency. Robotic fashion inductors deliver clear business benefits such as reduced operational costs, improved production consistency, and lower waste.
Automation of repetitive preparation tasks frees human workers to focus on higher skill activities such as quality inspection and finishing. Enhanced throughput and reduced rework contribute to shorter delivery cycles. Case studies from automated garment facilities report quality defect reductions and faster order fulfillment due to automated material handling.
By Component
The software segment leads with 56.9%, showing that digital platforms play a central role in managing smart tag and RFID-related processes. Software solutions are used for design control, data encoding, tracking, and integration with enterprise systems, which improves accuracy and production efficiency.
Growing demand for automation and real-time monitoring supports adoption of software components. Manufacturers rely on software to manage large data volumes, ensure quality control, and support seamless coordination across production and supply chain operations.
By Application
Smart tag and RFID inlay manufacturing accounts for 36.41%, reflecting strong use of digital solutions in tag design and production workflows. These applications require precise data handling, encoding, and validation to ensure reliable tag performance.
Growth in this segment is driven by rising adoption of RFID technology across retail, logistics, and industrial sectors. Software-supported manufacturing improves production speed, reduces defects, and supports scalable deployment of smart tagging solutions.
By End User
Smart apparel manufacturers represent 48.1%, highlighting strong demand for digital solutions in connected clothing production. These manufacturers integrate smart tags and RFID components to support inventory tracking, authentication, and consumer engagement.
Adoption is increasing as apparel brands focus on supply chain visibility and product traceability. Smart apparel manufacturers use digital tools to manage embedded technology while maintaining production efficiency and quality standards.
By Region
In 2024, North America holds 42.6%, supported by strong adoption of smart manufacturing and connected product technologies. The region benefits from advanced digital infrastructure and early use of RFID and smart tagging systems across industries.
The United States reached USD 62.72 Million with a CAGR of 16.48%, reflecting steady growth in smart tag and RFID-related solutions. Rising focus on automation, digital apparel, and supply chain transparency continues to support market expansion.
Emerging Trends
Emerging trends in this market highlight the increasing use of AI based vision systems to improve item recognition and grasp accuracy. Modern robotic fashion inductors are capable of achieving picking accuracy above 99%, even when handling deformable or reflective packaging.
Another notable trend is the shift toward modular system designs that allow easy integration into existing logistics facilities. High throughput capability is also becoming a focus, with some systems supporting more than 1,000 picks per hour, enabling faster processing during peak demand periods.
Growth Factors
Growth in the Robotic Fashion Inductor market is primarily driven by the expansion of e commerce and omnichannel retail in the fashion industry. Distribution centers are under pressure to reduce order processing time while maintaining accuracy, which has increased reliance on robotic induction solutions.
In addition, rising labor costs and workforce availability challenges are accelerating automation adoption. These systems help reduce manual workload, improve consistency, and support scalable operations, making them an essential component of modern fashion supply chains.
Key Market Segments
By Component
- Software
- Hardware
- Services
By Application
- Smart Tag & RFID Inlay Manufacturing
- Precision Embroidery & Circuit Printing
- Automated Garment Assembly with Integrated Electronics
- Others
By End-User
- Smart Apparel Manufacturers
- Luxury & High-Tech Fashion Houses
- Technical Sportswear Brands
- Others
Regional Analysis and Coverage
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherlands
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of Latin America
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Driver Analysis
Rising Demand for Efficient Apparel Handling
One major driver of this market is the growing complexity of fashion logistics operations. Fashion and apparel companies manage large volumes of diverse garments, accessories, and polybagged items that vary in shape, weight, and texture. Manual handling of these items is time-consuming and prone to error, especially in high-volume warehouses and fulfillment centers.
Another driver is the emphasis on faster order fulfillment and reduced lead times for fashion e-commerce. As online fashion retail expands, companies face pressure to process and sort orders quickly and accurately. Robotics like fashion inductors support this need by achieving high pick rates with consistent performance, enabling firms to handle peak demand periods without proportional increases in workforce size.
Restraint Analysis
Technical Complexity and Integration Requirements
A key restraint in the robotic fashion inductor market is the technical complexity required for implementation. These systems involve advanced vision systems, AI-trained models, and precise mechanical design to handle garments that are soft and deformable. Developing, calibrating, and integrating such systems into existing warehouse or sorting environments can require specialized expertise and time.
Another restraint comes from the variability of fashion items themselves. Items such as dresses, scarves, and accessories differ significantly in size and material, which complicates the task of creating universal robotic handling solutions. Some systems must be tuned or programmed for specific item categories, which increases setup time and cost. This can reduce the market appeal for operators seeking plug-and-play solutions.
Opportunity Analysis
Growth in Fashion Logistics Automation
There is a strong opportunity for robotic fashion inductors as fashion logistics networks modernize. Companies that operate large fulfillment centers or outsource logistics increasingly view automation as a way to manage labor constraints, reduce error rates, and improve throughput. Robotic modules that can integrate into warehouse management systems and sorters offer clear operational advantages by handling tasks that were traditionally manual.
Another opportunity lies in extending these robotic applications into adjacent parts of the fashion supply chain, including tagging, labeling, quality inspection, or packaging. As robotics become more capable at handling soft materials and diverse item types, their use cases can expand beyond initial induction into sorters. This provides suppliers with room to offer broader automation solutions that cover multiple stages of apparel logistics and distribution.
Challenge Analysis
Costs and Workforce Adjustment
A primary challenge in this market is the cost of acquiring and maintaining advanced robotic induction systems. These units combine robotics, AI, and vision in a way that represents a significant capital investment compared to more conventional mechanical sorters. Smaller fashion brands and logistics providers may hesitate to invest until they see clear and measurable return on investment.
Another challenge is workforce adaptation. As robotic systems take over tasks previously done by human workers, companies must manage changes in labor needs and employee skills. This includes training staff to work alongside robots, handle exceptions, and maintain the systems. Organizational adjustments and reskilling efforts can present barriers for some operators, especially in regions with limited access to robotics expertise.
Competitive Analysis
ABB, SoftWear Automation, Sewbo, and ZSK Stickmaschinen lead the robotic fashion inductor market by enabling automation across cutting, sewing, embroidery, and material handling processes. Their robotic systems help apparel manufacturers improve production speed, accuracy, and consistency while reducing manual dependency. These companies focus on precision control, fabric adaptability, and integration with digital manufacturing workflows.
Brother Industries, Tamicare, Kornit Digital, Sensory Robotics, and Gerber Technology strengthen the market with robotics and automation solutions tailored for textile processing, digital printing, and quality control. Their technologies support flexible manufacturing, short production runs, and mass customization. These providers emphasize smart sensing, software driven design integration, and reduced material waste.
Assyst GmbH, Prisca Vils, and other players expand the landscape with niche robotic solutions for fit analysis, pattern optimization, and automated finishing. Their offerings help fashion brands improve sizing accuracy and production planning. These companies focus on digital twins, AI driven garment simulation, and modular automation.
Top Key Players in the Market
- ABB, Ltd.
- SoftWear Automation, Inc.
- Sewbo, Inc.
- ZSK Stick- und Prüftechnik GmbH
- Brother Industries, Ltd.
- Tamicare Ltd.
- Kornit Digital, Ltd.
- Sensory Robotics
- Gerber Technology
- Assyst GmbH
- Prisca Vils AG
- Others
Recent Developments
- January, 2026 – Gerber Technology entered a memorandum of understanding for acquisition by Lectra, uniting cutting-edge software and hardware to fast-track Industry 4.0 in fashion manufacturing. The combo eyes deeper R&D for automated pattern-to-production flows. Expect boosted services for apparel brands chasing digital upgrades.
- March, 2025 – ABB Ltd. rolled out its Robotic Fashion Inductor, an AI-driven module that handles polybagged apparel at speeds up to 1,300 picks per hour, targeting logistics bottlenecks in fashion supply chains. This addition to their Item Picking family promises over 99.5% accuracy even with varied items, easing labor shortages in e-commerce returns and order fulfillment. Fashion retailers tested it early, highlighting its quick integration into existing setups.
- August, 2025 – SoftWear Automation closed a $20 million Series B1 funding round led by BESTSELLER’s Invest FWD arm, with the fashion giant’s CFO joining its board to push SEWBOT commercialization. This ties into BESTSELLER’s push for localized, low-waste production using SoftWear’s autonomous sewing lines. The cash will scale tech for on-demand apparel closer to markets.
- November, 2025 – Brother Industries snapped up Konrad Busche’s automation division, blending sewing expertise with automotive-grade robotics for non-apparel growth under its CS B2027 plan. The deal bolsters Brother’s edge in airbag and technical textile automation worldwide. It sets up joint innovations in handling complex fabrics at scale.
Future Outlook and Opportunities
The future outlook for the robotic fashion inductor market remains positive as apparel manufacturers pursue efficiency and quality gains. Future opportunities include integration with fully automated sewing systems, adaptation to custom and on demand manufacturing, and enhanced coordination with digital design systems.
As robotics and AI improve in handling soft and flexible materials, adoption is expected to expand. Industry insights suggest that material induction automation will be a key enabler for modular, flexible fashion production lines that support varied styles and fast changeovers.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 163.2 Mn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 898.6 Mn CAGR(2025-2034) 18.6% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue forecast, AI impact on Market trends, Share Insights, Company ranking, competitive landscape, Recent Developments, Market Dynamics and Emerging Trends Segments Covered By Component (Hardware, Software, Services), By Application (Smart Tag & RFID Inlay Manufacturing, Precision Embroidery & Circuit Printing, Automated Garment Assembly with Integrated Electronics, Others), By End-User (Smart Apparel Manufacturers, Luxury & High-Tech Fashion Houses, Technical Sportswear Brands, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of Latin America; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape ABB, Ltd., SoftWear Automation, Inc., Sewbo, Inc., ZSK Stick- und Prüftechnik GmbH, Brother Industries, Ltd., Tamicare Ltd., Kornit Digital, Ltd., Sensory Robotics, Gerber Technology, Assyst GmbH, Prisca Vils AG, Others Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three license to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Robotic Fashion Inductor MarketPublished date: Dec. 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Robotic Fashion Inductor MarketPublished date: Dec. 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- ABB, Ltd.
- SoftWear Automation, Inc.
- Sewbo, Inc.
- ZSK Stick- und Prüftechnik GmbH
- Brother Industries, Ltd.
- Tamicare Ltd.
- Kornit Digital, Ltd.
- Sensory Robotics
- Gerber Technology
- Assyst GmbH
- Prisca Vils AG
- Others













