Global Remittance Market Size, Share Report Analysis By Mode of Transfer (Digital, Traditional (Non-digital)), By Type (Inward Remittance, Outward Remittance), By Channel (Banks, Money Transfer Operators, Online Platforms (Wallets)), By End-use (Migrant Labor Workforce, Personal, Small Businesses, Others), By Regional Analysis, Global Trends and Opportunity, Future Outlook By 2025-2034
- Published date: Dec. 2025
- Report ID: 170736
- Number of Pages: 377
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
- Report Overview
- Top Market Takeaways
- Global and India-Specific Remittance
- By Mode of Transfer
- By Type
- By Channel
- By End Use
- By Region
- Increasing Adoption Technologies
- Investment and Business Benefits
- Key Market Segments
- Driver Analysis
- Restraint Analysis
- Opportunity Analysis
- Challenge Analysis
- Competitive Analysis
- Recent Developments
- Future Outlook and Opportunities
- Report Scope
Report Overview
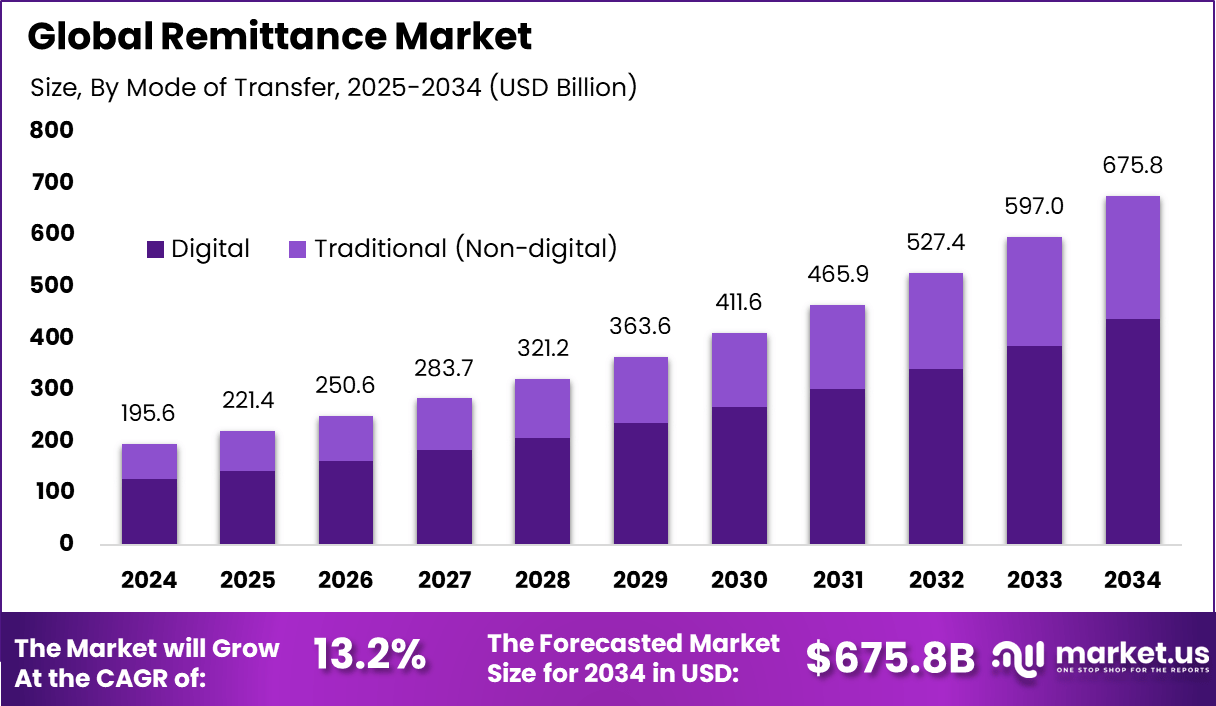
The Global Remittance Market size is expected to be worth around USD 675.8 Billion By 2034, from USD 221.4 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 13.2% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North America held a dominan Market position, capturing more than a 34.3% share, holding USD 67.0 Billion revenue.
The remittance market refers to the global flow of money transferred by individuals working abroad to family, friends, or business partners in their home countries. These transactions are typically conducted through banks, money transfer operators, mobile platforms, and emerging digital wallets. Remittances play a vital role in supporting household incomes, education, healthcare, and local economic activity in many developing and emerging economies.
According to global financial data, remittance flows have shown resilience and continuous growth, reflecting the importance of cross-border financial transfers in the global economy. Growth in the remittance market is driven by global migration trends, rising numbers of international workers, and expanding access to digital financial services. Many migrant workers send money home regularly to support family needs and long-term savings.
The adoption of mobile money and digital transfer platforms has lowered barriers for sending funds, especially where traditional banking infrastructure is limited. Cost pressures, regulatory reforms, and competitive pricing among transfer providers have also influenced market dynamics. Industry payment studies show that digital channels are increasingly preferred due to convenience and transparency in fees.
Demand for remittance services continues to rise as workers abroad seek fast, secure, and affordable ways to support families and dependents. Urbanization and international labor mobility contribute to sustained remittance flows. During economic downturns or crises, remittances often increase as migrants support relatives facing income disruptions. Data on financial inflows shows that remittances to developing countries account for a large share of global personal cross border transfers, reflecting sustained demand.
Top Market Takeaways
- Digital transfer modes lead with 64.7%, as users prefer faster, mobile-based, and low-cost remittance solutions.
- Inward remittances dominate with 58.9%, reflecting strong money flows from overseas workers to home countries.
- Banks remain the largest channel at 42.6%, supported by trust, regulatory compliance, and established cross-border networks.
- The migrant labor workforce accounts for 47.3% of end-use demand, highlighting remittances as a primary income support source for families.
- North America holds 34.3% of the global market, driven by a large migrant population and advanced financial infrastructure.
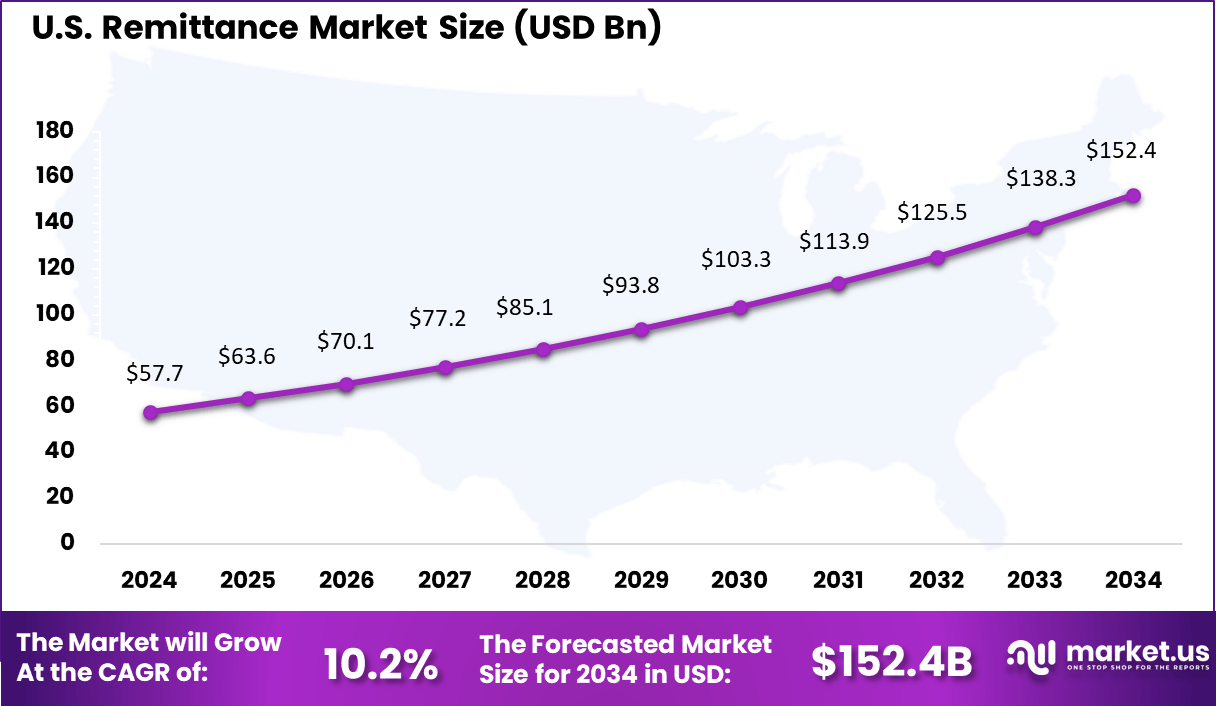
- The U.S. market reached USD 57.71 billion and is growing at a 10.2% CAGR, supported by rising digital adoption and steady immigration-led money flows.
Global and India-Specific Remittance
- India received USD 135.46 billion in remittance inflows in FY2024–25, marking a 14% year-on-year increase.
- India has remained the world’s largest remittance recipient for over ten years, reflecting sustained overseas employment strength.
- Remittances now contribute over 10% of India’s current account inflows and finance nearly half of the country’s trade deficit.
- Growth is increasingly driven by highly skilled Indian professionals in developed markets such as the U.S. and U.K., reducing reliance on traditional GCC sources.
- The United States leads as the top source of remittances to India with 27.7% share, followed by the UAE, UK, Saudi Arabia, and Singapore.
- Globally, remittance flows to developing countries reached USD 401 billion as early as 2012, with India, China, the Philippines, and Mexico as key beneficiaries.
- For recipient households, remittances often account for around 60% of total income, supporting essential spending on food, healthcare, and education.
By Mode of Transfer
Digital remittance leads with 64.7%, reflecting a strong shift toward mobile apps, online platforms, and digital wallets for cross-border money transfers. Users increasingly prefer digital channels due to faster processing times, transparent fees, and the convenience of initiating transfers from anywhere.
The growth of this segment is supported by widespread smartphone adoption and improved digital payment infrastructure. Digital platforms also provide real-time tracking, instant notifications, and better user experience, which strengthens trust and repeat usage among customers.
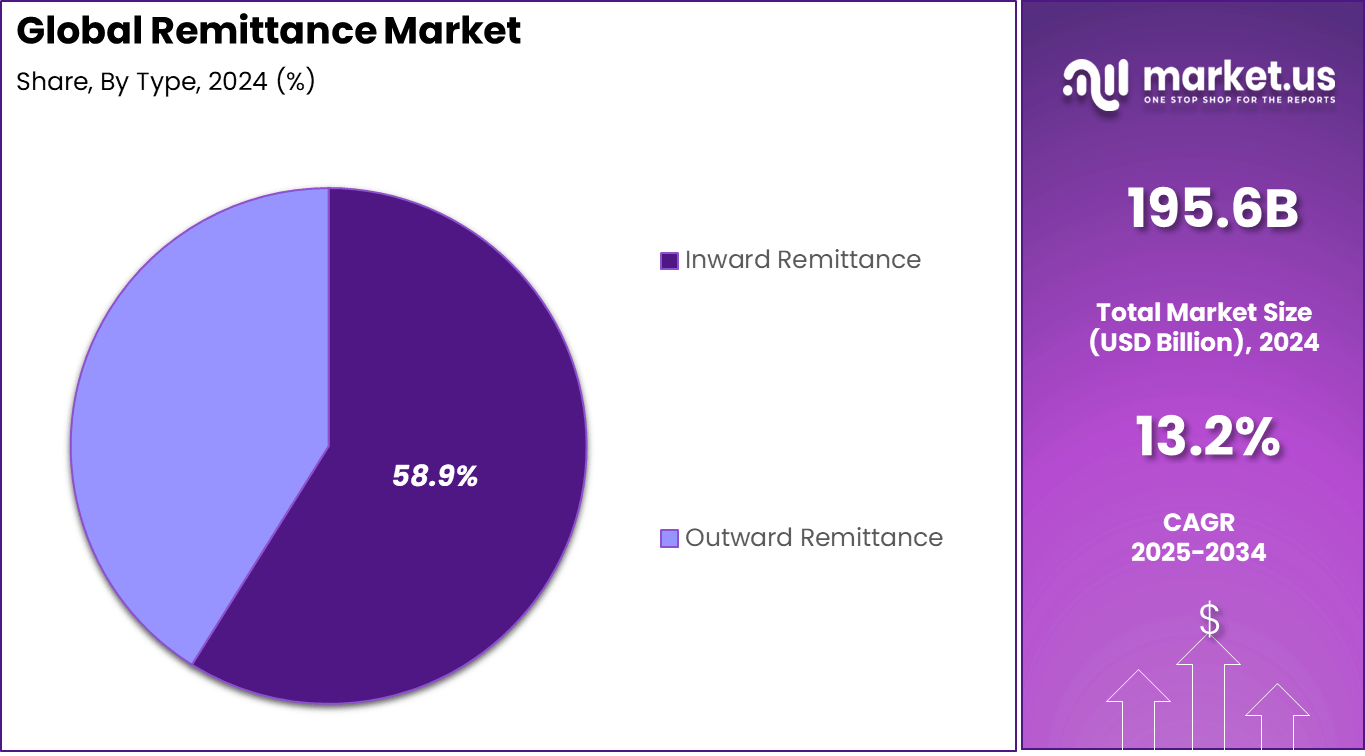
By Type
Inward remittance accounts for 58.9%, highlighting the importance of funds sent by overseas workers to their home countries. These transfers support essential household expenses such as food, housing, education, and healthcare.
The dominance of inward remittance is driven by steady global migration and employment opportunities abroad. Many developing economies rely heavily on inward remittances as a stable source of income for families and local communities.
By Channel
Banks hold 42.6%, maintaining their position as a trusted channel for remittance transactions. Customers rely on banks for secure transfers, regulatory compliance, and wide international network coverage. Bank-based remittance continues to be preferred for larger transaction values and formal documentation.
Strong customer relationships and established financial infrastructure support ongoing use of banking channels. This segment remains strong for higher-value transfers and formal transactions. Banks benefit from long-standing customer relationships, established branch networks, and integration with global financial systems.
By End Use
The migrant labor workforce represents 47.3%, highlighting their central role in global remittance flows. Migrant workers regularly send money to support families and dependents in their home countries. This segment grows as international labor mobility increases across construction, manufacturing, healthcare, and service sectors. Reliable remittance services are essential for maintaining financial stability among migrant communities.
Growth in this segment is linked to rising cross-border labor movement across construction, manufacturing, healthcare, and service industries. Reliable and affordable remittance services remain essential for the financial wellbeing of migrant communities.
By Region
North America holds 34.3%, supported by a large migrant population and strong financial infrastructure. The region acts as a major source of outward remittance flows to multiple global destinations.
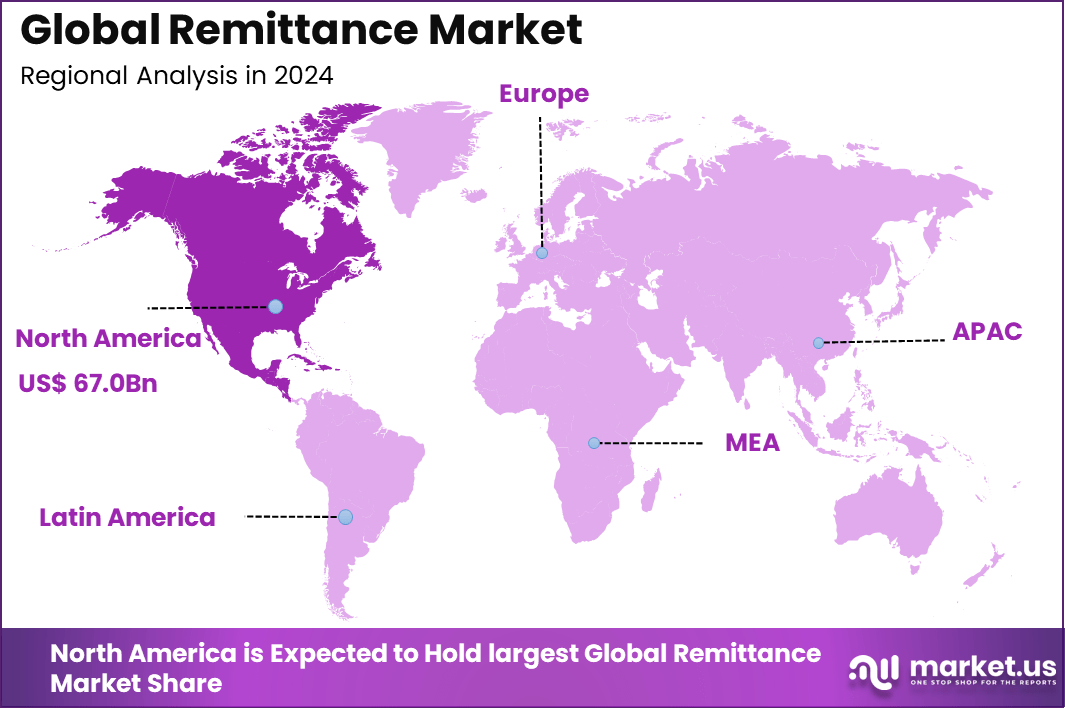
The United States reached USD 57.71 Bn with a CAGR of 10.2%, reflecting steady growth in digital and bank-based remittance usage. Rising employment opportunities for migrants and improved digital transfer options continue to support market expansion.
Increasing Adoption Technologies
Key technologies supporting adoption include mobile wallets, blockchain based transfer systems, and application programming interface linked bank platforms. Mobile money and online transfer apps have enabled near real time transfers, increased transparency, and reduced reliance on cash-based agents. Blockchain and distributed ledger technologies are being explored to improve settlement speed, reduce costs, and enhance traceability.
Advanced identity verification and biometric systems also support regulatory compliance. Technology adoption metrics show that digital remittance solutions have gained a growing share of total transaction volumes in recent years. Individuals and households adopt remittance services due to the need for secure, reliable, and timely cross-border funds transfer. Digital transfer platforms offer convenience, accessibility, and tracking that traditional channels may lack.
Lower costs and faster delivery times are strong motivators, especially when funds are needed for urgent household expenses. Improved regulatory frameworks that protect consumers and enhance transparency also support adoption. Surveys indicate that ease of use and cost-efficiency are among the top criteria for users when selecting remittance providers.
Investment and Business Benefits
Investment opportunities exist in digital remittance platforms, cross-border payment technologies, mobile wallet integration, and compliance solutions. Fintech players and traditional financial institutions are investing in technology to improve customer experience and expand service reach. Partnerships between platforms and local agents create hybrid service models that serve both urban and rural populations.
Opportunities also exist in enhancing interoperability among different payment ecosystems, enabling seamless transfers across multiple corridors. For service providers, the remittance market offers diversified revenue streams through transfer fees, foreign exchange margins, and value added financial services.
Digital remittance platforms can scale operations with relatively lower incremental costs compared to cash-based networks. Improved customer engagement and loyalty can result from transparent pricing and efficient service delivery. Providers with strong digital infrastructure also benefit from data insights that support product development and targeted marketing.
Key Market Segments
By Mode of Transfer
- Digital
- Traditional (Non-digital)
By Type
- Inward Remittance
- Outward Remittance
By Channel
- Banks
- Money Transfer Operators
- Online Platforms (Wallets)
By End-use
- Migrant Labor Workforce
- Personal
- Small Businesses
- Others
Regional Analysis and Coverage
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherlands
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of Latin America
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Driver Analysis
Increase in Global Migration and Cross-Border Workforce
A major driver of the remittance market is the steady rise in the global migrant population. Millions of workers move abroad for employment and send part of their earnings back to families. These transfers form an important economic link between host countries and home regions. As global mobility increases, the volume of international remittances continues to grow.
Another driver is the increasing use of formal financial channels by migrants. Many workers are shifting from informal cash transfers to regulated digital services because they offer better transparency and safer handling of funds. Governments and financial institutions also encourage formal channels to improve traceability and reduce risks associated with informal transfers.
Restraint Analysis
High Transaction Fees and Regulatory Requirements
A significant restraint is the cost of sending money across borders. Many corridors still have high fees due to currency conversion, compliance requirements, and limited competition. These costs reduce the amount received by families and may discourage frequent transfers. Lower-income workers are especially affected when fees represent a large share of their remittance value.
Another restraint comes from regulatory obligations linked to anti-money-laundering rules and identity verification. Remittance operators must follow strict compliance procedures, which increases operational costs and slows onboarding for new users. In regions with limited identity infrastructure, customers may face difficulty accessing regulated remittance services.
Opportunity Analysis
Expansion of Digital and Mobile Remittance Platforms
An important opportunity lies in the rapid adoption of mobile and online payment systems. Digital remittance platforms offer faster delivery times, lower fees, and easier access than traditional cash outlets. As smartphone usage increases, more customers are switching to app-based services. This creates room for providers to reach younger users and first-time remitters.
Another opportunity is the integration of remittance services into bank accounts, digital wallets, and local payment networks in receiving countries. When remittance funds can be stored and spent electronically, families gain safer and more efficient ways to manage money. This strengthens financial inclusion and opens room for additional services linked to remittance flows.
Challenge Analysis
Dependence on Exchange Rate Fluctuations and Corridor Variations
A major challenge is the sensitivity of remittances to exchange rate movements. Families may receive less money if currency values shift unfavorably. This uncertainty affects household budgeting and creates pressure on service providers to offer more stable conversion rates. Managing this risk is difficult in corridors with volatile currencies.
Another challenge is the uneven development of remittance infrastructure across countries. Some regions have advanced digital systems, while others still rely heavily on cash outlets. Differences in technology, regulation, and financial access create gaps in service availability. Providers often need to tailor solutions for each corridor, which increases operational complexity.
Competitive Analysis
Bank of America, Citigroup, Wells Fargo, and Western Union play a major role in the remittance market by leveraging large global banking and agent networks. Their services support high transaction volumes, strong compliance controls, and wide geographic coverage. These institutions focus on reliability, regulatory alignment, and trust among migrant workers and corporate users. Continued demand for cross border money transfers keeps their position strong.
ZEPZ, Ria Financial Services, OFX, PayPal, MoneyGram, and Wise strengthen the market with digital first remittance platforms that offer faster transfers and transparent pricing. Their solutions rely on mobile apps, online wallets, and real time exchange rate visibility. These players focus on user convenience, lower fees, and speed. Growing smartphone usage and preference for digital payments support their expansion.
Other participants contribute by serving niche corridors and underserved regions with tailored remittance services. Their offerings help improve financial inclusion and access to cross border payments. These companies focus on regional partnerships and cost efficiency. Increasing global migration and international trade continue to drive steady growth in the remittance market.
Top Key Players in the Market
- Bank of America Corporation
- ZEPZ
- Citigroup, Inc.
- Ria Financial Services, Inc.
- OFX
- Wells Fargo
- Western Union Holdings, Inc.
- PayPal
- MoneyGram International, Inc.
- Wise US, Inc.
- Others
Recent Developments
- September, 2025 – Citigroup teamed up with Dandelion to speed cross-border payments into digital wallets worldwide. This expands Citi’s WorldLink services for remittances, covering over 135 currencies and 150 destinations.
- August, 2025 – Western Union agreed to acquire Intermex for about $500 million, aiming to strengthen its Latin America reach and U.S. retail network. The move supports faster digital customer growth in key remittance corridors.
- April, 2025 – ZEPZ, the company behind WorldRemit and Sendwave, secured €152 million in financing from HSBC to boost its remittance operations. This funding helps speed up cross-border transfers and cut costs for users sending money home.
- In March 2025, the Financial Stability Board reported measurable progress on the G20 roadmap, with advances in interoperability standards designed to support long term reductions in cross border remittance fees.
- In January 2025, the Central Bank of the UAE announced plans for a wholesale retail central bank digital currency to improve domestic and cross border remittances under its Financial Infrastructure Transformation Program.
Future Outlook and Opportunities
The future outlook for the remittance market remains positive as global labor mobility and digital adoption continue. Emerging technologies are expected to further reduce costs, improve settlement times, and expand access for underserved populations.
Enhanced regulatory cooperation and cross-border payment standardization may improve efficiency. Demand is likely to grow in tandem with global migration patterns and increasing reliance on digital financial services. Observations of payment trends suggest that digital remittances will continue to capture a growing share of the overall market in the coming years.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 195.6 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 675.8 Bn CAGR(2025-2034) 13.2% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue forecast, AI impact on Market trends, Share Insights, Company ranking, competitive landscape, Recent Developments, Market Dynamics and Emerging Trends Segments Covered By Mode of Transfer (Digital, Traditional (Non-digital)), By Type (Inward Remittance, Outward Remittance), By Channel (Banks, Money Transfer Operators, Online Platforms (Wallets)), By End-use (Migrant Labor Workforce, Personal, Small Businesses, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of Latin America; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Bank of America Corporation, ZEPZ, Citigroup, Inc., Ria Financial Services, Inc., OFX, Wells Fargo, Western Union Holdings, Inc., PayPal, MoneyGram International, Inc., Wise US, Inc., Others Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three license to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Bank of America Corporation
- ZEPZ
- Citigroup, Inc.
- Ria Financial Services, Inc.
- OFX
- Wells Fargo
- Western Union Holdings, Inc.
- PayPal
- MoneyGram International, Inc.
- Wise US, Inc.
- Others










