Global Railway Cybersecurity Market Size, Share, Industry Analysis Report By Component (Solution (Risk and Compliance Management, Threat Intelligence and Response, Identity and Access Management, Data Loss Prevention, Others), Services (Consulting, Support, Integration)), By Security Type (Application Security, Network Security, Data Protection, Endpoint Security, System Administration), By Type (Infrastructure, On-board), By Sales Channel (Passenger Trains, Freight Trains, Metro/Monorail), By Regional Analysis, Global Trends and Opportunity, Future Outlook by 2025-2034
- Published date: Sept. 2025
- Report ID: 159589
- Number of Pages: 198
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
- Report Overview
- Key Insight Summary
- Role of Generative AI
- Investment and Business Benefits
- Government-led investments
- Asia Pacific Market Size
- By Component Analysis
- By Security Type Analysis
- By Type Analysis
- By Sales Channel
- Emerging Trends
- Growth Factors
- Key Market Segments
- Driver
- Restraint
- Opportunity
- Challenge
- Competitive Analysis
- Recent Developments
- Report Scope
Report Overview
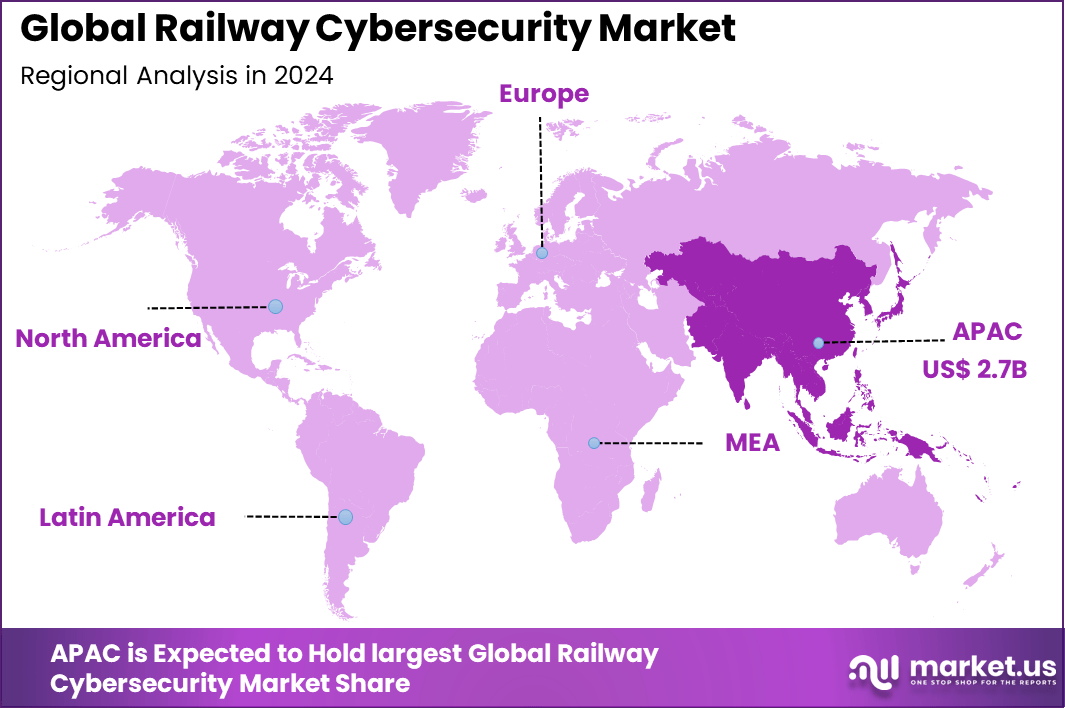
The Global Railway Cybersecurity Market size is expected to be worth around USD 19.7 Billion By 2034, from USD 8.1 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 9.3% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, APAC held a dominan market position, capturing more than a 33.9% share, holding USD 2.7 Billion revenue.
The railway cybersecurity market focuses on protecting the critical infrastructure and digital assets of the rail industry from cyber threats that have grown significantly with the rise of digitalization. Rail systems rely extensively on interconnected technologies for signaling, communication, ticketing, and operational management, making them vulnerable targets for cyberattacks. Cyberattacks on railways are doubling each year due to rising internet connectivity and complex operations.

Top driving factors for the market include the rising number of cyber threats targeting increasingly automated and connected rail systems. Modern railways depend on active internet connections for operational control, which creates multiple entry points for hackers. Governments are pushing for smarter, more connected transportation infrastructure as part of urbanization initiatives, which heightens the need for strong cybersecurity measures to secure smart city transit networks.
According to secureworld, Railway systems have become a growing target for cybercriminals, with reported cyberattacks increasing by 220% over the past five years. This surge highlights the rising vulnerabilities within digital rail infrastructure as operators adopt advanced signaling, communication, and monitoring technologies. The trend underscores the urgent need for stronger cybersecurity measures to protect critical transport networks from disruptions and potential safety risks.
Demand is greatest in regions with large and modern railway networks, especially in Europe, North America, and parts of Asia where high speed, urban transit, and freight systems are advanced. Passenger rail, metro, light rail, and freight sectors all require protection, though passenger networks often receive more focus because of public impact and visibility. Within rail operations, demand is strongest for securing control systems, signaling, communications, and train-to-ground links.
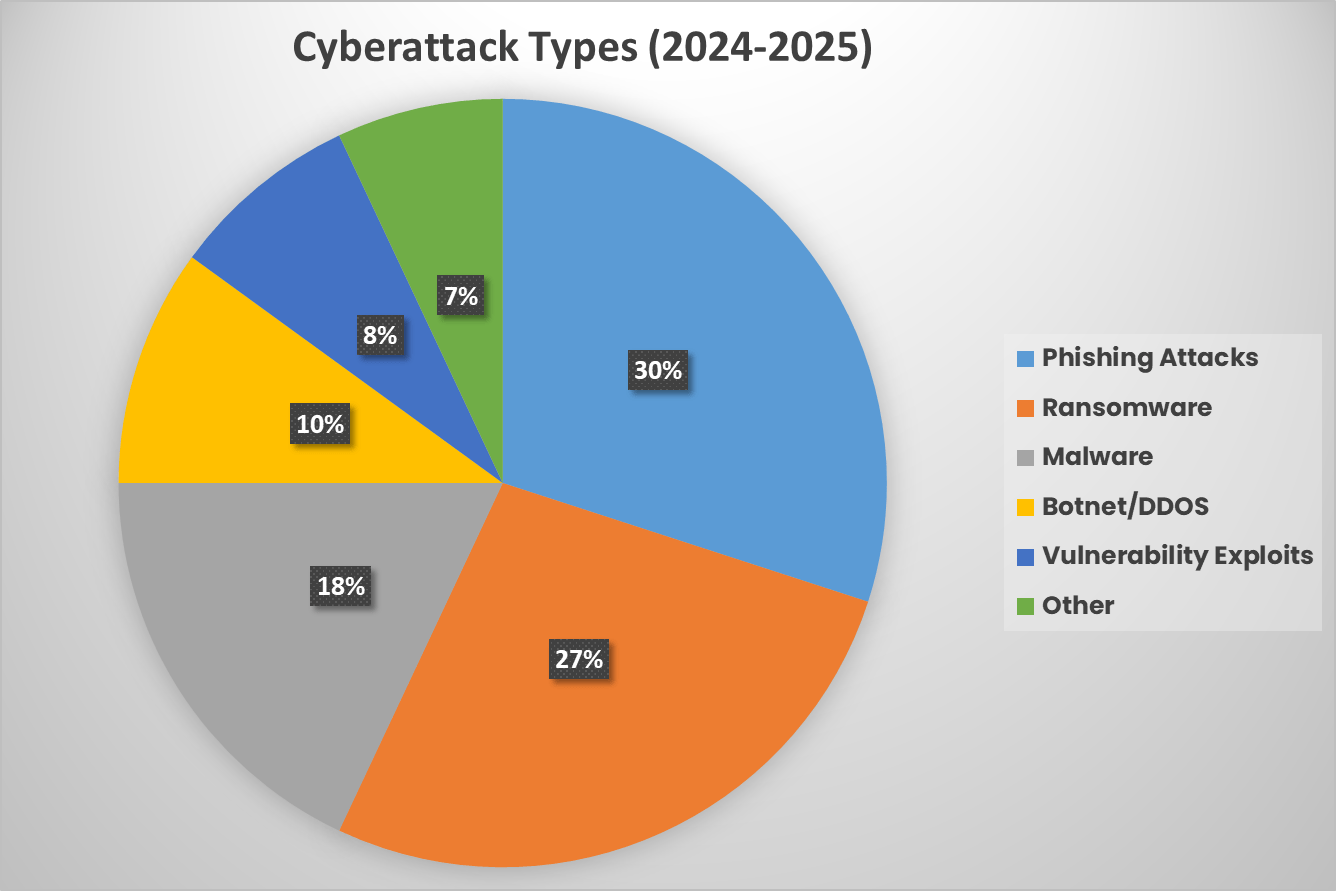
Key Insight Summary
- By component, the Solution segment dominated with a share of 63.5%, reflecting the critical role of software and platform-based offerings in securing railway systems.
- By security type, Network Security led the market with 32.3%, highlighting the importance of protecting communication and data exchange across railway networks.
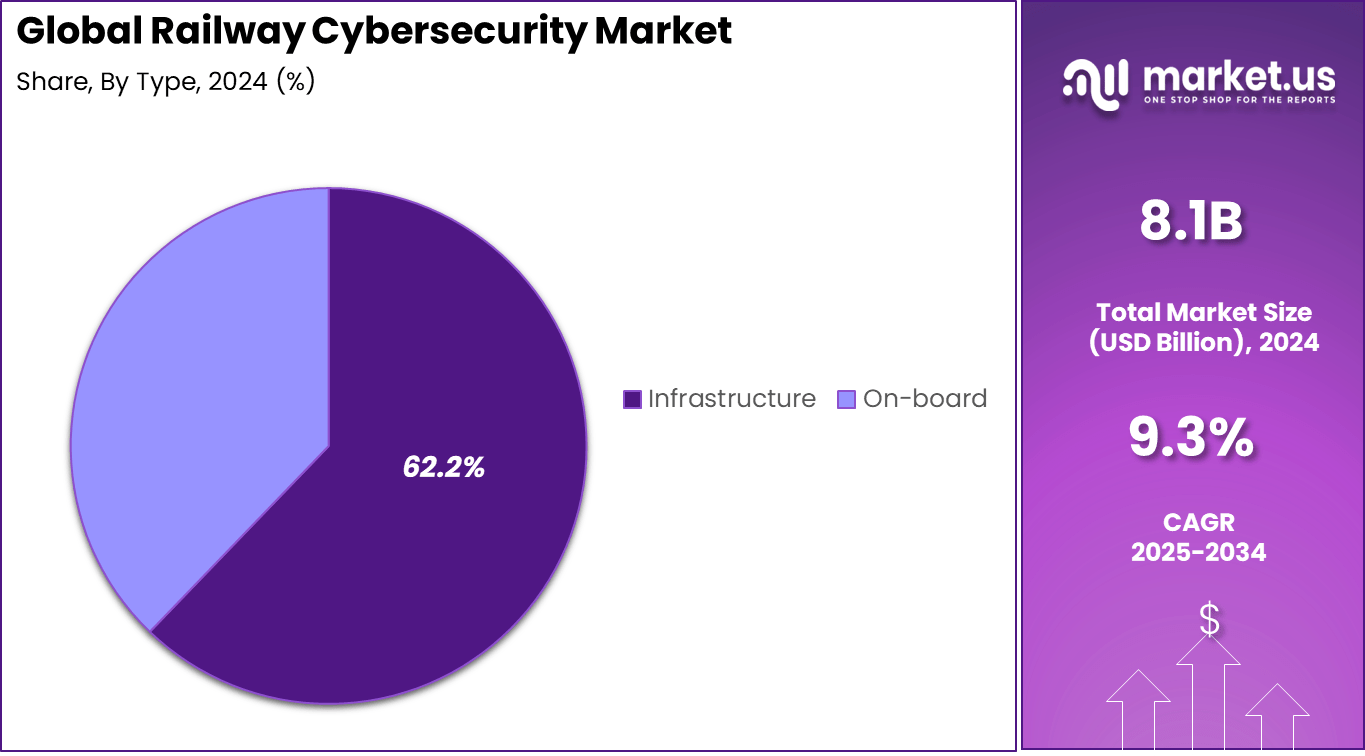
- By type, Infrastructure security held the largest share at 62.2%, showing the strong emphasis on safeguarding physical and digital railway infrastructure.
- Regionally, Asia Pacific led the industry with 33.9% of revenue, driven by rapid railway modernization, digital integration, and increasing cybersecurity investments across major economies.
Role of Generative AI
The role of generative AI in railway cybersecurity is increasingly vital. Generative AI models analyze large volumes of historical cybersecurity data specific to rail networks, which allows them to identify subtle patterns indicative of potential cyber threats. For example, these models can predict attacks before they occur, enabling railway operators to take preventive measures.
Additionally, generative AI aids in creating realistic cyber-attack scenarios for cybersecurity training, improving the readiness of response teams. It can also generate tailored security policies based on the operational environment and simulate phishing attempts to bolster detection systems.
Furthermore, generative AI helps by producing synthetic data sets that assist in training detection models without risking sensitive information. This proactive approach is helping railways strengthen defenses against increasingly sophisticated threats, with studies showing significant improvements in threat prediction and detection accuracy by over 30% using AI-driven methods.
Investment and Business Benefits
Investment opportunities exist in developing specialized cybersecurity platforms that address both operational technology (OT) and information technology (IT) aspects of railways. Large infrastructure investments in rail modernization across regions like Europe, Asia, and North America foster new demand.
Government regulations, such as mandatory cybersecurity directives, also create steady funding flows and incentives for solution providers. Emerging technology areas like edge computing, zero trust frameworks, and context-aware security analytics are expected to attract increased investment. Private-public partnerships are strengthening cybersecurity innovation and deployment, boosting overall market growth.
Business benefits from enhanced railway cybersecurity include improved operational efficiency through automated threat detection and reduced downtime. Secure rail networks enhance passenger confidence and regulatory compliance, enabling operators to meet safety standards consistently.
Improved data security enables safer ticketing and passenger information management. Companies also lower liabilities related to cyber incidents, minimizing potential loss of life and property. Cybersecurity is increasingly a crucial factor that supports digital transformation efforts within the rail industry, unlocking further business innovations.
Government-led investments
Government-led investments have played a crucial role in advancing railway cybersecurity. Notably, federal funding in the United States exceeded USD 66 billion in 2023 to improve rail infrastructure, with a focus on cybersecurity upgrades as part of this effort.
In Europe, programs with budgets exceeding €234 million have been allocated specifically to smart transportation and railway digitalization projects that include cybersecurity components. Governments in the Asia Pacific region, known for leading digital railway adoption, are also investing heavily in cybersecurity solutions to safeguard expanding high-speed networks.
These investments emphasize protecting both passenger data privacy and essential operational systems against cyberattacks. The strategic focus by governments globally on rail cybersecurity confirms its position as a critical area of infrastructure security, with funding aiding the adoption of AI-powered defenses and regulatory compliance measures.
Asia Pacific Market Size
Asia Pacific accounted for 33.9% of revenue in 2024. The region has been at the forefront of expanding rail capacity, with large investments in metro systems, cross-border rail lines, and high-speed rail development. This rapid modernization has necessitated advanced cybersecurity measures to ensure safety and resilience.
Countries in Asia Pacific are embracing digital rail transformation at varying speeds, but the demand for cybersecurity has grown universally across urban and intercity projects. The emphasis is on building secure digital ecosystems that enable both passenger convenience and operational efficiency while reducing the risks associated with cyber disruptions.
By Component Analysis
The solution segment dominated the railway cybersecurity market with 63.5% share in 2024. Railway operators are increasingly investing in advanced security solutions as the integration of digital systems in signaling, ticketing, and communication platforms rises. These solutions provide protection against vulnerabilities that can compromise operational continuity and passenger safety.
The shift toward automated control systems and connected rail infrastructure has made standalone services insufficient for long-term security needs. Solutions that combine software intelligence, monitoring, and real-time response capabilities are being prioritized, ensuring that operators can manage risks proactively in complex digital environments.
By Security Type Analysis
Network security held 32.3% share in 2024. Rail networks are highly dependent on interconnected systems for communication and signaling, making them a prime target for data breaches and service disruptions. The need to secure the movement of sensitive data across multiple endpoints has increased the adoption of robust firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption protocols.
The continued push toward smart rail initiatives and the expansion of IoT devices has widened the potential threat surface. As a result, railway stakeholders are focusing heavily on strengthening network-level protection to safeguard both operational technologies and enterprise IT systems that jointly sustain rail performance.
By Type Analysis
The infrastructure segment led with 62.2% share in 2024. Physical and digital infrastructures such as control centers, train management systems, and signaling equipment require continuous shielding from cyberattacks that could disrupt transport safety. The heavy reliance on interconnected infrastructure elements amplifies the importance of advanced protective solutions.
Upgrades in high-speed rail projects and smart transportation corridors are driving additional demand for securing core infrastructure. Protecting rolling stock alone is not sufficient; attention to integrated transport infrastructure has become a top priority for railway operators worldwide.
By Sales Channel
Passenger trains accounted for a leading market share in 2024. The heavy reliance on digital technologies to manage ticketing, on-board services, Wi-Fi systems, and passenger data storage has made this segment an important focus area. Protecting the customer experience and safeguarding personal information is driving rapid cybersecurity adoption across this channel.
With ridership volumes increasing following network expansions and smart railway upgrades, threats to passenger-facing platforms are also rising. Rail operators are investing more heavily in cybersecurity for passenger trains compared to freight services, as public trust and safety remain top priorities.
Emerging Trends
Emerging trends show that railway cybersecurity is evolving towards integrated IT and operational technology (OT) security, where real-time AI and machine learning systems monitor and detect anomalies with fewer false alarms. The focus is on protecting control and signaling systems, with innovations like end-to-end encryption running across operational data and passenger services.
There is also a growing emphasis on securing legacy systems through segmentation and stricter access controls, as they remain common in many networks. Additionally, zero trust architectures and micro-segmentation strategies are being adopted to limit breach impacts within railway OT networks.
Regulatory compliance is becoming a major driver, with authorities worldwide enforcing strict cybersecurity mandates that push investment into rail cybersecurity. This trend has led to a 28% increase in cyberattack detection on European railways in 2023, underscoring the rising challenge and the ongoing need for enhanced defenses.
Growth Factors
Growth in railway cybersecurity is fueled by several factors, including rapid digitalization of railway infrastructure and expanded use of IoT and connected devices within rail networks. Cyber threats are becoming more frequent and complex, particularly targeting communication-based train controls and passenger information systems.
The increasing reliance on digital systems for real-time operations creates new vulnerabilities that require advanced cybersecurity solutions. Moreover, governmental and regulatory pressures are significant growth drivers, as public safety concerns and data privacy laws push operators to invest in more resilient systems.
Studies highlight that in 2024 alone, cyberattacks targeting rail systems rose by more than 20%, prompting faster adoption of AI-enabled threat detection tools. Increasing integration of automated train systems and smart infrastructure also propels demand for cybersecurity solutions tailored to these new technologies.
Key Market Segments
-
By Component
- Solution
- Risk and Compliance Management
- Threat Intelligence and Response
- Identity and Access Management
- Data Loss Prevention
- Others
- Services
- Consulting
- Support
- Integration
- Solution
-
By Security Type
- Application Security
- Network Security
- Data Protection
- Endpoint Security
- System Administration
-
By Type
- Infrastructure
- On-board
-
By Sales Channel
- Passenger Trains
- Freight Trains
- Metro/Monorail
Regional Analysis and Coverage
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherlands
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of Latin America
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Driver
Increasing Cyberattacks on Railway Systems
Railways are becoming more vulnerable because they rely heavily on digital systems, such as signaling, train control, and passenger information, which are connected through networks. The rise in cyberattacks targeting these critical systems drives railway operators to invest heavily in cybersecurity. Hackers find ways to exploit weaknesses in IoT devices and control networks, threatening not only operations but also passenger safety.
Governments are pushing for stronger cybersecurity measures, which further fuels market growth in providing robust protection for railway infrastructure. The growing digitalization of railways also means that attacks are more frequent and sophisticated, raising the urgency for effective defense strategies. For instance, the increasing deployment of smart railway systems powered by IoT and AI means more entry points for attacks.
These systems exchange data digitally across onboard, wayside, and control center networks, creating a larger attack surface. The rise in ransomware and intrusion attempts in countries like the US and parts of Europe forces railway companies to seek advanced cybersecurity solutions, including network segmentation and real-time threat monitoring. This continuous threat landscape is a key factor driving the railway cybersecurity market momentum today.
Restraint
Complex Legacy Systems and Integration Issues
One major restraint in railway cybersecurity growth is the challenge around integrating modern cybersecurity solutions with old railway systems. Many rail networks operate legacy infrastructure that was designed before the rise of digital threats. These systems are often incompatible with newer security protocols, making it difficult to apply seamless protection across the entire network.
Additionally, the long lifecycle of railway equipment means outdated technology remains operational for years, creating vulnerabilities that are hard to patch or replace. For instance, communication protocols like MVB and CAN, common in older railway systems, have known security weaknesses that expose critical functions to attacks.
Upgrading these legacy systems involves high costs and operational risks that make railway operators reluctant to replace them quickly. This complexity slows down the adoption of comprehensive cybersecurity solutions and raises concerns about consistent security across all railway components. As a result, the sector faces a significant hurdle in delivering fully integrated, resilient cybersecurity frameworks in the near term.
Opportunity
Smart Rail and Digitalization Expansion
The ongoing global expansion of smart railway networks and high-speed rail infrastructure offers a significant opportunity for cybersecurity providers. As countries invest in modernizing rail transport with AI, automation, and IoT for real-time monitoring and control, cybersecurity demands increase exponentially. Cybersecurity solutions become essential to protect these sophisticated rail ecosystems that handle critical operational and passenger data.
For example, governments are funding smart rail projects and digital transformation initiatives, such as China’s extensive high-speed rail network or Europe’s digital signaling upgrades. These projects require advanced security layers to guard against hacking, data breaches, and operational disruptions.
The rise of Mobility-as-a-Service models linking rail with other transport modes is another driver encouraging investment in identity verification, secure APIs, and threat intel platforms. This digital wave creates a vibrant market space for new cybersecurity technologies tailored to the needs of modern rail systems.
Challenge
Balancing Safety, Availability, and Security
A key challenge in railway cybersecurity is ensuring security measures do not interfere with safety and service availability. Railways are safety-critical systems where downtime can cause major disruptions or risks to human life.
Cyber defenses must be designed to prevent attacks while maintaining continuous operation and fallback safety modes. This balance is difficult because some security controls may delay operations or trigger system shutdowns to isolate threats.
For instance, partitioning networks to block attacks might impact communication between signaling components or control centers, causing delays or failsafe modes. Regulatory frameworks require strong safety assurance even during cyber incidents, but legacy systems and evolving threats complicate compliance.
Competitive Analysis
The Railway Cybersecurity Market is supported by major technology firms such as Cisco Systems, IBM Corporation, and Fortinet. These companies provide critical infrastructure for secure communication, network protection, and threat detection across rail systems.
Railway-focused industrial players like Siemens Mobility GmbH, Thales Group, Alstom, and Hitachi Rail offer dedicated cybersecurity solutions embedded within rolling stock, signaling equipment, and smart rail platforms. These firms prioritize safety, availability, and compliance with railway cybersecurity standards such as IEC 62443.
Emerging companies such as Cylus and established industrial players like Nokia Networks, Huawei Technologies, ABB, and Toshiba Infrastructure Systems & Solutions contribute through secure communication systems, edge security, and encryption technologies. Wabtec Corporation and Atos SE also enhance security across freight and passenger systems.
Top Key Players in the Market
- Nokia Networks
- Huawei Technologies
- Cylus
- Cisco Systems
- IBM Corporation
- Raytheon Technologies
- Fortinet
- Thales Group
- Siemens Mobility GmbH
- Alstom
- Hitachi Rail
- ABB
- Toshiba Infrastructure Systems & Solutions
- Wabtec Corporation
- Atos SE
- Others
Recent Developments
- In January 2025, Siemens Mobility secured four significant contracts from HS2 Ltd to advance the 225-kilometer high-speed rail line connecting London and the West Midlands. As part of the Rail Systems Alliance, Siemens will provide an Engineering Management System for real-time equipment monitoring, work with Costain Ltd on high-voltage power supply systems, and deploy Operational Telecommunications and Security Systems throughout the HS2 route.
- May 2024: Hitachi Rail completed the acquisition of Thales’ Ground Transportation Systems for around €1.66 billion, a strategic move that greatly expands Hitachi’s footprint in railway technology, including cybersecurity capabilities integrated into operational systems. This acquisition aims to strengthen Hitachi’s position in delivering advanced and secure rail infrastructure solutions globally.
- September 2024: Alstom announced an enhanced cybersecurity partnership with Airbus Protect, focusing on industrial security risk assessment methodologies tailored for rail. This cooperation reflects Alstom’s commitment to integrating robust cyber defenses into its rail solutions to protect against rising cyber risks in transportation.
- August 2024: Cylus partnered with RailTel in India to deploy CylusOne, a rail-specific cybersecurity platform protecting signaling, trackside, onboard systems, and SCADA infrastructures. The collaboration also emphasizes growing expertise in cybersecurity across Indian railways through training programs, strengthening the sector’s defense against cyber threats.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 8.1 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 19.7 Bn CAGR(2025-2034) 9.3% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue forecast, AI impact on Market trends, Share Insights, Company ranking, competitive landscape, Recent Developments, Market Dynamics and Emerging Trends Segments Covered By Component (Solution (Risk and Compliance Management, Threat Intelligence and Response, Identity and Access Management, Data Loss Prevention, Others), Services (Consulting, Support, Integration)), By Security Type (Application Security, Network Security, Data Protection, Endpoint Security, System Administration), By Type (Infrastructure, On-board), By Sales Channel (Passenger Trains, Freight Trains, Metro/Monorail) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of Latin America; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Thales Group, Siemens Mobility, Alstom, Hitachi Rail, Nokia Networks, Huawei Technologies, Cylus, Cisco Systems, IBM Corporation, Raytheon Technologies, Fortinet, ABB, Toshiba Infrastructure Systems & Solutions, Wabtec Corporation, Atos SE and Others Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three license to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Railway Cybersecurity MarketPublished date: Sept. 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Railway Cybersecurity MarketPublished date: Sept. 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Nokia Networks
- Huawei Technologies
- Cylus
- Cisco Systems
- IBM Corporation
- Raytheon Technologies
- Fortinet
- Thales Group
- Siemens Mobility GmbH
- Alstom
- Hitachi Rail
- ABB
- Toshiba Infrastructure Systems & Solutions
- Wabtec Corporation
- Atos SE
- Others













