Global PMMA Recycling Market By Type(Post-Consumer Recycle, Industrial Recycle), By Recycling Process(Mechanical, Chemical), By Form(Pellet, Granule, Sheet, Others), By Application(Automotive Lights, Home Appliances, Lenses, Skylights, LCD Screens, Others), By End-use Industry(Automotive, Building and Construction, Textiles, Electrical and Electronics, Others), By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2024-2033
- Published date: May 2024
- Report ID: 119282
- Number of Pages: 220
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
The global PMMA Recycling Market size is expected to be worth around USD 743.94 Million by 2033, from USD 387.86 Million in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 6.73% during the forecast period from 2023 to 2033.
The “PMMA Recycling Market” refers to the industry involved in the collection, processing, and repurposing of Poly(methyl methacrylate), commonly known as PMMA or acrylic. PMMA is a transparent thermoplastic often used as a lightweight or shatter-resistant alternative to glass. It can be found in products like signs, sales displays, lenses, screens, and various other applications where a clear, durable material is required.
Recycling PMMA involves several steps collection of waste PMMA products, separation and cleaning, followed by mechanical recycling processes such as grinding and re-melting, or chemical recycling to break down the polymer into its monomers for fresh polymerization. The PMMA Recycling Market encompasses these activities, focusing on converting waste PMMA into usable raw materials to produce new PMMA products or other materials.
This market is driven by the growing awareness of environmental sustainability and the need to reduce landfill waste and conserve resources. Recycling PMMA not only helps reduce the environmental footprint associated with its disposal but also contributes to the circular economy by keeping the material in use for as long as possible. The PMMA Recycling Market is also influenced by regulations that encourage recycling and the use of recycled materials, technological advancements in recycling processes, and the increasing economic viability of recycling systems.
Key Takeaways
- Market Growth: PMMA Recycling Market is to reach USD 743.94 Million by 2033, from USD 387.86 Million in 2023, with a CAGR of 6.73%.
- Mechanical Recycling held a dominant market position in the PMMA recycling industry, capturing more than 69.3%
- Pyrolysis held a dominant market position in the PMMA recycling industry, capturing more than a 74.1% share.
- Automotive held a dominant market position in the PMMA recycling market, capturing more than a 28.3% share.
- North America leads the global PMMA Recycling Market, holding a significant share of 44.5%.
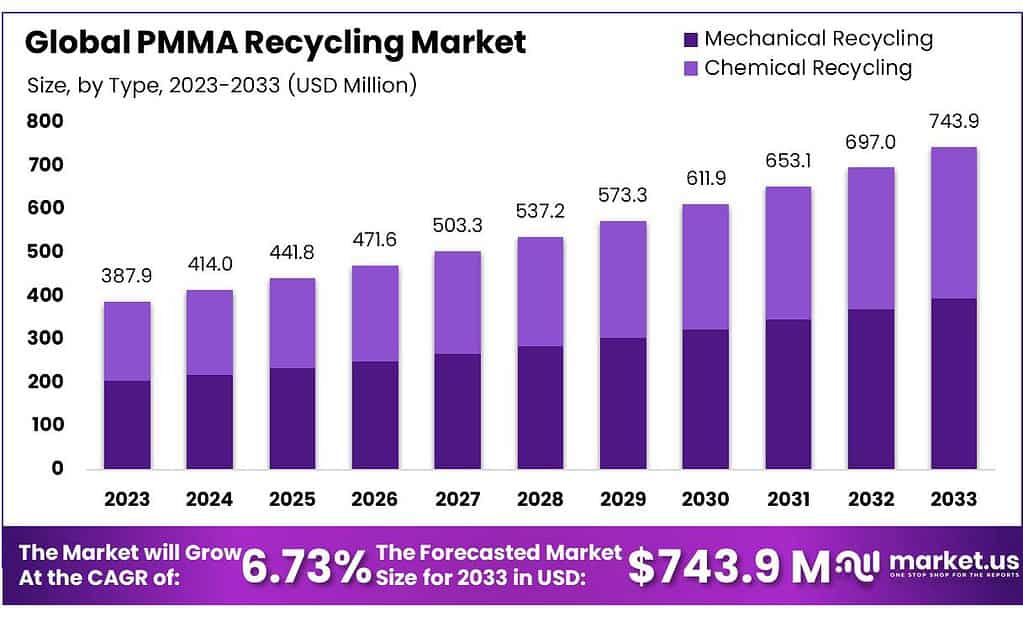
By Type
In 2023, Mechanical Recycling held a dominant market position in the PMMA recycling industry, capturing more than a 69.3% share. This method is prevalent due to its cost-effectiveness and straightforward process, which involves physically processing waste PMMA into new forms without altering its chemical structure.
Mechanical recycling is favored for its efficiency and lower energy consumption compared to more complex techniques. It is primarily utilized for applications where the inherent properties of recycled PMMA can be maintained without the need for purity at a molecular level.
On the other hand, Chemical Recycling, while holding a smaller share of the market, is gaining traction for its ability to break down PMMA into its monomers, which can then be polymerized to form new PMMA. This method is particularly valuable for producing high-purity PMMA suitable for use in more demanding applications, such as in the medical or automotive industries.
Chemical recycling addresses the limitations of mechanical recycling by allowing contaminated or mixed polymers to be fully recycled, thus supporting the circular economy within the plastics sector. As sustainability concerns rise and technology advances, chemical recycling is expected to grow, potentially reshaping the market dynamics in the coming years.
By Recycling Process
In 2023, Pyrolysis held a dominant market position in the PMMA recycling industry, capturing more than a 74.1% share. This process is popular because it involves the thermal decomposition of PMMA in the absence of oxygen, converting it into monomers that can be repurposed to manufacture new PMMA.
Pyrolysis is highly efficient for processing large volumes of PMMA waste, making it a preferred choice for industrial-scale recycling. It is particularly effective for recovering high-quality raw materials from PMMA, supporting sustainable production practices.
Depolymerization, though less prevalent, plays a critical role in the PMMA recycling market. This method involves breaking down PMMA into its molecular components using chemical agents. Depolymerization is essential for applications requiring extremely pure PMMA, as it ensures that the recycled material maintains the same properties as virgin PMMA.
This process is gaining attention for its potential to facilitate the recycling of PMMA from complex waste streams, such as mixed plastics or contaminated materials, thereby contributing to more sustainable material usage and waste reduction efforts.
By End Use
In 2023, Automotive held a dominant market position in the PMMA recycling market, capturing more than a 28.3% share. This segment benefits significantly from recycled PMMA due to its application in vehicle light covers, interior panels, and displays, which require high-quality, durable materials. The automotive industry’s push towards more sustainable manufacturing processes and materials has amplified the use of recycled PMMA to meet environmental targets and reduce production costs.
Consumer Goods also makes extensive use of recycled PMMA, applying it in products such as household appliances, lighting fixtures, and decorative items. Recycled PMMA is valued in this sector for its aesthetic qualities and durability, making it a preferred choice for manufacturers looking to enhance the sustainability of their products.
In Electronics, recycled PMMA is used in components such as smartphone screens, television panels, and other device enclosures. The electronics sector values PMMA for its clarity and resistance to impact, which are essential for the longevity and functionality of consumer electronics.
The Construction sector utilizes recycled PMMA in applications like windows, light diffusers, and signage. Its weather resistance and insulating properties make it suitable for outdoor and structural uses, driving its adoption in eco-friendly building projects.
Furniture manufacturers use recycled PMMA to produce items like tables, chairs, and decorative fittings. The material’s versatility and aesthetic appeal contribute to its popularity in modern furniture designs, which often feature clear or tinted forms of PMMA.

Key Market Segments
By Type
- Mechanical Recycling
- Chemical Recycling
Recycling Process
- Pyrolysis
- Depolymerization
End-Use
- Consumer Goods
- Automotive
- Electronics
- Construction
- Furniture
- Others
Drivers
Growing Environmental Awareness and Regulatory Support for Sustainable Practices
A significant driver for the PMMA Recycling Market is the increasing global environmental awareness coupled with strong regulatory support for sustainable material practices. As societies become more conscious of environmental impacts, there is a growing push towards reducing waste and promoting recycling activities across all sectors. PMMA, widely used in various industries due to its durability and clarity, has become a focal point in recycling efforts due to the environmental concerns associated with plastic waste.
The shift towards sustainability is particularly evident in the regulations that govern waste management and recycling. Governments worldwide are implementing stricter regulations that encourage the recycling of plastics, including PMMA.
These regulations often come with incentives for recycling and penalties for non-compliance, making it economically advantageous for companies to invest in recycling technologies and systems. For example, the European Union’s directives on waste management prioritize recycling and reuse of materials, which directly supports the growth of the PMMA Recycling Market.
Furthermore, the demand for sustainable products is increasing among consumers, who are now more likely to choose products made with recycled materials. This shift in consumer behavior is prompting manufacturers to use recycled PMMA in their products, thereby fostering a circular economy where materials are used for as long as possible. The use of recycled PMMA not only helps reduce the environmental footprint of products but also aligns with consumer expectations and brand strategies focused on sustainability.
In addition to consumer and regulatory pressures, technological advancements in recycling processes also play a crucial role in driving the PMMA Recycling Market. Improved recycling technologies have made it possible to efficiently break down and repurpose PMMA, enhancing the quality and viability of recycled PMMA for use in high-value applications such as automotive components, building materials, and consumer goods. These advancements are crucial in overcoming previous barriers to PMMA recycling, such as the degradation of material properties during processing.
The economic benefits associated with PMMA recycling also contribute to its growth as a market. Recycling PMMA reduces the need for raw material extraction, thereby lowering production costs and mitigating the environmental impacts associated with the mining and processing of virgin materials. Additionally, as landfill space becomes increasingly scarce and expensive, the cost advantages of recycling over disposal are becoming more apparent, further driving investment in PMMA recycling initiatives.
Restraints
Technological and Economic Challenges in Recycling PMMA
A major restraint facing the PMMA Recycling Market is the technological and economic challenges associated with the recycling process. PMMA, or Poly(methyl methacrylate), commonly known as acrylic or plexiglass, presents specific difficulties in both mechanical and chemical recycling methods that can limit the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of these processes.
Mechanical recycling of PMMA, while less expensive and more straightforward, often leads to a degradation of the material’s properties. Each time PMMA is mechanically recycled, its molecular weight is reduced, which can adversely affect its clarity, strength, and overall performance. This degradation limits the number of times PMMA can be recycled and reduces the range of applications for which recycled PMMA is suitable. Products requiring high-performance specifications, particularly in optical and high-strength applications, may not always be feasible with mechanically recycled PMMA.
Chemical recycling, on the other hand, involves breaking down PMMA to its monomers and repolymerizing them to form new PMMA. This process can maintain the quality of the PMMA, but it is significantly more complex and costly than mechanical recycling. The high costs associated with chemical recycling infrastructure and the process itself make it a less attractive option for many stakeholders in the recycling market. Furthermore, the chemical recycling process involves the use of solvents and other chemicals, which can pose environmental and safety risks if not managed properly.
Economic challenges also play a crucial role in restraining the PMMA Recycling Market. The initial setup cost for recycling facilities, whether for mechanical or chemical recycling, is high. Moreover, the profitability of recycling PMMA can be impacted by fluctuations in the prices of virgin and recycled PMMA, which are influenced by global oil prices and market demand. When the cost of virgin PMMA drops, it can make recycled PMMA less competitive, discouraging investment in PMMA recycling technologies and reducing market growth.
Regulatory challenges can further complicate the economic landscape for PMMA recycling. In regions where regulations concerning plastic recycling are less stringent or poorly enforced, there is less incentive for companies to invest in recycling technologies. Additionally, the lack of standardized regulations across different regions can create uncertainties and inconsistencies in the recycling market, hindering global trade in recycled PMMA.
Opportunity
Advancements in Recycling Technologies as a Gateway to Market Expansion
A significant opportunity within the PMMA Recycling Market lies in the advancements in recycling technologies. These technological improvements have the potential to overcome existing challenges in the recycling process, enhance the efficiency of recycling PMMA, and expand its applicability in various high-value applications. As environmental concerns continue to grow and the demand for sustainable materials increases, the development of innovative recycling technologies offers a promising pathway to capitalize on these market dynamics.
Currently, the primary methods for recycling PMMA include mechanical and chemical processes, each with its limitations. Mechanical recycling can lead to material degradation, which limits the usability of recycled PMMA in applications requiring high optical clarity or structural integrity. On the other hand, chemical recycling, while maintaining the material’s properties, is cost-intensive and complex. The opportunity for market growth lies in enhancing these technologies to address their respective drawbacks. For instance, innovations that improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of chemical recycling could make this option more viable for widespread use, thereby increasing the overall market supply of high-quality recycled PMMA.
Emerging technologies such as enzymatic recycling and solvent-based purification are also paving the way for more effective recycling methods. These technologies promise to recycle PMMA without significant loss of properties and at potentially lower costs than traditional chemical recycling. By reducing the ecological footprint of the recycling process and ensuring the production of high-grade recycled PMMA, these technologies could significantly broaden the scope of PMMA recycling applications.
Moreover, as global regulations tighten around waste management and recycling, there is an increasing push for developing robust recycling infrastructures. Advancements in PMMA recycling technologies could be strategically aligned with these regulatory changes, positioning companies that invest in these technologies favorably within the market. Such alignment not only meets regulatory requirements but also caters to the growing consumer demand for sustainable products, offering a competitive edge in the marketplace.
Another aspect of this opportunity involves the integration of digital technologies with recycling processes. The use of AI and machine learning in sorting and processing waste can greatly enhance the precision and efficiency of recycling operations, leading to higher yields of recyclable PMMA and reducing operational costs. This integration can transform traditional recycling facilities into smart operations that adapt to changing material inputs and market demands, further boosting the economic viability of recycling PMMA.
The development of a circular economy model, where waste materials are continuously reintegrated into production cycles, also presents significant opportunities for the PMMA Recycling Market. By establishing closed-loop recycling systems, industries can significantly reduce their reliance on virgin materials, decrease waste, and improve sustainability. Such systems are particularly relevant in industries like automotive and electronics, where PMMA is extensively used.
Trends
Increasing Integration of Recycled PMMA in Premium Applications
A significant trend in the PMMA Recycling Market is the increasing integration of recycled PMMA into premium applications. This trend is driven by technological advancements that enhance the quality of recycled PMMA, making it comparable to virgin material.
These advancements address previous limitations where recycled PMMA was often relegated to lower-value applications due to concerns about its purity and performance. As the quality of recycled PMMA improves, it is finding its way into more demanding and high-value applications, such as in automotive components, high-end electronics, and medical devices.
The shift towards high-value applications is facilitated by growing environmental awareness and the push for sustainable manufacturing practices across industries. Companies are under increasing pressure from consumers, investors, and regulatory bodies to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability.
Using recycled PMMA allows companies to reduce their environmental footprint by minimizing the extraction and processing of new raw materials and decreasing waste. Furthermore, as industries strive to meet stringent environmental regulations, the use of recycled materials becomes an attractive proposition to comply with these standards while maintaining product quality and performance.
In the automotive industry, for instance, recycled PMMA is used in elements like light covers and interior components where its optical clarity and durability are essential. In electronics, recycled PMMA serves in applications such as smartphone screens and light guide panels, where high optical quality is crucial. The medical sector also presents a growing opportunity for recycled PMMA, particularly in products like disposable medical devices and diagnostic components, where sterility and clarity are paramount.
Moreover, advancements in recycling technologies such as improved sorting and purification processes have significantly reduced impurities in recycled PMMA, enhancing its performance and broadening its usability. These technological improvements have made it possible to consistently produce recycled PMMA that meets the high standards required for these premium applications.
Additionally, the development of certification schemes and standards for recycled content is playing a crucial role in this trend. These certifications assure the quality and sustainability of recycled materials, which is critical for manufacturers and consumers alike. They help build trust and credibility for recycled PMMA products, supporting their adoption in industries that traditionally rely on high specifications and strict material compliance.
The economic aspect also drives this trend. As the cost of virgin PMMA fluctuates with market and geopolitical influences, recycled PMMA can offer a more stable and potentially less expensive alternative. This economic advantage, coupled with environmental benefits, presents a compelling case for industries to adopt recycled PMMA in their high-value products.
Regional Analysis
The Asia Pacific region stands out as a leading market for PMMA recycling, holding a significant market share of 37.5%. The market is expected to reach a valuation of USD 151.0 million during the forecast period, driven by robust adoption across key sectors such as consumer goods, automotive, and electronics.
This growth is primarily fueled by countries like China, India, Japan, and Australia, which are experiencing a substantial increase in PMMA recycling activities. These nations are responding to the escalating demand for sustainable and environmentally friendly recycling solutions, highlighting the region’s commitment to innovative recycling practices.
In North America, the PMMA recycling market is also expanding steadily. This growth is supported by the increasing demand from industries that utilize recycled PMMA to manufacture eco-friendly products. The region’s diverse industrial base and advancements in recycling technologies are crucial in promoting the use of recycled PMMA.
Europe, similarly, is witnessing growth in the PMMA recycling market. This is driven by greater consumer awareness of sustainable practices and the availability of recycled PMMA in various industrial applications. The region’s strict environmental regulations and focus on sustainable manufacturing processes further enhance the market’s growth potential.

Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- The US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia & CIS
- Rest of Europe
- APAC
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- ASEAN
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
The PMMA (Polymethyl methacrylate) recycling market is witnessing significant growth, fueled by the increasing demand for sustainable solutions and the rising awareness about environmental conservation. This analysis delves into the key players shaping the landscape of the PMMA recycling market, examining their strategies, contributions, and market presence.
Market Key Players
- Vanden Global Ltd.
- Renov8
- Heathland B.V.
- Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd.
- Plastic Expert
- Trinseo
- Lucite International Alpha B.V.
- Starlinger
- Pekutherm Kunststoffe GmbH
- Mitsubishi
Recent Development
September 2023, Vanden Global solidified its position through strategic partnerships, further bolstering its recycling capabilities and market presence
June 2023 Renov8, the facility became operational, enabling Renov8 to process PMMA waste efficiently and effectively.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2023) US$ 4.3 Bn Forecast Revenue (2033) US$ 18.8 Bn CAGR (2024-2033) 15.9% Base Year for Estimation 2023 Historic Period 2020-2022 Forecast Period 2024-2033 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, COVID-19 Impact, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Type(Post-Consumer Recycle, Industrial Recycle), By Recycling Process(Mechanical, Chemical), By Form(Pellet, Granule, Sheet, Others), By Application(Automotive Lights, Home Appliances, Lenses, Skylights, LCD Screens, Others), By End-use Industry(Automotive, Building and Construction, Textiles, Electrical and Electronics, Others) Regional Analysis North America – The US & Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia & CIS, Rest of Europe; APAC– China, Japan, South Korea, India, ASEAN & Rest of APAC; Latin America– Brazil, Mexico & Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa– GCC, South Africa, & Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Vanden Global Ltd., Renov8, Heathland B.V., Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd., Plastic Expert, Trinseo, Lucite International Alpha B.V., Starlinger, Pekutherm Kunststoffe GmbH, Mitsubishi Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Name the major industry players in the PMMA Recycling Market?Vanden Global Ltd., Renov8, Heathland B.V., Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd., Plastic Expert, Trinseo, Lucite International Alpha B.V., Starlinger, Pekutherm Kunststoffe GmbH, Mitsubishi

-
-
- Vanden Global Ltd.
- Renov8
- Heathland B.V.
- Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd.
- Plastic Expert
- Trinseo
- Lucite International Alpha B.V.
- Starlinger
- Pekutherm Kunststoffe GmbH
- Mitsubishi










