Global Plant Phenotyping Market Size, Share, Growth Analysis By Type (Equipment, Sensors, Software), By Application (High-Throughput Screening, Trait Identification, Photosynthetic Performance, Morphology and Growth Assessment, Others), By End-User (Greenhouse, Laboratory, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Sep 2025
- Report ID: 157903
- Number of Pages: 353
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
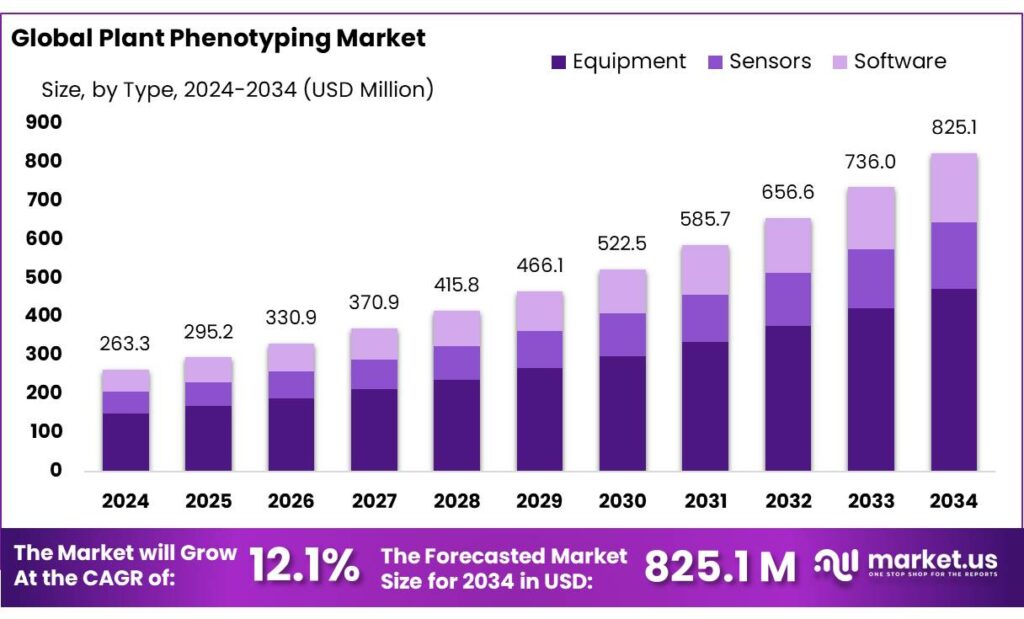
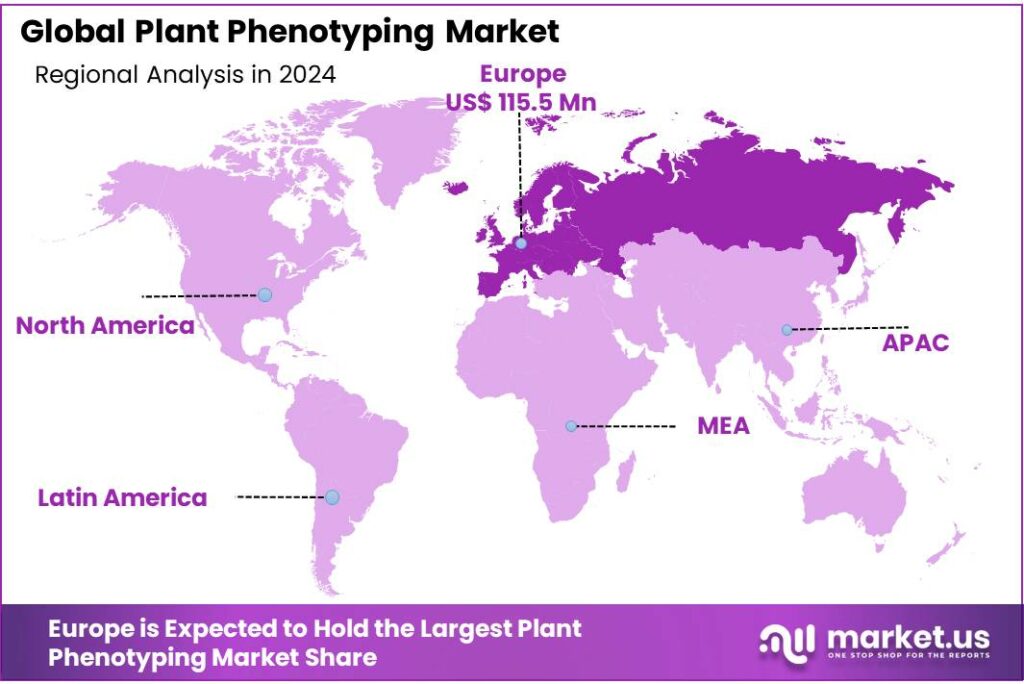
The Global Plant Phenotyping Market size is expected to be worth around USD 825.1 Million by 2034, from USD 263.3 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 12.1% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024 Europe held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.9% share, holding USD 115.5 Million in revenue.
Plant phenotyping is a pivotal discipline in modern agriculture, focusing on the comprehensive analysis of plant traits to enhance crop breeding and management. Utilizing advanced technologies such as high-throughput imaging, robotics, and artificial intelligence, this field enables the precise assessment of plant characteristics, facilitating the development of resilient and high-yielding crop varieties. The integration of phenotypic data with genomic information bridges the genotype-phenotype gap, accelerating the breeding process and promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
Government support extends beyond infrastructure development. The Department of Biotechnology (DBT) provides financial assistance to various institutions for research and development in plant sciences. For instance, the Punjab Agricultural University (PAU) in Ludhiana secured a ₹4 crore project from the DBT to advance predictive breeding in guava, focusing on enhancing fruit quality and shelf life through genomic tools.
The Clean Plant Programme (CPP), approved by the Union Cabinet with an investment of ₹1,765.67 crore, aims to revolutionize India’s horticulture sector. Under this initiative, nine clean plant nurseries will be established across the country, including centers in Pune, Nagpur, and Solapur. These nurseries are expected to produce 8 crore disease-free seedlings annually, enhancing the quality and productivity of fruit crops.
The growth of the plant phenotyping industry is further supported by various government schemes aimed at enhancing agricultural productivity and sustainability. The ‘Clean Plant’ initiative, launched by the Union Ministry of Agriculture, is a notable example. With an investment of ₹300 crore, this project aims to establish nine clean plant nurseries across India, including facilities in Pune, Nagpur, and Solapur. These nurseries are expected to produce approximately 8 crore disease-free seedlings annually, benefiting from international collaborations with countries like Israel and the Netherlands.
Key Takeaways
- Plant Phenotyping Market size is expected to be worth around USD 825.1 Million by 2034, from USD 263.3 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 12.1%.
- Equipment held a dominant market position in the Plant Phenotyping Market, capturing more than a 57.3% share.
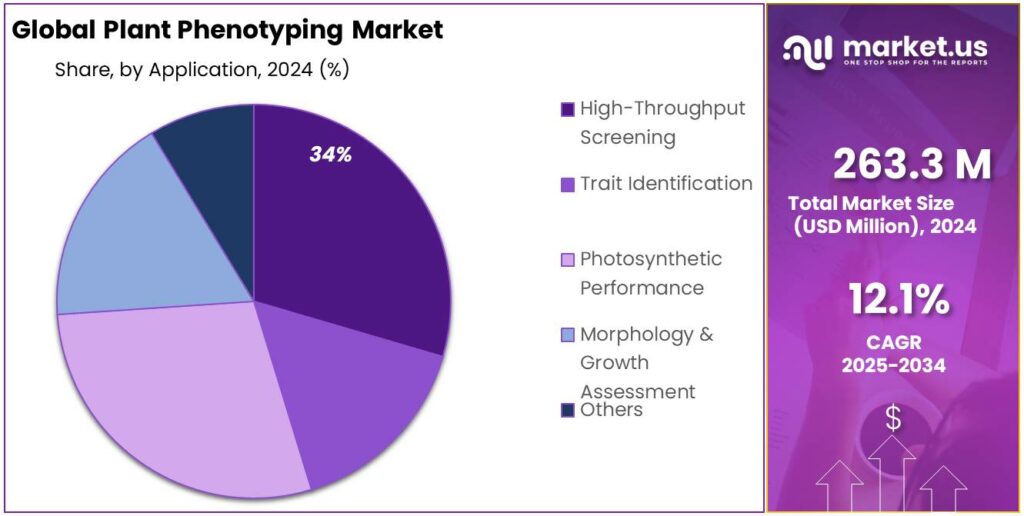
- High-Throughput Screening held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 34.6% share in the Plant Phenotyping Market.
- Laboratory held a dominant market position in the Plant Phenotyping Market, capturing more than a 48.9% share.
- Europe emerged as the dominant region in the global Plant Phenotyping Market, capturing a substantial 43.9% share, equivalent to USD 115.5 million.
By Type Analysis
Equipment dominates the Plant Phenotyping Market with 57.3% share in 2024 due to technological advancements.
In 2024, Equipment held a dominant market position in the Plant Phenotyping Market, capturing more than a 57.3% share. The high market share is attributed to continuous technological innovations in plant analysis tools and systems. These advancements allow for more precise and high-throughput phenotypic data collection, which is crucial for crop research and development.
As the demand for more accurate and automated phenotyping methods increases, the adoption of specialized equipment has accelerated. Technologies such as imaging systems, sensors, and robotics play a key role in improving the efficiency and accuracy of phenotypic evaluations. These tools enable researchers to gather data on plant traits such as growth rate, disease resistance, and water usage efficiency, which are essential for developing high-yield, climate-resilient crops.
By Application Analysis
High-Throughput Screening dominates with 34.6% share in 2024 due to its efficiency in crop analysis.
In 2024, High-Throughput Screening held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 34.6% share in the Plant Phenotyping Market. This segment’s growth is largely driven by its ability to efficiently analyze large numbers of plant samples in a short amount of time. High-throughput screening technologies allow researchers to evaluate multiple phenotypic traits simultaneously, enabling faster and more accurate identification of desirable plant characteristics.
The rising demand for rapid, data-driven decisions in crop breeding and genetics is significantly contributing to the expansion of this segment. This method is especially popular in genomics and molecular biology, where the speed and scale of data collection are essential for accelerating plant breeding programs.
By End-User Analysis
Laboratory dominates the Plant Phenotyping Market with 48.9% share in 2024 due to its critical role in research.
In 2024, Laboratory held a dominant market position in the Plant Phenotyping Market, capturing more than a 48.9% share. This dominance is primarily due to the increasing reliance on laboratories for advanced research and testing in plant breeding, genetics, and crop improvement. Laboratories provide controlled environments that are essential for performing accurate phenotypic evaluations, which require specialized equipment and techniques.
With the growing focus on precision agriculture, laboratories have become a key hub for data collection, analysis, and interpretation. The demand for high-quality, reproducible results from phenotyping processes has made laboratories the preferred end-user in this segment. Furthermore, the rise in government and private sector funding for agricultural research continues to support the growth of laboratory-based phenotyping efforts.
Key Market Segments
By Type
- Equipment
- Growth Chambers/Phytotrons
- Imaging Systems
- Robotics and Automation
- Phenomobiles
- Sensors
- Environmental Sensors
- Physiological Sensors
- Spectral Sensors
- Software
- Imaging Analysis Software
- Data Management & Integration Software
- Statistical Analysis
- Modeling Software
- Others
By Application
- High-Throughput Screening
- Trait Identification
- Photosynthetic Performance
- Morphology & Growth Assessment
- Others
By End-User
- Greenhouse
- Laboratory
- Others
Emerging Trends
Integration of Artificial Intelligence in Plant Phenotyping
A significant and transformative trend in plant phenotyping is the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) technologies to enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and scalability of phenotypic assessments. These advancements are revolutionizing traditional phenotyping methods, enabling researchers and farmers to obtain precise and real-time data on plant traits, growth patterns, and stress responses.
In India, the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) has been at the forefront of promoting AI-driven agricultural research. In its Annual Report for 2024-25, the DBT highlighted the funding of several projects that utilize AI and ML to improve crop resilience and productivity. For instance, the DBT has supported initiatives focusing on genome editing and functional genomics in crops, which are closely linked with phenotypic assessments to develop improved crop varieties.
Furthermore, the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) has been actively involved in integrating AI into plant phenotyping. Through various research programs and collaborations, ICAR aims to develop AI-based tools for the rapid and accurate assessment of plant traits, thereby accelerating the breeding of climate-resilient crops.
The application of AI in plant phenotyping offers several advantages. It allows for high-throughput analysis of large plant populations, reducing the time and labor required for manual measurements. AI algorithms can process complex datasets to identify patterns and correlations that may not be apparent through traditional methods. This capability is particularly beneficial in identifying traits related to drought tolerance, disease resistance, and nutrient use efficiency.
Drivers
Government Initiatives and Infrastructure Development
One of the most significant driving factors propelling the growth of plant phenotyping in India is the robust support from governmental bodies, particularly through the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) and the Department of Biotechnology (DBT). These institutions have not only invested heavily in state-of-the-art infrastructure but have also implemented strategic programs to address the challenges posed by climate change and the need for sustainable agriculture.
A prime example of this commitment is the establishment of the Nanaji Deshmukh Plant Phenomics Centre at the Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI) in New Delhi. Inaugurated in October 2017, this facility is the largest of its kind in India and ranks among the best in terms of analytical capabilities among public-funded institutions globally. The center, developed with funding from the National Agricultural Science Fund (NASF), features a climate-controlled facility with eight different greenhouse chambers, enabling the study of plant responses under various environmental conditions. This infrastructure is pivotal for advancing research in crop resilience and productivity.
Further reinforcing this initiative is the National Initiative on Climate Resilient Agriculture (NICRA), launched by ICAR in February 2011. This mega project aims to enhance the resilience of Indian agriculture to climate variability and change through strategic research, technology demonstrations, and capacity building. Under NICRA, significant investments have been made in developing and applying improved production and risk management technologies, including the establishment of phenomics platforms for rapid screening of crop germplasm for drought and heat tolerance.
The Department of Biotechnology (DBT) has also played a crucial role by providing financial support for research projects that integrate plant phenotyping technologies. For instance, DBT has funded initiatives focusing on genome editing and functional genomics in crops, which are closely linked with phenotypic assessments to develop improved crop varieties.
Restraints
High Costs and Infrastructure Constraints
One of the most significant barriers to the widespread adoption of plant phenotyping in India is the high cost associated with advanced phenotyping equipment and the infrastructure challenges prevalent in rural areas. Plant phenotyping technologies, such as high-throughput imaging systems, multispectral cameras, and automated data analysis platforms, require substantial investment. For instance, the establishment of a state-of-the-art phenotyping facility can cost upwards of ₹10 crore, a sum that is often beyond the reach of many research institutions and agricultural startups in India. This financial constraint limits the accessibility of these technologies to a broader audience, thereby hindering the potential for large-scale implementation.
The lack of standardized protocols and methodologies in plant phenotyping also contributes to the challenges faced by researchers and practitioners. Without universally accepted standards, data generated from different studies may not be comparable, leading to inconsistencies and difficulties in data interpretation. This lack of standardization hampers collaborative efforts and slows down the progress in the field. Moreover, the absence of standardized data formats makes it challenging to integrate and analyze large datasets, further complicating the research process.
To address these challenges, the Indian government has initiated several programs aimed at promoting the adoption of plant phenotyping technologies. The National Agricultural Innovation Project (NAIP) and the National Mission on Agricultural Extension and Technology (NMAET) are two such initiatives that provide financial support to farmers and researchers for the procurement and utilization of modern agricultural equipment, including phenotyping tools. Additionally, the Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY) offers subsidies and incentives to encourage the adoption of advanced agricultural technologies.
Opportunity
Government-Funded Research and Development Initiatives
A significant growth opportunity for plant phenotyping in India lies in the robust support provided by government-funded research and development initiatives. These programs not only offer financial backing but also foster collaboration between public research institutions, universities, and the private sector, thereby accelerating the adoption and advancement of plant phenotyping technologies.
The Department of Biotechnology (DBT), under the Ministry of Science and Technology, Government of India, plays a pivotal role in this regard. For instance, the DBT has awarded a ₹4 crore project to Punjab Agricultural University (PAU) for the development of predictive breeding techniques in guava. This initiative aims to enhance fruit quality, shelf life, and processing traits using advanced genomic tools, marking a significant step towards precision agriculture in horticultural crops.
Moreover, the DBT’s Agriculture Biotechnology programme supports innovative biotechnological research to achieve sustainable agriculture. This includes leveraging the latest advances in genomics, proteomics, transgenics, and gene editing technologies to enhance food security, rural employment, and environmental sustainability.
These government initiatives not only provide the necessary funding but also create an ecosystem that encourages the development and application of plant phenotyping technologies. By aligning research objectives with national agricultural priorities, such as climate resilience and food security, these programs ensure that plant phenotyping contributes meaningfully to the advancement of agriculture in India.
Regional Insights
Europe leads the Plant Phenotyping Market with 43.9% share in 2024, valued at USD 115.5 million.
In 2024, Europe emerged as the dominant region in the global Plant Phenotyping Market, capturing a substantial 43.9% share, equivalent to USD 115.5 million in market value. This leadership is attributed to Europe’s robust agricultural research infrastructure, significant investments in sustainable farming technologies, and a strong emphasis on precision agriculture. Countries like Germany, France, and the Netherlands are at the forefront, hosting numerous research institutions and agritech companies that drive innovation in plant phenotyping.
The European Union’s commitment to enhancing food security and addressing climate change challenges has led to increased funding for agricultural research and development. Initiatives such as the PhotoBoost project, which aims to improve photosynthetic efficiency in crops like rice and potato, exemplify Europe’s proactive approach to advancing plant phenotyping technologies. Additionally, the establishment of networks like the Nordic-Baltic Plant Phenotyping Network (NBPPN) underscores the region’s collaborative efforts to standardize and promote phenotyping practices across member countries.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
LemnaTec is a global leader in digital plant phenotyping and seed testing solutions. Since 1998, the company has developed advanced imaging and AI-powered analysis systems for researchers in laboratories, greenhouses, and fields. Their products, such as the PhenoAIxpert and HyperAIxpert, enable high-throughput, non-invasive measurement of plant traits, supporting applications in breeding, stress testing, and quality assessments.
Established in 1971, Delta-T Devices specializes in environmental measurement instruments, including soil moisture sensors, pyranometers, and plant science tools. Their products, such as the WET150 sensor and WinDIAS leaf image analysis system, are widely used in agriculture, horticulture, and environmental research. The company is known for its commitment to quality and customer support, with a strong international presence.
Phenospex is a biotech company that develops automated plant screening and phenotyping systems. Their product lineup includes the PlantEye F600 multispectral 3D scanner, TraitFinder for lab and greenhouse phenotyping, and FieldScan for high-throughput field phenotyping. These solutions enable precise and efficient analysis of plant traits, supporting applications in breeding, agrochemicals, and sustainable agriculture.
Top Key Players Outlook
- LemnaTec
- Delta-T Devices
- Heinz Walz
- Phenospex
- KeyGene
- Phenomix
- Quibit Phenomics
- Photon System Republic
- WPS
- Rothamstad Research Limited
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024, LemnaTec’s flagship product, the PhenoAIxpert HT, was installed in over 20 locations globally, supporting more than 200 scientific publications.
In 2024, Phenospex’s flagship product, the PlantEye F600, a multispectral 3D scanner, was widely adopted across research institutions and agricultural enterprises.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 263.3 Mn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 825.1 Mn CAGR (2025-2034) 12.1% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Type (Equipment, Sensors, Software), By Application (High-Throughput Screening, Trait Identification, Photosynthetic Performance, Morphology and Growth Assessment, Others), By End-User (Greenhouse, Laboratory, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape LemnaTec, Delta-T Devices, Heinz Walz, Phenospex, KeyGene, Phenomix, Quibit Phenomics, Photon System Republic, WPS, Rothamstad Research Limited Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- LemnaTec
- Delta-T Devices
- Heinz Walz
- Phenospex
- KeyGene
- Phenomix
- Quibit Phenomics
- Photon System Republic
- WPS
- Rothamstad Research Limited










