Global Pharmaceutical Enzymes Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Product Type (Carbohydrases, Proteases, Lipases, Polymerases And Nucleases, Others), By Source (Plants, Animals, Microorganisms), By Formulation (Powder, Liquid), By Production Method (Submerged Fermentation, Solid-state Fermentation), By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends, and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Oct 2025
- Report ID: 161488
- Number of Pages: 319
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
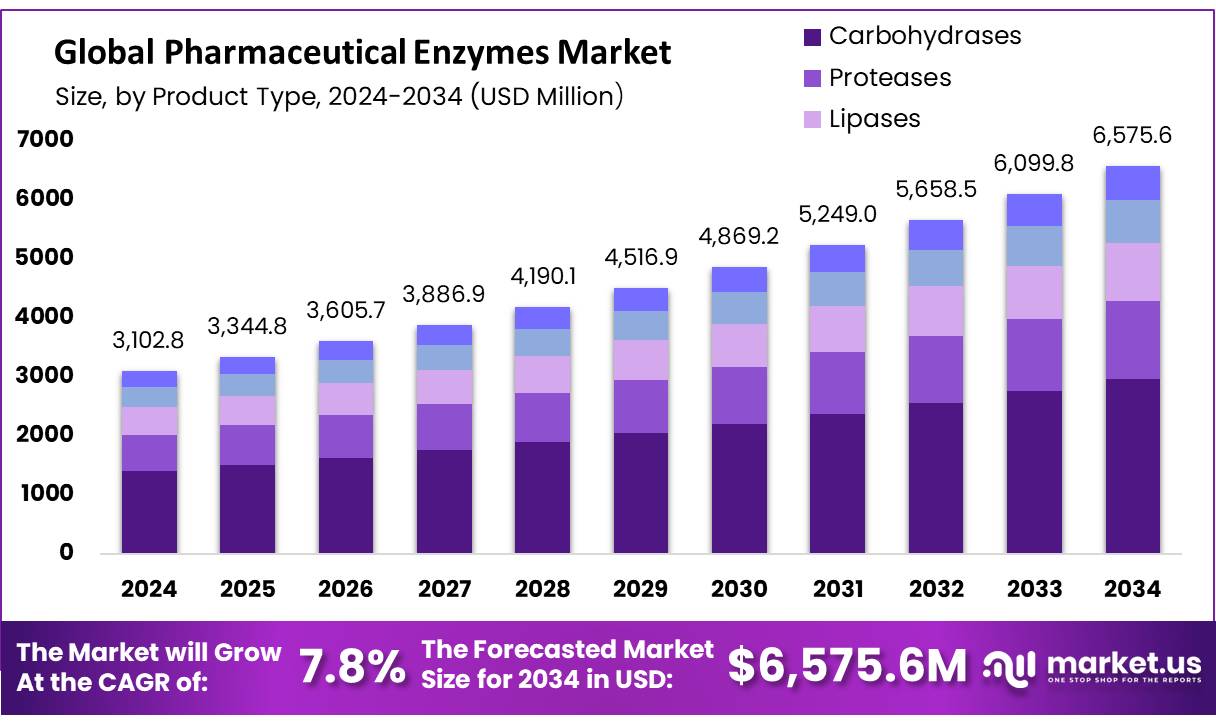
The global pharmaceutical enzymes market size is expected to be worth around USD 6,575.6 Million by 2034, from USD 3,102.8 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 7.8% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024 Europe held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 39.6% share, holding USD 1.4 Billion in revenue.
Enzymes have become integral components of the pharmaceutical industry, serving critical functions in drug development, synthesis, and quality control. As biological catalysts, they provide exceptional specificity, efficiency, and environmental sustainability, making them indispensable for contemporary pharmaceutical processes. The increasing emphasis on green chemistry, cost-effectiveness, and precision in formulation has further driven their adoption across both conventional manufacturing and advanced biotechnological applications.
As active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), enzymes are transforming drug development by enabling precise and efficient therapeutic solutions. They facilitate personalized medicine, minimize adverse effects, and promote eco-friendly production methods. Although challenges such as stability and regulatory constraints remain, continuous advancements in enzyme technology are paving the way for novel treatments targeting complex diseases, thereby profoundly influencing modern healthcare.
- For instance, iIn April 2025, eXoZymes Inc. launched BioClick, an innovative initiative aimed at accelerating enzyme engineering for sophisticated chemical reactions. Supported by a $300,000 grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), this project is poised to redefine the production of pharmaceuticals and bio-based compounds.
Among the most widely used enzymes in pharmaceutical applications are proteases, lipases, and amylases. Proteases catalyze the breakdown of proteins into amino acids and are instrumental in therapies for clotting disorders and digestive health. Lipases act on fats and play key roles in treating lipid-related conditions, while amylases decompose starches and support various digestive treatments. Collectively, these enzymes exemplify the versatility and therapeutic potential of enzyme-based pharmaceuticals.
Key Takeaways
- The global pharmaceutical enzymes market was valued at USD 3,102.8 million in 2024
- In 2024, among product type, carbohydrases accounted for the largest market share of 45.2%
- Among source, microorganisms held major market share of 70.2% in 2024
- By formulation, in 2024 powder pharmaceutical enzymes accounted for the largest market share of 61.8%
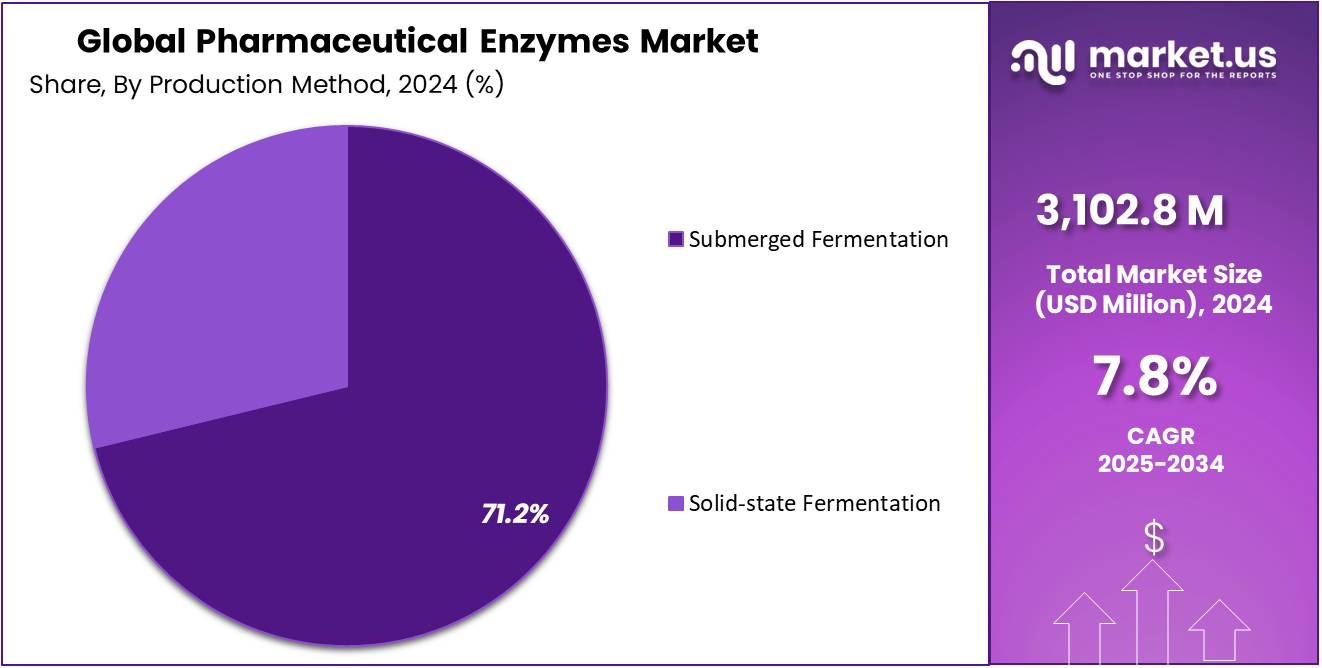
- By production method, submerged fermentation has dominated the market in 2024 with 71.2% market share
- In 2024, North America led the global pharmaceutical enzymes market with substaintial market share of 36.8%. Furthermore, in the region US was the major contributor with market value of USD 1,024.2 million in the 2024.
Product Type Analysis
In 2024, carbohydrases emerged as the largest product segment in the global pharmaceutical enzymes market, representing approximately 45.2% of total market share. This dominance is largely driven by their broad utilization in drug formulation, excipient modification, and active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) synthesis. Among the various types of carbohydrases, amylases and cellulases are particularly prominent due to their efficiency in catalyzing the breakdown and modification of complex carbohydrates into simpler, bioactive molecules essential for pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Amylases play a pivotal role in the development of starch-based excipients and derivatives that enhance solubility, stability, and controlled drug release in modern formulations. Their contribution to sustained and targeted delivery systems underscores their significance in advanced dosage design. Conversely, cellulases are extensively used in modifying cellulose-based excipients to improve tablet binding properties and overall bioavailability. Additionally, cellulases are increasingly applied in biotransformation processes, enabling the synthesis of high-value intermediates with superior stereoselectivity.
Source Analysis
In 2024, microorganisms accounted for a dominant 70.2% share of the global pharmaceutical enzymes market, reaffirming their pivotal role in the production of therapeutic enzymes. Bacteria and fungi are particularly valued as enzyme sources due to their capacity to produce highly active and stable enzymes through cost-effective large-scale fermentation processes. Their genetic adaptability further enables precise modifications to enhance catalytic efficiency, structural stability, and therapeutic specificity, solidifying their indispensability in pharmaceutical manufacturing and drug development.
Microbial enzymes are extensively utilized across diverse therapeutic areas, including oncology, cardiovascular health, inflammatory diseases, and metabolic disorders. For instance, L-asparaginase is a cornerstone in the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia, functioning by depleting extracellular asparagine to inhibit cancer cell growth. Serratiopeptidase is recognized for its anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and fibrinolytic properties, while collagenase plays a critical role in wound healing, burn care, and the management of conditions such as Peyronie’s disease. In cardiovascular medicine, microbial enzymes like streptokinase and nattokinase are widely employed for their ability to dissolve fibrin-based clots and restore blood flow. Emerging enzymes such as EndoS from Streptococcus pyogenes are also gaining prominence for their potential to reduce antibody-mediated cell damage, reflecting the expanding therapeutic scope and innovation within microbial enzyme research.
Formulation Analysis
In 2024, the powder formulation segment held a dominant position with 61.8% market share in the global pharmaceutical enzymes market, driven by its superior stability, ease of handling, and extended shelf life. Powdered enzyme formulations are widely preferred in pharmaceutical manufacturing due to their ability to maintain enzymatic activity over longer storage periods, even under variable environmental conditions. This stability is particularly advantageous for global distribution and large-scale production, where temperature fluctuations and transportation constraints can impact product quality.
The powder form also offers enhanced versatility in dosage design and formulation development. It allows for precise measurement and controlled incorporation into various pharmaceutical products, including tablets, capsules, and dry powder inhalers. Additionally, powdered enzymes are easier to transport, store, and reconstitute when required, providing cost-effective solutions for both manufacturers and healthcare providers.
Production Method Analysis
In 2024, submerged fermentation (SmF) emerged as the dominant production method in the global pharmaceutical enzymes market, accounting for a significant 71.2% share. This technique has become the industry benchmark owing to its scalability, precise process control, and consistent enzyme yield and quality. By cultivating microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi in liquid nutrient media under tightly regulated conditions, SmF enables high productivity, efficient downstream processing, and uniform product output—attributes that make it the preferred method for large-scale pharmaceutical enzyme manufacturing.
The prevalence of submerged fermentation is driven by its versatility in producing a broad range of enzymes, including proteases, lipases, amylases, and cellulases, which are vital in treating cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and digestive disorders. Moreover, SmF facilitates the genetic modification and optimization of microbial strains, allowing producers to enhance enzyme activity, stability, and specificity in alignment with stringent pharmaceutical standards. The method’s ability to maintain precise control over parameters such as pH, temperature, and oxygen concentration ensures reproducibility—an essential requirement for enzymes utilized in regulated drug development and manufacturing processes.
Key Market Segments
By Product Type
- Carbohydrases
- Amylases
- Cellulases
- Others
- Proteases
- Lipases
- Polymerases & Nucleases
- Others
By Source
- Plants
- Animals
- Microorganisms
By Formulation
- Powder
- Liquid
By Production Method
- Submerged Fermentation
- Solid-state Fermentation
Drivers
Rising Demand for Enzyme-Based Therapeutics
The demand for enzyme-based therapeutics continues to grow, particularly in the treatment of genetic and metabolic disorders. In cases where individuals suffer from enzyme deficiencies, enzyme replacement therapies supply the specific enzymes that are absent or malfunctioning in the body. These treatments have proven highly effective for conditions such as Gaucher disease, Fabry disease, and various lysosomal storage disorders, restoring normal cellular function and significantly improving patient outcomes.
- Mitochondrial diseases, which affect approximately one in every 5,000 individuals worldwide, remain among the most challenging to treat due to the intricate nature of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). Many of these disorders—including mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes syndrome (MELAS), as well as mitochondrial diabetes—are linked to mutations such as m.3243A>G in the MT-TL1 gene. Traditional therapeutic tools for modifying mtDNA have been limited. However, Japanese researchers have recently developed an advanced enzyme technology capable of precisely adjusting the levels of mutated mtDNA in patient-derived stem cells, representing a major breakthrough in the potential treatment of mitochondrial disorders.
Enzyme technology is also advancing therapeutic options for inflammatory and oncological diseases. Certain enzymes are utilized to regulate immune responses, thereby reducing inflammation in conditions such as arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease. In cancer therapy, engineered enzymes are designed to specifically target malignant cells, either by degrading their protective structures or by activating drugs selectively within tumor sites. These precision-based strategies are transforming cancer treatment by concentrating therapeutic effects on diseased tissues while minimizing collateral damage to healthy cells.
Restraints
Presence of Strengthened Rules and Regulations
The regulation of enzymes in therapeutic applications is governed by stringent standards designed to ensure safety, efficacy, and quality. Adherence to these complex regulatory frameworks is critical to safeguarding patient health while maximizing the therapeutic benefits of enzyme-based treatments. Leading authorities such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) establish comprehensive guidelines that pharmaceutical companies must comply with throughout the entire lifecycle of enzyme-based products. When utilized as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), enzymes are subject to region-specific regulatory requirements.
- For instance, in the United States, for example, the FDA provides detailed guidance on the submission of chemical and technological data pertaining to enzyme preparations. These regulations ensure that enzyme-based APIs meet defined quality and performance criteria prior to approval.
The production of enzyme APIs must also comply with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), which mandate strict controls over purity, identity, and potency. Manufacturers are required to minimize contamination risks and maintain consistent quality across production batches. Prior to market authorization, enzyme APIs undergo extensive preclinical evaluations and clinical trials to confirm their safety, therapeutic efficacy, and potential side effect profiles. This rigorous oversight framework reinforces public trust and ensures the reliability of enzyme-based therapeutics in modern medicine.
Opportunity
Increasing Adoption of Enzymes in the Pharmaceutical Sector
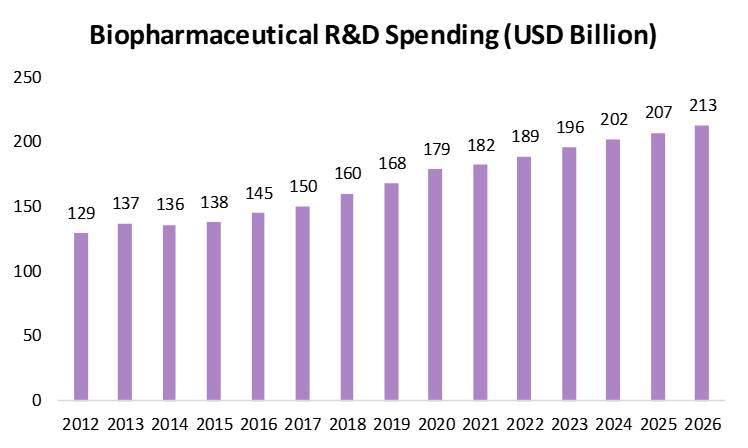
The growing adoption of enzymes within the pharmaceutical sector represents a significant opportunity for innovation and advancement. The research-driven biopharmaceutical industry continues to play a crucial role in the discovery and development of novel medicines and vaccines, aimed at preventing and treating a wide range of diseases while enhancing patient quality of life worldwide. Through substantial financial investment and dedicated scientific research, the industry continues to expand the boundaries of medical science, driving both healthcare progress and societal well-being.
- Globally, more than 12,700 drug candidates are currently in various stages of clinical development, with approximately 1,200 categorized as gene therapies. Nearly half of these drug candidates are biologics, while the remainder are small molecules, demonstrating a balanced and diverse research landscape that supports the integration of enzyme-based technologies across therapeutic areas.
The biopharmaceutical sector also stands out as one of the most research-intensive industries worldwide, maintaining robust investment in R&D even during economic downturns. Its annual research expenditure surpasses that of other high-technology sectors—8.1 times greater than aerospace and defense, 7.2 times more than chemicals, and 1.2 times higher than software and computer services.
Trends
Genetic Engineering and Novel Enzyme Strains: Advancements in genetic engineering are driving the development of next-generation enzymes with superior functional properties. Researchers are increasingly focusing on engineering enzymes to achieve greater stability, catalytic efficiency, and substrate specificity, thereby broadening their potential applications in pharmaceutical research and drug manufacturing. These breakthroughs are expected to lead to the creation of novel enzyme-based therapies, reinforcing the pivotal role of enzymes in modern medicine and precision therapeutics.
Artificial Intelligence in Enzyme Discovery and Drug Design: Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming the landscape of enzyme research and drug development. By leveraging AI-driven computational models, scientists can efficiently analyze extensive biological datasets, predict enzyme behaviors, and simulate molecular interactions with remarkable accuracy. This integration of AI not only expedites the identification of novel enzymes but also enhances their design and optimization for therapeutic use. As a result, AI is emerging as a critical tool in accelerating the discovery and refinement of enzyme-based drug candidates, paving the way for more effective and targeted treatment solutions.
Geopolitical Impact Analysis
In 2025, the United States introduced a sweeping set of tariffs that significantly reshaped the global pharmaceutical and healthcare landscape. Aimed at reinforcing domestic manufacturing capabilities, the policy imposed a 10% tariff on all imported goods, with particularly steep levies reaching up to 245% on Chinese active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and 25% on medical devices sourced from Canada and Mexico. While these measures were intended to stimulate local production, they have created substantial challenges for the pharmaceutical enzymes industry and the broader healthcare sector.
The intensified tariffs have driven up the cost of essential inputs such as APIs, enzymes, and medical components, placing additional strain on already complex global supply chains. Pharmaceutical companies are facing increased production expenses and logistical hurdles, leading to potential price escalations for drugs and therapeutic enzymes. Moreover, these trade restrictions risk disrupting patient access to critical treatments, particularly those dependent on imported biocatalysts. As a result, organizations are being compelled to re-evaluate sourcing strategies, diversify supply networks, and invest in domestic enzyme production to maintain competitiveness in an evolving geopolitical and economic environment.
Regional Analysis
In 2024, North America emerged as the leading region in the global pharmaceutical enzymes market, commanding a substantial market share of 36.8%. Within the region, the United States accounted for approximately 89.7% of total pharmaceutical enzyme consumption, reflecting its position as a global hub for biopharmaceutical innovation and production. The U.S. remains the world leader in biopharmaceutical research and development (R&D), with firms investing nearly $96 billion in R&D activities in 2023, according to the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA). That same year, R&D expenditures represented more than 20% of total biopharmaceutical sales, underscoring the sector’s commitment to scientific advancement and innovation.
The economic impact of the U.S. biopharmaceutical industry continues to be profound. In 2022, biopharmaceutical exports valued at over $25 billion originated from majority foreign-owned firms operating within the country, while these firms collectively invested nearly $26 billion in R&D. Furthermore, foreign direct investment (FDI) in pharmaceuticals and medicines reached $503.4 billion in 2023, highlighting the nation’s attractiveness as a global investment destination.
The United States maintains one of the most conducive environments worldwide for the development and commercialization of pharmaceuticals, supported by limited market barriers and strong institutional frameworks. Key strengths include a robust intellectual property system that safeguards innovation, a rigorous science-based regulatory framework, an extensive research base driven by leading academic institutions, and sustained government funding for scientific research. In addition, the country’s well-developed capital markets play a crucial role in supporting growth, with venture capital investments in pharmaceuticals and biotechnology accounting for 13% of total U.S. venture capital investments in 2023.
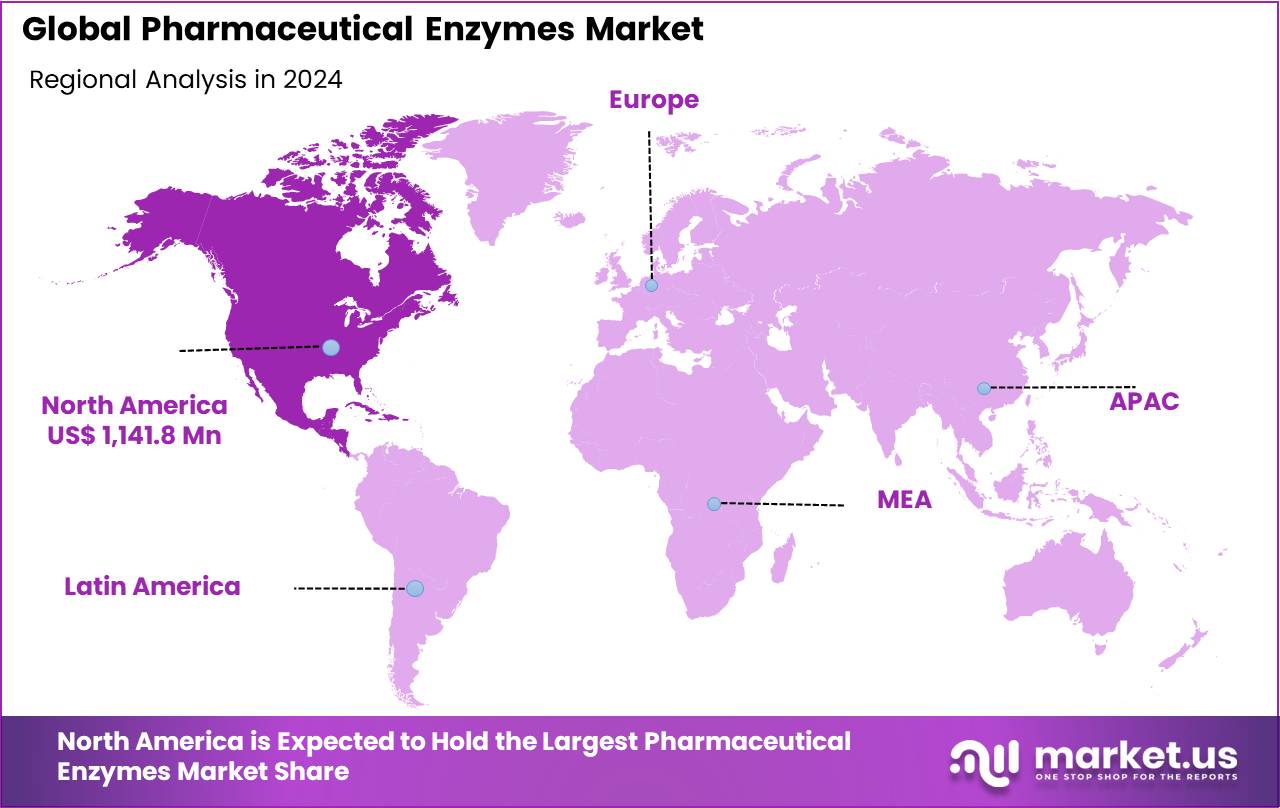
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- The US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia & CIS
- Rest of Europe
- APAC
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- ASEAN
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
The global pharmaceutical enzymes market is characterized by a diverse and competitive mix of multinational corporations, specialized biotechnology firms, and niche enzyme producers, each playing a vital role in advancing innovation and market growth. Industry leaders such as Novozymes (Novonesis) and DSM-Firmenich leverage decades of expertise in industrial biotechnology to deliver customized enzyme solutions for pharmaceutical manufacturing and therapeutic use. Companies like BASF SE and Kerry Group plc further strengthen the market by integrating enzyme technologies within their broader life sciences and nutrition portfolios.
Specialized firms, including Codexis, Inc., Amano Enzyme Inc., and Biocatalysts Ltd., are at the forefront of protein engineering and biocatalysis, developing highly selective enzymes for drug synthesis, biotransformation, and personalized medicine. BRAIN Biotech AG and Aumgene Biosciences contribute significantly through their strengths in microbial enzyme production and genetic engineering, offering cost-effective and sustainable biotechnological solutions.
On the therapeutic side, companies such as Halozyme Therapeutics and Sanofi are leading advancements in enzyme-based treatments for oncology, metabolic, and genetic disorders. Meanwhile, Merck KGaA and Asymchem Inc. integrate enzymatic processes into their drug discovery and development pipelines to enhance efficiency and precision. Emerging participants, including Bioseutica BV and Infinita Biotech, add further diversity with specialized enzyme formulations and strong regional market presence.
The major players in the industry
- Novozymes / Novonesis
- Codexis, Inc.
- BASF SE
- DSM (DSM-Firmenich)
- Amano Enzyme Inc.
- Biocatalysts Ltd.
- BRAIN Biotech AG
- Sanofi
- Merck KGaA
- Asymchem Inc.
- Halozyme Therapeutics
- Kerry Group plc
- Aumgene Biosciences
- Bioseutica BV
- Infinita Biotech Private Limited
- Other Key Players
Recent Development
- In May 2025, BioMarin Pharmaceutical Inc. announced the acquisition of Inozyme Pharma, Inc. through an all-cash transaction valued at approximately $270 million (or $4.00 per share). This strategic move substantially enhances BioMarin’s enzyme therapy portfolio by incorporating INZ-701, a Phase 3 enzyme replacement therapy currently in development for ENPP1 deficiency, a rare genetic disorder characterized by abnormal calcification and bone mineralization.
- In May 2025, WuXi Biologics and CANbridge Pharmaceuticals achieved a major milestone in China’s biopharmaceutical industry with the launch of the nation’s first locally developed enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) for Gaucher disease. This breakthrough marks a significant advancement in China’s capacity for domestic innovation in rare disease treatment, reducing reliance on imported enzyme therapies and improving accessibility for local patients.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 3,102.8 Mn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 6,575.6 Mn CAGR (2025-2034) 7.8% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Product Type (Carbohydrases, Proteases, Lipases, Polymerases & Nucleases, Others), By Source (Plants, Animals, Microorganisms), By Formulation (Powder, Liquid), By Production Method (Submerged Fermentation, Solid-state Fermentation) Regional Analysis North America – The US & Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia & CIS, Rest of Europe; APAC- China, Japan, South Korea, India, ASEAN & Rest of APAC; Latin America- Brazil, Mexico & Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa- GCC, South Africa, & Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Novozymes / Novonesis, Codexis, Inc., BASF SE, DSM (DSM-Firmenich), Amano Enzyme Inc., Biocatalysts Ltd., BRAIN Biotech AG, Sanofi, Merck KGaA, Asymchem Inc., Halozyme Therapeutics, Kerry Group plc, Aumgene Biosciences, Bioseutica BV, Infinita Biotech Private Limited, Other Key Players Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Pharmaceutical Enzymes MarketPublished date: Oct 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Pharmaceutical Enzymes MarketPublished date: Oct 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Novozymes / Novonesis
- Codexis, Inc.
- BASF SE
- DSM (DSM-Firmenich)
- Amano Enzyme Inc.
- Biocatalysts Ltd.
- BRAIN Biotech AG
- Sanofi
- Merck KGaA
- Asymchem Inc.
- Halozyme Therapeutics
- Kerry Group plc
- Aumgene Biosciences
- Bioseutica BV
- Infinita Biotech Private Limited
- Other Key Players










