Global Parkinson's Disease Treatment Market Analysis By Drug Class (Levodopa/Carbidopa, Dopamine Agonists, MAO-B Inhibitors, COMT Inhibitors, Anticholinergics, Adenosine A2A Antagonists, Glutamate Antagonists, Cholinesterase Inhibitors, Others), By Disease Stage (Early-Stage, Advanced-Stage), By Route of Administration (Oral, Subcutaneous, Transdermal, Inhalation), By Distribution Channel (Hospital Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies, Online Pharmacies) By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Oct 2025
- Report ID: 160750
- Number of Pages: 391
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
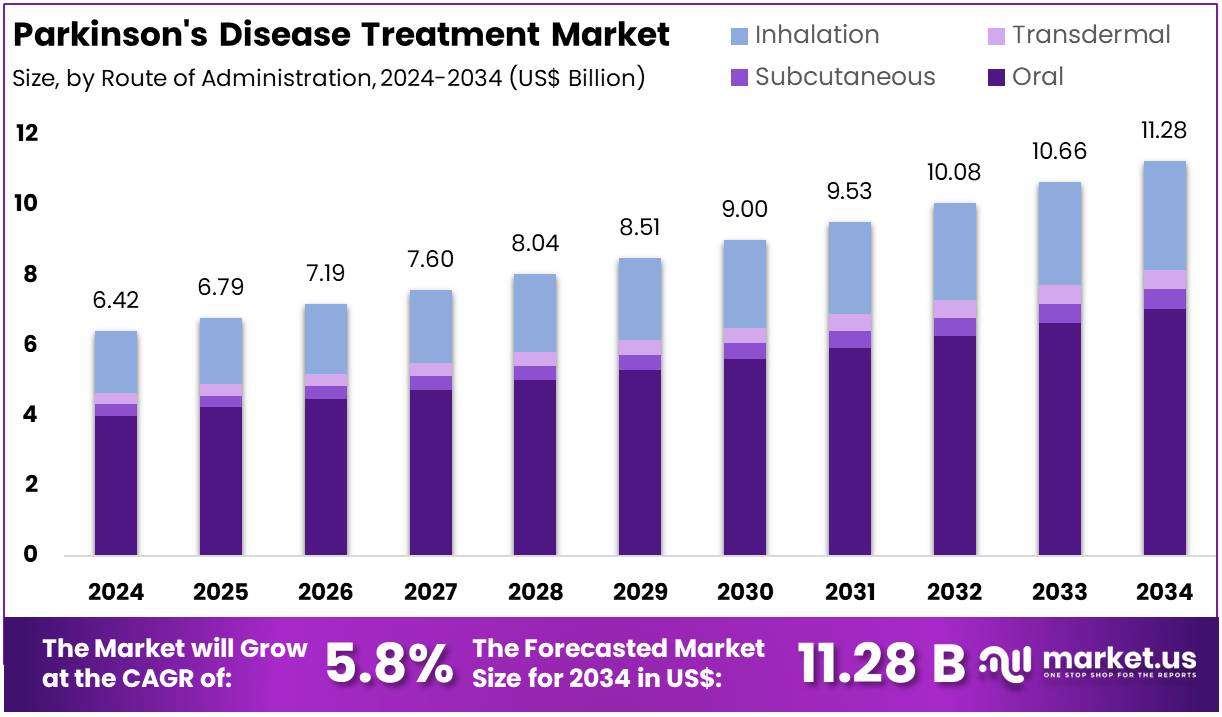
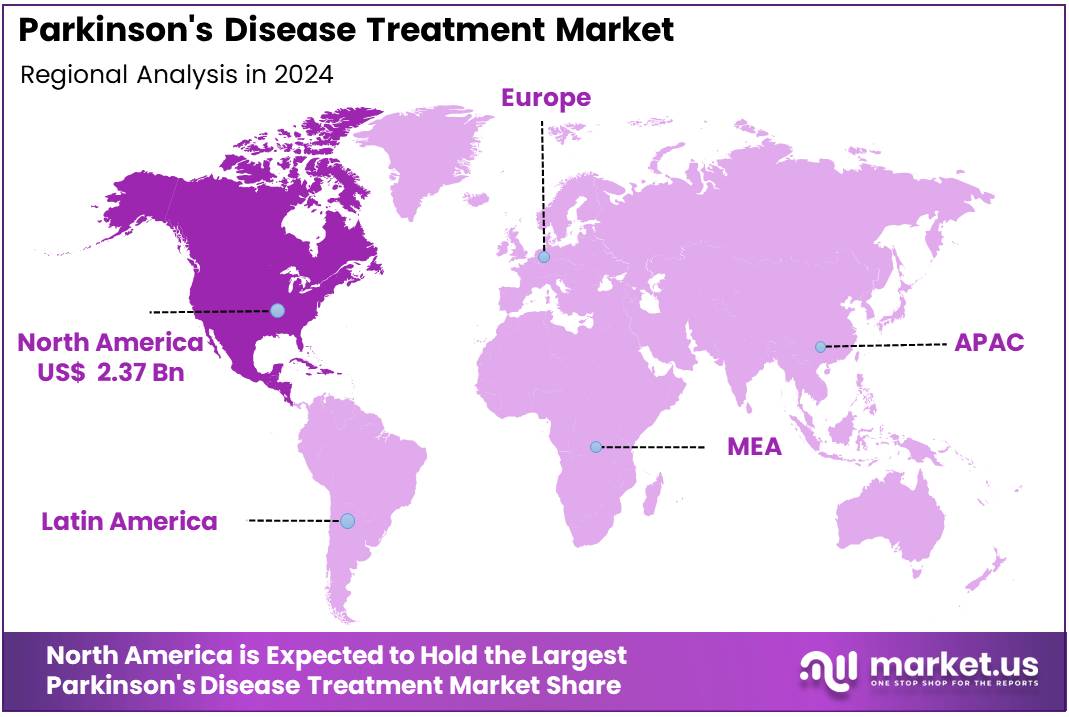
The Global Parkinson’s Disease Treatment Market size is expected to be worth around US$ 11.28 Billion by 2034, from US$ 6.42 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 5.8% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. North America held a dominant position in the Parkinson’s Disease Treatment Market, capturing over 36.9% share and reaching a market value of around US$ 2.37 billion.
Parkinson’s disease (PD) treatment includes medical, surgical, and therapeutic approaches aimed at managing motor and non-motor symptoms of this progressive neurodegenerative disorder. The treatment does not cure the condition but helps control tremors, rigidity, and slowed movements. Pharmacological options such as levodopa, dopamine agonists, and monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors are widely prescribed. Non-drug therapies, including physiotherapy and speech therapy, improve motor control and quality of life, while advanced cases often benefit from deep brain stimulation (DBS).
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), more than 8.5 million people were living with Parkinson’s disease in 2019, and approximately 329,000 deaths were attributed to it. The prevalence of the disease has doubled over the past 25 years, making it one of the fastest-growing neurological disorders globally. The rising incidence is linked to aging populations and longer life expectancy. For instance, in 2021, there were about 1.34 million new Parkinson’s cases worldwide, with an age-standardised incidence rate increasing from 11.24 per 100,000 in 1990 to 15.63 per 100,000 in 2021.
The market is expanding due to growing demand for medications, devices, and rehabilitation services. North America leads the global market owing to advanced healthcare infrastructure, strong reimbursement frameworks, and high disease awareness. In the U.S. and Canada, Parkinson’s incidence ranges between 108 and 212 per 100,000 among those aged 65 and older, reflecting a large treatment base. According to The Lancet, India recorded around 771,000 Parkinson’s cases in 2019, with approximately 45,300 deaths, underscoring the growing disease burden across emerging economies.
Global policy attention has strengthened in recent years. The World Health Assembly’s Intersectoral Global Action Plan on Epilepsy and Other Neurological Disorders (2022–2031) has prioritized neurological health. This plan promotes better access to diagnosis and care and encourages national strategies to expand treatment capacity. Increased policy focus, coupled with aging demographics, is expected to sustain long-term demand for innovative therapies, neurorehabilitation services, and patient support infrastructure across all regions.
Market Dynamics and Regulatory Developments
Recent regulatory milestones are reshaping the treatment landscape. In October 2024, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved foscarbidopa/foslevodopa, marketed as VYALEV, the first 24-hour subcutaneous levodopa infusion for advanced Parkinson’s patients with motor fluctuations. The same prodrug combination, marketed as PRODUODOPA, was launched earlier in the European Union. These approvals mark an important step beyond oral levodopa and are expected to drive adoption of infusion therapies, especially where reimbursement systems support them.
Incremental improvements in oral therapies also continue. For example, the FDA approved the extended-release carbidopa/levodopa formulation Crexont (IPX203) in 2024. This formulation aims to prolong “on-time” and reduce dosing frequency, thereby improving adherence and patient outcomes. Device-based interventions are evolving as well. MR-guided focused ultrasound has gained expanded indications for unilateral pallidotomy in advanced Parkinson’s disease. Deep brain stimulation (DBS) systems have also advanced through enhanced programming and sensing capabilities, supporting growth in procedural volumes and device sales.
Research and regulatory collaboration are improving trial design and efficiency. In August 2024, the FDA issued a Letter of Support promoting the study of alpha-synuclein seed amplification assays in cerebrospinal fluid as biomarkers. In October 2024, the agency endorsed wearable-based gait datasets to refine Parkinson’s measurement science. Such initiatives enhance precision medicine approaches and reduce development risk for emerging therapies. These measures are likely to attract further investment in disease-modifying drugs and biologics.
Public-sector funding continues to sustain research momentum. The U.S. National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) remains the lead agency for Parkinson’s research, supporting initiatives in genetics, biomarkers, and therapeutic innovation. Active clinical programs listed on ClinicalTrials.gov include studies on therapeutic antibodies, GBA-associated disease, ambroxol, and cell- or gene-based therapies. These programs highlight a strong development pipeline and the growing focus on disease modification rather than symptom management.
The Parkinson’s disease treatment market is poised for steady growth, driven by the aging population, increased prevalence, and regulatory advancements. Policy initiatives such as the WHO action plan, coupled with new FDA approvals and expanding clinical trials, are supporting innovation and global access. Technological advances in neuromodulation, infusion systems, and biomarker development are improving treatment outcomes and creating long-term opportunities for industry stakeholders worldwide.
Key Takeaways
- The global Parkinson’s disease treatment market is projected to reach approximately US$ 11.28 billion by 2034, growing from US$ 6.42 billion in 2024 at a CAGR of 5.8%.
- In 2024, the Levodopa/Carbidopa segment dominated the drug class category, accounting for over 50.9% of the total market share globally.
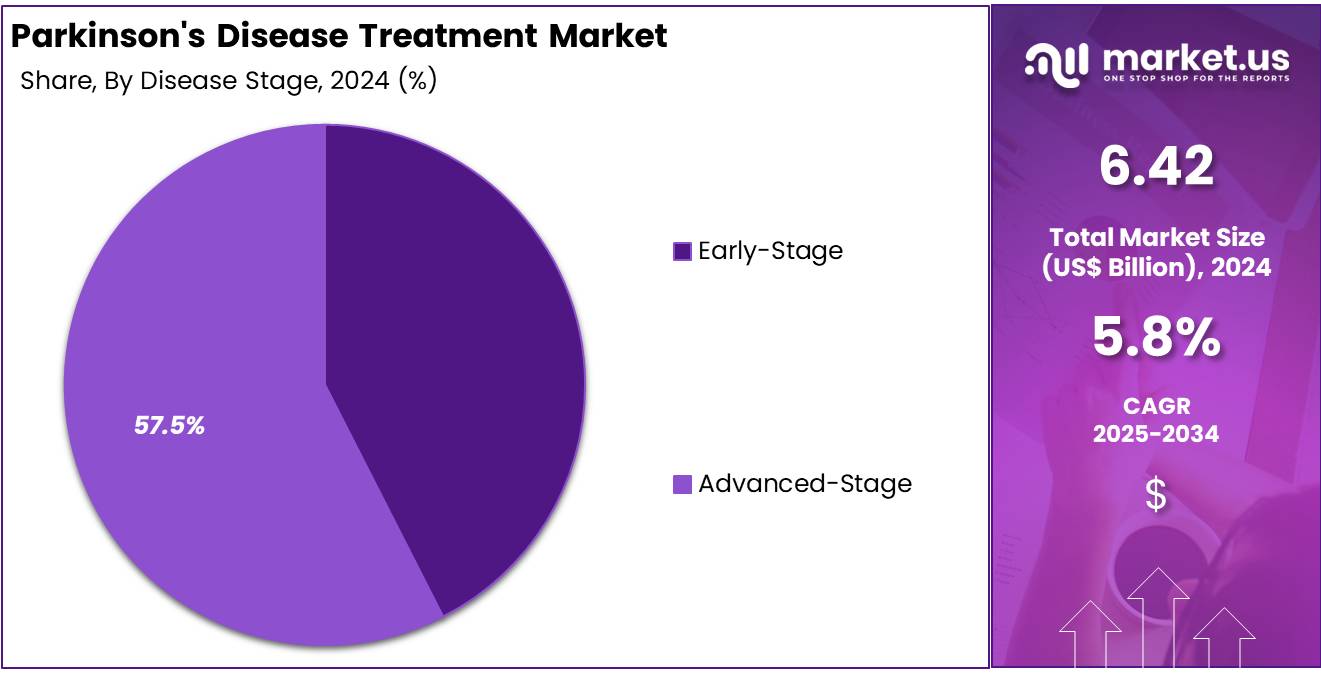
- The advanced-stage section led the disease stage segment in 2024, capturing more than 57.5% of the overall Parkinson’s disease treatment market.
- In terms of route of administration, the oral segment held a dominant 62.4% share of the market in 2024, reflecting patient preference and accessibility.
- The hospital pharmacies segment represented the leading distribution channel in 2024, securing over 45.2% of total global Parkinson’s disease treatment sales.
- North America maintained a dominant regional position in 2024, contributing approximately 36.9% of the market, valued at around US$ 2.37 billion.
Drug Class Analysis
In 2024, the Levodopa/Carbidopa section held a dominant market position in the Drug Class Segment of the Parkinson’s Disease Treatment Market and captured more than a 50.9% share. This dominance was linked to its strong clinical effectiveness and broad use as a first-line therapy. The drug combination helps restore dopamine balance in the brain, reducing motor symptoms such as tremors and stiffness. Its proven results and ability to improve quality of life continue to strengthen its market position.
Dopamine Agonists also accounted for a considerable market share. These drugs imitate dopamine action and are prescribed either alone in early stages or with Levodopa in later stages. Agents like Pramipexole and Ropinirole are key examples. MAO-B Inhibitors, including Rasagiline and Selegiline, are gaining traction for their ability to slow dopamine breakdown. Their neuroprotective role and safe profile make them a preferred option among patients and healthcare providers.
COMT Inhibitors such as Entacapone and Opicapone enhance Levodopa effectiveness by extending its duration. Anticholinergics remain used in limited cases, mainly for tremor control, though their side effects limit growth. Adenosine A2A Antagonists, led by Istradefylline, show promise for managing motor complications. Glutamate Antagonists like Amantadine help control dyskinesia in long-term treatment. Cholinesterase Inhibitors support cognitive health in Parkinson’s-related dementia, while new therapies under development indicate expanding treatment possibilities.
Disease Stage Analysis
In 2024, the Advanced-Stage Section held a dominant market position in the Disease Stage Segment of the Parkinson’s Disease Treatment Market and captured more than a 57.5% share. This dominance was driven by the high prevalence of patients in advanced stages and the growing use of complex treatment therapies. Advanced-stage Parkinson’s disease often requires multi-drug regimens, including levodopa-carbidopa combinations and deep brain stimulation. These treatments are more expensive and contribute significantly to the overall market revenue.
The advanced-stage segment was further strengthened by advancements in neurostimulation technologies and the rise of personalized treatment plans. A growing focus on patient-centered approaches and symptom-specific therapies supported this segment’s expansion. Continuous drug infusion systems and combination drug formulations enhanced treatment effectiveness. Moreover, pharmaceutical innovations and clinical trials targeting motor and non-motor symptoms added to the demand for advanced therapies in this stage of Parkinson’s disease.
The early-stage segment, although smaller in size, showed steady development during the same period. Its growth was supported by early disease detection, improved patient awareness, and increased adoption of first-line drugs such as MAO-B inhibitors and dopamine agonists. These medications help delay disease progression and improve daily functioning. As early diagnosis becomes more common and clinical outcomes improve, this segment is expected to expand further, contributing to balanced growth across both disease stages.
Route of Administration Analysis
In 2024, the Oral section held a dominant market position in the Route of Administration Segment of the Parkinson’s Disease Treatment Market and captured more than a 62.4% share. This dominance was mainly due to the ease of use and wide patient acceptance of oral drugs. Tablets and capsules such as levodopa and carbidopa remained the first choice for most patients. The affordability, familiarity, and availability of multiple brands and generics further supported the large market share of this segment.
The Subcutaneous segment was observed to grow steadily during the same period. This growth was linked to the increasing use of infusion pumps and injectable therapies for advanced-stage Parkinson’s disease. Continuous drug delivery helped reduce fluctuations in symptoms. Innovations in apomorphine injections and portable delivery systems improved treatment convenience. These advancements allowed healthcare providers to manage patients more effectively, especially those who responded poorly to oral medications.
The Transdermal and Inhalation routes also showed notable progress. Transdermal patches, such as rotigotine, provided a steady drug release and minimized gastrointestinal side effects. This route was especially beneficial for older patients with swallowing issues. The inhalation route gained attention with the launch of fast-acting levodopa inhalers that provided quick relief during “off” periods. However, high costs and limited availability restricted their adoption. Together, these alternative routes reflected the growing shift toward patient-friendly and innovative treatment options.
Distribution Channel Analysis
In 2024, the Hospital Pharmacies Section held a dominant market position in the Distribution Channel Segment of the Parkinson’s Disease Treatment Market, and captured more than a 45.2% share. This dominance was mainly due to the rising number of hospital-based treatments and advanced neurological care facilities. Hospital pharmacies were preferred for their access to prescription-only Parkinson’s drugs. The presence of skilled neurologists and the assurance of quality medicines further strengthened the preference for this distribution channel among patients and healthcare professionals.
The Retail Pharmacies Segment accounted for a significant portion of the market in 2024. Its growth was supported by the easy availability of prescribed and over-the-counter medications. Patients in semi-urban and rural areas preferred retail pharmacies due to their convenience and localized access. The guidance offered by pharmacists also helped improve patient trust. However, despite steady growth, this segment faced rising competition from the expanding network of online pharmacies.
The Online Pharmacies Segment is projected to record the fastest growth during the forecast period. The increasing adoption of digital healthcare platforms and home-delivery services has supported this trend. Patients are drawn to online channels for their affordability, discounts, and convenience. In addition, improved regulatory support for e-pharmacy operations has increased consumer confidence. The growing preference for remote healthcare and subscription-based drug delivery systems is expected to further accelerate the demand for online distribution of Parkinson’s disease treatments.
Key Market Segments
By Drug Class
- Levodopa/Carbidopa
- Dopamine Agonists
- MAO-B Inhibitors
- COMT Inhibitors
- Anticholinergics
- Adenosine A2A Antagonists
- Glutamate Antagonists
- Cholinesterase Inhibitors
- Others
By Disease Stage
- Early-Stage
- Advanced-Stage
By Route of Administration
- Oral
- Subcutaneous
- Transdermal
- Inhalation
By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies
Drivers
Advancements in Adaptive Deep Brain Stimulation (aDBS)
According to recent technological developments, the adoption of closed-loop or adaptive deep brain stimulation (aDBS) systems is significantly transforming Parkinson’s disease (PD) treatment. These advanced systems provide real-time feedback-based stimulation, optimizing therapy for individual patients. For instance, Medtronic received CE mark approval and U.S. regulatory clearance for its adaptive DBS system, which automatically adjusts stimulation parameters. This innovation enables more precise symptom management and positions Medtronic as the leading player in this high-end neuromodulation segment.
Clinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy and safety of adaptive DBS, strengthening its position in advanced PD care. A study published in JAMA Network found that adaptive DBS offered symptom control comparable to conventional DBS, with improved “on-time” and reduced dyskinesia. Similarly, MDPI reported that aDBS minimized speech-related side effects, enhancing patient outcomes. These findings validate adaptive DBS as a superior therapeutic alternative and have encouraged broader clinical acceptance and investment in adaptive neuromodulation systems.
According to Nature, the ADAPT-PD clinical trial revealed that sensing-enabled DBS systems successfully identified reliable local field potential (LFP) signals in over 90% of patients. This capability supports the feasibility of implementing effective feedback loops essential for adaptive stimulation. Such robust signal detection ensures consistent and precise stimulation adjustments. Consequently, device manufacturers are accelerating research and development in sensing-enabled implants, underscoring the growing trust in adaptive DBS technology.
The demonstrated technical feasibility and early clinical success of adaptive DBS are fueling market expansion in Parkinson’s disease treatment. For example, Medtronic’s regulatory achievements have set a competitive benchmark for innovation in neuromodulation. The ability of these systems to deliver personalized and dynamic therapy is attracting significant demand among healthcare providers and patients seeking advanced care options. Therefore, the adoption of adaptive DBS is expected to be a major driver for the global Parkinson’s disease treatment market in the coming years.
Restraints
Complexity and Regulatory Challenges for Novel Therapies
The development of new treatment modalities for Parkinson’s disease is highly complex and resource-intensive. Novel approaches such as gene and cell therapies require precise brain delivery, long-term safety validation, and strategies to overcome immune rejection. These scientific and technical hurdles, combined with regulatory uncertainty, slow down commercialization. For example, Bayer’s bemdaneprocel (a cell therapy for Parkinson’s) has reached Phase III trials, but approval is not expected before 2028 or 2029, demonstrating the lengthy timelines and risk involved.
According to PubMed, as of January 31, 2024, there were 136 active Phase 1–3 Parkinson’s drug trials. Among these, 58% were in Phase 2, 30% in Phase 1, and only 12% in Phase 3. The limited number of late-stage disease-modifying trials highlights the high barriers to entry and the extended development cycles. This imbalance indicates that despite promising innovations, the transition from early to advanced clinical stages remains slow and uncertain for transformative therapies.
A study by MDPI has emphasized that the translation of molecular discoveries into approved Parkinson’s treatments is hindered by critical gaps in biomarker validation, endpoint standardization, and translational readiness. For instance, the lack of reliable biomarkers complicates the assessment of disease-modifying effects, delaying clinical progress. These challenges increase the regulatory and scientific risks, limiting investment in next-generation therapies until more defined pathways and evaluation criteria are established.
Thus, although innovation in Parkinson’s research is advancing rapidly, regulatory and development complexities continue to restrain market growth. The absence of clear regulatory guidelines, coupled with scientific uncertainties, discourages many pharmaceutical players from entering or scaling in this segment. As a result, the progression of disease-modifying therapies remains slow, and the market continues to rely heavily on symptomatic treatment options.
Opportunities
Expansion Into Assistive Digital Systems For Daily Living And Safety
The Parkinson’s disease treatment landscape is evolving toward technologies that enhance patient independence and safety. Assistive digital systems present a strong growth opportunity in this direction. These systems focus on improving patients’ daily living and autonomy. For instance, PANDA, a multi-modality driving assistance and alert system, is being designed to monitor driving behavior in real time. It warns patients of irregular actions, ensuring safety and mobility. Such innovations extend treatment value beyond symptom control, opening new revenue avenues for healthcare and technology collaborations.
The growing focus on drug repurposing also strengthens opportunities within Parkinson’s disease treatment. According to the Parkinson’s Foundation, over one-third of current clinical trials are testing repurposed drugs as potential disease-modifying therapies. This approach reduces research risk and accelerates clinical development timelines. It enables pharmaceutical companies to leverage existing safety data while exploring new therapeutic indications for Parkinson’s, resulting in faster access to novel treatment options for patients.
Recent studies further highlight the promise of translational and genetic approaches in Parkinson’s research. A study published in Nature identified 175 Parkinson’s risk genes (pdRGs) and applied drug repurposing models. For example, simvastatin was associated with a 9% lower risk of Parkinson’s incidence and a reduced risk of dementia outcomes. Such findings indicate that integrating genetic profiling with repurposing strategies can support precision medicine and long-term disease modification in Parkinson’s care.
Additionally, advanced therapeutic modalities are emerging to complement repurposing efforts. For example, CGTlive reported that seven gene and cell therapy candidates are under investigation as long-term, disease-modifying solutions for Parkinson’s. These therapies aim to address the root causes of neurodegeneration rather than merely controlling symptoms. Combined with digital health systems and translational research, these innovations collectively position the Parkinson’s disease treatment market for sustainable growth and diversified investment opportunities.
Trends
Rise Of Rational Drug Repurposing And Translational Aggregating Protein Inhibitors
The Parkinson’s disease treatment landscape is witnessing a major shift toward disease-modifying and precision-based approaches. The focus is moving beyond symptomatic dopamine replacement to targeting the root causes of neurodegeneration. Rational drug repurposing and translational protein aggregation inhibitors are gaining prominence. For instance, therapies such as Translational Inhibitors of Neurotoxic Aggregating Proteins (TINAPs) and Sigma-1 receptor agonists are being explored to prevent toxic protein buildup and restore cellular homeostasis, marking a shift toward long-term disease control.
This evolution is also supported by the growing use of multimodal data and biomarker-based approaches. For example, a study published in npj Digital Medicine demonstrated how integrative analyses of clinical, imaging, and omics data helped define Parkinson’s disease PACE subtypes. Such methods enhance patient stratification, improve trial efficiency, and enable more personalized therapeutic interventions. These advancements are paving the way for more precise and data-driven drug development strategies in Parkinson’s disease management.
Additionally, the integration of sensing and neural feedback data is strengthening the use of biomarkers in PD treatment. The ADAPT-PD trial, for instance, showed that bilateral local field potential (LFP) signal detection—65% in medicated and 78% in unmedicated states—supports wider adoption of closed-loop neuromodulation. This indicates that real-time biomarker feedback can optimize therapy delivery, improving outcomes through adaptive stimulation systems.
However, despite strong progress, challenges remain in biomarker standardization and translational application. Reviews from MDPI emphasize that harmonizing biomarker frameworks across trials is crucial to ensure reproducibility and regulatory acceptance. Nonetheless, the growing alignment of digital health tools, biomarker integration, and patient stratification is steadily transforming Parkinson’s disease treatment into a more targeted, data-driven, and personalized therapeutic field.
Regional Analysis
In 2024, North America held a dominant position in the Parkinson’s Disease Treatment Market, capturing over 36.9% share and reaching a market value of around US$ 2.37 billion. The region’s leadership is supported by advanced healthcare infrastructure, strong awareness programs, and the presence of major pharmaceutical companies. The high diagnosis rate and early adoption of innovative treatment options have further strengthened its market position. Continuous improvements in healthcare delivery systems have enhanced patient access to advanced therapies and specialized neurological care.
The growth of the market in North America is mainly driven by a higher prevalence of Parkinson’s disease. The aging population contributes significantly to the increasing patient pool across the United States and Canada. Early diagnosis and better disease management approaches have supported higher treatment adoption. The demand for effective therapies continues to rise, supported by government initiatives and private healthcare investments. These factors together establish North America as a critical hub for neurological disorder management and treatment advancement.
The region benefits from a strong research and development ecosystem focused on neurodegenerative diseases. Universities, research institutions, and pharmaceutical firms actively conduct clinical trials for innovative drug formulations. Technological advances in drug delivery systems and precision medicine have improved treatment efficiency. Strategic collaborations between public organizations and private companies have accelerated new product approvals. This strong R&D network provides a competitive edge to the region, enabling faster commercialization of effective Parkinson’s therapies and supporting sustainable long-term growth in the treatment landscape.
North America’s future outlook in the Parkinson’s Disease Treatment Market remains positive. Increasing healthcare spending and expanding patient awareness programs are expected to sustain the region’s leadership. Growing investments in gene therapy, neuroprotective drugs, and personalized treatments will further enhance therapeutic outcomes. Supportive reimbursement structures and government funding for clinical research will encourage early adoption of novel therapies. The continued focus on innovation and accessibility will ensure North America maintains its leading position in the global Parkinson’s disease treatment market.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherland
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- New Zealand
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
The Parkinson’s disease treatment market is highly competitive and includes global pharmaceutical leaders focusing on both symptomatic and disease-modifying therapies. Companies are investing in innovative drug delivery systems, neuroprotective research, and long-acting formulations. The growing prevalence of Parkinson’s disease and the increasing need for advanced treatment options have encouraged continuous product development. Strategic collaborations, research partnerships, and new product approvals are shaping the competitive landscape and driving steady market expansion across major regions.
AbbVie Inc. remains a significant player with its infusion-based therapies such as Duopa/Duodopa and the newly approved VYALEV™, a 24-hour subcutaneous levodopa infusion. This innovation reduces the need for invasive procedures and enhances patient compliance. AbbVie’s focus on advanced drug delivery and global expansion strengthens its leadership position. Similarly, UCB S.A. maintains a stable presence through Neupro®, a transdermal dopamine agonist, ensuring consistent revenue in chronic symptom management. Both companies are expected to drive future market growth.
Other major players such as Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., GlaxoSmithKline plc, and Boehringer Ingelheim GmbH contribute primarily through their established products and generics. Teva’s Azilect® and Boehringer’s Mirapex® continue to hold relevance despite patent expiries. GlaxoSmithKline’s Requip® has transitioned to generic form but retains therapeutic importance. These companies leverage brand recognition, broad distribution networks, and legacy portfolios to maintain competitiveness amid growing biologic and infusion-based innovations.
Emerging and research-driven players such as Roche Holding AG, Amgen Inc., and Sanofi S.A. are focusing on disease-modifying approaches. Roche’s prasinezumab, targeting α-synuclein aggregation, has shown potential in late-stage trials. Sanofi’s collaborations in neuroscience and Amgen’s R&D in neuroprotection represent promising long-term opportunities. Meanwhile, generic producers like Viatris (Mylan N.V.) and Sunovion Pharmaceuticals ensure accessibility in cost-sensitive markets. Overall, the market’s competitive dynamics are expected to intensify as new therapies and continuous infusion technologies gain adoption globally.
Market Key Players
- AbbVie Inc.
- Amgen Inc.
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
- GlaxoSmithKline plc
- Merck & Co. Inc.
- Pfizer Inc.
- UCB S.A.
- Lundbeck A/S
- Boehringer Ingelheim GmbH
- Sanofi S.A.
- Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Mylan N.V.
- Roche Holding AG
- Other key players
Recent Developments
- In April 2025: Amgen emphasises neurology / neurodegenerative programs at R&D Day: In its “First Research & Development Day” disclosure, Amgen highlighted that its neurology program is focused on discovering and developing therapeutics targeting neurodegenerative diseases, including Parkinson’s disease. This signals that Amgen is actively positioning or advancing projects in the neurology / Parkinson’s sphere, even if specific molecule names or trial details were not publicly disclosed in that announcement.
- In November 2024: A multi-target strategic alliance was announced with Vesalius Therapeutics to discover and develop Parkinson’s disease (PD) treatments. GSK agreed to provide $80 million in upfront and equity payments, with total potential biobucks up to ~$570 million, and obtained worldwide rights to a preclinical small-molecule program initially focused on PD, plus options to advance additional neurodegeneration programs.
- In July 2024: Participation was confirmed in the FNIH Accelerating Medicines Partnership in Parkinson’s Disease & Related Disorders (AMP PDRD), a $21 million public-private biomarker initiative. The program is designed to validate seed amplification assays and identify biomarkers that differentiate PD from related synucleinopathies, supporting precision drug development.
- In May 2024: Teva announced U.S. FDA approval of AUSTEDO XR, an extended-release, once-daily tablet formulation of deutetrabenazine (VMAT2 inhibitor) for the treatment of tardive dyskinesia and chorea in Huntington’s disease. While AUSTEDO is not explicitly a Parkinson’s drug, its use in movement disorder pharmacology is adjacent to Parkinson’s therapy spaces, and the XR formulation represents a strategic expansion of Teva’s movement / neurodegenerative disorder offerings.
- In January 2024: AbbVie launched PRODUODOPA® (foslevodopa/foscarbidopa) in the European Union for people with advanced Parkinson’s disease suffering from severe motor fluctuations. PRODUODOPA is the first and only subcutaneous 24-hour infusion of a levodopa-based therapy for this indication, providing continuous dopaminergic delivery to reduce off times and stabilize motor symptoms.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) US$ 6.42 Billion Forecast Revenue (2034) US$ 11.28 Billion CAGR (2025-2034) 5.8% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, COVID-19 Impact, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Drug Class (Levodopa/Carbidopa, Dopamine Agonists, MAO-B Inhibitors, COMT Inhibitors, Anticholinergics, Adenosine A2A Antagonists, Glutamate Antagonists, Cholinesterase Inhibitors, Others), By Disease Stage (Early-Stage, Advanced-Stage), By Route of Administration (Oral, Subcutaneous, Transdermal, Inhalation), By Distribution Channel (Hospital Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies, Online Pharmacies) Regional Analysis North America – The US, Canada, & Mexico; Western Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Portugal, Ireland, Austria, Switzerland, Benelux, Nordic, & Rest of Western Europe; Eastern Europe – Russia, Poland, The Czech Republic, Greece, & Rest of Eastern Europe; APAC – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia & New Zealand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, & Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Colombia, Chile, Argentina, Costa Rica, & Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – Algeria, Egypt, Israel, Kuwait, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, & Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape AbbVie Inc., Amgen Inc., Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., GlaxoSmithKline plc, Merck & Co. Inc., Pfizer Inc., UCB S.A., Lundbeck A/S, Boehringer Ingelheim GmbH, Sanofi S.A., Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc., Mylan N.V., Roche Holding AG, Other key players Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Parkinson’s Disease Treatment MarketPublished date: Oct 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Parkinson’s Disease Treatment MarketPublished date: Oct 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- AbbVie Inc.
- Amgen Inc.
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
- GlaxoSmithKline plc
- Merck & Co. Inc.
- Pfizer Inc.
- UCB S.A.
- Lundbeck A/S
- Boehringer Ingelheim GmbH
- Sanofi S.A.
- Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Mylan N.V.
- Roche Holding AG
- Other key players










