Global Nucleic Acid Amplification Testing Market Analysis By Technology (Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), Isothermal Nucleic Acid Amplification Technology (INAAT), Ligase Chain Reaction (LCR)), By Product (Instruments and systems, Consumables & kits), By Application (Infectious disease testing, Oncology testing, Genetic & mitochondrial disease testing, Blood Screening & Transplant Testing, Research and Forensic Applications, Others), By End-User (Hospitals, Central & Reference Laboratories, Academic & Research Institutes, Others) By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Nov 2025
- Report ID: 164574
- Number of Pages: 363
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
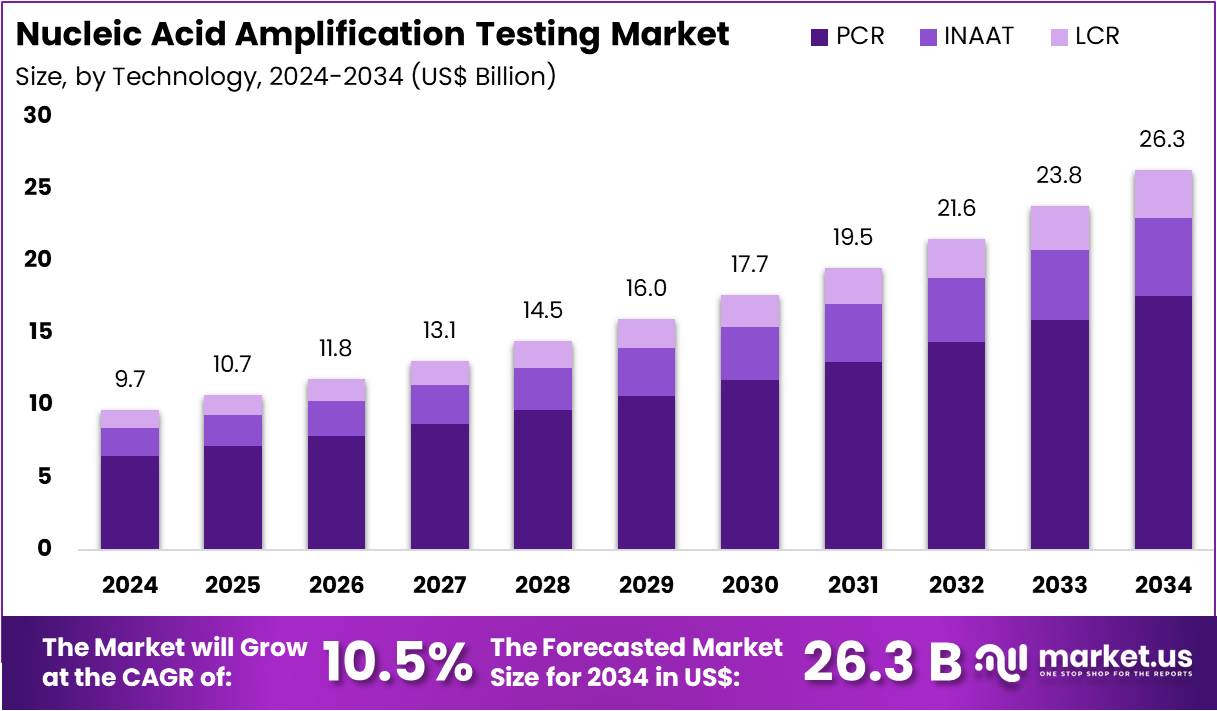
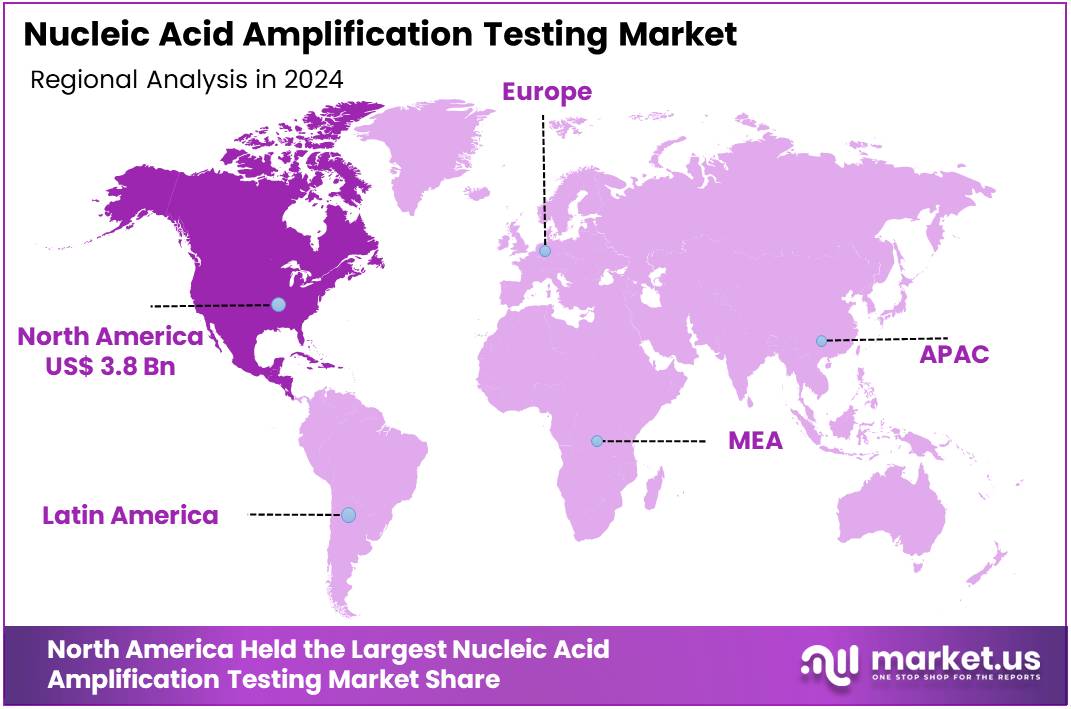
The Global Nucleic Acid Amplification Testing Market size is expected to be worth around US$ 26.3 Billion by 2034, from US$ 9.7 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 10.5% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 39.4% share and holds US$ 3.8 Billion market value for the year.
Nucleic Acid Amplification Testing is recognized as a core molecular method that enhances the detection of pathogenic DNA or RNA. The technique is widely applied because targeted genetic material is amplified before measurement, which increases sensitivity. According to global laboratory practice, this process allows pathogens to be identified even at very low concentrations. The approach supports early diagnosis, more accurate clinical decisions, and greater reliability compared to many conventional laboratory methods.
Adoption of molecular diagnostics has widened as healthcare systems seek faster and more precise results. Clinical laboratories and hospitals rely on NAAT because the method improves case-finding during early infection stages. This trend is visible in tuberculosis testing. Study by the WHO reported that a rapid molecular test was used as the first diagnostic step for 48 percent of newly detected tuberculosis cases in 2023. This value equaled 3.9 million of 8.2 million cases and reflected an increase from 47 percent in 2022.
Procurement stability has strengthened due to clearer regulatory pathways for molecular systems. More countries are now able to acquire standardized NAAT platforms because prequalification reduces purchasing barriers. This improvement was demonstrated when WHO listed Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra on 29 November 2024. According to the public listing, the prequalification supports streamlined government procurement. For instance, lower-income regions are expected to benefit because funding agencies typically rely on prequalified products to approve large-volume orders.
Long-term investment in laboratory infrastructure has also increased global NAAT readiness. Many countries expanded molecular capacity after the pandemic revealed gaps in diagnostic coverage. The World Bank–hosted Pandemic Fund announced that 885 million US dollars had been awarded through its first two rounds. This financing catalyzed more than 6 billion US dollars in additional support and funded activities in 75 countries. According to the Fund, these projects include upgrades to laboratory systems, disease surveillance, and workforce training.
Key Policy Catalysts and Evolving Diagnostic Demand
Public-health agencies continue to position NAAT as the preferred method for confirming respiratory infections. Clinical settings rely on NAAT because its analytical accuracy remains higher than many rapid alternatives. WHO guidance states that NAAT such as rRT-PCR provides the most sensitive and specific confirmation for COVID-19. The ECDC also advises testing respiratory specimens with multiplex PCR to detect influenza, SARS-CoV-2, and other viruses. For example, such recommendations keep testing volumes elevated during seasonal disease peaks.
Broadened diagnostic needs have expanded NAAT use beyond traditional respiratory and tuberculosis applications. More countries are integrating molecular testing into surveillance for emerging infections such as mpox. According to updated WHO guidance issued in 2024, mpox confirmation must rely on NAAT. The organization further reported that nine mpox NAATs had been included under its Emergency Use Listing by September 2025. For instance, this listing signals that molecular throughput will remain high as mpox surveillance becomes routine.
Sexual health programs have also sustained NAAT demand because molecular detection improves case-finding for common infections. Health agencies prefer NAAT for identifying conditions that require high sensitivity. CDC surveillance recorded more than 2.5 million reportable STI cases in 2022, creating substantial testing volumes. According to CDC recommendations, clinicians should also use molecular methods when evaluating suspected influenza or COVID-19 in symptomatic patients. These guidelines indicate that regular cartridge consumption is expected to remain stable.
Molecular confirmation is equally important for chronic viral infections and antimicrobial resistance programs. Hepatitis C case-finding requires NAAT after a positive antibody result to determine active infection. CDC guidance names real-time PCR as the preferred tool for detecting Candida auris colonization, reflecting rising concern around resistant pathogens. Study by CDC noted that no high-throughput FDA-approved assays exist for colonization swabs, requiring laboratories to validate PCR workflows. This gap has created ongoing demand for NAAT screening in high-risk facilities.
Stronger diagnostic infrastructure for influenza further supports market growth. Many national laboratories maintain robust NAAT capacity because rapid identification is essential during zoonotic or seasonal outbreaks. An ECDC survey confirmed that 94 percent of responding national laboratories use RT-PCR for avian influenza, with many running multiplex panels. OECD data reported that per-capita health spending rose by an average of 3.3 percent annually from 2019 to 2022, with slight positive growth estimated for 2023. According to these spending trends, multi-year procurement of NAAT systems and consumables has become more feasible, supporting stable and recurrent market expansion.
Key Takeaways
- The global nucleic acid amplification testing market is projected to reach nearly US$ 26.3 billion by 2034, supported by a steady 10.5 percent CAGR from 2025.
- The polymerase chain reaction segment was reported to command over 66.8% of the technology share in 2024, reflecting its broad clinical adoption and reliability.
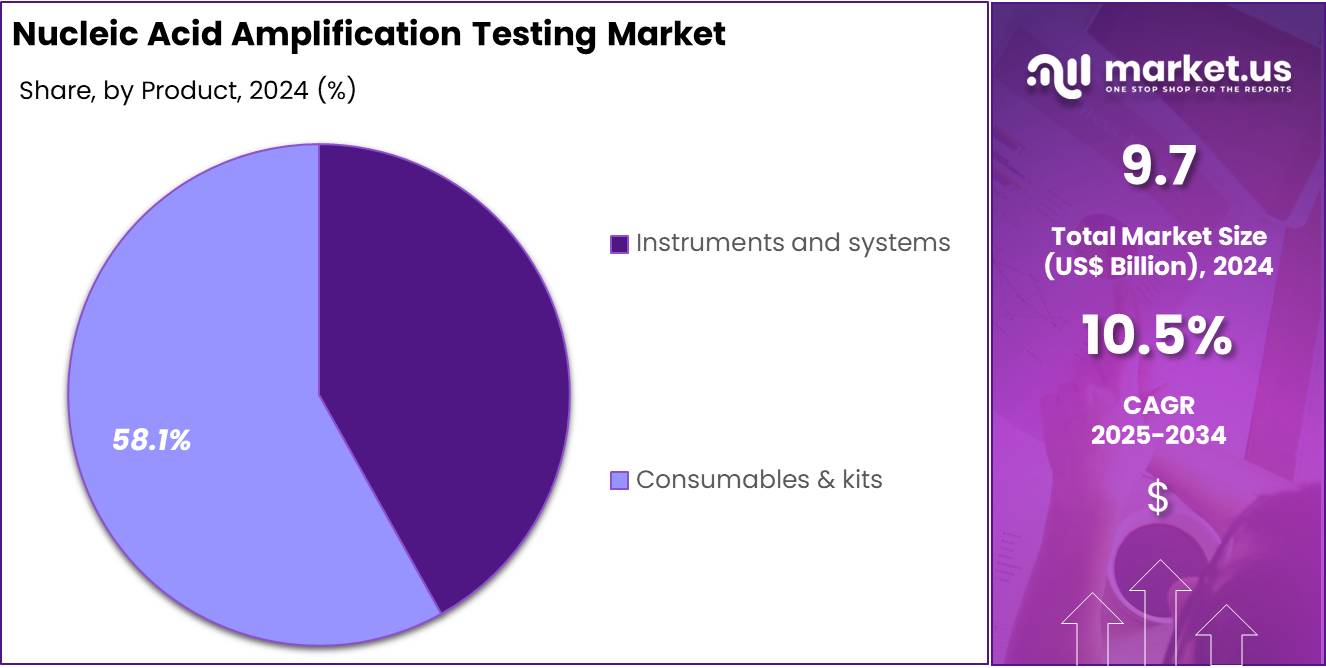
- Consumables and kits were noted to account for more than 58.1% of the product share in 2024, driven by recurring demand in diagnostic workflows.
- Infectious disease testing was observed to hold over 47.5% of the application share in 2024, supported by rising screening needs across global healthcare systems.
- Hospitals were seen to secure more than 40.2% of the end user share in 2024, as these facilities remained primary centers for advanced molecular diagnostics.
- In 2024, North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 39.4% share and holds US$ 3.8 billion market value for the year.
Technology Analysis
In 2024, the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Section held a dominant market position in the Technology Segment of the Nucleic Acid Amplification Testing Market, and captured more than a 66.8% share. This trend was observed due to the strong clinical reliability of PCR. Its high sensitivity supported broad diagnostic coverage. Real-time systems improved accuracy. Laboratories favored its stable workflows. These factors strengthened its adoption. PCR systems also supported scalable testing. This contributed to consistent use across healthcare settings.
The Isothermal Nucleic Acid Amplification Technology (INAAT) section was noted for steady growth. Its expansion was supported by faster reactions and low equipment needs. These features enhanced point-of-care testing. LAMP assays gained strong attention due to simple designs. TMA platforms showed progress in high throughput testing. NEAR and HDA methods saw moderate uptake. CRISPR-based amplification was highlighted for high specificity. SDA and other INAAT formats remained useful in selective applications across emerging diagnostic workflows.
The Ligase Chain Reaction (LCR) section was identified as a smaller but relevant segment. Its growth remained gradual. Usage was focused on mutation detection and targeted analyses. Adoption patterns reflected specialized clinical and research demands. Broader market trends indicated rising interest in rapid testing formats. Increasing awareness of accurate pathogen detection supported overall technology advancement. The shift toward decentralized diagnostics continued. These factors contributed to a positive outlook for innovation across nucleic acid amplification technologies.
Product Analysis
In 2024, the Consumables & Kits section held a dominant market position in the product segment of the Nucleic Acid Amplification Testing market, and captured more than a 58.1% share. This position was viewed as a result of high testing frequency across clinical settings. Each diagnostic cycle required primers, probes, and reagents. These items were used repeatedly. Their continuous use supported strong revenue generation. Increased adoption of molecular tests also strengthened the segment’s overall influence.
The prominence of this segment was described as a natural outcome of its replacement cycle. Every test consumed specific kits and reagents. This pattern created predictable demand. Hospitals and laboratories depended on these products for routine workflows. Testing volumes expanded in infectious disease screening. This expansion increased consumption rates. Industry observers noted that recurring purchases formed the core of the segment’s growth. The steady adoption of molecular diagnostics added further momentum.
The Instruments and Systems segment accounted for the remaining market share. Its progress was considered stable. New platform installations supported its growth. Automation features improved testing efficiency. Throughput enhancements increased laboratory interest. However, the purchase cycle for instruments was longer. This limited rapid market expansion. Analysts observed that upgrades in clinical and research facilities sustained moderate growth. The overall product landscape continued to rely on consumable components. This reliance was expected to shape future demand patterns.
Application Analysis
In 2024, the Infectious disease testing section held a dominant market position in the Application Segment of the Nucleic Acid Amplification Testing Market, and captured more than a 47.5% share. The strong position was supported by the high burden of viral and bacterial infections. The rising use of molecular assays in routine diagnostics also contributed to this dominance. The demand for fast and accurate pathogen detection increased further due to the growth of hospital-acquired infections. As a result, testing volumes continued to rise across public and private laboratories.
The adoption of advanced instruments and systems increased steadily. Growth was driven by the shift toward fully automated platforms. These platforms offered improved workflow efficiency and greater sensitivity. The integration of real-time monitoring technologies supported the rise in adoption. System upgrades were encouraged by the need for high-throughput testing. The expansion of laboratory networks also contributed to higher installation rates. The overall revenue from instruments and systems showed stable growth across developed markets.
Consumables and kits accounted for a significant share of recurring revenue. Their growth was supported by continuous testing needs in clinical and research settings. The increased use of cartridge-based assays strengthened the consumables segment. High utilization rates were observed in infectious disease diagnostics. This trend was supported by rising test volumes and expanding pathogen panels. The availability of ready-to-use reagents ensured streamlined workflows and reduced turnaround times. As a result, consumables and kits remained a key revenue driver in this market.
The dominance of infectious disease testing created long-term momentum for both equipment and consumables. Instruments and systems benefited from ongoing automation trends. Consumables and kits benefited from repeat purchases driven by high test frequency. The combined performance of both segments indicated sustained market growth. Future expansion is expected to be supported by broader adoption in point-of-care and decentralized testing environments.
End-User Analysis
In 2024, the Hospitals Section held a dominant market position in the End-User Segment of the Nucleic Acid Amplification Testing Market, and captured more than a 40.2% share. This position was supported by large testing volumes. The wider use of advanced molecular systems in hospital laboratories also strengthened growth. Increased demand for rapid pathogen detection was observed. Adoption in emergency units and inpatient services added further support. These factors were viewed as key drivers of the segment.
The demand for instruments and systems within hospitals increased steadily. Higher installation rates were linked to expanded molecular testing capacity. Automation improved workflow efficiency in many facilities. High-throughput platforms were adopted to manage rising sample loads. Reliability and reduced turnaround times were considered important benefits. Consumables and kits also showed stable demand. Regular use of reagents and assays supported recurring revenue. Hospital-acquired infection monitoring programs further increased consumables usage across multiple departments.
Diagnostic laboratories maintained the second-largest share of end users. Their adoption of NAAT platforms was driven by outsourcing trends. Many labs sought greater accuracy and faster processing. Standardized workflows supported wider acceptance. Research institutes and academic centers contributed a smaller share. Their demand was linked to genetic studies and assay development. Funding programs encouraged the use of advanced NAAT systems. Overall market expansion was supported by higher infectious disease burdens and growing awareness of molecular testing benefits.
Key Market Segments
By Technology
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
- Isothermal Nucleic Acid Amplification Technology (INAAT)
- Nicking endonuclease amplification reaction (NEAR)
- Transcription mediated amplification (TMA)
- Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP)
- Helicase-dependent amplification (HDA)
- Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)
- Strand displacement amplification (SDA)
- Others
- Ligase Chain Reaction (LCR)
By Product
- Instruments and systems
- Consumables & kits
By Application
- Infectious disease testing
- Tuberculosis testing
- Influenza testing
- COVID-19 testing
- Hepatitis testing
- Sexually transmitted infections testing
- Mosquito borne disease testing
- Others
- Oncology testing
- Genetic & mitochondrial disease testing
- Blood Screening & Transplant Testing
- Research and Forensic Applications
- Others
By End-User
- Hospitals
- Central & Reference Laboratories
- Academic & Research Institutes
- Others
Drivers
Expanding Infectious-Disease Burden Driving NAAT Adoption
The rising burden of infectious diseases has been strengthening the adoption of nucleic acid amplification testing. Growth has been supported by the need for rapid and accurate detection, particularly in settings where conventional diagnostics face performance limitations. High global case volumes have sustained the requirement for sensitive tools that identify infections at early stages. NAAT has been preferred because its detection limits enable identification of pathogens present in very small quantities, which supports timely treatment and reduces transmission risk.
Significant increases in priority infections have reinforced the reliance on molecular testing. An estimated 10.6 million people developed tuberculosis in 2022, according to the World Health Organization. High incidence rates in South-East Asia, Africa, and the Western Pacific have maintained testing needs across public health programs. The presence of TB and HIV coinfections has further increased the demand for high-sensitivity diagnostics. NAAT methods have been used because they detect low bacterial loads that traditional tests may miss.
Sustained levels of sexually transmitted infections and malaria have also contributed to NAAT uptake. More than 2.5 million chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis cases were recorded in the United States in 2022, and the burden remained above 2.2 million in 2024. Testing programs continued to rely on NAAT because of its precision in detecting asymptomatic infections. In malaria elimination settings, NAAT has been valued for its ability to detect infections below 1 parasite per microliter. This capability supports case identification where microscopy and rapid tests show limited sensitivity.
Restraints
High Cost and Infrastructure Requirements
High operational and infrastructure demands continue to restrict wider adoption of nucleic acid amplification testing. Implementation requires advanced instruments, climate-controlled environments, and trained laboratory personnel. These needs raise capital and operational expenditures, especially in decentralized and resource-limited settings. As a result, scaling remains constrained. Stakeholders often report that laboratories outside major centers face difficulties in sustaining equipment maintenance and meeting quality system requirements, which reinforces the overall cost burden and slows broader deployment.
Economic pressure is intensified by the high share of consumables in the total test cost. Cartridge prices for GeneXpert MTB/RIF Ultra were reduced to US$7.97 in 2023, yet affordability concerns persist in low- and middle-income countries. Cost analyses indicate that consumables account for about 67 percent of total per-test expenses. Additional variability arises from site-level overheads and staffing costs. These combined factors elevate the real-world financial load and continue to influence procurement decisions.
Regulatory developments have further expanded compliance obligations. The FDA’s final rule on laboratory-developed tests in April 2024 introduced new validation and reporting requirements. Providers and laboratories now face heightened documentation and oversight needs. These adjustments increase administrative costs and contribute to operational complexity. Legal challenges have emerged, adding uncertainty for some NAAT operators. This evolving regulatory landscape, when combined with persistent cost and infrastructure barriers, continues to limit the pace of NAAT scale-up across diverse healthcare environments.
Opportunities
Growth Opportunity in Decentralized NAAT Platforms
The expansion of point-of-care molecular platforms is expected to create strong growth potential for nucleic acid amplification testing. Wider authorization of portable NAAT systems has increased availability across clinical settings. Their rapid turnaround times and high analytical accuracy have supported broader acceptance among healthcare providers. The market outlook has been strengthened by continued regulatory activity, as emergency and traditional approval pathways have enabled a steady flow of decentralized molecular tests.
Adoption has been reinforced by the rise of compact, cartridge-based devices that function outside centralized laboratories. The presence of multiple FDA-authorized point-of-care molecular assays between 2022 and 2024 indicates growing maturity of portable NAAT solutions. These platforms have improved patient access in urgent care, emergency departments and underserved areas. Their operational simplicity and minimal training requirements have advanced the shift toward near-patient molecular diagnostics.
Regulatory progress has further accelerated commercialization prospects. Approvals such as Visby Medical’s handheld sexual health NAAT, which obtained 510(k) clearance and a CLIA waiver in 2023, demonstrate expanding acceptance of decentralized molecular testing. The ability of such systems to deliver single-use, laboratory-quality results supports their integration into routine clinical workflows. As a result, decentralized NAAT technologies are positioned to play a key role in expanding testing coverage and supporting market growth.
Trends
Expansion of Automation and Digital Workflows in NAAT Platforms
The adoption of advanced automation systems has been strengthening the operational landscape for nucleic acid amplification testing. Automated sample preparation and integrated high-throughput instruments have been improving the precision of NAAT workflows. The growth of these systems has been driven by the need to reduce manual steps and lower human error. Evidence from recent reviews has shown that automation supports stable test performance and enables laboratories to manage higher specimen volumes with consistent reliability.
Digital workflow integration has been advancing the efficiency of NAAT operations. Cloud-enabled reporting and links with laboratory information systems have been shortening turnaround times. These tools have created standardized data pathways and reduced reporting inconsistencies. Findings from 2022 to 2024 have indicated that Lean and automation-based approaches provide measurable gains in turnaround time. The improvements have strengthened the ability of laboratories to deliver rapid molecular results during periods of high demand.
Multiplex molecular solutions have been gaining broader adoption within NAAT platforms. Clinical assessments from 2023 and 2024 have reinforced that NAAT maintains the highest sensitivity for SARS-CoV-2 and other respiratory pathogens. The shift toward multiplex panels cleared through established regulatory pathways has supported more efficient pathogen detection. These panels allow simultaneous testing and decrease the need for multiple assays. The combination of automation, multiplexing, and digital reporting has expanded the capacity of laboratories to deliver timely and accurate molecular diagnoses.
Regional Analysis
In 2024, North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 39.4% share and holds US$ 3.8 billion market value for the year. This position was viewed as the outcome of mature diagnostic networks and strong clinical adoption of nucleic acid amplification testing. Consistent testing demand across hospitals and laboratories supported regional strength. The widespread integration of advanced molecular platforms further reinforced usage. Steady investment in diagnostic technologies also contributed to the stability and scale of the market.
Regional growth was understood to be driven by a high incidence of infectious diseases, which increased the need for precise detection tools. Early diagnosis practices encouraged the adoption of amplification methods. Point of care expansion improved test availability in underserved areas. Regulatory frameworks ensured product reliability and guided technical progress. These factors collectively strengthened the region’s ability to maintain leadership. Ongoing improvements in laboratory capacity also supported continuous uptake.
Observers noted that sustained research activity contributed significantly to market advancement. Universities and diagnostic developers worked on improving sensitivity and reducing processing time. Public and private funding accelerated innovation and supported faster movement from prototype to commercial use. This environment enabled laboratories to adopt new assays more rapidly. As testing technologies became more refined, user confidence increased. These conditions created a stable foundation for long term regional competitiveness in nucleic acid amplification testing.
Reimbursement structures were seen as a key factor shaping adoption patterns. Coverage for molecular tests reduced cost barriers for clinical providers and patients. This improved test utilization across diverse care settings. Laboratories invested in upgraded systems to meet rising diagnostic needs. Strong healthcare expenditure, combined with enhanced disease surveillance, further supported market resilience. Analysts expect North America to retain its lead as new automated and high throughput platforms enter the field, strengthening diagnostic efficiency and supporting sustained market expansion.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherland
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- New Zealand
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
The nucleic acid amplification testing market has been shaped by major global diagnostics companies. F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. has maintained a strong position due to its automated PCR systems and broad infectious disease menu. Abbott Laboratories has expanded its molecular testing footprint through high-throughput and point-of-care platforms. Becton Dickinson and Company has focused on integrated workflows that improve operational efficiency. Danaher Corporation has strengthened its share through rapid, cartridge-based technologies that support decentralized testing in clinical settings worldwide.
bioMérieux SA has advanced its position with multiplex PCR systems that deliver faster pathogen detection. Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. has supported large testing volumes through its wide reagent and instrument portfolio. QIAGEN N.V. has remained competitive due to strong sample preparation technologies and expanding syndromic panels. Siemens Healthineers has integrated molecular diagnostics into broader laboratory ecosystems. Each company has used strategic investments to enhance testing accuracy, reduce turnaround times, and address rising global diagnostic needs.
Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc. has contributed to market expansion through PCR platforms and quality assurance tools. Seegene Inc. has built a strong presence with its advanced multiplex assay design and automated workflows. Hologic Inc. has increased adoption of high-throughput NAAT systems that support women’s health testing. Agilent Technologies Inc. has leveraged its molecular reagents and analytical systems to strengthen its clinical footprint. These companies have focused on automation, standardization, and innovation to support rising demand across laboratories and healthcare networks.
Molbio Diagnostics Limited has expanded NAAT accessibility through portable PCR solutions designed for decentralized settings. Illumina Inc. has supported the ecosystem with genomic technologies that complement NAAT workflows. Mylab Discovery Solutions has increased adoption in developing regions with cost-efficient kits and instruments. Randox Laboratories Ltd. has strengthened its reach using integrated molecular platforms that support multiplex testing. Collectively, these companies have contributed to growing test capacity, improved disease surveillance, and broader molecular diagnostic coverage across global healthcare systems.
Market Key Players
- F. Hoffmann‑La Roche Ltd.
- Abbott Laboratories
- Becton Dickinson and Company
- Danaher Corporation
- bioMérieux SA
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- QIAGEN N.V.
- Siemens Healthineers
- Bio‑Rad Laboratories Inc.
- Seegene Inc.
- Hologic Inc.
- Agilent Technologies Inc.
- Molbio Diagnostics Limited
- Illumina Inc.
- Mylab Discovery Solutions
- Randox Laboratories Ltd.
Recent Developments
- In March 2024: FDA approval was granted for Roche’s cobas® Malaria NAAT for use on the cobas® 6800/8800 Systems to screen U.S. blood donors for Plasmodium DNA/RNA, the first FDA-approved molecular test for donor screening of malaria in the U.S.
- In June 2024: The cobas® liat SARS-CoV-2, Influenza A/B & RSV rapid multiplex NAAT received U.S. FDA Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) and CE-IVDR marking, enabling ~20-minute point-of-care detection and differentiation of four respiratory viruses.
- In October 2024: The World Health Organization granted Emergency Use Listing for Abbott’s Alinity m MPXV assay, a real-time PCR nucleic acid amplification test for detection of monkeypox (clade I/II), expanding global access to NAAT-based mpox diagnostics.
- In August 2023: The U.S. FDA granted 510(k) clearance and a CLIA waiver for Abbott’s ID NOW COVID-19 2.0 rapid NAAT, permitting point-of-care use for qualitative detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA.
- In May 2024: U.S. FDA approval (PMA supplement) for the BD Onclarity HPV Assay for use on the BD Viper LT and BD COR systems, enabling nucleic acid detection and extended genotyping of 14 high-risk HPV types for cervical cancer screening. This reinforced BD’s NAAT portfolio in women’s health.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) US$ 9.7 Billion Forecast Revenue (2034) US$ 26.3 Billion CAGR (2025-2034) 10.5% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, COVID-19 Impact, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Technology (Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), Isothermal Nucleic Acid Amplification Technology (INAAT) (Nicking endonuclease amplification reaction (NEAR), Transcription mediated amplification (TMA), Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP), Helicase-dependent amplification (HDA), Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR), Strand displacement amplification (SDA), Others), Ligase Chain Reaction (LCR)), By Product (Instruments and systems, Consumables & kits), By Application (Infectious disease testing (Tuberculosis testing, Influenza testing, COVID-19 testing, Hepatitis testing, Sexually transmitted infections testing, Mosquito borne disease testing, Others), Oncology testing, Genetic & mitochondrial disease testing, Blood Screening & Transplant Testing, Research and Forensic Applications, Others), By End-User (Hospitals, Central & Reference Laboratories, Academic & Research Institutes, Others) Regional Analysis North America – The US, Canada, & Mexico; Western Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Portugal, Ireland, Austria, Switzerland, Benelux, Nordic, & Rest of Western Europe; Eastern Europe – Russia, Poland, The Czech Republic, Greece, & Rest of Eastern Europe; APAC – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia & New Zealand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, & Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Colombia, Chile, Argentina, Costa Rica, & Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – Algeria, Egypt, Israel, Kuwait, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, & Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape F. Hoffmann‑La Roche Ltd., Abbott Laboratories, Becton Dickinson and Company, Danaher Corporation, bioMérieux SA, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., QIAGEN N.V., Siemens Healthineers, Bio‑Rad Laboratories Inc., Seegene Inc., Hologic Inc., Agilent Technologies Inc., Molbio Diagnostics Limited, Illumina Inc., Mylab Discovery Solutions, Randox Laboratories Ltd. Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Nucleic Acid Amplification Testing MarketPublished date: Nov 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Nucleic Acid Amplification Testing MarketPublished date: Nov 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- F. Hoffmann‑La Roche Ltd.
- Abbott Laboratories
- Becton Dickinson and Company
- Danaher Corporation
- bioMérieux SA
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- QIAGEN N.V.
- Siemens Healthineers
- Bio‑Rad Laboratories Inc.
- Seegene Inc.
- Hologic Inc.
- Agilent Technologies Inc.
- Molbio Diagnostics Limited
- Illumina Inc.
- Mylab Discovery Solutions
- Randox Laboratories Ltd.










