Global Microgreens Market By Type (Broccoli, Cabbage, Cauliflower, Mesclun, Peas, Radish, Basil, Carrots, Lettuce and Chicory, Beetroot, Sunflower, Others), By Farming Method (Indoor Vertical Farming, Commercial Greenhouse Farming, Others), By Growth Medium (Peat Moss, Soil, Coconut Coir, Tissue Paper, Others), By End-User (Commercial, Residential), By Distribution Channel (Retail Store, Online Store, Farmers Market, Hypermarkets/ Supermarkets, Restaurants, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Sep 2025
- Report ID: 158662
- Number of Pages: 206
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
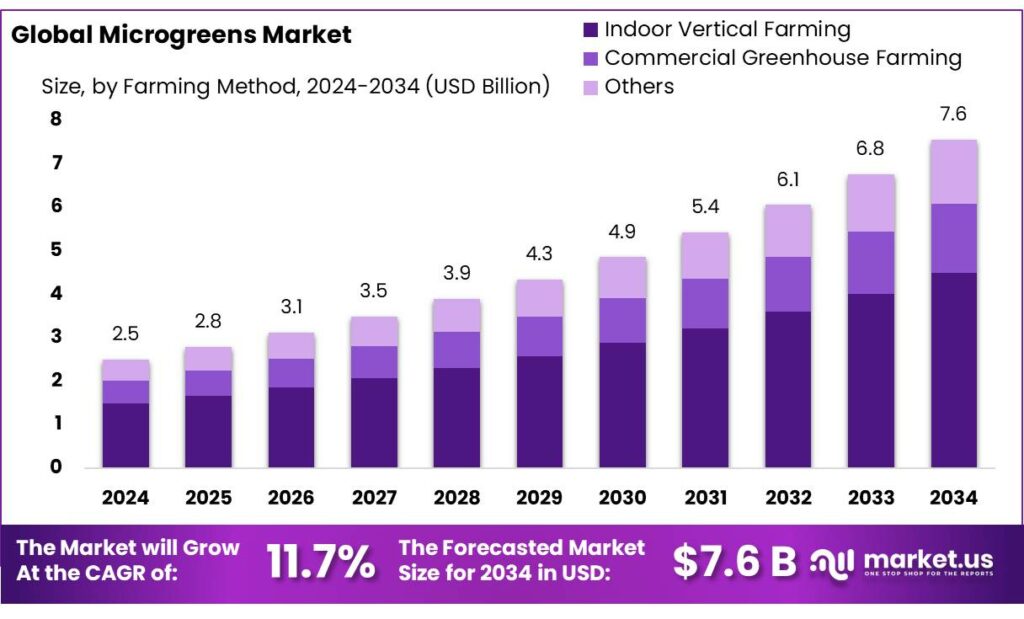
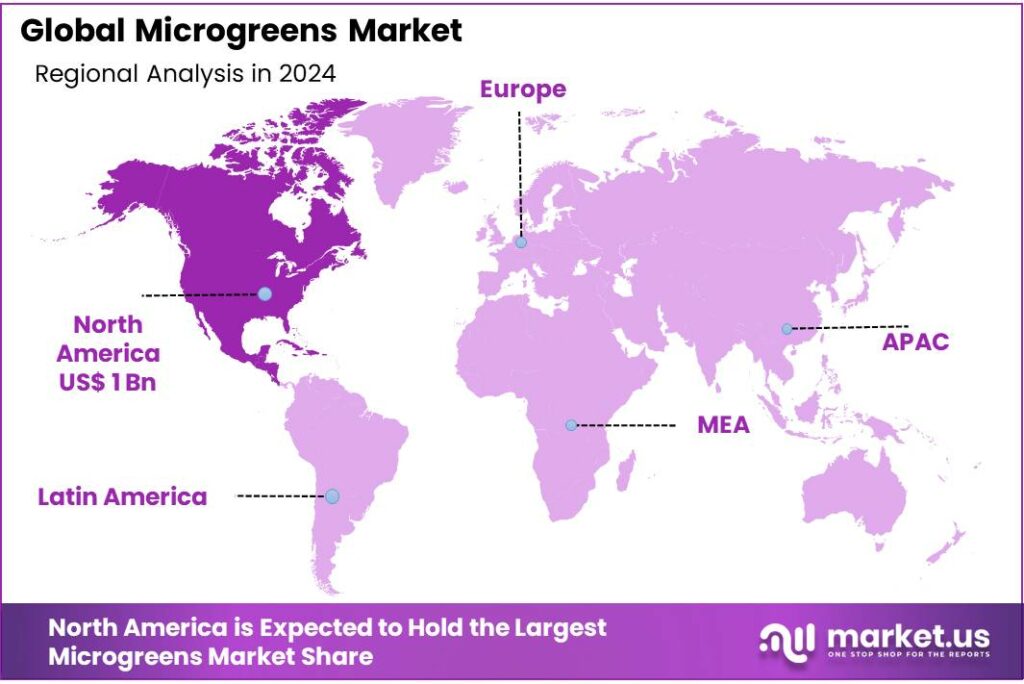
The Global Microgreens Market size is expected to be worth around USD 7.6 Billion by 2034, from USD 2.5 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 11.7% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024 North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.9% share, holding USD 1.0 Billion in revenue.
The microgreens industry in India is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing health consciousness, urbanization, and government support. Microgreens—young edible plants harvested shortly after germination—are gaining popularity for their high nutritional value and rapid growth cycles.
Urban centers like Bengaluru, Pune, and Hyderabad are witnessing a surge in microgreens cultivation, particularly through vertical farming and hydroponic systems. These methods are well-suited for limited spaces and urban environments, aligning with the growing trend of urban agriculture. The adoption of such techniques is further supported by government initiatives aimed at promoting sustainable farming practices.
Government schemes such as the Pradhan Mantri Formalisation of Micro Food Processing Enterprises (PMFME) Scheme provide financial, technical, and business support to micro food processing enterprises. The scheme, operational from 2020-21 to 2024-25 with an outlay of Rs. 10,000 crore, aims to formalize and promote micro food processing units across the country. Additionally, the Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY) offers subsidies for implementing innovative urban farming projects, including hydroponics and vertical farming, thereby encouraging the cultivation of microgreens in urban areas.
The National Horticulture Mission (NHM) also plays a pivotal role in promoting horticulture, including microgreens, by providing financial assistance for infrastructure development and capacity building. This support aids farmers in adopting modern farming techniques and improving productivity
Key Takeaways
- Microgreens Market size is expected to be worth around USD 7.6 Billion by 2034, from USD 2.5 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 11.7%.
- Broccoli microgreens are projected to capture a significant 21.8% share of the global microgreens market.
- Indoor vertical farming emerged as the leading method for microgreens cultivation, commanding a substantial 59.4% share.
- Soil-based cultivation accounted for 33.8% of the global microgreens market, making it the second most prevalent growth medium after peat moss.
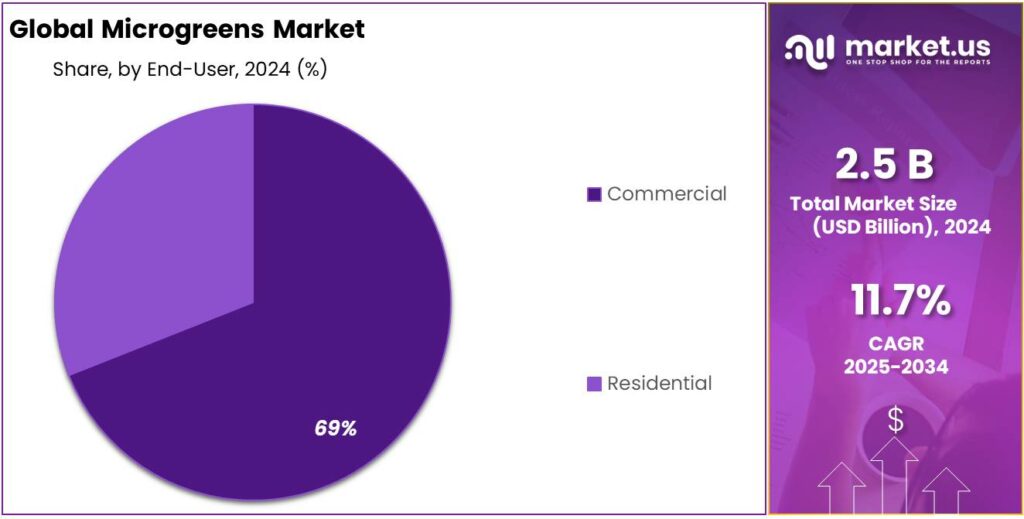
- Commercial sector emerged as the leading end-user of microgreens, capturing a substantial 69.7% share of the global market.
- Hypermarkets and supermarkets emerged as the leading distribution channels for microgreens, commanding a substantial 37.6% share of the global market.
- North America dominated the global microgreens market, capturing approximately 43.9% of the total market share, equivalent to an estimated value of USD 1.0 billion.
By Type Analysis
Broccoli Microgreens Lead Market with 21.8% Share in 2025
In 2025, broccoli microgreens are projected to capture a significant 21.8% share of the global microgreens market. This dominance is attributed to their exceptional nutritional profile, which resonates strongly with health-conscious consumers. Rich in vitamins A, B, C, E, and K, as well as essential minerals, broccoli microgreens offer impressive health benefits in a small package. Their mild, slightly peppery flavor also makes them versatile for culinary applications, allowing for easy incorporation into a wide range of dishes from salads to smoothies.
This expansion is fueled by several key factors, including the rising consumer demand for nutritious and convenient foods, the increasing adoption of hydroponic and aeroponic farming techniques that allow for year-round production, and the expansion of the food service industry, particularly restaurants and cafes incorporating microgreens into their menus.
By Farming Method Analysis
Indoor Vertical Farming Dominates Microgreens Market with 59.4% Share in 2024
In 2024, indoor vertical farming emerged as the leading method for microgreens cultivation, commanding a substantial 59.4% share of the global market. This dominance is attributed to several key factors that align with the growing demand for sustainable and efficient agricultural practices. Vertical farming systems, which utilize stacked layers in a controlled indoor environment, offer significant advantages over traditional farming methods. These include reduced land usage, minimized water consumption, and the ability to produce crops year-round, irrespective of external weather conditions.
The rapid adoption of vertical farming techniques has been further propelled by advancements in technology and automation. Innovations such as hydroponic and aeroponic systems, coupled with artificial lighting and climate control, have optimized growing conditions for microgreens. This technological integration not only enhances yield but also ensures consistent quality, meeting the increasing consumer preference for fresh and nutritious produce.
By Growth Medium Analysis
Soil-Based Microgreens Cultivation Holds 33.8% Market Share in 2024
In 2024, soil-based cultivation accounted for 33.8% of the global microgreens market, making it the second most prevalent growth medium after peat moss. This method remains popular due to its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and the natural growing environment it provides for microgreens. Soil-based systems are particularly favored by small-scale urban farmers, home gardeners, and educational institutions due to their low startup costs and minimal need for specialized equipment.
The soil-based approach offers several advantages, including the ability to use organic and locally sourced soil, which appeals to environmentally conscious consumers. Additionally, soil provides a stable medium for root development, which can lead to robust plant growth and enhanced flavor profiles in microgreens. This method also allows for easy integration into existing gardening practices, making it accessible to a wide range of growers.
By End-User Analysis
Commercial End-User Segment Dominates Microgreens Market with 69.7% Share in 2024
In 2024, the commercial sector emerged as the leading end-user of microgreens, capturing a substantial 69.7% share of the global market. This dominance is primarily attributed to the widespread adoption of microgreens in the foodservice industry, including restaurants, hotels, and catering services, where they are utilized for garnishing and enhancing the visual appeal of dishes. The rapid growth cycle and high yield of microgreens make them an attractive option for commercial growers aiming to meet the increasing demand for fresh, nutritious, and aesthetically pleasing ingredients.
The commercial sector’s significant share underscores the growing recognition of microgreens as a valuable addition to culinary offerings. Their vibrant colors, intense flavors, and nutritional benefits align with current consumer trends favoring health-conscious and visually appealing food options. As the demand for such ingredients continues to rise, the commercial sector’s reliance on microgreens is expected to expand, further solidifying their position in the global market.
By Distribution Channel Analysis
Hypermarkets/Supermarkets Capture 37.6% of Microgreens Market in 2024
In 2024, hypermarkets and supermarkets emerged as the leading distribution channels for microgreens, commanding a substantial 37.6% share of the global market. This dominance is attributed to their extensive reach, established supply chains, and the growing consumer preference for convenient, ready-to-eat fresh produce. Major retail chains have increasingly incorporated microgreens into their fresh produce sections, responding to the rising demand for healthy and nutritious food options.
The strategic placement of microgreens in high-traffic areas within these retail outlets enhances visibility and accessibility, driving consumer impulse purchases. Additionally, the packaging of microgreens in ready-to-use formats aligns with the fast-paced lifestyles of modern consumers, further boosting sales. Retailers benefit from the extended shelf life of microgreens, which, when properly stored, can remain fresh for extended periods, reducing waste and improving profitability.
Key Market Segments
By Type
- Broccoli
- Cabbage
- Cauliflower
- Mesclun
- Peas
- Radish
- Basil
- Carrots
- Lettuce and Chicory
- Beetroot
- Sunflower
- Others
By Farming Method
- Indoor Vertical Farming
- Commercial Greenhouse Farming
- Others
By Growth Medium
- Peat Moss
- Soil
- Coconut Coir
- Tissue Paper
- Others
By End-User
- Commercial
- Residential
By Distribution Channel
- Retail Store
- Online Store
- Farmers Market
- Hypermarkets/Supermarkets
- Restaurants
- Others
Emerging Trends
Hydroponic Microgreens Farming: A Sustainable Urban Agriculture Trend
In recent years, hydroponic farming has emerged as a significant trend in urban agriculture, particularly in the cultivation of microgreens. This method involves growing plants without soil, using mineral nutrient solutions in an aqueous solvent, and has gained popularity due to its efficiency and suitability for urban environments.
Hydroponic systems offer several advantages, including faster plant growth, higher yields, and the ability to grow in areas with limited space and soil quality. These systems are particularly beneficial in urban areas where land is scarce and the demand for fresh, locally grown produce is high.
The Indian government has recognized the potential of hydroponic farming and has introduced various initiatives to support its adoption. For instance, the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY) includes components that promote the adoption of innovative irrigation techniques, such as hydroponics, to enhance water-use efficiency and increase agricultural productivity. Under this scheme, farmers can receive financial assistance for setting up hydroponic systems, making it more accessible for urban dwellers to engage in sustainable farming practices.
Additionally, the National Horticulture Board (NHB) provides subsidies for the construction of greenhouses and polyhouses, which are essential for hydroponic farming. These structures create controlled environments that are ideal for growing microgreens, allowing for year-round production regardless of external weather conditions. The NHB offers up to a 50% subsidy for greenhouse construction, with an upper limit of INR 56 lakhs, making it financially viable for farmers to adopt hydroponic methods.
Drivers
Urbanization and Health Consciousness: Key Drivers of Microgreens Adoption
The surge in urbanization and heightened health awareness among consumers are pivotal factors propelling the growth of the microgreens industry in India. Urban centers like Pune, Bengaluru, and Delhi are witnessing a significant shift towards healthier eating habits, with microgreens emerging as a preferred choice due to their compact size, rapid growth, and rich nutritional profile.
Microgreens, which are young edible plants harvested just after the first true leaves have developed, are celebrated for their high concentrations of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. This nutritional density aligns with the increasing consumer demand for functional foods that contribute to overall well-being. The fast-paced urban lifestyle, coupled with limited space for traditional gardening, has further fueled the adoption of microgreens, as they can be cultivated in small indoor spaces using methods like hydroponics and vertical farming.
Government initiatives have played a crucial role in supporting the microgreens sector. The Pradhan Mantri Formalisation of Micro Food Processing Enterprises (PMFME) Scheme, launched in 2020, aims to enhance the competitiveness of micro food processing units by providing financial, technical, and business support.
- Under this scheme, micro food processing enterprises are eligible for a 35% capital subsidy on eligible project costs, with a maximum ceiling of ₹10 lakh per unit. Additionally, the scheme offers seed capital of ₹40,000 per Self-Help Group (SHG) member for working capital and purchase of small tools. This initiative has been instrumental in encouraging urban farming and the establishment of microgreens cultivation units across various states
Furthermore, the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH) provides support for the holistic growth of the horticulture sector, including the promotion of microgreens. The mission focuses on improving production and productivity through area expansion and rejuvenation, promoting modern technologies in horticulture, and providing training and skill development. These efforts contribute to the establishment of microgreens as a viable and sustainable agricultural practice in urban areas
Restraints
Limited Cold Storage and Supply Chain Infrastructure: Hindering Microgreens Distribution
One of the significant challenges facing the microgreens industry in India is the inadequate cold storage and supply chain infrastructure. Microgreens are highly perishable due to their small size and high moisture content, making them susceptible to rapid deterioration if not stored and transported under optimal conditions. In India, less than 5% of horticultural produce benefits from cold chain infrastructure, leading to substantial post-harvest losses.
The absence of a robust cold chain system results in microgreens losing their freshness and nutritional value during transit, especially over long distances. This not only affects the quality of the produce but also limits its shelf life, making it challenging for farmers and producers to reach distant markets. Consequently, microgreens often fail to meet the quality standards expected by consumers and retailers, leading to reduced demand and profitability.
Recognizing this issue, the Indian government has initiated several programs to develop and strengthen the cold chain infrastructure. The National Centre for Cold-chain Development (NCCD) was established to serve as a think tank to guide the development of the cold chain sector in the country. The NCCD focuses on promoting investment in cold storage facilities, improving transportation logistics, and setting standards for perishable goods handling
Opportunity
Government Support for Urban Farming: A Gateway to Microgreens Cultivation
The Indian government’s initiatives to promote urban farming have opened significant avenues for microgreens cultivation, especially in metropolitan areas. With urban spaces becoming more health-conscious and inclined towards sustainable living, microgreens—nutritious, fast-growing, and space-efficient crops—have emerged as a viable solution.
Under various schemes, the government offers substantial subsidies to encourage urban farming. For instance, eligible urban farmers can receive up to 75% of their project cost as a subsidy, making it more affordable to start and maintain urban farms. These financial incentives cover expenses like setting up rooftop gardens, vertical farming systems, and hydroponic setups, which are ideal for cultivating microgreens in limited spaces.
The Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH) is another pivotal program supporting urban agriculture. Through MIDH, the government provides subsidies ranging from 50% to 75% for establishing horticulture projects, including microgreens cultivation. This support encompasses infrastructure development, adoption of modern farming techniques, and capacity building, thereby enhancing the scalability and sustainability of microgreens farming.
Additionally, the Pradhan Mantri Formalisation of Micro Food Processing Enterprises (PMFME) Scheme aims to formalize and promote micro food processing units across the country. Under this scheme, 2,00,000 micro food processing units will be directly assisted with credit-linked subsidies, facilitating the growth of microgreens processing businesses and ensuring better market access for producers.
Regional Insights
North America Leads Global Microgreens Market with 43.9% Share in 2024
In 2024, North America dominated the global microgreens market, capturing approximately 43.9% of the total market share, equivalent to an estimated value of USD 1.0 billion. This significant share underscores the region’s leadership in the microgreens industry, driven by several key factors.
The United States, in particular, plays a pivotal role in this dominance, accounting for a substantial portion of the North American market. The country’s advanced agricultural infrastructure, coupled with a growing consumer preference for healthy and sustainable food options, has propelled the demand for microgreens. The adoption of innovative farming techniques, such as indoor vertical farming and hydroponics, has further enhanced production efficiency and year-round availability of microgreens.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
AeroFarms is a leading vertical farming company that specializes in growing microgreens using aeroponic technology. With a focus on sustainability, AeroFarms grows crops indoors without soil, using up to 95% less water than traditional farming methods. The company is recognized for its innovation in urban agriculture and commitment to delivering fresh, nutritious microgreens to markets across the U.S. and beyond.
Fresh Origins is a major supplier of high-quality microgreens, specializing in both conventional and organic varieties. Known for its commitment to sustainability, Fresh Origins provides top-tier, farm-to-table microgreens to restaurants, chefs, and retailers. With a focus on freshness, flavor, and nutritional value, Fresh Origins continues to lead the industry in premium microgreens production.
Gotham Greens operates sustainable greenhouses in urban locations, producing fresh, locally grown microgreens, leafy greens, and herbs. The company leverages hydroponic and vertical farming techniques to produce high-quality, pesticide-free microgreens. Gotham Greens’ greenhouses are strategically placed in metropolitan areas, minimizing the carbon footprint associated with transportation and ensuring a constant supply of fresh produce.
Top Key Players Outlook
- AeroFarms
- Fresh Origins
- Gotham Greens
- Madar Farms
- 2BFresh
- The Chef’s Garden Inc
- Farmbox Greens LLC
- Living Earth Farm
- Good Leaf Farms
- Metro Microgreens
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024 AeroFarms, commanded over 70% of the U.S. retail microgreens market, positioning itself as a dominant player in the sector. Utilizing patented aeroponic technology, AeroFarms grows microgreens without soil, pesticides, or sunlight, employing artificial intelligence, robotics, and automated systems to optimize plant growth.
In January 2024, Gotham Greens opened its largest greenhouse to date in Seagoville, Texas, spanning 210,000 square feet, marking a significant expansion in its operations.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 2.5 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 7.6 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 11.7% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Type (Broccoli, Cabbage, Cauliflower, Mesclun, Peas, Radish, Basil, Carrots, Lettuce and Chicory, Beetroot, Sunflower, Others), By Farming Method (Indoor Vertical Farming, Commercial Greenhouse Farming, Others), By Growth Medium (Peat Moss, Soil, Coconut Coir, Tissue Paper, Others), By End-User (Commercial, Residential), By Distribution Channel (Retail Store, Online Store, Farmers Market, Hypermarkets/ Supermarkets, Restaurants, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape AeroFarms, Fresh Origins, Gotham Greens, Madar Farms, 2BFresh, The Chef’s Garden Inc, Farmbox Greens LLC, Living Earth Farm, Good Leaf Farms, Metro Microgreens Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- AeroFarms
- Fresh Origins
- Gotham Greens
- Madar Farms
- 2BFresh
- The Chef's Garden Inc
- Farmbox Greens LLC
- Living Earth Farm
- Good Leaf Farms
- Metro Microgreens










