Global Tricalcium Phosphate Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Product Type (Food Grade, Feed Grade, Pharmaceutical Grade, Industrial Grade), By Application (Food Additives, Feed Additives, Medical Use, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends, and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Oct 2025
- Report ID: 161616
- Number of Pages: 367
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
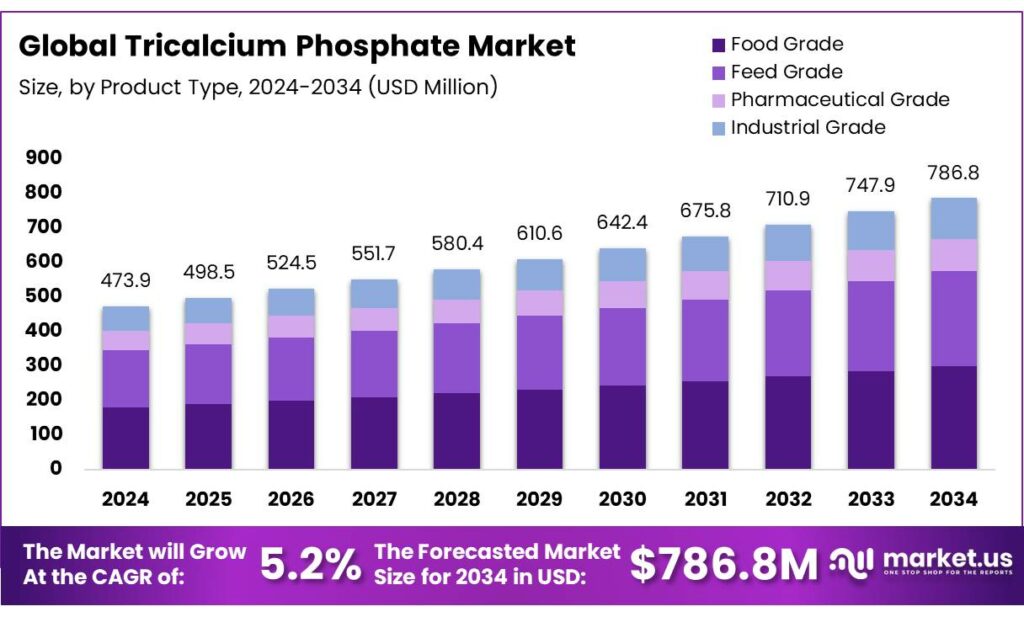
The Global Tricalcium Phosphate Market size is expected to be worth around USD 786.8 Million by 2034, from USD 473.9 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 5.2% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024 Europe held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 39.6% share, holding USD 1.4 Billion in revenue.
Tricalcium phosphate sits at the intersection of food technology, pharma-nutraceuticals, and advanced ceramics. In foods, regulators recognise TCP as safe when used under good manufacturing practice; in the U.S. it is listed as “generally recognized as safe” (GRAS) for calcium phosphates in 21 CFR §182.1217. Global risk assessors have also set intake guardrails: the European Food Safety Authority established a group ADI for phosphates of 40 mg phosphorus/kg body weight/day, a benchmark widely used by industry and authorities to design safe use ranges.
Industrial demand for TCP is anchored upstream in phosphate rock mining and purified phosphoric acid. According to the U.S. Geological Survey, global phosphate capacity (as P₂O₅) is projected to rise from 65.0 Mt in 2024 to 70.6 Mt by 2028, reflecting sustained investments across Africa, the Middle East and Asia—capacity that underpins food-grade and technical phosphate supply chains including TCP. World fertilizer consumption reached 45.7 Mt P₂O₅ in 2023 and is projected at 50 Mt by 2027, reinforcing availability of intermediates that feed into specialty phosphates manufacturing.
Policy support further underpins phosphate affordability and demand visibility. India’s Nutrient-Based Subsidy continues to stabilize P&K fertilizers (DAP/TSP chains relevant to TCP): the government approved ₹37,216.15 crore for Kharif 2025, while the DAP subsidy was ₹21,911/ton for Rabi 2024-25—mechanisms that sustain phosphate flows across food and feed systems where TCP participates. In Europe, phosphate rock is treated as a strategic raw material under the EU’s critical-raw-materials framework, reinforcing attention to resilient sourcing and recycling pathways for phosphorus derivatives used alongside TCP.
Energy and policy context matter for cost curves and sustainability positioning. The industrial sector consumed 37% (166 EJ) of global energy in 2022, and the chemical sector is the largest industrial energy consumer, though only the third-largest direct CO₂ emitter given feedstock uses—framing why electrification, efficiency, and low-carbon heat will increasingly influence phosphate derivative costs.
Key Takeaways
- Tricalcium Phosphate Market size is expected to be worth around USD 786.8 Million by 2034, from USD 473.9 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 5.2%.
- Food-grade tricalcium phosphate (TCP) emerged as the leading segment in the global TCP market, commanding an estimated 46% share.
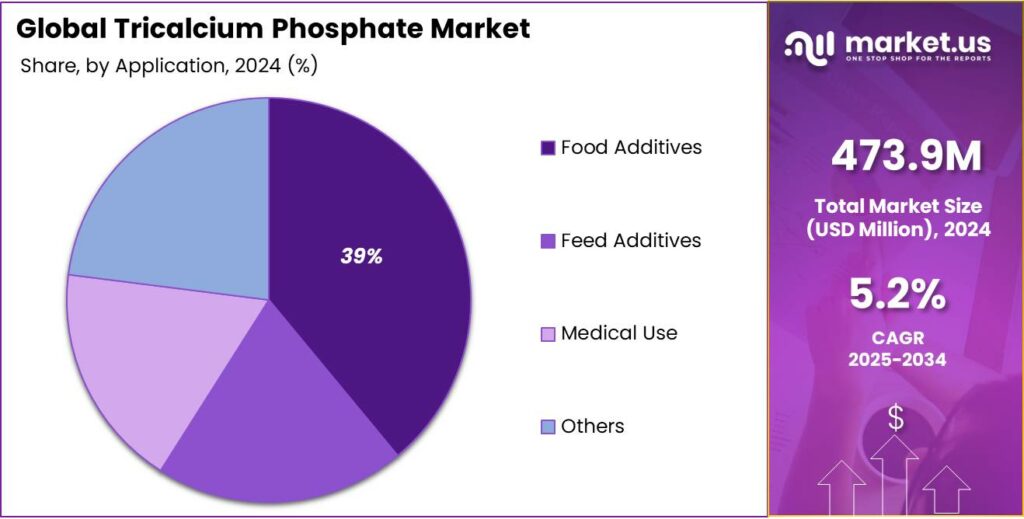
- Food additives segment emerged as the dominant application for tricalcium phosphate (TCP), capturing an estimated 59.9% share.
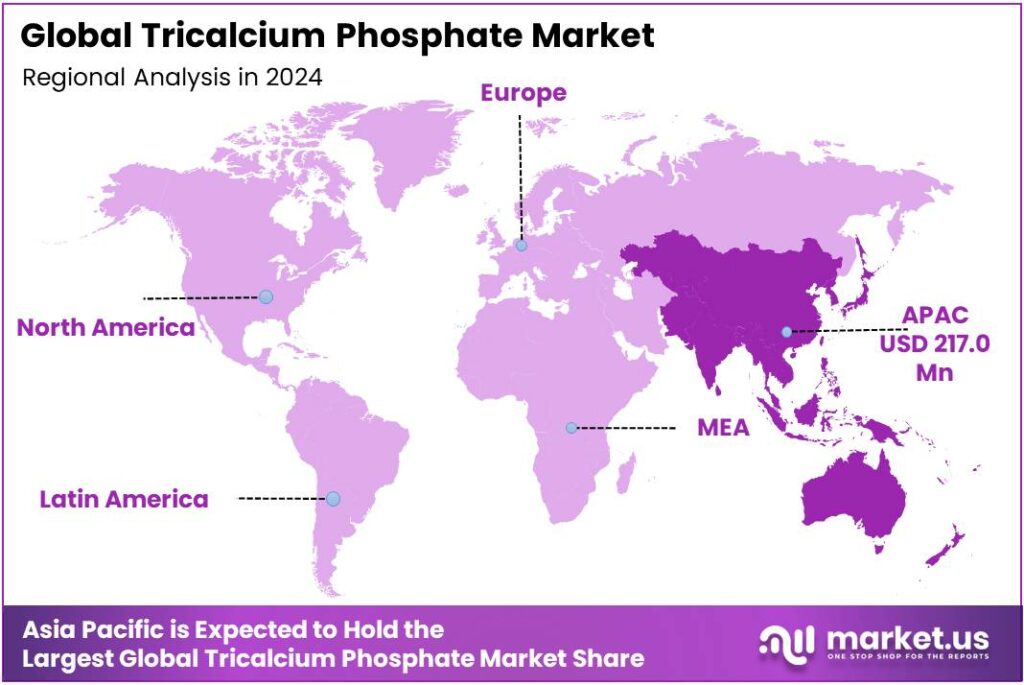
- Asia Pacific region held a dominant position in the global tricalcium phosphate (TCP) market, capturing a substantial 45.8% share, equating to approximately USD 217 million.
By Product Type Analysis
Food Grade Tricalcium Phosphate Dominates with 46% Share in 2024
In 2024, food-grade tricalcium phosphate (TCP) emerged as the leading segment in the global TCP market, commanding an estimated 46% share, equating to approximately 103,500 tonnes out of a total market volume of 225,000 tonnes. This dominance is primarily attributed to its extensive application in the food and nutraceutical sectors, where it serves as a vital ingredient in fortified foods and dietary supplements.
The utilization of TCP in food products is multifaceted, encompassing roles as an anti-caking agent, calcium fortifier, and emulsifier. Industry surveys indicate that nearly 60% of manufacturers incorporate TCP for these purposes, underscoring its significance in enhancing the quality and nutritional value of food items. Moreover, approximately 41% of research and development expenditures in calcium fortification during 2024 were directed towards food-grade improvements, highlighting the ongoing innovation and focus on this segment.
By Application Analysis
Food Additives Lead Tricalcium Phosphate Market with 59.9% Share in 2024
In 2024, the food additives segment emerged as the dominant application for tricalcium phosphate (TCP), capturing an estimated 59.9% share of the global market. This translates to approximately 134,775 tonnes out of a total consumption of 225,000 tonnes. The widespread use of TCP in food products is primarily due to its role as an anti-caking agent, calcium fortifier, and emulsifier, which enhances the quality and nutritional value of various food items.
The demand for TCP in food additives is driven by the increasing consumer preference for fortified foods and beverages. As health consciousness rises, consumers are seeking products that offer additional nutritional benefits, leading to a surge in the incorporation of TCP in items such as snacks, cereals, and dairy products. Additionally, the growing trend of clean-label products has further propelled the use of TCP, as it is considered a safe and effective ingredient for improving food quality.
Key Market Segments
By Product Type
- Food Grade
- Feed Grade
- Pharmaceutical Grade
- Industrial Grade
By Application
- Food Additives
- Feed Additives
- Medical Use
- Others
Emerging Trends
Phosphate-Smart Fortification and Reformulation
A clear, fast-moving trend in tricalcium phosphate (TCP) is “phosphate-smart” fortification: brands are adding calcium to everyday foods while reformulating to meet strict additive rules and exposure guidance. TCP fits because it improves flow in powders and brings stable calcium without strong taste. Regulators also give a predictable rulebook. In the Codex GSFA, TCP (INS 341(iii)) is listed for multiple technological functions—anticaking, stabilizer, emulsifier, flour treatment agent—so developers can use one familiar ingredient across categories.
At the same time, formulators are reformulating with precision because authorities have tightened phosphate risk management. EFSA set a group ADI of 40 mg phosphorus/kg body weight/day for phosphates (E 338–341, E 343, E 450–452), steering companies to dose conservatively, blend calcium sources, and justify additive levels in supplements and foods. That push does not eliminate TCP; it encourages “right-sizing” use, cleaner labels, and better exposure accounting—skills that large food makers are rapidly adopting.
- Codex recognition of TCP’s roles, 979 Mt of global milk acting as a calcium vehicle, staple-fortification evidence like the UK’s 13–14% intake contribution, modeling at 156 mg/100 g flour, and EFSA’s 40 mg/kg bw/day ADI together define how developers now add calcium: precise, policy-aligned, and technically robust—with TCP at the center of many formulations.
Drivers
Nutrition Fortification & Maternal Health Programs
The strongest demand engine for tricalcium phosphate (TCP) is the push to close calcium gaps in everyday diets and in maternal health programs—where TCP is a dependable, label-familiar calcium source in milk, powders, premixes, and bakery mixes recognized by Codex as an anticaking, stabilizing, and emulsifying additive (INS 341(iii)). This regulatory clarity means formulators can use TCP across many food categories while staying within Codex provisions, which lowers compliance risk and speeds reformulation cycles.
Large-scale fortification is scaling, especially in milk, a natural carrier for calcium. FAO projects world milk production at ~979 million tonnes in 2024 (up 1.4% year-on-year), creating a vast substrate for mineral fortification that directly benefits TCP uptake in dairy powders, recombined milk, and ready-to-mix beverages. As dairy trade and production rise, the available volume for fortified SKUs expands, which encourages cost-efficient, standardized calcium premixes built around phosphate salts.
- Government programs add real volume. India’s food regulator (FSSAI) has formal fortification standards for milk and other staples, which has already pushed fortified milk into mass distribution. A national consultation reported ~78 lakh litres/day of milk fortified through 13 state dairy cooperatives, reaching ~52 million people—a concrete signal that public procurement and cooperative dairies can institutionalize mineral additions such as calcium.
Maternal health guidance is another decisive tailwind. The World Health Organization recommends 1.5–2.0 g/day of elemental calcium in populations with low dietary intake to reduce the risk of pre-eclampsia—a leading cause of maternal and neonatal complications. This recommendation translates into national antenatal protocols and public-health supply chains that purchase calcium ingredients for tablets, sachets, and fortified foods—channels in which TCP is a practical, cost-stable calcium donor for foods and specialized nutrition.
Restraints
Regulatory Safety Limits and Phosphate Exposure Constraints
One of the most significant restraints on growth for tricalcium phosphate (TCP) is the tightening of regulatory safety limits on phosphate additives and growing concern about excess phosphorus intake in diets. These constraints create usage ceilings, compliance burdens, and public health scrutiny that make formulators more cautious about how much TCP (or any phosphate) they can incorporate.
Phosphates are already regulated in many jurisdictions with maximum permitted levels (MPLs). For example, in the European Union, phosphates E 338–341, E 343, E 450–452 are currently authorized food additives with MPLs ranging from 500 to 20,000 mg/kg depending on the food category. This means a product maker cannot simply increase TCP indefinitely; beyond a ceiling, switches to non-phosphate alternatives may be forced.
EFSA has set a group Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI) for phosphates expressed as phosphorus at 40 mg per kg body weight per day. For a 70 kg adult, that represents an upper safe intake of about 2,800 mg phosphorus per day from all sources. When diets already include phosphorus naturally, the headroom for added phosphates like TCP becomes limited. In many regions, dietary phosphorus intake is already high—US NHANES data from 2011–2012 showed mean intake exceeding 1,000 mg/day across age groups, and in males ≥12 years often over 1,400 mg/day.
Opportunity
Expansion via Calcium Fortification in Staple Foods
One of the clearest openings for tricalcium phosphate (TCP) lies in the growing movement to fortify staple foods with calcium, turning everyday flour, rice, or water into nutrient vehicles. Because many populations worldwide don’t meet their recommended calcium needs, policies and programs aiming to close this “calcium gap” can create persistent, large-scale demand for functional calcium salts like TCP.
Globally, about 66% of people are estimated to consume inadequate calcium. This gap is not just a statistic—it’s a health burden, influencing bone health, child growth, and maternal outcomes. Recognizing this, public health agencies and governments are increasingly turning to food fortification as a cost-effective strategy. The World Health Organization supports food fortification as a foundational tool to reduce micronutrient deficiencies.
From the technical side, TCP is attractive: it is stable, relatively neutral in taste, and already accepted under many food additive regimes (e.g. as INS 341). But it is not without challenges—fortification programs must carefully dose added calcium so as not to distort flavor, texture, or exceed safe upper bounds. That said, studies and modeling efforts suggest that fortifying flour or even water with calcium could bring meaningful intake improvements in vulnerable groups.
Regional Insights
Asia Pacific Leads Tricalcium Phosphate Market with 45.8% Share in 2024
In 2024, the Asia Pacific region held a dominant position in the global tricalcium phosphate (TCP) market, capturing a substantial 45.8% share, equating to approximately USD 217 million. This dominance is attributed to the region’s robust industrial base, expanding food and beverage sector, and increasing health consciousness among consumers.
Countries such as China and India are pivotal contributors to this growth, driven by their large populations, rising disposable incomes, and heightened awareness of nutritional supplements. The demand for fortified foods and beverages, particularly those enriched with calcium, has surged, propelling the need for TCP as a key ingredient. Additionally, the pharmaceutical industry’s expansion in these nations has further augmented the demand for TCP in medical applications.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Prayon is a leading global player in phosphate chemistry, with a heritage spanning over 130 years. The company manufactures a wide range of phosphate products, including tricalcium phosphate (TCP), for various applications across industries such as food, agriculture, and pharmaceuticals. Prayon’s TCP products are known for their high purity and consistency, making them suitable for use in food additives, animal feed, and pharmaceutical formulations.
SoleChem is a reputable supplier of tricalcium phosphate (TCP) in Europe, offering high-quality TCP products for food, pharmaceutical, and animal nutrition applications. The company provides TCP in various grades, ensuring compliance with industry standards and customer specifications. SoleChem’s commitment to quality and reliability has established it as a trusted partner for TCP supply in the European market.
Norkem Limited is a global distributor of chemical products, including tricalcium phosphate (TCP), serving a wide range of industries such as agriculture, food, and pharmaceuticals. With over 45 years of experience, Norkem offers TCP products sourced from reputable manufacturers, ensuring quality and consistency. The company’s extensive distribution network enables it to supply TCP to customers worldwide, meeting the diverse needs of its clientele.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Innophos
- Himed
- Prayon
- SoleChem
- Norkem Limited
- CG Chemikalien GmbH & Co. KG
- Shanghai Caifeng
- Lianxing Chemical
- Hubei Xingfa Chemicals
- Lianyungang Dongzhou
- Great Chemicals
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024, Prayon, a global leader in phosphorus chemistry with over 130 years of experience, continued to strengthen its position in the tricalcium phosphate (TCP) market. The company, employing approximately 1,500 professionals worldwide, is renowned for its commitment to delivering innovative solutions across various sectors, including food, health, and industrial applications
In 2024 SoleChem, was valued at approximately USD 476.20 million, with TCP products being integral in various applications such as food additives, pharmaceuticals, and animal feed.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 473.9 Mn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 786.8 Mn CAGR (2025-2034) 5.2% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Product Type (Food Grade, Feed Grade, Pharmaceutical Grade, Industrial Grade), By Application (Food Additives, Feed Additives, Medical Use, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Innophos, Himed, Prayon, SoleChem, Norkem Limited, CG Chemikalien GmbH & Co. KG, Shanghai Caifeng, Lianxing Chemical, Hubei Xingfa Chemicals, Lianyungang Dongzhou, Great Chemicals Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Tricalcium Phosphate MarketPublished date: Oct 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Tricalcium Phosphate MarketPublished date: Oct 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Innophos
- Himed
- Prayon
- SoleChem
- Norkem Limited
- CG Chemikalien GmbH & Co. KG
- Shanghai Caifeng
- Lianxing Chemical
- Hubei Xingfa Chemicals
- Lianyungang Dongzhou
- Great Chemicals










