Global Solar Cell Metal Paste Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Type (Silver Paste, Silver Aluminum Paste, Aluminum Paste), By Application (Multicrystalline Silicon Solar Cell, Monocrystalline Silicon Solar Cell, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Oct 2025
- Report ID: 160641
- Number of Pages: 217
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
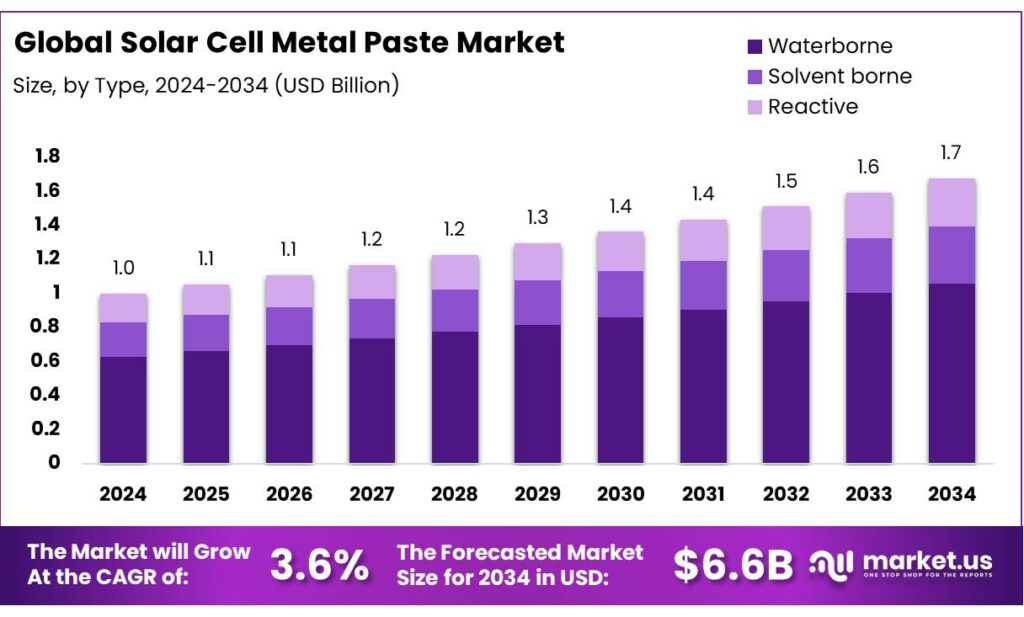
The Global Solar Cell Metal Paste Market size is expected to be worth around USD 1.7 Billion by 2034, from USD 1.0 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 3.6% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
The solar cell metal paste industry plays a pivotal role in the photovoltaic (PV) sector, serving as a critical component in the manufacturing of solar cells. These metal pastes, primarily composed of silver and aluminum, are essential for creating the electrical contacts on solar cells, facilitating the efficient conversion of sunlight into electricity. The global market for solar cell metal paste has witnessed significant growth, driven by the escalating demand for renewable energy solutions and advancements in solar technology.
The demand for silver paste, a key component in solar cell metallization, is also on the rise. With global solar demand exceeding 600 gigawatts, the solar industry’s silver paste demand is estimated to be around 6,000 tons. This surge in demand is contributing to increased silver prices, which have reached over $28 per ounce, the highest in more than a decade.
Government initiatives play a crucial role in driving the growth of the solar cell metal paste market. For instance, the International Energy Agency (IEA) reported that global investment in solar photovoltaic manufacturing more than doubled to $80 billion, with China significantly increasing its investment between 2022 and 2023. These investments are fostering innovation and scaling up production capacities, thereby enhancing the availability and affordability of solar cell metal pastes.
Government initiatives play a pivotal role in accelerating market growth. For instance, India aims to increase its non-fossil fuel capacity to 500 GW by 2030, up from approximately 156 GW, with a focus on enhancing domestic manufacturing capabilities. The Indian government has mandated the use of locally produced solar cells in clean energy projects from June 2026, encouraging companies like Tata Power, Reliance Industries, and Adani Group to expand their solar cell manufacturing facilities.
Key Takeaways
- Solar Cell Metal Paste Market size is expected to be worth around USD 1.7 Billion by 2034, from USD 1.0 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 3.6%.
- Silver Paste held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 63.2% share.
- Multicrystalline Silicon Solar Cell held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 58.8% share.
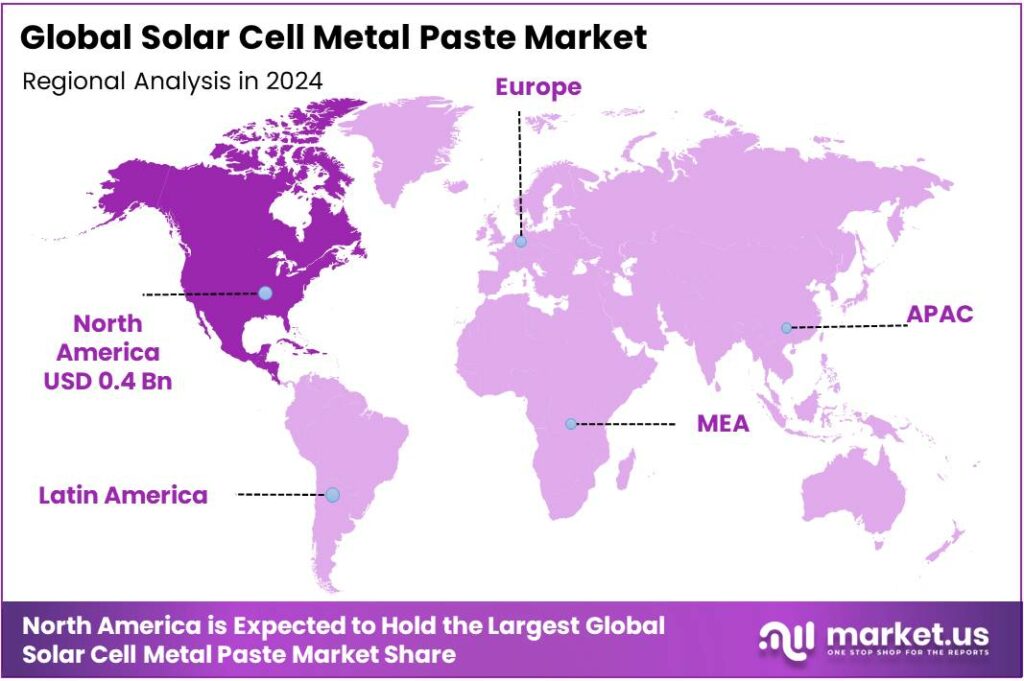
- North America held a dominant position in the global solar cell metal paste market, capturing more than 46.2% of the market share, equating to approximately USD 1.5 billion.
By Type Analysis
Silver Paste dominates with 63.2% market share in 2024
In 2024, Silver Paste held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 63.2% share in the global solar cell metal paste industry. The prevalence of Silver Paste can be attributed to its superior electrical conductivity, excellent adhesion properties, and compatibility with high-efficiency solar cells, making it the preferred choice among manufacturers. Its ability to support advanced solar technologies such as PERC and HJT cells has reinforced its dominance, allowing solar modules to achieve higher energy conversion rates and longer operational lifespans.
The year 2024 witnessed increased production of Silver Paste to meet the rising demand for photovoltaic installations worldwide. Government policies promoting renewable energy, such as the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act and China’s carbon neutrality goals, indirectly fueled the consumption of high-quality silver-based conductive pastes in solar cells. Manufacturers leveraged this demand by scaling up production capacity and improving paste formulations to reduce silver consumption while maintaining performance, thereby balancing cost and efficiency.
By Application Analysis
Multicrystalline Silicon Solar Cell leads with 58.8% market share in 2024
In 2024, Multicrystalline Silicon Solar Cell held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 58.8% share in the solar cell metal paste market. This dominance is largely due to its cost-effectiveness and established manufacturing processes, which make it a preferred choice for large-scale solar installations. The material’s ability to deliver reliable performance at a lower production cost compared to monocrystalline cells has reinforced its widespread adoption in utility-scale solar projects and commercial rooftops.
During 2024, the demand for multicrystalline silicon solar cells surged in regions focusing on rapid solar capacity expansion, supported by government initiatives and renewable energy targets. Countries such as China, India, and the United States significantly increased solar installations, indirectly driving the consumption of metal pastes compatible with multicrystalline silicon technology. The silver and aluminum pastes used in these cells ensure efficient electrical contacts, which are critical for maintaining energy conversion efficiency and long-term reliability.
Key Market Segments
By Type
- Silver Paste
- Silver Aluminum Paste
- Aluminum Paste
By Application
- Multicrystalline Silicon Solar Cell
- Monocrystalline Silicon Solar Cell
- Others
Emerging Trends
Shift Toward Low-Silver and Lead-Free Metal Pastes in Solar Cells
A significant trend in the solar cell metal paste market is the industry’s transition towards low-silver and lead-free formulations. This shift is driven by the need to reduce material costs, mitigate environmental impact, and comply with increasingly stringent regulations.
Silver has traditionally been a key component in solar cell metal pastes due to its excellent electrical conductivity. However, the high cost and price volatility of silver have prompted manufacturers to explore alternatives. For instance, in 2024, silver prices surged by 19.4%, primarily due to increased industrial demand and supply constraints. This volatility poses challenges for solar panel manufacturers, as silver constitutes a substantial portion of the material costs in photovoltaic (PV) cell production.
In response to these challenges, researchers and manufacturers are developing low-silver and lead-free metal pastes. These formulations aim to reduce the reliance on precious metals and toxic substances while maintaining or enhancing the performance of solar cells. For example, advancements in material science have led to the development of silver-coated copper pastes for Heterojunction (HJT) cells, achieving comparable performance while reducing silver content by up to 30%.
Governments are also playing a crucial role in promoting these sustainable practices. In India, for example, the government has implemented measures to boost domestic silver production and reduce import duties, aiming to stabilize the supply and cost of silver for industrial use. Such initiatives are crucial in ensuring the long-term viability and competitiveness of the solar industry.
Drivers
Technological Advancements in Solar Cell Efficiency
One of the primary drivers of growth in the solar cell metal paste market is the continuous evolution of solar cell technologies aimed at enhancing efficiency and performance. Innovations such as Passivated Emitter and Rear Contact (PERC), Tunnel Oxide Passivated Contact (TOPCon), and Heterojunction (HJT) cells have significantly improved the energy conversion rates of photovoltaic (PV) modules. These advancements necessitate the development of specialized metal pastes that can meet the stringent requirements of these high-efficiency cells.
For instance, PERC technology, which involves adding a passivation layer to the rear side of the solar cell, has been widely adopted due to its ability to reduce recombination losses and enhance efficiency. This has led to an increased demand for rear-side silver (Ag) pastes that offer excellent conductivity and adhesion properties. Similarly, TOPCon and HJT technologies, which incorporate advanced contact structures and materials, require metal pastes with low-temperature sintering capabilities and minimal silver content to optimize cost-effectiveness and performance.
The global push towards reducing the carbon footprint and transitioning to renewable energy sources has further accelerated the adoption of these advanced solar technologies. Governments worldwide are implementing policies and incentives to promote solar energy. For example, the U.S. Department of Energy’s Solar Energy Technologies Office (SETO) has been funding research to develop next-generation solar cell technologies that can achieve higher efficiencies and lower costs. Such initiatives are expected to drive the demand for specialized metal pastes that are compatible with these advanced cell architectures.
Restraints
Volatility of Silver Prices Impacting Solar Cell Metal Paste Costs
A significant challenge facing the solar cell metal paste industry is the volatility of silver prices, which directly affects the cost structure of photovoltaic (PV) cell manufacturing. Silver is a critical component in metal pastes used for metallization in solar cells, particularly in high-efficiency technologies like Passivated Emitter and Rear Contact (PERC), Tunnel Oxide Passivated Contact (TOPCon), and Heterojunction (HJT) cells.
In recent years, silver prices have experienced substantial fluctuations. For instance, in September 2025, silver prices surged by 19.4%, driven by strong industrial demand, especially from the solar energy sector, and tightening global supply. This increase in silver prices poses a significant challenge for solar panel manufacturers, as silver constitutes a substantial portion of the material costs in PV cell production.
The rising cost of silver has led to increased production expenses for solar panel manufacturers, impacting their profitability and potentially leading to higher prices for end consumers. This situation underscores the importance of developing cost-effective alternatives and strategies to mitigate the impact of silver price volatility on the solar industry.
To address this issue, manufacturers are exploring several approaches. One strategy involves reducing the amount of silver used in each solar cell. For example, advancements in printing technology and paste formulations have enabled the reduction of silver paste consumption from 400 milligrams per watt in 2007 to approximately 130 milligrams per watt by 2016. Such reductions help lower material costs and decrease sensitivity to silver price fluctuations.
Additionally, there is a growing interest in alternative materials and technologies that can replace or reduce the reliance on silver. For instance, silver-coated copper pastes have been developed for HJT cells, achieving comparable performance while reducing silver content by up to 30%. These innovations not only help in cost reduction but also contribute to the sustainability of solar panel production.
Opportunity
Transition to Copper-Based Metal Pastes in Solar Cells
A significant growth opportunity in the solar cell metal paste market lies in the transition from silver-based pastes to copper-based alternatives. This shift is driven by the need to reduce material costs and mitigate the impact of silver price volatility on solar cell manufacturing.
Silver has traditionally been the material of choice for metallization in solar cells due to its excellent electrical conductivity. However, silver prices have experienced significant fluctuations in recent years. For instance, in 2024, silver prices surged by 19.4%, reaching levels not seen in over a decade, primarily due to increased industrial demand and supply constraints. This volatility poses challenges for solar panel manufacturers, as silver constitutes a substantial portion of the material costs in photovoltaic (PV) cell production.
In response to these challenges, researchers and manufacturers are exploring copper-based metal pastes as a viable alternative. Copper is more abundant and less expensive than silver, making it an attractive option for reducing production costs. The U.S. Department of Energy’s Solar Energy Technologies Office (SETO) is actively funding projects aimed at replacing silver in solar cell electrical contacts with copper and aluminum. These initiatives focus on developing new copper- and aluminum-based metal pastes that can be screen-printed onto silicon solar cells, potentially reducing the cost of adding metal contacts to the cell by 50% while maintaining or improving cell efficiency
The adoption of copper-based metal pastes is particularly promising for advanced solar cell technologies such as Passivated Emitter and Rear Contact (PERC) and Tunnel Oxide Passivated Contact (TOPCon) cells. These technologies require precise metallization to achieve high efficiency, and the development of compatible copper-based pastes is crucial for their widespread adoption.
Regional Insights
North America leads with 46.2% market share in 2024
In 2024, North America held a dominant position in the global solar cell metal paste market, capturing more than 46.2% of the market share, equating to approximately USD 1.5 billion in value. This significant share reflects the region’s robust adoption of solar energy technologies and substantial investments in renewable energy infrastructure.
The United States, in particular, has been a key driver of this growth, propelled by federal and state-level incentives aimed at promoting clean energy. Initiatives such as the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) have allocated substantial funds to support solar energy projects, thereby stimulating demand for high-efficiency photovoltaic (PV) components, including metal pastes. These policies have encouraged both residential and commercial solar installations, further bolstering the need for advanced metallization materials.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
DuPont is a leading provider of metallization pastes for the solar industry, offering advanced materials under the Solamet® brand. Their Solamet® PV21A paste is designed to enhance fine line printability, contributing to improved cell efficiency. DuPont’s commitment to innovation is evident in their continuous development of high-performance materials aimed at increasing the power output and reliability of solar cells. Their products are widely used in various photovoltaic technologies, supporting the global transition to renewable energy.
Heraeus Photovoltaics is a global leader in the development and supply of metallization pastes for the solar industry. Their SOL 7 Series includes high-performance pastes designed to increase solar cell efficiency by up to 0.15%. Heraeus emphasizes the importance of reducing silver consumption while maintaining high efficiency, aligning with industry trends towards cost-effective and sustainable solutions. Their products are widely adopted across various solar cell technologies, contributing to the advancement of photovoltaic energy.
Toyo Aluminium K.K. is a leading manufacturer of aluminum products, including metallization pastes for solar cells. Their ALSOLAR® series offers a range of pastes suitable for various solar cell technologies, including PERC, PERT, and TopCon. Toyo Aluminium’s commitment to quality and innovation ensures that their products meet the high standards required for efficient and reliable solar energy generation.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Dupont
- Heraeus
- Samsung SDI
- Giga Solar
- Toyo Aluminium K.K.
- Noritake
- Namics
- AG PRO
- TTMC
- Daejoo Electronic Materials
Recent Industry Developments
Giga Solar is a Taiwanese firm that makes conductive paste for solar cells and related electronic components. In the first quarter of 2024, the company’s sales rose to TWD 1,520.31 million from TWD 776.02 million in Q1 2023, showing strong growth in demand.
In 2024 Noritake, sales in its Ceramics & Materials group for electronic paste rose from ¥4.9 billion in the same period of FY2023 to ¥5.4 billion in FY2024 H1, an increase of ¥0.5 billion year-on-year.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 1.0 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 1.7 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 3.6% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Type (Silver Paste, Silver Aluminum Paste, Aluminum Paste), By Application (Multicrystalline Silicon Solar Cell, Monocrystalline Silicon Solar Cell, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Dupont, Heraeus, Samsung SDI, Giga Solar, Toyo Aluminium K.K., Noritake, Namics, AG PRO, TTMC, Daejoo Electronic Materials Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Solar Cell Metal Paste MarketPublished date: Oct 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Solar Cell Metal Paste MarketPublished date: Oct 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Dupont
- Heraeus
- Samsung SDI
- Giga Solar
- Toyo Aluminium K.K.
- Noritake
- Namics
- AG PRO
- TTMC
- Daejoo Electronic Materials










