Global Silage Additives Market Size, Share, Growth Analysis By Product Type (Homofermentative Inoculants, Heterofermentative Inoculants, Combination Products, Acids and Acid Salts, Molasses or Sugar, Enzymes, Non-Protein Nitrogen Compound), By Form (Powder, Liquid), By Function (Stimulation Treatment, Inhibition Treatment, Others), By Crop Type (Corn, Alfalfa, Sorghum, Oats, Barley, Rye, Others), By Application (Cereals, Pulses, Others) – Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Sep 2025
- Report ID: 157248
- Number of Pages: 331
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
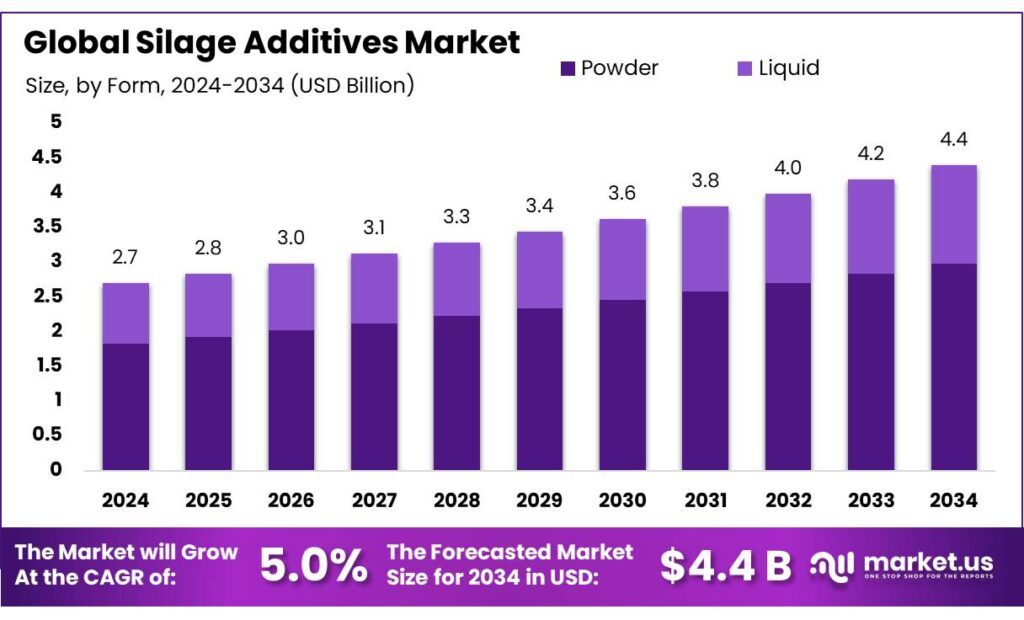
The Global Silage Additives Market size is expected to be worth around USD 4.4 Billion by 2034, from USD 2.7 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 5.0% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024 North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.8% share, holding USD 1.1 Billion in revenue.
Silage additives are technological inputs—primarily lactic-acid bacteria inoculants, enzymes, and organic acids—used to steer fermentation, preserve dry matter (DM), and stabilize feed at feed-out. Their role is expanding as dairies and beef producers push for higher forage quality to support rising milk and protein output. FAO estimated world milk production at roughly 944 million tonnes in 2023, and the OECD-FAO Outlook projects global milk output to grow about 1.8% per year to 1,146 million tonnes by 2034, underscoring sustained demand for well-preserved forages.
The industrial backdrop is large and operationally intensive. In the United States, USDA reports 2024 corn silage production at 123 million tons on 6.10 million acres, framing the scale at which preservation and aerobic stability matter for feed efficiency and margins. Concurrently, U.S. milking cow numbers hovered around 9.37 million head in late-2024, reinforcing the structural need for consistent silage quality. In India, milk production reached 239.3 million tonnes in 2023-24 with per-capita availability at 471 g/day—an enormous forage base where minimizing losses materially affects supply security.
Regulatory regimes continue to shape product portfolios and on-farm use. In the EU, feed additives (including silage inoculants) are authorized under Regulation (EC) No 1831/2003, with EFSA routinely reassessing strain safety and efficacy; for example, EFSA’s 2024 opinion confirms Lactiplantibacillus plantarum DSM 18114 as a technological additive for silage.
In the US, FDA treats most silage ingredients under food/additive or GRAS frameworks and issued GFI #293 (2024) clarifying its enforcement policy for AAFCO-defined feed ingredients. Numeric specifications exist: formic acid may be used as a silage preservative up to 2.25% of silage on a dry-matter basis (or 0.45% when direct-cut), with additional labeling and safety conditions. These clear rules de-risk adoption and encourage product innovation.
Key Takeaways
- Silage Additives Market size is expected to be worth around USD 4.4 Billion by 2034, from USD 2.7 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 5.0%.
- Homofermentative Inoculants held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 26.7% share of the silage additives market.
- Powder held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 67.8% share of the silage additives market.
- Stimulation Treatment held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 58.3% share of the silage additives market.
- Corn held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.4% share of the silage additives market.
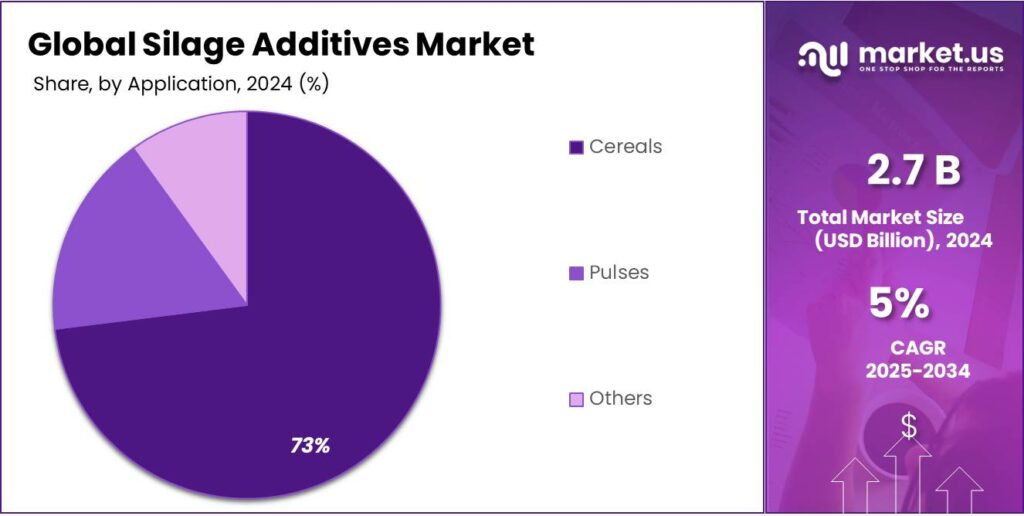
- Cereals held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 73.1% share of the silage additives market.
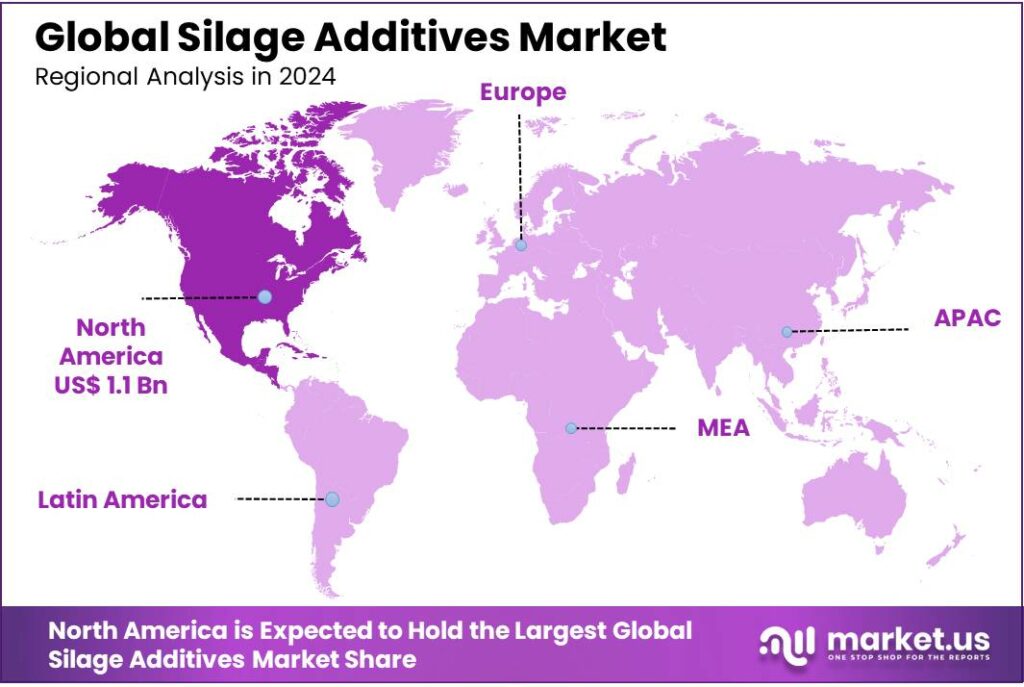
- North America held a dominant market position in the global silage additives sector, capturing more than a 43.8% share, equating to approximately USD 1.1 billion.
By Product Type Analysis
Homofermentative Inoculants dominate with 26.7% share due to their efficient fermentation process
In 2024, Homofermentative Inoculants held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 26.7% share of the silage additives market. These inoculants are widely used by farmers due to their efficiency in promoting the fermentation of silage, enhancing the preservation of nutrients and improving feed quality for livestock. Homofermentative inoculants work by converting sugars in the forage into lactic acid, which lowers the pH and helps preserve the silage for longer periods, reducing spoilage and nutrient loss.
Their widespread adoption is driven by the need for higher quality feed and the increasing awareness of their cost-effectiveness in preserving silage quality. Farmers are seeking ways to improve livestock nutrition, and these inoculants deliver consistent results, making them a trusted choice in silage production. Moreover, innovations in strain development and product formulations are expected to further boost the effectiveness and appeal of homofermentative inoculants, ensuring their continued dominance in the market.
By Form Analysis
Powder dominates with 67.8% share, offering convenience and stability in silage production
In 2024, Powder held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 67.8% share of the silage additives market. This form remains the preferred choice due to its ease of handling, longer shelf life, and versatility in application. Powdered silage additives are often mixed directly with forage, ensuring uniform distribution and consistent fermentation. The powdered form also offers farmers the flexibility to adjust the quantity based on the specific needs of the silage, whether they are dealing with different types of forage or varying moisture content.
This is driven by the ongoing need for more efficient and cost-effective methods of silage preservation. The powder form’s ability to maintain effectiveness over time without requiring refrigeration, along with its convenience for large-scale use, further solidifies its leading position in the market. The continued focus on improving feed quality and nutritional value for livestock ensures that powder-based additives will remain central to the silage production process.
By Function Analysis
Stimulation Treatment dominates with 58.3% share, enhancing silage quality for better livestock feed
In 2024, Stimulation Treatment held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 58.3% share of the silage additives market. This function is critical for improving the fermentation process and ensuring that the silage remains nutrient-rich and free from spoilage during storage. Stimulation treatments typically involve adding specific bacterial strains or enzymes that promote a faster, more efficient fermentation, which is crucial for maintaining the quality of silage used as livestock feed. The treatment also helps in reducing the loss of nutrients, improving digestibility, and enhancing the overall health benefits of the feed.
Farmers are increasingly looking for ways to improve the quality of their silage while reducing waste and spoilage, and stimulation treatments offer a cost-effective solution to these challenges. With increasing demand for high-quality, nutrient-dense feed and a greater focus on sustainability in farming practices, stimulation treatments are set to remain a key function in the silage additives market.
By Crop Type Analysis
Corn dominates with 38.4% share, driving growth in silage additives for livestock feed
In 2024, Corn held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.4% share of the silage additives market. This is due to corn’s widespread use as a primary feed source for livestock, especially in regions where it is a staple crop for silage production. The high-energy content of corn makes it an essential part of the livestock diet, and silage additives help preserve its nutritional value during fermentation. The demand for silage additives in corn production is driven by the need to improve feed quality, reduce spoilage, and ensure optimal digestion for livestock.
Farmers are increasingly turning to additives that enhance fermentation and prevent the loss of nutrients in corn silage, ensuring better feed efficiency and productivity. With corn remaining a primary ingredient in animal feed, the need for quality silage additives is set to rise, securing its dominant position in the market for years to come.
By Application Analysis
Cereals dominate with 73.1% share, ensuring top-quality feed through effective silage preservation
In 2024, Cereals held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 73.1% share of the silage additives market. This dominance is largely due to the widespread use of cereals like corn, wheat, and barley in animal feed, which makes them a key component in silage production. Silage additives for cereals play an essential role in improving fermentation, preserving nutrients, and reducing spoilage, which enhances feed quality and livestock productivity. Cereal-based silage is especially popular in regions where these crops are staple feed sources for dairy cattle, poultry, and livestock.
As cereal silage continues to form the backbone of livestock diets globally, the need for effective additives to optimize fermentation and preserve the nutritional value of the feed will remain high. The increasing awareness of feed quality and the rise of precision farming methods will likely ensure the ongoing dominance of cereals in the silage additives market.
Key Market Segments
By Product Type
- Homofermentative Inoculants
- Heterofermentative Inoculants
- Combination Products
- Acids and Acid Salts
- Molasses or Sugar
- Enzymes
- Non-Protein Nitrogen Compound
By Form
- Powder
- Liquid
By Function
- Stimulation Treatment
- Inhibition Treatment
- Others
By Crop Type
- Corn
- Alfalfa
- Sorghum
- Oats
- Barley
- Rye
- Others
By Application
- Cereals
- Pulses
- Others
Emerging Trends
Precision Agriculture Brings Smarter, Gentler Use of Silage Additives
Across the world, farmers are no longer applying additives by guesswork or routine. Instead, they’re starting to monitor silage conditions—moisture, temperature, fermentation progress—with sensors and data tools that help them decide exactly how much additive to use, and where. That’s the essence of precision agriculture: using digital tools to treat every bale and batch as unique. Research notes this integration—precision farming techniques alongside liquid silage additives—helps “optimize additive usage patterns,” letting farmers adjust real‑time and reduce waste. It’s a smart, resource‑saving move.
What’s even more compelling is how well this fits into wider efforts in sustainable agriculture. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and others have championed digital agriculture—not just for crops, but across the agri‑food system—with an aim to boost efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and help feed our growing world in smarter ways. When silage additives become part of that digital shift, they’re no longer just ingredients—they’re precision tools in a farm’s carefully managed ecosystem.
Governments and institutions are stepping in to reinforce this trend, too. Many sustainable farming schemes now include digital agriculture or precision‑farming components—supporting sensors, training, and data systems—not because they sound flashy, but because they help reduce input waste, improve quality, and support resilient farms. While silage additives may not always be singled out, they ride this larger wave of precision and sustainability.
Drivers
Cutting Feed Loss with Better Fermentation Control
A big reason farmers are leaning into silage additives is simple: too much feed disappears between harvest and the feed bunk, and every lost ton hurts milk, margins, and now—methane targets. The FAO estimates that 13.2% of food is lost post-harvest globally; livestock feed sits inside that reality, so preservation matters. When you scale that loss across forage systems, even small efficiency gains translate into real tons saved and more consistent milk output.
In the United States alone, USDA reports 2024 corn silage production at about 123 million tons, harvested from 6.10 million acres at an average 20.2 tons per acre. If storage and feedout losses nibble away at this mountain of feed, the financial and nutritional hit is huge—which is exactly where additives earn their keep by tightening fermentation and suppressing spoilage.
On-farm reality backs this up. Under good management, bunker-silo storage still suffers 10–15% dry-matter loss; with poor sealing and oxygen control, losses can balloon to 30–40%. Additives—whether lactic-acid bacteria inoculants, enzymes, or acid salts—work alongside good practices to push the curve the right way: faster pH drop, less heating, and fewer yeasts and molds at feedout. That combination protects energy and protein you already paid to grow.
This push is visible in concrete programs. Denmark earmarked 518 million DKK to help farmers use methane-reducing feed additives, citing reductions of up to 30%. The EU’s methane strategy targets a 35–37% cut in methane by 2030 versus 2005. These initiatives are primarily aimed at enteric methane, but they set the tone across the feed chain: documentable improvements and measurable outcomes. Forage additives fit neatly into this mindset because they generate data farmers can track—lower dry-matter loss, cooler face temperatures, steadier intakes—and they are relatively fast to deploy.
Restraints
High Cost of Silage Additives and Limited Awareness
One of the significant challenges hindering the widespread adoption of silage additives in India is their relatively high cost and the limited awareness among farmers regarding their benefits. While silage additives can enhance the nutritional quality and preservation of fodder, the initial investment required for their purchase and application can be a barrier for many smallholder farmers. This is particularly concerning given that a substantial portion of India’s farming community comprises small-scale producers with limited financial resources.
According to a study on buffalo husbandry in India, there is a notable gap between awareness and adoption of modern dairy production technologies. While awareness about silage-making stands at 71.5%, the actual adoption rate is only 32.9%, indicating a 38.6-point deficit. This discrepancy underscores the need for targeted interventions to bridge the knowledge gap and promote the benefits of silage additives among farmers.
To address these challenges, the Government of India has implemented several initiatives aimed at promoting the use of silage additives and improving fodder management practices. Under the National Livestock Mission (NLM), the government provides a 50% capital subsidy, up to a maximum of ₹50 lakh, for establishing feed and fodder value addition units, including silage-making units. This subsidy aims to encourage entrepreneurs and farmers to invest in modern fodder preservation technologies
Additionally, the Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF) offers financial support to eligible entities, including individual entrepreneurs, private companies, and farmer producer organizations (FPOs), for setting up animal feed manufacturing plants and strengthening existing units. Under this scheme, beneficiaries can avail loans up to 90% of the project cost, with a 3% interest subvention and a two-year moratorium period.
Opportunity
Surging Global Milk Demand Lights the Way for Silage Additives
The most compelling growth opportunity for silage additives stems from the steady rise in global milk production. According to the OECD‑FAO Agricultural Outlook 2025–2034, world milk output is projected to grow at 1.8% per year, reaching approximately 1,146 million tonnes by 2034. That’s a remarkable increase of around 208 million tonnes compared to the 2022–2024 average.
This momentum isn’t just a statistic to me—it’s deeply human. In regions like South Asia and Africa, rising incomes and urbanization are fueling demand for animal‑source foods. The Outlook emphasizes that most additional dairy consumption will occur in low‑ and middle‑income countries, where people are shifting diets toward more nutritious options.
Take India as an example. The USDA’s Foreign Agricultural Service forecasts milk production to climb from 211.7 million metric tons in 2024 to 216.5 million metric tons in 2025, driven by modest increases in herd size and smarter, sustainable feeding strategies. That’s more milk on the way—meaning farmers and cooperatives are pressed to preserve more feed, better.
Moreover, governments are paying attention. Large‑scale dairy-support schemes—like India’s National Programme for Dairy Development (NPDD), the Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM), and the Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF)—all funnel significant resources into livestock infrastructure, cooperative strengthening, and production capacity. These programs create a supportive ecosystem within which silage additives can flourish.
Regional Insights
North America leads with 43.8% share, valued at USD 1.1 billion in 2024
In 2024, North America held a dominant market position in the global silage additives sector, capturing more than a 43.8% share, equating to approximately USD 1.1 billion in market value. This leadership is primarily attributed to the region’s robust agricultural infrastructure, extensive livestock farming, and advanced silage management practices.
The United States, in particular, plays a pivotal role, with corn silage production reaching 130 million metric tons in 2023 and forage output exceeding 73.6 million metric tons. Such figures underscore the substantial demand for silage additives to enhance fermentation processes, preserve nutrients, and improve feed quality.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
ADM is a leading global agricultural processor and food ingredient provider. The company offers a wide range of silage preservatives under the Ecosyl brand, including biological inoculants and fermentation aids, to enhance silage quality and feed efficiency. With a strong presence in North America, ADM supports farmers with science-based solutions for improved animal nutrition and productivity.
ADDCON is a German-based company specializing in silage additives. Its product line includes KOFASIL® and GraSAAT® brands, offering both chemical and biological solutions to improve fermentation, prevent reheating, and enhance aerobic stability in silage. With over 60 years of experience, ADDCON serves a global market, providing reliable and effective additives for various forage types.
BASF is a global chemical company that provides innovative feed additives, including silage preservatives. Products like Lupro-Cid® and Luprosil® are designed to improve fermentation processes, enhance aerobic stability, and protect feed against microbial deterioration. BASF’s solutions support sustainable livestock production by ensuring high-quality silage and feed safety.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Archer Daniels Midland Company
- ADDCON GROUP GmbH.
- BASF SE
- Cargill Inc
- Brett Brothers Ltd.
- Evonik Industries AG
- LALLEMAND Inc.
- DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
- Kemin
- Eastman
Recent Industry Developments
In December 2024 BASF increased its ammonium chloride production capacity by 50% at its Ludwigshafen site—this chemical often plays a supportive role in feed sanitation and moisture control, which ties back to silage integrity.
In 2024, Brett Brothers Ltd., an established Irish family-run agricultural supplier with over 75 years of experience, continued supporting Northern Europe’s silage industry through practical solutions that farmers trust.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 2.7 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 4.4 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 5.0% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Product Type (Homofermentative Inoculants, Heterofermentative Inoculants, Combination Products, Acids and Acid Salts, Molasses or Sugar, Enzymes, Non-Protein Nitrogen Compound), By Form (Powder, Liquid), By Function (Stimulation Treatment, Inhibition Treatment, Others), By Crop Type (Corn, Alfalfa, Sorghum, Oats, Barley, Rye, Others), By Application (Cereals, Pulses, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Archer Daniels Midland Company, ADDCON GROUP GmbH., BASF SE, Cargill Inc, Brett Brothers Ltd., Evonik Industries AG, LALLEMAND Inc., DuPont de Nemours, Inc., Kemin, Eastman Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Archer Daniels Midland Company
- ADDCON GROUP GmbH.
- BASF SE
- Cargill Inc
- Brett Brothers Ltd.
- Evonik Industries AG
- LALLEMAND Inc.
- DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
- Kemin
- Eastman










