Hepatitis A Vaccine Market By Product Type (Inactivated Vaccine and Live Attenuated Vaccine), By Application (Government Institutions, Private Sectors, and Others), Region and Companies – Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: July 2025
- Report ID: 152402
- Number of Pages: 250
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
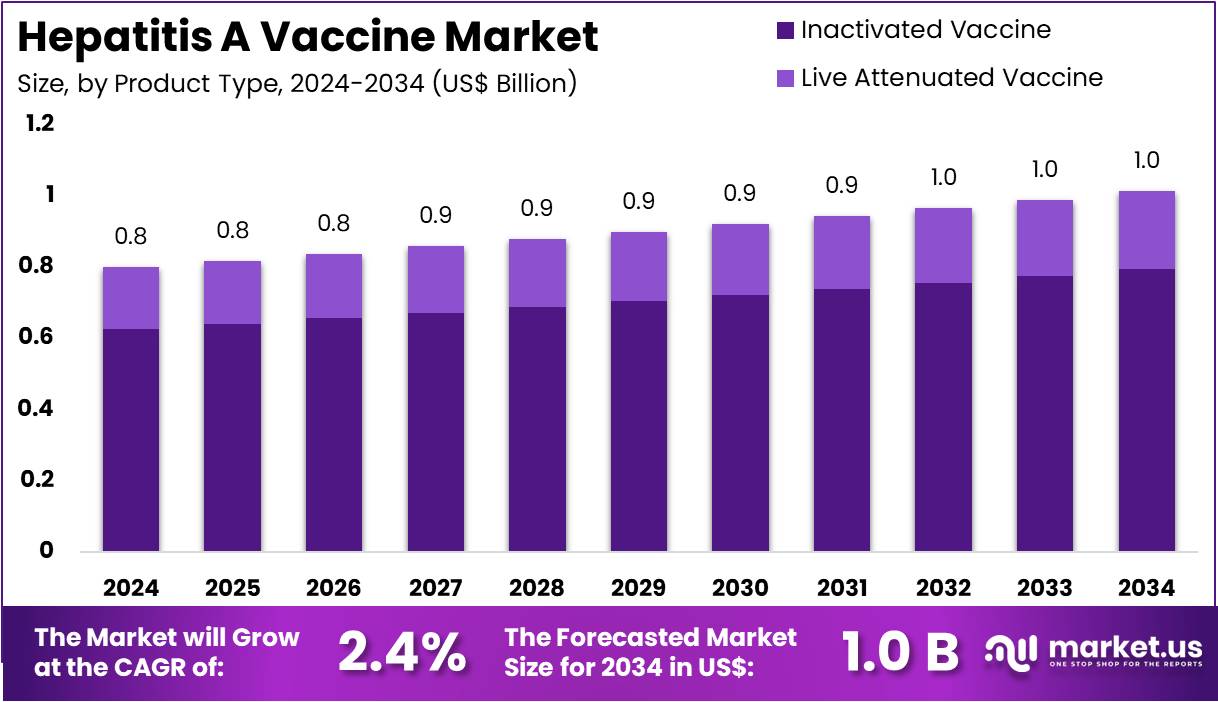
The Hepatitis A Vaccine Market Size is expected to be worth around US$ 1.0 billion by 2034 from US$ 0.8 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 2.4% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
Rising global awareness of the importance of vaccination and the increasing focus on preventing viral infections are driving the growth of the hepatitis A vaccine market. Hepatitis A, a contagious liver disease caused by the hepatitis A virus (HAV), can lead to severe health complications, particularly in young children and high-risk populations. The growing need for preventive measures and the expansion of vaccination programs are key factors propelling the market, with governments and health organizations pushing for widespread immunization.
In addition to routine vaccinations, the rise in travel-related infections and the increasing awareness of hepatitis A in non-endemic regions have further bolstered demand. The market is also witnessing greater adoption of combination vaccines, which include protection against multiple diseases, streamlining immunization schedules and improving compliance.
In September 2024, Indian Immunologicals Limited (IIL) launched the pediatric version of India’s first indigenous hepatitis A vaccine, Havisure (0.5 ml). This launch underscores IIL’s commitment to providing cost-effective and high-quality vaccines, particularly for children, ensuring broader access to immunization. The increasing focus on improving access to vaccines in developing countries, where hepatitis A remains a significant health threat, presents significant opportunities for growth.
Moreover, the continued development of vaccines with improved safety profiles and the potential for enhanced protection against multiple strains of the virus offers new avenues for market expansion. As awareness of hepatitis A prevention continues to grow, the vaccine market is set to benefit from innovations that make vaccines more accessible, affordable, and effective.
Key Takeaways
- In 2024, the market for hepatitis A vaccine generated a revenue of US$ 0.8 billion, with a CAGR of 2.4%, and is expected to reach US$ 1.0 billion by the year 2034.
- The product type segment is divided into inactivated vaccine and live attenuated vaccine, with inactivated vaccine taking the lead in 2023 with a market share of 78.3%.
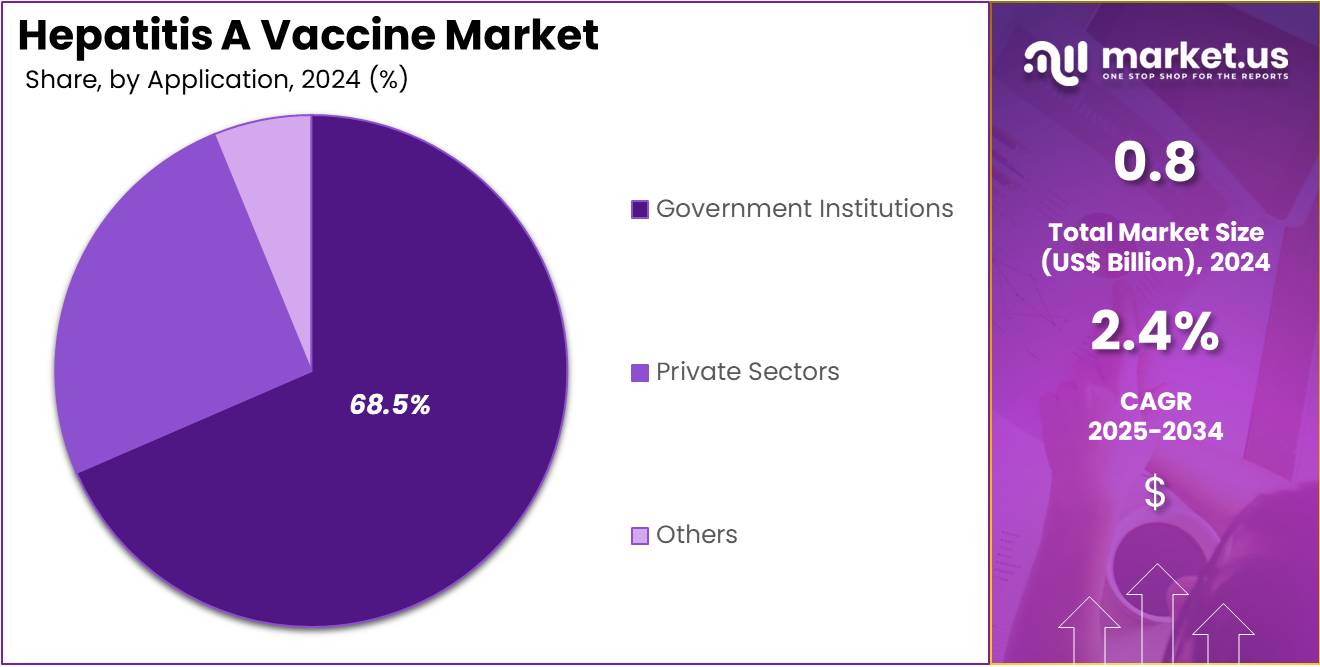
- Considering application, the market is divided into government institutions, private sectors, and others. Among these, government institutions held a significant share of 68.5%.
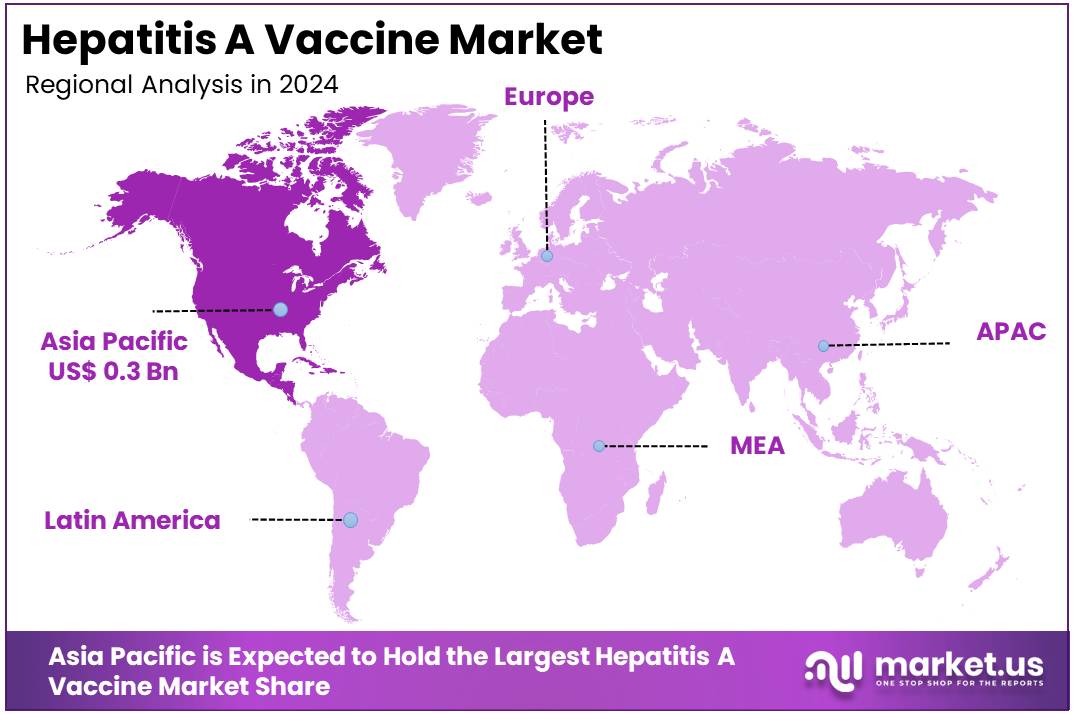
- Asia Pacific led the market by securing a market share of 37.4% in 2023.
Product Type Analysis
Inactivated vaccines dominate the hepatitis A vaccine market with a significant share of 78.3%. This dominance is expected to continue due to the higher safety profile of inactivated vaccines compared to live attenuated versions, particularly for individuals with compromised immune systems. The growing global adoption of inactivated hepatitis A vaccines, especially in developing regions where hepatitis A prevalence remains high, is projected to further solidify this segment’s leading position. The vaccine’s long shelf life and the ability to store it at a wider range of temperatures make it more accessible for distribution, particularly in remote areas.
The increasing government and NGO support for vaccination campaigns is likely to enhance the distribution of inactivated vaccines, further driving demand. Additionally, inactivated vaccines are commonly used in combination with other vaccines, making them more convenient for vaccination schedules. The growing focus on global immunization programs, especially in countries with high hepatitis A incidence, is anticipated to contribute to the continued growth of this segment. As public health awareness increases and vaccination rates improve, the market for inactivated hepatitis A vaccines is expected to expand.
Application Analysis
Government institutions hold a dominant share of 68.5% in the hepatitis A vaccine market. This dominance is primarily driven by government-led vaccination programs aimed at preventing the spread of hepatitis A in both endemic and non-endemic regions. The increasing focus on public health and the growing commitment by governments to offer affordable vaccines are expected to accelerate growth in this segment.
Government institutions are projected to continue being the largest purchaser and distributor of hepatitis A vaccines due to their role in funding large-scale immunization campaigns, particularly in countries where hepatitis A remains a major health concern. The expanding healthcare budgets in emerging markets and the increasing recognition of vaccination as a cost-effective measure to prevent disease outbreaks are anticipated to drive demand in this segment.
Moreover, international health organizations and global initiatives are likely to boost government efforts to increase vaccination rates, particularly in underdeveloped regions. The adoption of routine immunization schedules in national healthcare systems is projected to further contribute to the sustained growth of government-led hepatitis A vaccination initiatives. With these programs, government institutions will continue to play a critical role in maintaining and expanding the reach of hepatitis A vaccination efforts worldwide.
Key Market Segments
By Product Type
- Inactivated Vaccine
- Live Attenuated Vaccine
By Application
- Government Institutions
- Private Sectors
- Others
Drivers
Increasing Global Travel and Risk of Outbreaks is Driving the Market
The increasing global travel and the associated risk of Hepatitis A outbreaks are significant drivers propelling the Hepatitis A vaccine market. Hepatitis A virus (HAV) is highly contagious and often transmitted through contaminated food or water, making travelers to endemic regions particularly vulnerable. As international tourism and business travel continue to expand, the likelihood of exposure to the virus in various parts of the world increases, leading to a higher demand for pre-travel vaccination.
Many public health organizations, including the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), strongly recommend Hepatitis A vaccination for individuals traveling to countries with high or intermediate levels of Hepatitis A prevalence. The CDC’s “Yellow Book” for International Travel Health, updated as of April 2025, specifically identifies Hepatitis A as one of the most common vaccine-preventable infections acquired during travel, even for travelers staying in standard tourist accommodations.
This continuous movement of people across borders creates a sustained need for preventive measures. While global travel patterns fluctuate, the underlying trend towards increased international mobility remains, driving the need for vaccination among a broader segment of the population. The World Health Organization (WHO) also emphasizes the importance of vaccination in controlling Hepatitis A globally, recognizing international travel as a key factor in its spread. The growing awareness among travelers and healthcare providers about this risk further stimulates demand for the vaccine.
Restraints
Challenges in Vaccine Cold Chain Management and Distribution are Restraining the Market
Significant challenges in maintaining the vaccine cold chain and ensuring efficient distribution are notably restraining the Hepatitis A vaccine market. Hepatitis A vaccines, like many other vaccines, require strict temperature control throughout their journey from manufacturing sites to administration points to maintain their potency and efficacy.
Any deviation from the recommended temperature range (typically 2°C to 8°C) can render the vaccine ineffective, leading to wastage and compromised immunization programs. This “cold chain” involves complex logistics, specialized equipment such as refrigerators and freezers, and continuous monitoring. In many developing regions, inadequate infrastructure, unreliable electricity supply, and a lack of trained personnel pose substantial hurdles to effective cold chain management.
The World Health Organization (WHO) consistently highlights vaccine wastage due to cold chain failures as a persistent problem in global immunization efforts. For instance, a study published on PubMed Central in June 2025, analyzing vaccine wastage rates in parts of Uganda for March-August 2022, showed varying wastage rates for different vaccines, with specific challenges related to maintaining cold chain integrity.
While not specific to Hepatitis A vaccines, these broader cold chain issues directly impact the availability and effectiveness of all temperature-sensitive vaccines. Failures in maintaining the cold chain result in substantial financial losses for public health programs and pharmaceutical companies and, more critically, lead to missed vaccination opportunities and continued disease transmission, thereby impeding market growth and public health objectives.
Opportunities
Integration into Routine Childhood Immunization Programs is Creating Growth Opportunities
The increasing integration of Hepatitis A vaccine into routine childhood immunization programs, particularly in regions with transitioning epidemiology, is creating significant growth opportunities. Historically, Hepatitis A vaccination was primarily recommended for risk groups or travelers. However, as some countries move from high to intermediate endemicity, older cohorts remain susceptible, making universal childhood vaccination a highly effective strategy to prevent future outbreaks and achieve broader population immunity.
This shift in policy by national health authorities and the World Health Organization (WHO) provides a stable and expanding demand base for the vaccine. The WHO, in its updated position paper on Hepatitis A vaccines (February 2023), reiterated that childhood vaccination is highly effective in preventing clinical disease and confers long-term protection. This paper supports the inclusion of the vaccine in national immunization programs, either with single or two-dose schedules of inactivated vaccines.
Such routine integration ensures a consistent uptake of the vaccine among new birth cohorts, contributing to sustained market growth. Countries that implement these programs demonstrate a commitment to long-term disease control, providing a predictable procurement environment for vaccine manufacturers. As more countries adopt these recommendations and roll out widespread childhood vaccination, the market for Hepatitis A vaccine experiences steady expansion beyond targeted adult populations.
Impact of Macroeconomic / Geopolitical Factors
Macroeconomic and geopolitical factors significantly influence the Hepatitis A vaccine market, shaping both its challenges and its trajectory. Economic conditions, such as global inflation rates and the varying levels of national healthcare spending, directly impact the affordability and procurement of vaccines. During periods of high inflation, the cost of raw materials, manufacturing, and distribution for vaccines can increase, potentially leading to higher product prices for governments and public health organizations.
For instance, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported that the Producer Price Index for Pharmaceutical Preparation and Medicament Manufacturing increased by 2.6% from May 2023 to May 2024, indicating pervasive inflationary pressures on drug production. This pressure can strain national immunization budgets, particularly in lower-income countries reliant on international aid or self-financing. Geopolitical events, including trade disputes, regional conflicts, or widespread health emergencies, can disrupt global vaccine supply chains, affecting the availability and timely distribution of Hepatitis A vaccines.
For example, export restrictions or logistical challenges in conflict zones can impede vaccine access. However, such global events can also underscore the critical importance of robust public health infrastructure and vaccine preparedness, potentially spurring increased investment in vaccine procurement and domestic manufacturing capabilities in some regions. This can lead to more diversified and resilient global supply networks in the long run.
Current US tariffs have both direct and indirect impacts on the Hepatitis A vaccine market. Tariffs on imported raw materials, specialized manufacturing equipment, or even certain finished pharmaceutical products directly increase costs for vaccine manufacturers operating in or importing into the US. These higher input costs force pharmaceutical companies to either absorb the additional expenses, which reduces their profit margins and limits investment in research and development (R&D), or pass these costs on to healthcare providers, ultimately increasing the price of essential vaccines and impacting public health programs.
A June 2025 analysis by the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health revealed that US pharmaceutical imports more than doubled in value, from US$ 73 billion in 2014 to over US$ 215 billion in 2024, underscoring the heavy reliance of the US on global supply chains that tariffs can disrupt. The analysis also noted that high tariffs on Chinese APIs, reaching up to 245%, could significantly raise the cost of Chinese APIs, which are critical components for the production of vaccines.
Indirectly, these tariffs could create trade uncertainties, potentially discouraging foreign investment in US-based vaccine manufacturing and R&D. However, such tariff policies could also act as a strong incentive for domestic manufacturing and innovation, encouraging vaccine producers to invest more in US-based production facilities for vaccines. This shift toward domestic production could foster job creation, enhance supply chain security, and ultimately strengthen the resilience of the US vaccine market, ensuring a more reliable and independent supply of crucial vaccines.
Latest Trends
Development of Combination Vaccines and Novel Delivery Systems is a Recent Trend
A prominent recent trend significantly impacting the Hepatitis A vaccine market in 2024 and continuing into 2025 is the development of combination vaccines and novel delivery systems. Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly focusing on creating combination vaccines that include Hepatitis A alongside other antigens, such as Hepatitis B (e.g., Twinrix), or even other common childhood vaccines. These combination vaccines offer the advantage of reducing the number of injections, simplifying vaccination schedules, improving patient compliance, and potentially increasing overall vaccination coverage. This approach is particularly appealing for pediatric immunization programs and for travelers requiring multiple vaccine protections.
Furthermore, research into novel delivery systems, such as intranasal or oral vaccines, aims to enhance patient acceptability, especially for individuals with needle phobia, and to potentially reduce the need for specialized medical personnel for administration. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regularly reviews and approves new vaccine formulations, and while specific new Hepatitis A combination vaccines might not have received a novel approval in 2024-2025 (apart from existing ones like Twinrix), the general trend in vaccinology focuses on convenience and broadened coverage.
A June 2025 review on ResearchGate highlighted recent advances in mRNA-based vaccines against several hepatitis viruses, indicating ongoing research into advanced vaccine technologies, though Hepatitis A mRNA vaccines are still in early stages. This continuous innovation in formulation and delivery seeks to improve the user experience and expand the reach of Hepatitis A immunization programs globally.
Regional Analysis
Asia Pacific is leading the Hepatitis A Vaccine Market
Asia Pacific dominated the market with the highest revenue share of 37.4% owing to increasing public health awareness campaigns, expanding routine immunization programs, and improving healthcare access across diverse populations. Many countries in the region recognize the importance of preventing hepatitis A, particularly in areas where sanitation infrastructure may still be developing or where outbreaks occur periodically.
For example, China maintains a robust national immunization program, with vaccine coverage consistently above 95% for routine vaccines, and hepatitis A vaccine is included in its national immunization schedule, as highlighted in the China Country Profile by DCVMN. This wide coverage ensures a consistent demand for the immunization doses. In India, the Indian Academy of Pediatrics (IAP) Advisory Committee on Vaccines and Immunization Practices (ACVIP) continues to recommend hepatitis A immunization for children, with guidelines updated in 2023. These recommendations influence private sector procurement and increasing public awareness.
While specific regional revenues for hepatitis A immunization are typically part of broader vaccine segments for key players, companies like GSK and Sanofi, with strong established presences in Asia Pacific, are likely to continue leveraging their distribution networks and public health partnerships to meet the increasing demand. This concerted push towards comprehensive preventative healthcare and disease control is projected to significantly accelerate the market for hepatitis A immunization across the Asia Pacific region.
The North America region is expected to experience the highest CAGR during the forecast period
North America is expected to grow with the fastest CAGR owing to a sustained focus on public health initiatives and active responses to localized outbreaks. Although the reported number of hepatitis A cases in the United States saw a decrease from 2,265 in 2022 to 1,648 in 2023, the 2023 figure still remained 1.2 times higher than in 2015, the year before widespread outbreaks began, as reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). This fluctuating but elevated baseline underscores the continued need for vaccination to control sporadic outbreaks and maintain population immunity, particularly among at-risk adult populations and children.
In Canada, public health efforts also address outbreak responses, such as the investigation in 2022 of hepatitis A infections linked to imported fresh organic strawberries, which resulted in 10 laboratory-confirmed cases across Alberta and Saskatchewan, as reported by Public Health Ontario. Such events prompt immediate public health interventions, including recommendations for vaccination of exposed individuals, thereby stimulating demand for the vaccine.
While specific hepatitis A vaccine revenues are often consolidated within broader vaccine portfolios, GSK, a prominent manufacturer, reported its Vaccines turnover at US$ 11,418 million for 2024. Similarly, Sanofi’s vaccine segment contributes significantly to its overall financial performance, with its investor relations indicating strong vaccine sales across its portfolio, demonstrating robust demand from routine immunization programs and outbreak response efforts.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherland
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Key players in the hepatitis A vaccine market implement several growth strategies to strengthen their position. They focus on expanding vaccine accessibility through partnerships with governments and healthcare organizations, especially in regions with high disease prevalence. Companies invest in research and development to improve vaccine formulations, offering more efficient and longer-lasting protection.
They also expand their geographic reach by targeting emerging markets where vaccination rates are low. Strategic acquisitions allow companies to diversify their portfolios and boost production capabilities. Additionally, they enhance public health awareness campaigns to increase vaccine uptake and reduce disease transmission.
One key player, GSK (GlaxoSmithKline), is a global healthcare company that leads in vaccines and pharmaceutical treatments. GSK produces Havrix, a widely used hepatitis A vaccine. The company focuses on advancing vaccine technologies and improving immunization programs globally. GSK’s ongoing commitment to R&D and collaboration with public health bodies enables it to expand its vaccine offerings and enhance disease prevention efforts worldwide.
Top Key Players in the Hepatitis A Vaccine Market
- Sanofi
- KM Biologics
- Johnson & Johnson
- Janssen Vaccines
- Instituto Butantan
- Indian Immunologicals Limited
- GlaxoSmithKline plc
- Changchun Institute of Biological Products
Recent Developments
- In April 2023, Sanofi introduced its inactivated hepatitis A vaccine, Avaxim Junior, in the UK for children aged 12 months to 15 years. Based on data from 20 clinical trials across 14 countries, the vaccine demonstrated an effective immune response in over 95% of recipients within just two weeks.
- For the financial year 2023-24, GlaxoSmithKline plc reported strong performance, with total sales reaching £30.3 billion (approximately US$38.1 billion). Vaccine sales saw a 25% increase, contributing to the company’s robust growth. The reported operating profit for the year stood at £6.7 billion (approximately US$ 8.5 billion), reflecting the company’s continued market strength.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) US$ 0.8 billion Forecast Revenue (2034) US$ 1.0 billion CAGR (2025-2034) 2.4% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, COVID-19 Impact, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Product Type (Inactivated Vaccine and Live Attenuated Vaccine), By Application (Government Institutions, Private Sectors, and Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Sanofi, KM Biologics, Johnson & Johnson, Janssen Vaccines, Instituto Butantan, Indian Immunologicals Limited, GlaxoSmithKline plc, Changchun Institute of Biological Products. Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Hepatitis A Vaccine MarketPublished date: July 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Hepatitis A Vaccine MarketPublished date: July 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Sanofi
- KM Biologics
- Johnson & Johnson
- Janssen Vaccines
- Instituto Butantan
- Indian Immunologicals Limited
- GlaxoSmithKline plc
- Changchun Institute of Biological Products










