Global Electric Vehicles Battery Packs Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Battery Type (Lithium-ion, Nickel-Metal Hydride, Solid-State, Lead-Acid, Others), By Vehicle Type (Passenger Cars, Commercial Vehicles, Two-Wheelers, Others), By Capacity (Less than 50 kWh, 50-100 kWh, 100-200 kWh, More than 200 kWh), By Sales Channel (OEM, Aftermarket) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Dec 2025
- Report ID: 169663
- Number of Pages: 358
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
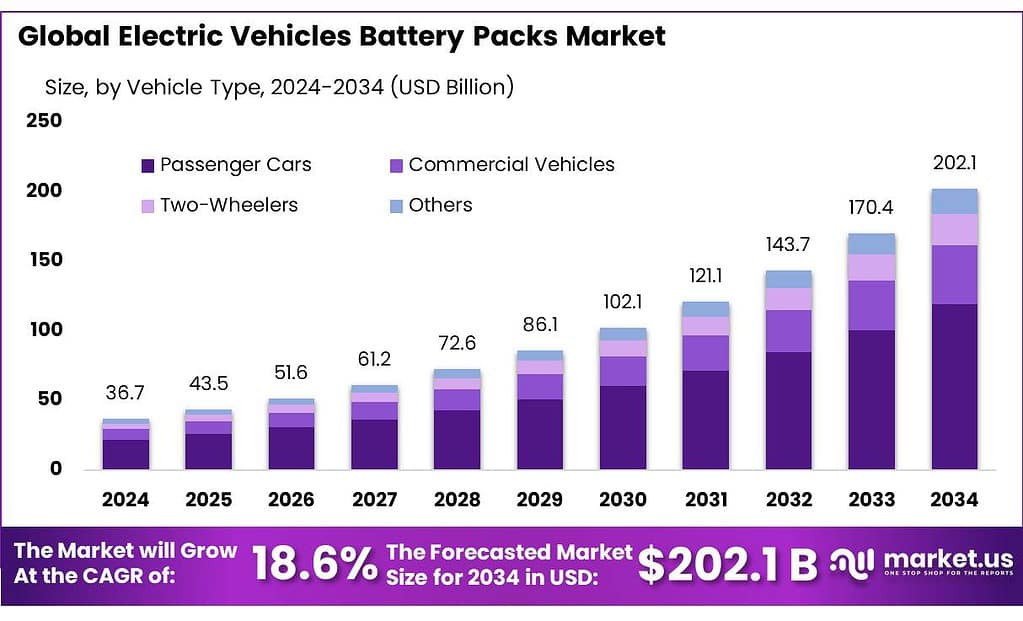
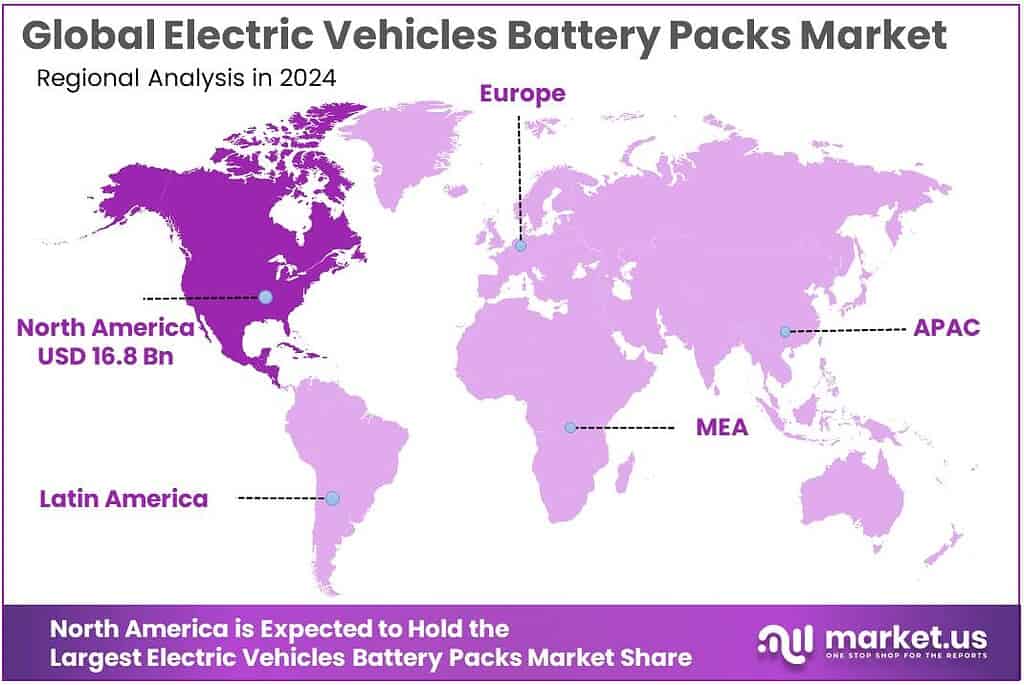
The Global Electric Vehicles Battery Packs Market size is expected to be worth around USD 202.1 Billion by 2034, from USD 36.7 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 18.6% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 45.8% share, holding USD 16.8 Billion revenue.
Electric vehicle (EV) battery packs sit at the heart of the transition from internal combustion to electrified transport. They integrate cells, thermal management, battery management systems and housing into a safety-critical module that defines vehicle range, performance and cost. Global electric car registrations reached around 14 million units in 2023, taking the stock on the road to about 40 million according to the International Energy Agency (IEA), underlining the scale of demand for traction battery packs.
On the industrial side, EV batteries have become a strategic manufacturing sector. The IEA estimates that demand for EV batteries reached more than 750 GWh in 2023, up about 40% versus 2022, with EVs accounting for nearly 90% of all lithium-ion battery demand. In 2024, total battery demand in the energy sector crossed 1 TWh, and EV batteries alone exceeded 950 GWh, or over 85% of that demand. Battery manufacturing capacity reached roughly 2.5 TWh in 2023, after adding about 780 GWh of new capacity in a single year, signalling rapid industrial build-out in China, Europe and North America.
Cost reduction remains a defining driver. BloombergNEF reports global average lithium-ion battery pack prices falling 20% in 2024 to around US$115/kWh, with EV-specific packs dipping below US$100/kWh for the first time. Their latest 2025 survey indicates a further decline to about US$108/kWh, despite higher metal prices, aided by overcapacity, competition and the shift to lower-cost LFP chemistries. These trends improve total cost of ownership for EVs and support pack makers as they scale higher-energy and more affordable designs.
Policy support strongly shapes the industry’s trajectory. In the United States, the Inflation Reduction Act extends a “New Clean Vehicle Tax Credit” of up to US$7,500 per vehicle through 2032, split between critical mineral and battery component criteria. This is driving local battery-pack and cell investment to meet sourcing rules. In China, where NEV ownership exceeded 30 million by the end of 2024, battery and EV incentives, industrial policies and export-oriented strategies have created the world’s largest integrated EV-battery value chain.
Key driving factors include ongoing electrification of passenger cars, two-wheelers and commercial fleets, tightening CO₂ and air-quality regulations, and corporate decarbonization targets in logistics and mobility services. The IEA notes that Korean and Japanese producers together supplied almost 30% of global electric-car battery demand in 2024, reflecting intense competition and technology race in high-nickel and emerging solid-state designs. At the same time, OEMs are pushing for higher pack energy density, faster charging and improved safety, which reinforces demand for advanced management systems and thermal solutions.
Key Takeaways
- Electric Vehicles Battery Packs Market size is expected to be worth around USD 202.1 Billion by 2034, from USD 36.7 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 18.6%.
- Lithium-ion held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 77.2% share.
- Passenger Cars held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 59.7% share.
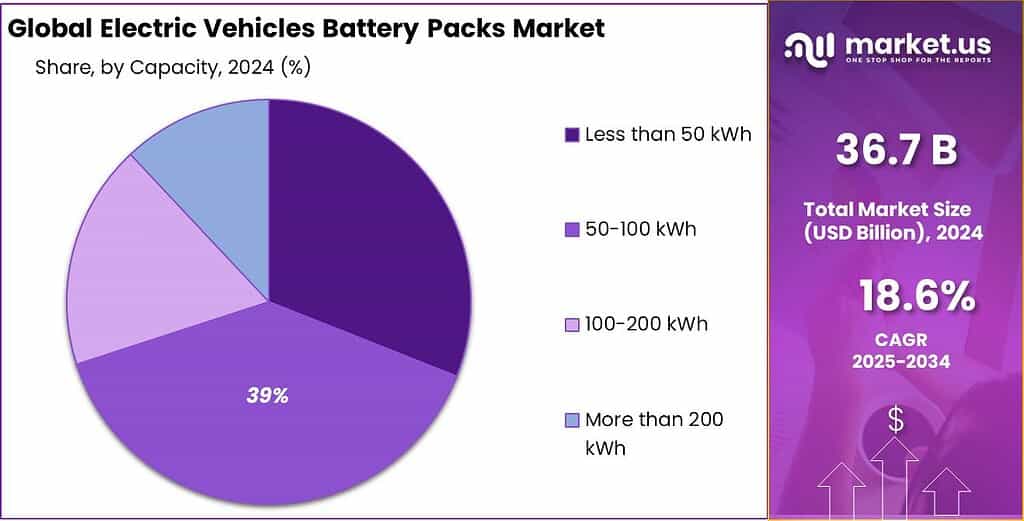
- 50-100 kWh held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.9% share.
- OEM held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 89.6% share.
- North America region emerged as the dominant region for electric-vehicle battery packs, accounting for 45.8% of global revenue and roughly USD 16.8 billion.
By Battery Type Analysis
Lithium-ion dominates with a 77.2% share in 2024, driven by superior energy density and falling costs.
In 2024, Lithium-ion held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 77.2% share, and the segment was characterized by widespread adoption across battery form factors and vehicle classes (BEV, PHEV, HEV). The preference for lithium-ion was driven by improvements in specific energy and cycle life, which enabled longer vehicle range and lower total cost of ownership; accordingly, production volumes were scaled up and supply-chain investments were accelerated. Cell chemistry refinements and larger format cells were favored for passenger cars, while modular pack architectures were increasingly adopted for commercial vehicles to simplify thermal management and serviceability.
Battery cost declines and standardized manufacturing processes were reflected in procurement strategies, and recycling and second-life programs were initiated to address end-of-life value recovery. By 2025, the lithium-ion segment was further consolidated in market mix, with continued emphasis placed on efficiency gains, safety enhancements, and circularity measures to support broader electrification targets.
By Vehicle Type Analysis
Passenger Cars dominate with 59.7% as the primary driver of battery pack demand.
In 2024, Passenger Cars held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 59.7% share. This dominance was driven by rising electrification of mid- and small-size vehicle fleets, where longer ranges and improved battery economics were prioritized. Production of battery packs for passenger cars was scaled to benefit from manufacturing efficiencies, and larger procurement volumes enabled reductions in per-kWh pack cost. Vehicle architectures were increasingly optimized for integrated battery placement, improving packaging and weight distribution.
Policy support for passenger electric vehicles and expansion of public and private charging infrastructure further underpinned demand, while aftermarket and second-life battery programs were initiated to reduce total cost of ownership. By 2025, the passenger car segment continued to be the largest contributor to battery pack volumes, with attention shifted toward improving pack energy density, safety features, and recyclability to support sustained consumer uptake.
By Capacity Analysis
50–100 kWh (Large) leads with 38.9% as the preferred capacity for longer-range passenger and commercial EVs.
In 2024, 50-100 kWh held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.9% share. This capacity band was favored because it balanced range and cost for mid-size and larger vehicles, enabling manufacturers to deliver competitive driving distances without excessive weight or packaging penalties. Production was adjusted to accommodate larger-format modules and improved thermal management, while pack designs emphasized modularity to simplify service and scaling across model lines.
Procurement and manufacturing processes were optimized to reduce per-pack costs, and reuse and recycling initiatives were initiated to recover value at end of life. By 2025, the 50-100 kWh segment remained a central focus for vehicle makers seeking to meet consumer expectations for range and value.
By Sales Channel Analysis
OEM dominates with 89.6% as the primary route for battery pack delivery.
In 2024, OEM held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 89.6% share. This dominance was driven by direct integration of battery pack design into vehicle architectures, which enabled better packaging, safety controls, and warranty alignment; procurement was centralized and scale efficiencies were realized through high-volume contracts. Technical responsibilities for thermal management and battery management systems were retained by vehicle makers, and serviceability and aftersales processes were coordinated within OEM networks to preserve product reliability.
Supply-chain investments and long-term component sourcing were prioritized to secure production continuity. In 2025, the OEM channel remained the principal conduit for battery pack deployment, with ongoing emphasis on tighter vehicle–pack integration, lifecycle management, and supplier consolidation to support broader electrification goals.
Key Market Segments
By Battery Type
- Lithium-ion
- Nickel-Metal Hydride
- Solid-State
- Lead-Acid
- Others
By Vehicle Type
- Passenger Cars
- Commercial Vehicles
- Two-Wheelers
- Others
By Capacity
- Less than 50 kWh
- 50-100 kWh
- 100-200 kWh
- More than 200 kWh
By Sales Channel
- OEM
- Aftermarket
Emerging Trends
Growing Shift to LFP Battery Chemistry — A New Trend in EV Battery Packs
A major recent trend in the electric-vehicle (EV) battery pack industry is the growing shift toward using lithium-iron-phosphate (LFP) battery chemistry instead of older, cobalt- or nickel-rich chemistries. This shift reflects evolving concerns around cost, safety, and supply-chain resilience — and it’s reshaping how battery packs are made and adopted worldwide.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) reports that in 2024 nearly half of all EV battery sales globally came from LFP-based batteries. This is a striking share — and it shows that LFP is no longer a niche chemistry meant for inexpensive entry-level EVs; it’s becoming a mainstream choice even for many higher volume models. The appeal of LFP comes from its lower cost, better thermal stability, and simpler supply chains. This shift reduces dependence on critical and often geopolitically-sensitive minerals.
In addition to cost and supply security, advances in battery-pack design have helped improve energy density for LFP batteries. Innovations mean LFP packs now deliver far better energy per unit weight than older generations, narrowing the performance gap with nickel-rich batteries. At the same time, battery pack manufacturers increasingly adopt more integrated architectures — for example, moving from module-based assemblies to “cell-to-pack” (CTP) designs that eliminate separate modules and pack cells directly into the pack structure. This reduces weight, complexity, and cost, making LFP even more attractive.
From a human and societal angle: this shift makes EVs more accessible by reducing costs, which means more people — not just affluent buyers — can consider electric mobility. It also reduces pressure on scarce minerals like cobalt, which are often sourced under difficult environmental and social conditions. That has real-world significance: safer, more affordable EV batteries help accelerate the transition to cleaner transport, lowering emissions and improving air quality for communities everywhere.
Drivers
Strong Electric Vehicle Adoption Directly Increases Battery Pack Demand
One major driving factor for the Electric Vehicles (EV) Battery Packs market is the fast and steady rise in global electric vehicle adoption. As more countries move away from petrol and diesel vehicles, demand for reliable and high-capacity battery packs grows automatically because batteries are the most expensive and essential part of an electric vehicle.
- According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), global electric car sales crossed 14 million units in 2023, accounting for about 18% of all car sales worldwide. This figure was only 4% in 2020, showing how quickly EV adoption is accelerating.
Government climate policies are a key reason behind this demand surge. Transport contributes nearly 23% of global energy-related CO₂ emissions, as reported by the IEA. To reduce this impact, governments are introducing strong EV policies that indirectly push battery pack production. For example, the European Union approved a regulation banning the sale of new internal combustion engine cars by 2035, creating long-term certainty for EV investment. Every electric car sold under this mandate requires a battery pack, ensuring continuous market expansion.
China remains the largest single EV market and a powerful demand driver for battery packs. The China Association of Automobile Manufacturers (CAAM) reported that new energy vehicle sales exceeded 9.5 million units in 2023, representing over 31% of total vehicle sales in the country. This scale alone requires massive battery pack volumes, ranging from entry-level lithium iron phosphate packs to high-energy density systems for premium vehicles.
In the United States, federal support plays a similar role. The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) offers up to USD 7,500 in tax credits for new electric vehicles, provided battery components and critical minerals meet domestic or allied sourcing rules. This policy directly supports battery pack manufacturing within North America, encouraging automakers to invest in local battery facilities. The U.S. Department of Energy states that battery manufacturing capacity in the country is expected to increase more than five times between 2022 and 2030, driven largely by EV demand.
Restraints
Critical Mineral Supply Constraints Slow Battery Pack ScalingOne major restraining factor for the Electric Vehicles (EV) Battery Packs industry is the limited and uneven supply of critical minerals such as lithium, nickel, cobalt, graphite, and manganese. These materials are essential for making lithium-ion battery cells, and any disruption in their supply directly affects battery pack production, cost stability, and delivery timelines. While EV demand is rising quickly, mineral supply expansion is struggling to keep pace, creating a structural bottleneck for the battery value chain.According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), demand for lithium from the energy sector increased more than 8 times between 2017 and 2023, largely driven by EV batteries. However, new mining and refining projects typically take 7 to 10 years to become operational. This time gap makes it difficult for supply to respond quickly to demand growth, causing shortages and price swings.- Cost volatility is a direct outcome of this imbalance. Data from the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) shows that the average lithium carbonate price rose from under USD 10,000 per metric ton in 2020 to over USD 70,000 per metric ton in 2022, before falling again in 2023. Such sharp price movements make battery pack pricing unpredictable, complicating long-term contracts for automakers and battery manufacturers.
Geographic concentration further increases risk. The World Bank reports that over 70% of global cobalt mining comes from the Democratic Republic of Congo, while more than 60% of lithium processing capacity is located in China. Any geopolitical tension, export restriction, or local disruption in these regions can quickly affect global battery supply. For battery pack producers, this leads to higher procurement risk and supply insecurity.Opportunity
Local Battery Manufacturing and Recycling Creates Long-Term Growth
One major growth opportunity for Electric Vehicles (EV) Battery Packs lies in the rapid expansion of local battery manufacturing and recycling ecosystems. As governments aim to reduce dependence on imports and secure clean-energy supply chains, battery pack production is increasingly moving closer to vehicle manufacturing and end markets. This shift is opening significant opportunities for capacity expansion, job creation, and technology upgrades across regions.
Government policy is the strongest enabler of this opportunity. In the United States, the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) has committed large-scale support for domestic battery supply chains. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, announced investments in U.S. battery manufacturing exceeded USD 130 billion between 2022 and 2024, covering cells, battery packs, and material processing.
Europe is following a similar path. The European Commission estimates that the EU must install battery manufacturing capacity of at least 550 GWh per year by 2030 to meet its electric mobility and energy storage goals. To support this, the EU has approved multiple Important Projects of Common European Interest (IPCEI) focused on batteries, allowing billions of euros in state aid for manufacturing and innovation. This directly boosts battery pack demand, especially for region-specific designs suited to European vehicle platforms.
India presents another strong growth opportunity. Under the government’s Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for Advanced Chemistry Cell batteries, incentives worth INR 18,100 crore (roughly USD 2.2 billion) have been allocated to promote domestic battery production. The Indian government projects EV penetration to reach 30% of new vehicle sales by 2030, which would require large volumes of affordable battery packs adapted for two-wheelers, three-wheelers, and compact cars.
Battery recycling is another fast-growing opportunity closely tied to pack manufacturing. As EV adoption increases, large numbers of used battery packs will reach end-of-life over the next decade. The International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates that recycling could supply up to 10% of global lithium demand by 2030 and significantly reduce reliance on new mining. This creates opportunities for battery pack producers to integrate recycling, refurbishment, and second-life energy storage into their business models.
Regional Insights
North America commands with 45.8% share USD 16.8 billion revenue
In 2024, the North America region emerged as the dominant region for electric-vehicle battery packs, accounting for 45.8% of global revenue and roughly USD 16.8 billion in sales. The strong position of this region can be attributed to robust demand for EVs in the United States and Canada, supported by favourable government incentives, tax credits, and emissions regulations that accelerated adoption of electric mobility. Localisation trends in battery production and pack assembly were further reinforced, as major automakers and battery manufacturers increased investments in domestic gigafactory construction and supply-chain integration to reduce reliance on imports.
Manufacturing efficiency gains were realised through scaling of production, bulk procurement of raw materials, and standardisation of pack designs — resulting in lower per-kWh pack costs. These cost improvements, combined with improved charging infrastructure and consumer awareness, strengthened the uptake of EVs across passenger and light commercial segments. The US subsidiary of North America contributed a majority portion of this regional share, reflecting its leadership in both EV sales and battery supply-chain investments.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Panasonic Energy remains a key supplier of automotive lithium-ion cells and pack technology, advancing larger format and higher-capacity cells for vehicle integration. The company has announced readiness for mass production of next-generation 4680 cells and continues to supply cylindrical and prismatic formats for mobility partners. Emphasis has been placed on expanding local production, improving cell energy density, and reducing manufacturing cost per kWh to meet increasing OEM demand for longer range and lower total cost of ownership.
BYD’s vertically integrated model—covering cell manufacture, pack assembly, and vehicle production—enabled rapid capacity scale-up and cost control. The company leveraged blade-battery designs and in-house cell production to supply its large passenger-vehicle output and growing export markets. This integration supported competitive pricing and rapid model rollouts, while investment in production and R&D sustained improvements in energy density and safety. BYD’s combined cell and vehicle strategy underpinned its strong installed capacity and rising global market share through 2024.
Samsung SDI focuses on advanced cell formats and collaborative manufacturing projects to serve premium EV segments and strategic OEMs. The company has pursued joint ventures and large-scale plant investments—targeting diversified cell types including cylindrical and prismatic formats—to expand capacity in North America and Europe. Technology efforts concentrate on higher energy density, fast-charging capability, and pack integration for luxury and performance vehicles. Strategic partnerships with automakers reinforce its position as a supplier of differentiated, high-performance battery solutions.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Hitachi
- Panasonic
- General Motors
- CATL
- BYD
- Samsung SDI
- LG Energy Solution
- AESC
- Volkswagen
- Saft
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024 Samsung SDI reported annual revenue of KRW 16.59 trillion (battery and related businesses) and a battery-business Q3 revenue of KRW 3.67 trillion, reflecting supply-chain pressure and market adjustment. Samsung SDI finalised a $3.5 billion joint venture with General Motors to build an initial 27–36 GWh U.S. plant, and continued large investments with Stellantis for multi-GWh capacity in Indiana, signalling heavy capital commitments to localised production and scale.
In 2024 Hitachi reported consolidated revenue of JPY 9,728.7 billion and net income of JPY 626.7 billion, reflecting continued investment capacity for mobility and energy initiatives.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 36.7 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 202.1 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 18.6% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Battery Type (Lithium-ion, Nickel-Metal Hydride, Solid-State, Lead-Acid, Others), By Vehicle Type (Passenger Cars, Commercial Vehicles, Two-Wheelers, Others), By Capacity (Less than 50 kWh, 50-100 kWh, 100-200 kWh, More than 200 kWh), By Sales Channel (OEM, Aftermarket) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Hitachi, Panasonic, General Motors, CATL, BYD, Samsung SDI, LG Energy Solution, AESC, Volkswagen, Saft Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Electric Vehicles Battery Packs MarketPublished date: Dec 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Electric Vehicles Battery Packs MarketPublished date: Dec 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Hitachi
- Panasonic
- General Motors
- CATL
- BYD
- Samsung SDI
- LG Energy Solution
- AESC
- Volkswagen
- Saft










