Global Bioinformatics Market Analysis By Product (Bioinformatics platforms (Sequence analysis platforms, Sequence manipulation platforms, Sequence alignment platforms, Structural and functional analysis platforms, Others), Bioinformatics services (Sequencing Services, Data Analysis Services, Gene Expression Services, Drug Discovery Services, Database Management, Others), Biocontent management (Generalized biocontent, Specialized biocontent)), By Application (Genomics, Molecular phylogenetics, Metabolomics, Proteomics, Transcriptomics, Cheminformatics and drug design, Agricultural & Animal Genomics, Others), By End-User (Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies, Academic Institutes & Research Centers, CROs, Hospitals & Clinics, Others) By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Sep 2025
- Report ID: 159303
- Number of Pages: 350
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
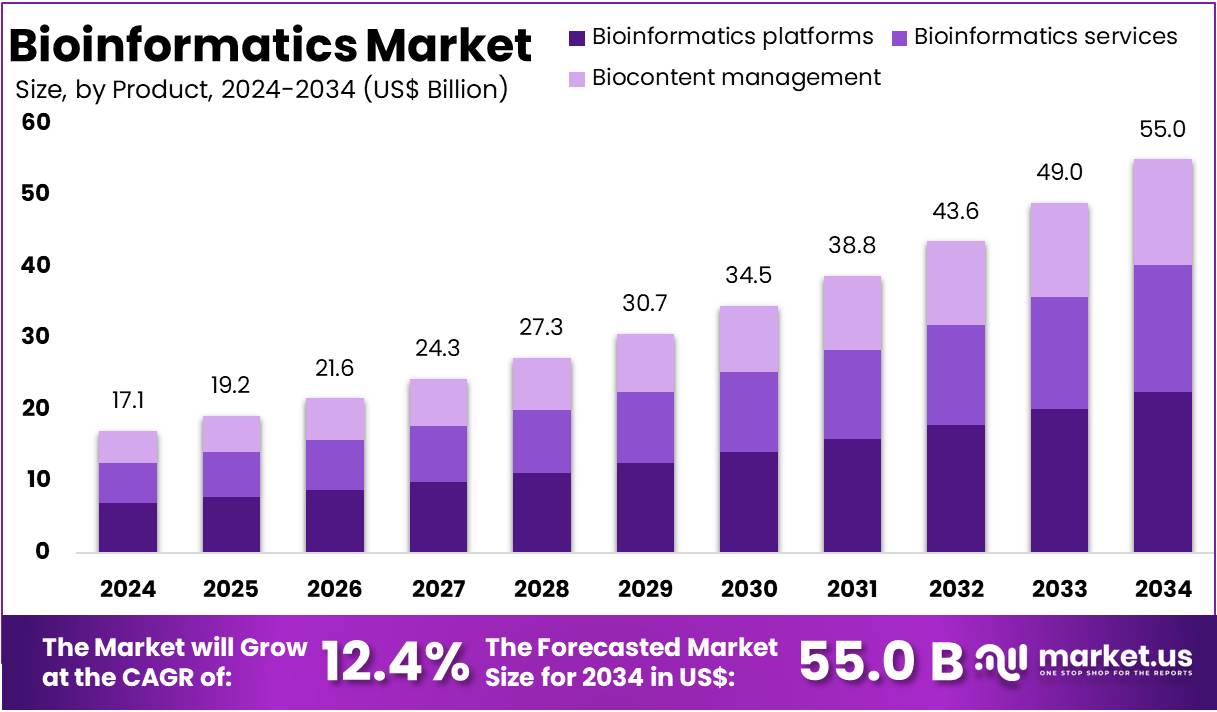
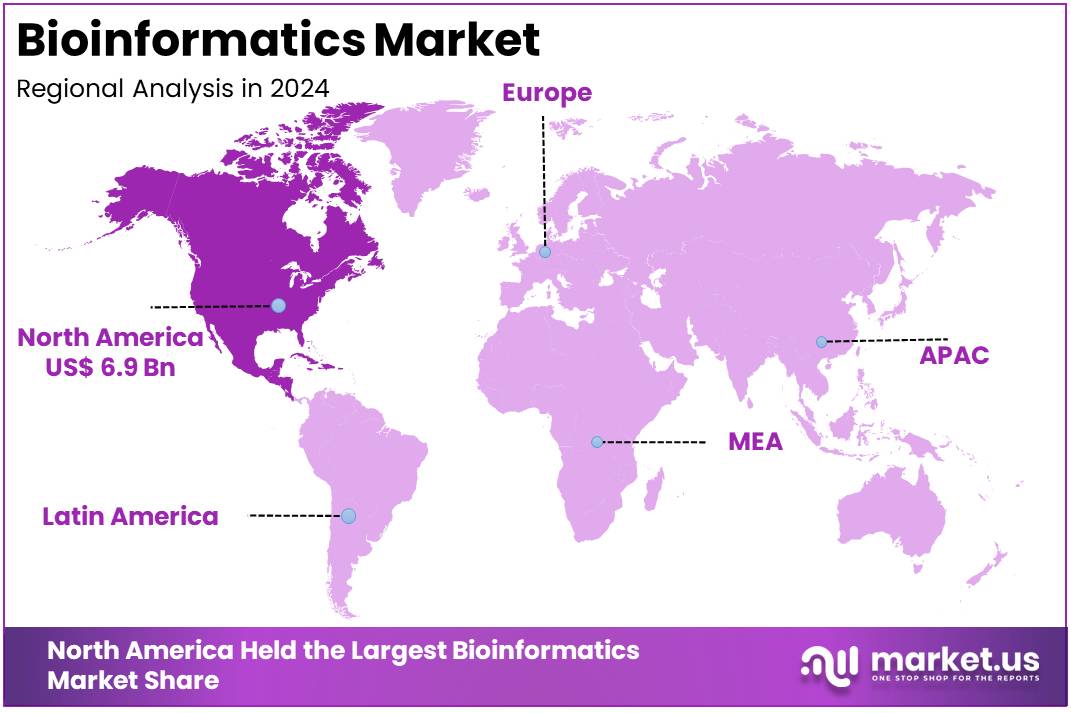
The Global Bioinformatics Market size is expected to be worth around US$ 55 Billion by 2034, from US$ 17.1 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 12.4% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 40.2% share and holds US$ 6.9 Billion market value for the year.
Bioinformatics is an interdisciplinary field that combines biology, computer science, mathematics, and statistics to analyze biological data. It plays a central role in decoding genomic sequences, protein structures, and molecular interactions. Advanced algorithms and software tools are widely used to interpret genetic variations and disease mechanisms. Bioinformatics has become crucial in applications such as drug discovery, personalized medicine, agricultural biotechnology, and environmental research. The integration of next-generation sequencing (NGS), artificial intelligence, and machine learning has further expanded its capabilities.
The bioinformatics market has grown rapidly due to rising demand for genomics research and precision medicine. Increasing adoption in clinical diagnostics, microbiology, and agricultural biotechnology has supported expansion. North America dominates the global market, owing to strong research infrastructure, while Asia-Pacific is projected to record significant growth. Market opportunities are shaped by innovation, collaborations, and growing investments in computational biology. Additionally, the adoption of cloud computing has created scalable and cost-efficient solutions, enabling research programs and clinical institutions to handle large data sets effectively.
Global health strategies have driven adoption at scale. The World Health Organization launched a 10-year Global Genomic Surveillance Strategy to strengthen sequencing capacity and data sharing. This initiative has boosted demand for secure data platforms, large-scale analysis pipelines, and interpretation tools. Furthermore, WHO’s International Pathogen Surveillance Network signals long-term investment in genomic data exchange. These frameworks have increased the variety and velocity of data, creating steady demand for bioinformatics software and services worldwide.
Declining sequencing costs have become a core structural driver of the industry. According to the U.S. National Human Genome Research Institute, the cost of sequencing continues to fall, enabling routine genome analysis. Hospitals and research programs now generate larger datasets per patient and per study. This trend has accelerated the need for efficient pipelines, storage platforms, and quality control software. As sequencing becomes faster and more affordable, routine use in both research and clinical care has created predictable market demand and long-term growth opportunities.
Bioinformatics Expansion Through Genomics, Surveillance, and Policy Support
The expansion of large-scale genomic programs has significantly influenced the bioinformatics sector. The U.S. NIH’s All of Us Research Program reported more than 414,000 whole-genome sequences available for analysis in 2025. With millions of clinical records linked to research datasets, scalable cloud computing and harmonized metadata are now essential. These national cohorts require reproducible workflows and advanced bioinformatics platforms. The scale of such programs has increased demand for analytical tools and skilled professionals to manage complex biological data.
Public health systems have mainstreamed genomics in surveillance programs. The U.S. CDC operates the National Wastewater Surveillance System across more than 1,200 sites, tracking multiple pathogens using sequencing technologies. In addition, the CDC’s traveler-based genomic surveillance identifies emerging variants of concern. These activities require continuous bioinformatics support for lineage assignment, variant calling, and dashboard reporting. As governments embed genomics into regular operations, recurring contracts and long-term procurement for analytics and software are being created.
Clinical genomics has moved from pilot projects to routine services. England’s NHS Genomic Medicine Service delivered more than 810,000 genomic tests in 2024, representing an 8% year-on-year increase. Testing across cancer, rare disease, and inherited disorders now requires validated bioinformatics pipelines and integration with electronic health records. Secure data exchange and workforce training remain central to these developments. This transition has strengthened predictable demand for accredited solutions in clinical decision-making and bioinformatics-driven diagnostics.
Policy frameworks further support growth. WHO’s Global Strategy on Digital Health has been extended through 2033, ensuring common standards for data governance and interoperability. Similarly, European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control guidance integrates genomic and big data approaches into outbreak reporting. Antimicrobial resistance surveillance is another key driver. Genomic evidence of multi-drug resistant Enterobacterales in Europe highlights the demand for sequencing, resistance gene detection, and transmission mapping. Together, these factors confirm bioinformatics as a sustained and structural requirement across healthcare and research sectors.
Statistics About Bioinformatics / Genomic Surveillance Drawn From Government Or Public Health / Health Organization
- As of January 2022, 68% of countries had capacity for genomic surveillance of pathogens, up from 54% in March 2021.
- Also by January 2022, the number of countries publishing their pathogen sequence data had increased by 43%, compared to a year before.
- The WHO’s 10-year Global Genomic Surveillance Strategy aims that by 2032, all 194 WHO Member States will have timely access to genomic sequencing for pathogens with pandemic and epidemic potential.
- England’s NHS Genomic Medicine Service (GMS) carries out over 680,000 genomic tests per year, for common/rare/inherited diseases, pharmacogenomics, and cancer.
- In England, approximately 10% of those genomic tests done by the NHS GMS are by whole genome sequencing, mostly in complex cases.
- More than 100,000 whole genomes have been sequenced through NHS GMS as of August 2024.
- The public scheme “Generation Study” in England plans to screen 100,000 newborn babies using whole genome sequencing for over 200 genetic conditions.
- As of 2023, over 14 million SARS-CoV-2 whole genomes had been released in public databases (e.g. GISAID, NCBI) globally.
- By October 2022, England’s genomic test directory included 357 rare disease clinical indications, covering around 3,200 rare and inherited diseases, and 203 cancer clinical indications.
- In March 2021, just 54% of countries reported pathogen genomic surveillance capacity; by January 2022 that had risen to 68%, showing rapid growth.
Key Takeaways
- The Global Bioinformatics Market is projected to reach US$ 55 billion by 2034, growing from US$ 17.1 billion in 2024, at a 12.4% CAGR.
- In 2024, Bioinformatics Platforms dominated the market, holding a significant share of over 41% within the product segment.
- The Genomics segment led the bioinformatics application market in 2024, accounting for more than 32.7% of the global market share.
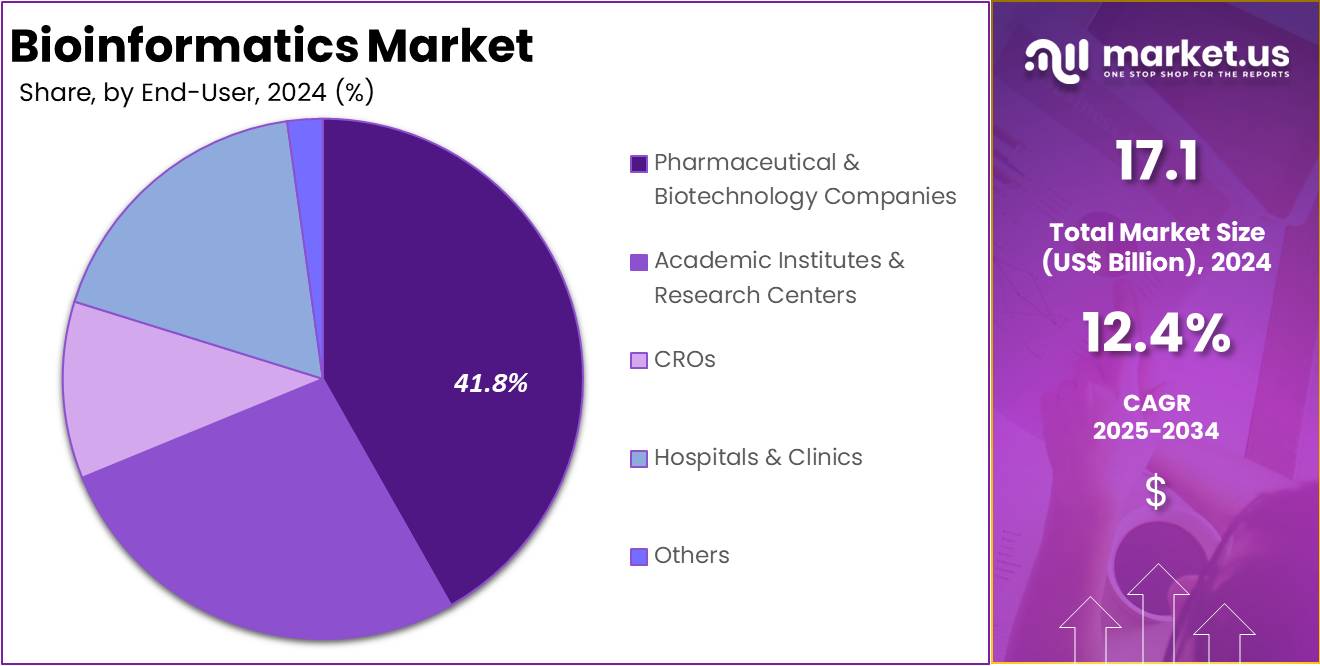
- Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies held the largest share in the End-User Segment of the Bioinformatics Market, with a 41.8% market share in 2024.
- North America maintained a dominant position in the market, capturing more than 40.2% of the market share, with a value of US$ 6.9 billion in 2024.
Product Analysis
In 2024, the Bioinformatics Platforms section held a dominant market position in the product segment of the Bioinformatics market, capturing more than a 41% share. This segment includes various platforms designed to analyze and manipulate biological data. These platforms support sequence analysis, sequence alignment, and structural and functional analysis. Technological advancements in genomic research and the increasing use of next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies have significantly contributed to the segment’s growth.
The rise of personalized medicine further drives the demand for bioinformatics platforms. These platforms are essential for processing large volumes of genomic data and transforming it into actionable insights. Additionally, integrating artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies has enhanced the platforms’ analytical capabilities. As a result, they are becoming indispensable tools for both biological research and clinical applications, especially in areas like precision medicine and drug development.
The Bioinformatics Services segment is also witnessing significant growth. This includes services such as sequencing, data analysis, gene expression, and drug discovery services. With the increasing complexity of biological data, specialized expertise is required to interpret the information accurately. This demand for expert services is pushing growth in the bioinformatics services market. These services are crucial for advancing drug discovery, clinical diagnostics, and personalized medicine.
Biocontent Management plays a critical role in managing the vast amounts of biological data. This segment accounts for a significant share of the Bioinformatics market. It involves organizing and storing generalized and specialized biocontent. With the growing volume of omics data, efficient biocontent management is vital for ensuring data integrity, accessibility, and regulatory compliance. Enhanced data formats and metadata annotations improve the usability and interoperability of biological databases, supporting research and clinical applications.
Application Analysis
In 2024, the Genomics segment held a dominant position in the bioinformatics application market, capturing more than 32.7% of the global share. This dominance is due to the rapid advancements in genomic sequencing technologies. The volume of data generated has significantly increased. This has led to the growing use of bioinformatics tools for data analysis. Genomics continues to be essential for understanding diseases and developing personalized treatments.
Molecular phylogenetics is another key application in bioinformatics. It uses genetic data to trace the evolutionary relationships between species. Bioinformatics tools play a crucial role in constructing accurate phylogenetic trees. These trees help researchers understand how species are related and how they have evolved over time. The field is vital for areas like taxonomy, evolutionary biology, and conservation genetics.
Proteomics is another major application, focusing on the large-scale study of proteins. It involves identifying proteins and understanding their roles in biological functions. Bioinformatics tools assist in protein identification, quantification, and structural analysis. This is particularly useful for drug discovery and disease research. These tools also help identify biomarkers, providing insights into the molecular mechanisms of various diseases.
Metabolomics studies the metabolites within organisms. Bioinformatics tools support the identification and quantification of metabolites. This data is critical for understanding metabolic processes and pathways. Researchers use these insights to identify biomarkers for diseases. Integrating metabolomics with genomics and proteomics further improves our understanding of cellular functions and disease mechanisms. This approach contributes significantly to the development of personalized medicine.
Bioinformatics is also applied in agricultural and animal genomics. It aids in improving crop yields and livestock quality through genomic data analysis. Bioinformatics tools help identify key traits in plants and animals. This supports the development of genetically improved species. It also plays a role in sustainable agriculture, helping ensure food security and better farming practices. This area continues to expand with the increasing demand for agricultural innovations.
End-User Analysis
In 2024, the Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies segment held a dominant market position in the End-User Segment of the Bioinformatics Market, capturing more than a 41.8% share. This dominance is largely due to the increasing use of bioinformatics tools to improve drug discovery and development processes. Pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies use bioinformatics for target identification, biomarker discovery, and optimizing clinical trials. The rise of artificial intelligence and advanced analytics further boosts the demand for these solutions.
The Academic Institutes & Research Centers segment is another key player in the bioinformatics market. These institutions utilize bioinformatics tools to support research in genomics, proteomics, and other biological fields. With a growing number of research projects and increased government funding, the adoption of bioinformatics is expanding. Academic institutions rely on these solutions to analyze complex biological data, derive insights, and push forward scientific discovery, further driving the market’s growth.
Contract Research Organizations (CROs) & Research Institutes are also significant contributors to the bioinformatics market. CROs offer outsourced research services to pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies. They use bioinformatics to support drug development, clinical trials, and research studies. This segment benefits from the increasing need for specialized research services, which drives the demand for bioinformatics solutions. As pharmaceutical companies continue to outsource research activities, CROs will remain an important market segment.
Hospitals & Clinics are increasingly adopting bioinformatics tools to enhance patient care. Bioinformatics helps healthcare providers analyze genetic and molecular data, enabling personalized treatment plans for patients. This adoption supports the growing trend of precision medicine, improving clinical outcomes. As bioinformatics integrates with healthcare systems, it enables better decision-making and improves treatment effectiveness. This trend is likely to continue, expanding the role of bioinformatics in clinical settings and supporting overall market growth.
Key Market Segments
By Product
- Bioinformatics platforms
- Sequence analysis platforms
- Sequence manipulation platforms
- Sequence alignment platforms
- Structural and functional analysis platforms
- Others
- Bioinformatics services
- Sequencing Services
- Data Analysis Services
- Gene Expression Services
- Drug Discovery Services
- Database Management
- Others
- Biocontent management
- Generalized biocontent
- Specialized biocontent
By Application
- Genomics
- Molecular phylogenetics
- Metabolomics
- Proteomics
- Transcriptomics
- Cheminformatics and drug design
- Agricultural & Animal Genomics
- Others
By End-User
- Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies
- Academic Institutes & Research Centers
- CROs
- Hospitals & Clinics
- Others
Drivers
Falling Sequencing Costs and Wider Clinical Adoption
The bioinformatics market is strongly driven by the continued decline in genomic sequencing costs. According to the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), sequencing costs have dropped sharply since 2008, with sustained reductions recorded through 2022 and 2023. This trend enabled vendors in 2024 to claim sequencing at under $100 per genome, significantly lowering the barrier for population-scale adoption. For example, this affordability allows healthcare systems to integrate sequencing into clinical workflows, making genomic testing routine and cost-effective.
As sequencing becomes more accessible, healthcare providers and research institutions are increasingly turning to bioinformatics platforms for data interpretation. Earlier, sequencing was restricted to specialized laboratories due to high costs, but now it is widely used in diagnostics, drug discovery, and personalized therapies. Study by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) highlights that companion diagnostics (CDx) are steadily expanding, supporting treatment decisions in oncology and pharmacogenomics. This shift illustrates how reduced costs fuel the widespread integration of bioinformatics into precision medicine.
Expanding Genomic Data and Precision-Medicine Pipelines
Another major driver is the explosion in sequencing volume and genomic data. Public repositories, such as the International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration (INSDC), reported rapid growth, with the Sequence Read Archive expanding from ~25.6 petabases in 2021 to over 107 petabases by late 2024. For instance, the European Nucleotide Archive also documented 62.8 petabases of downloadable data in 2024, underscoring the increasing need for advanced bioinformatics to manage and analyze these massive datasets.
Precision-medicine initiatives have further accelerated this trend. The NIH “All of Us” program analyzed ~250,000 whole genomes in 2024 and expanded to over 414,000 genomes by 2025, generating more than 275 million new genetic variants. For example, such large-scale projects demonstrate how bioinformatics supports the translation of raw sequencing data into actionable clinical insights. As companion diagnostics and pharmacogenomic labeling grow—covering more than 217 drugs by 2024. Bioinformatics platforms play a crucial role in enabling personalized treatment decisions.
Restraints
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
According to data from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS OCR), healthcare breach volume remained structurally high, with 720 large breaches in 2022 and 725 breaches in 2024. This persistence highlights a critical barrier for bioinformatics adoption, as genomic and patient data are highly sensitive. Any misuse or unauthorized access can lead to ethical and legal consequences. Healthcare providers, therefore, remain cautious about data sharing, which restricts collaboration and limits large-scale bioinformatics integration.
A study by IBM reported that the global average cost of a data breach rose to US$4.88 million in 2024, a 10% increase compared with 2023. Healthcare is consistently identified as the most expensive sector for breaches. For instance, in 2023, 133 million records were exposed, highlighting the growing risk to personal health information (PHI). These escalating costs add to the implicit “risk-adjusted” expense of bioinformatics adoption, making institutions reluctant to expand genomic and clinical data pipelines without strong security assurances.
Regulatory pressures further intensify the challenge. Under GDPR, genetic and health data are treated as “special categories” requiring strict compliance safeguards (GDPR Article 9). Enforcement remains active, with fines totaling about €1.2 billion in 2024 (DLA Piper). Compliance demands governance frameworks, audits, and legal reviews, which impose significant financial and operational burdens. As a result, both large and mid-sized organizations face delays and higher costs when adopting bioinformatics solutions in healthcare-driven research and clinical applications.
Infrastructure and Storage Limitations
The scale of data produced by genomic sequencing is immense, often measured in petabytes. For example, the U.S. National Cancer Institute’s Cancer Research Data Commons (CRDC) reported that genomic data more than doubled from 3.7 PB in 2022 to 8.8 PB in 2024, with multi-omic data surpassing 10 PB. Such exponential growth in datasets creates a pressing need for robust, high-performance computing infrastructures. Many hospitals and research institutions, however, lack both the budget and technical resources to meet these requirements.
Storage costs further exacerbate the restraint. According to CRDC analysis, storage using standard models may cost ~$51 per TB annually. Compression and intelligent tiering can reduce this to ~$12 per TB, but these methods introduce trade-offs related to access patterns and licensing complexities. For instance, institutions with unpredictable research demands may struggle with slower data retrieval, affecting efficiency. These infrastructure trade-offs hinder research speed and reduce the seamless application of bioinformatics in clinical and pharmaceutical environments.
Centralized cloud architectures can provide partial relief. A study on national research cohorts indicated that maintaining a central cloud copy of large-scale genomic data could cost approximately US$1.14 million per year, yielding up to 99.9% savings compared with distributed redundancy. While this reduces cost exposure and improves access control, not all organizations can implement such controlled systems. As a result, infrastructure limitations, coupled with economic and operational challenges, continue to slow down the broad integration of bioinformatics across healthcare research ecosystems.
Opportunities
AI-Driven Acceleration of Drug Discovery
The integration of bioinformatics with artificial intelligence offers a transformative opportunity in drug discovery. According to a study published in Nature (2024), AlphaFold 3 introduced diffusion-based models capable of simulating protein, nucleic acid, and small-molecule interactions. For instance, this advancement supports more precise disease modeling and ligand–receptor interaction analysis. Such capabilities significantly reduce the reliance on traditional manual processes. By enabling early identification of drug candidates, AI shortens research timelines and lowers costs in clinical development pipelines.
For example, independent evaluations in 2024 reported that AlphaFold 3 delivers strong, context-specific predictions of binding free-energy changes. These evaluations inform researchers on when to incorporate the tool in docking and lead-optimization workflows. As pharmaceutical companies seek efficiency, this integration positions bioinformatics as a critical enabler of personalized therapies. The ability to simulate disease pathways and predict drug interactions enhances precision medicine. Consequently, AI-driven bioinformatics is set to accelerate therapeutic innovation and strengthen its adoption in the healthcare sector.
Biomarker Discovery and Personalized Medicine
Biomarker identification presents another major growth avenue supported by bioinformatics and AI. According to the European Nucleotide Archive, more than 2.7 billion annotated sequences were available in 2022, providing vast datasets for biomarker discovery. For example, machine learning models trained on genomic and proteomic archives can detect subtle biological signals missed by conventional methods. This capability supports early disease detection, prognosis, and monitoring. As healthcare moves toward preventive approaches, biomarker integration into decision-making processes is becoming increasingly important.
The cost-effectiveness of genome sequencing further amplifies this opportunity. A study by the NHGRI reported that the price of sequencing a human genome fell to around $600 by 2022. This affordability enables large-scale validation cohorts for biomarker-driven research. For instance, the use of AI-driven analytics can match genomic data with treatment outcomes, supporting personalized therapeutic strategies. With rising demand for targeted medicine, the synergy of AI and bioinformatics strengthens healthcare delivery. This advancement positions biomarker discovery as a cornerstone of precision medicine growth.
Trends
Scalability and Flexibility of Cloud Platforms
The adoption of cloud-based bioinformatics platforms is strongly supported by their scalability and flexibility. These systems provide dynamic storage and computational power, which can be adjusted according to the complexity of research projects. With the rising volume of genomic data from high-throughput sequencing, researchers require efficient systems that ensure speed and accuracy. Cloud platforms meet these needs by offering on-demand resources, smooth workflows, and collaborative accessibility. This scalability improves productivity and supports advanced research across institutions and pharmaceutical companies.
Cloud technology removes the constraints of traditional systems by enabling rapid adjustments in data processing capacity. Researchers no longer face delays caused by limited hardware, as cloud platforms deliver seamless performance for complex genomic analysis. This adaptability ensures that bioinformatics projects can handle data of any scale with high precision. The result is an improvement in research outcomes, faster discovery cycles, and broader collaboration opportunities. Such benefits are driving higher adoption rates across academia, biotech firms, and global pharmaceutical organizations.
Cost Efficiency and Wider Accessibility
The cost efficiency of cloud-based bioinformatics solutions is another major growth driver. Traditional systems demand high investments in hardware, maintenance, and upgrades, which create financial barriers for smaller organizations. Cloud models eliminate these challenges by offering subscription-based or pay-per-use pricing. This approach reduces operational costs and allows institutions to access advanced analytical tools without heavy capital expenditure. As a result, even smaller biotechnology firms and academic research groups can participate in cutting-edge genomic studies.
By lowering financial barriers, cloud platforms expand accessibility to bioinformatics resources worldwide. Researchers can focus on innovation and discovery rather than infrastructure management. The flexibility of cost structures also supports institutions with limited budgets, ensuring equal opportunities to perform complex genomic analysis. This affordability, combined with scalable performance, positions cloud-based solutions as a transformative force in the bioinformatics industry. Consequently, their adoption is expected to grow rapidly, reshaping how biological research is conducted in the coming years.
Regional Analysis
In 2024, North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 40.2% share and holds a US$ 6.9 billion market value for the year. This regional dominance is largely attributed to the advanced research infrastructure in the United States, which includes top-tier universities, research institutions, and substantial government funding. These elements foster innovation, particularly in areas like genomics and data analytics, giving North America a competitive edge in bioinformatics advancements. The region’s investment in research fuels continued growth in this sector.
North America also benefits from significant technological advancements that have shaped the bioinformatics market. The region has been a pioneer in genomic sequencing technologies and computational biology. These innovations are crucial for bioinformatics applications, which require sophisticated data processing and analysis capabilities. Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning has accelerated bioinformatics development, contributing to the expansion of the market. These technological advancements position North America as a leader in bioinformatics.
The rising demand for personalized medicine has further solidified North America’s dominance in the bioinformatics market. The region’s healthcare system is highly developed, allowing for the implementation of advanced technologies that support precision medicine. Bioinformatics plays a pivotal role in personalized medicine by analyzing genetic data to create tailored treatments for patients. As personalized healthcare becomes more prevalent, North America’s capabilities in bioinformatics remain a key driver of the market’s growth and development.
Finally, the presence of key bioinformatics companies in North America strengthens its market position. Companies such as Illumina, Thermo Fisher Scientific, and QIAGEN are actively involved in genomic sequencing, data analysis, and molecular biology. These companies are instrumental in driving innovation and expanding the bioinformatics market. The strong public-private partnerships, along with government funding programs from entities like the NIH, further bolster the region’s bioinformatics industry, ensuring sustained growth in the global market.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherland
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- New Zealand
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
The bioinformatics market is rapidly growing, driven by advancements in genomics and the increasing demand for data-driven insights in healthcare and research. DNAnexus, Seven Bridges (Velsera), BGI Group, Partek, Thermo Fisher Scientific and Many Other key players shaping this industry. These companies provide comprehensive solutions across various bioinformatics workflows, from data collection and integration to analysis and visualization. Their continued innovation and strategic partnerships are expected to further strengthen their leadership in this dynamic market. The bioinformatics market is evolving quickly with these leaders at the forefront.
DNAnexus Inc. is a prominent player in cloud-based bioinformatics. The company offers scalable platforms for managing and analyzing large biomedical datasets. Its cloud infrastructure enables real-time collaboration, crucial for researchers across institutions. The platform integrates various data types, including genomic, proteomic, and clinical data, vital for precision medicine. DNAnexus has formed strategic partnerships with leading healthcare organizations, further cementing its position in the market. Its adherence to strict regulatory standards ensures its reliability in clinical research environments.
Seven Bridges, now rebranded as Velsera, provides end-to-end bioinformatics solutions. The company focuses on enhancing scalability and collaboration by utilizing cloud technologies. Velsera excels in integrating large-scale omics data, which is crucial for efficient genomic analysis. Its cloud infrastructure fosters collaboration, making bioinformatics analyses faster and more reliable. The company serves a wide global clientele, with a significant presence in healthcare and pharmaceuticals. This broad reach has strengthened its position as a trusted provider in bioinformatics, especially in the healthcare sector.
BGI Group, founded in 1999, is one of the largest genomics organizations globally. The company is known for its advanced genomic sequencing capabilities, contributing to international research projects. BGI offers integrated genomic solutions, including sequencing, data analysis, and bioinformatics tools. Its services are widely used in academic, clinical, and pharmaceutical research. This broad application demonstrates BGI’s influential role in bioinformatics. The company continues to drive innovation in genomics, significantly impacting healthcare and research globally, making it a key player in the industry.
Partek Inc. offers advanced bioinformatics software solutions for analyzing genomic data. The company’s platform is known for its ease of use, making it popular among both novice and experienced researchers. Partek’s solutions excel in analyzing next-generation sequencing (NGS) data, a vital tool in genomic research. Its software supports a wide range of applications, from basic research to clinical diagnostics. Partek has strengthened its product offering through strategic partnerships, including integrations with major sequencing platforms like Illumina. This ensures seamless workflows for users across various research fields.
Thermo Fisher Scientific is a global leader in the bioinformatics market, offering a broad range of products for molecular biology research. The company provides essential tools for sequencing, diagnostics, and bioinformatics, supporting a variety of industries. Thermo Fisher’s extensive product portfolio includes data storage, computational resources, and bioinformatics tools. The company continues to innovate through acquisitions, expanding its technology offerings. With a strong global presence, Thermo Fisher serves sectors such as academia, government, and pharmaceuticals. This broad customer base solidifies its leadership in the bioinformatics industry.
Market Key Players
- DNAnexus Inc.
- Seven Bridges Genomics
- BGI Group
- Partek Inc.
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- Qiagen
- Agilent Technologies
- Illumina
- PerkinElmer
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
- Dassault Systèmes SE (BIOVIA)
- Genedata AG
- 3rd Millennium Inc.
- Data4Cure Inc.
- Ontoforce NV
- Geneious
- Gene42 Inc.
Recent Developments
- In February 2025: Velsera introduced the Clinical Genomics Workspace (CGW) Plus, an advanced version of its platform designed to streamline the analysis and reporting of genetic sequence data for clinical laboratories. CGW Plus incorporates enhanced workflows for variant quality assessment and clinical evidence review, facilitating more accurate and efficient genomic analyses. This development underscores Velsera’s commitment to improving clinical decision-making processes and supporting the broader adoption of precision medicine.
- In January 2024: QIAGEN announced a strategic initiative to increase investments in its bioinformatics division, QIAGEN Digital Insights (QDI), over the next five years. This initiative aims to bolster QDI’s position as a market leader, with 2023 sales approximating $100 million. The investment plan includes the launch of at least five new products and enhancements to existing offerings. Key areas of focus encompass the development of additional omics knowledge bases, integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and natural language processing (NLP) capabilities, and the creation of a new regulatory-compliant secondary analysis solution for rapid NGS analysis within clinical laboratories. These efforts are designed to address informatics challenges in precision medicine and care, thereby expanding QDI’s reach across new geographic regions and market segments.
- In January 2024: DNAnexus partnered with Ovation, an omics data company, to streamline large-scale omics data analysis. The collaboration focuses on analyzing inflammatory bowel disease omics data, including whole genome and transcriptome sequencing linked to clinical data. The initiative aims to extend into immunology, oncology, and cardiometabolic therapeutic areas, leveraging DNAnexus’ Precision Health Data Cloud to manage and analyze complex multimodal data.
- In August 2023: Thermo Fisher Scientific’s subsidiary, The Binding Site, launched the EXENT® Solution, a mass spectrometry-based diagnostic tool for the management of monoclonal gammopathy. The solution received In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR) certification, enabling its use in clinical settings across Europe. The EXENT® Solution addresses an unmet clinical need by providing a more accurate and efficient method for monitoring monoclonal gammopathies, including multiple myeloma. This innovation aligns with Thermo Fisher’s strategy to expand its specialty diagnostics portfolio and improve patient outcomes through advanced diagnostic technologies.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) US$ 17.1 Billion Forecast Revenue (2034) US$ 55 Billion CAGR (2025-2034) 12.4% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, COVID-19 Impact, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Product (Bioinformatics platforms (Sequence analysis platforms, Sequence manipulation platforms, Sequence alignment platforms, Structural and functional analysis platforms, Others), Bioinformatics services (Sequencing Services, Data Analysis Services, Gene Expression Services, Drug Discovery Services, Database Management, Others), Biocontent management (Generalized biocontent, Specialized biocontent)), By Application (Genomics, Molecular phylogenetics, Metabolomics, Proteomics, Transcriptomics, Cheminformatics and drug design, Agricultural & Animal Genomics, Others), By End-User (Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies, Academic Institutes & Research Centers, CROs, Hospitals & Clinics, Others) Regional Analysis North America – The US, Canada, & Mexico; Western Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Portugal, Ireland, Austria, Switzerland, Benelux, Nordic, & Rest of Western Europe; Eastern Europe – Russia, Poland, The Czech Republic, Greece, & Rest of Eastern Europe; APAC – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia & New Zealand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, & Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Colombia, Chile, Argentina, Costa Rica, & Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – Algeria, Egypt, Israel, Kuwait, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, & Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape DNAnexus Inc., Seven Bridges Genomics, BGI Group, Partek Inc., Thermo Fisher Scientific, Qiagen, Agilent Technologies, Illumina, PerkinElmer, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Dassault Systèmes SE (BIOVIA), Genedata AG, 3rd Millennium Inc., Data4Cure Inc., Ontoforce NV, Geneious, Gene42 Inc. Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- DNAnexus Inc.
- Seven Bridges Genomics
- BGI Group
- Partek Inc.
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- Qiagen
- Agilent Technologies
- Illumina
- PerkinElmer
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
- Dassault Systèmes SE (BIOVIA)
- Genedata AG
- 3rd Millennium Inc.
- Data4Cure Inc.
- Ontoforce NV
- Geneious
- Gene42 Inc.










