Global Bio-based Polypropylene Market Size, Share Report By Feedstock (Sugarcane, Com Starch, Cellulose, Lignocellulosic Biomass), By Production Process (Melt Mass Polymerization (MMP), Solution Polymerization, Gas Phase Polymerization), By Extrusion Type (Sheet Extrusion, Film Extrusion, Pipe Extrusion), By End-user (Packaging, Automotive, Consumer Goods, Textile, Medical and Healthcare, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: July 2025
- Report ID: 154088
- Number of Pages: 393
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
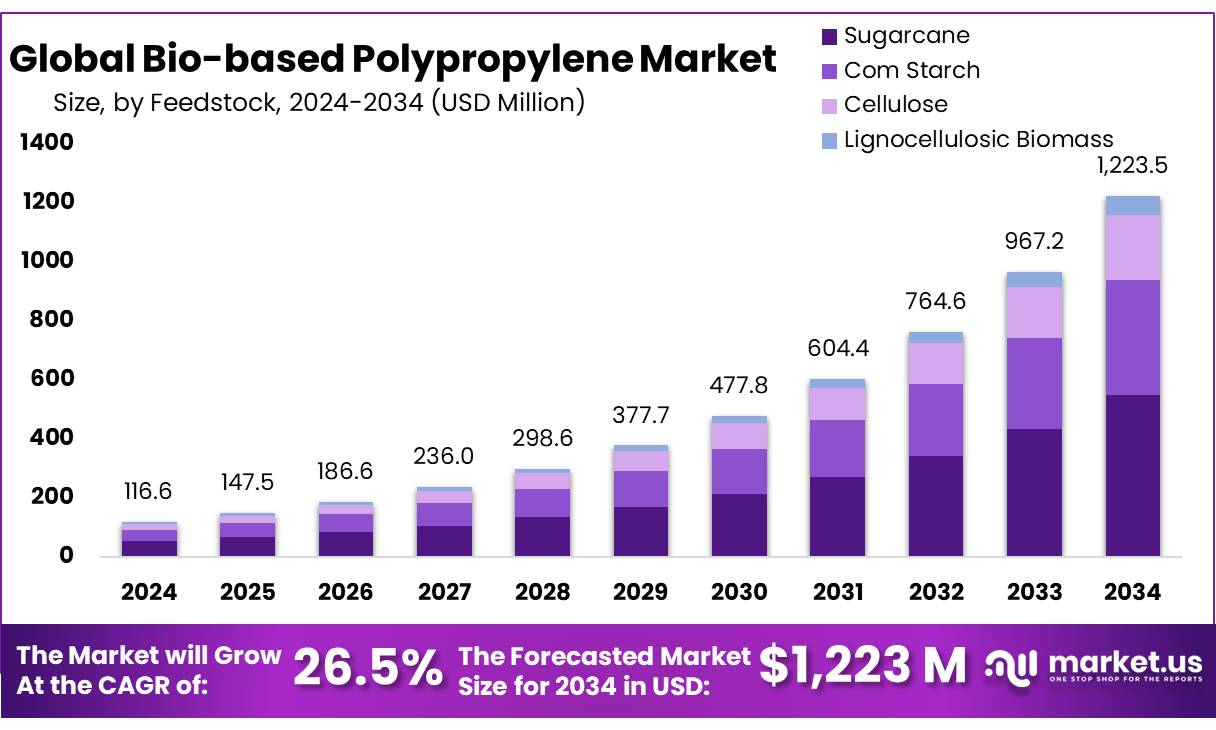
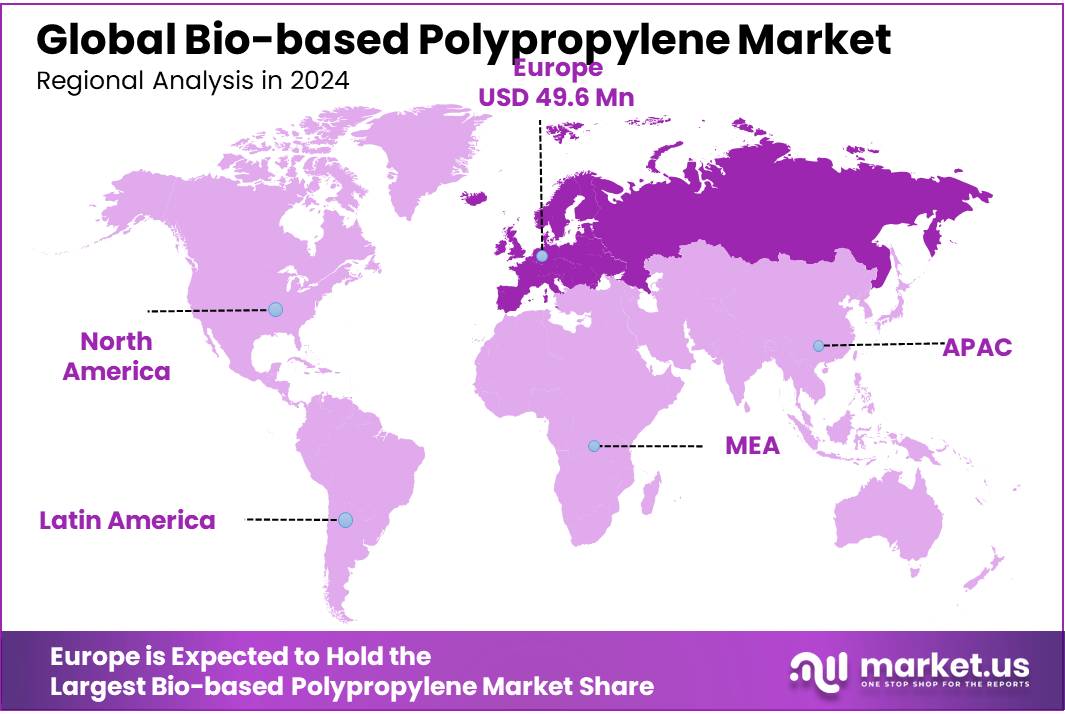
The Global Bio-based Polypropylene Market size is expected to be worth around USD 1223.5 Million by 2034, from USD 116.6 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 26.5% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.2% share, holding USD 0.4 billion in revenue.
Bio-based polypropylene (Bio-PP) is an emerging sustainable alternative to traditional polypropylene, made from renewable sources such as plant-based feedstocks. It serves as an environmentally friendly solution to reduce carbon emissions and dependency on fossil fuels. Bio-based polypropylene is gaining significant attention due to its potential to replace conventional plastic materials in various industries, including packaging, automotive, and textiles. The increasing demand for eco-friendly materials has driven substantial growth in the bio-based plastics market, with Bio-based polypropylene positioned as a leading segment in the transition towards a circular economy.
The Bio-based polypropylene is characterized by significant investments and technological advancements. For instance, Braskem, a leading biopolymer producer, has undertaken a project to evaluate the production of carbon-negative Bio-PP in the U.S., utilizing its proprietary technology to convert bioethanol into Bio-based polypropylene. In Brazil, Braskem expanded its bio-based ethylene plant by 30%, increasing production capacity from 200,000 to 260,000 tons per year, underscoring the growing demand for sustainable products.
Government initiatives play a crucial role in promoting the adoption of Bio-based polypropylene. In the United States, the Department of Energy invested $13.4 million in 2022 to support next-generation plastics technologies aimed at reducing energy consumption and carbon emissions associated with single-use plastics. Additionally, the USDA’s BioPreferred Program encourages the use of biobased products through federal procurement and certification, enhancing market access for Bio-based polypropylene.
In the United States, the Biden Administration’s “Bold Goals Report” aims for over 90% of commercial polymers to be recyclable-by-design and biobased by 2043, with current biobased plastic production capacity at 0.71%. Similarly, Braskem, a leading producer, announced plans to evaluate the production of carbon-negative Bio-PP in the U.S., targeting a capacity of 1 million tons by 2030.
Key Takeaways
- Bio-based Polypropylene Market size is expected to be worth around USD 1223.5 Million by 2034, from USD 116.6 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 26.5%.
- Sugarcane held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 44.8% share of the global bio-based polypropylene market.
- Melt Mass Polymerization (MMP) held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 48.3% share of the global bio-based polypropylene market.
- Sheet Extrusion held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.1% share of the bio‑based polypropylene market.
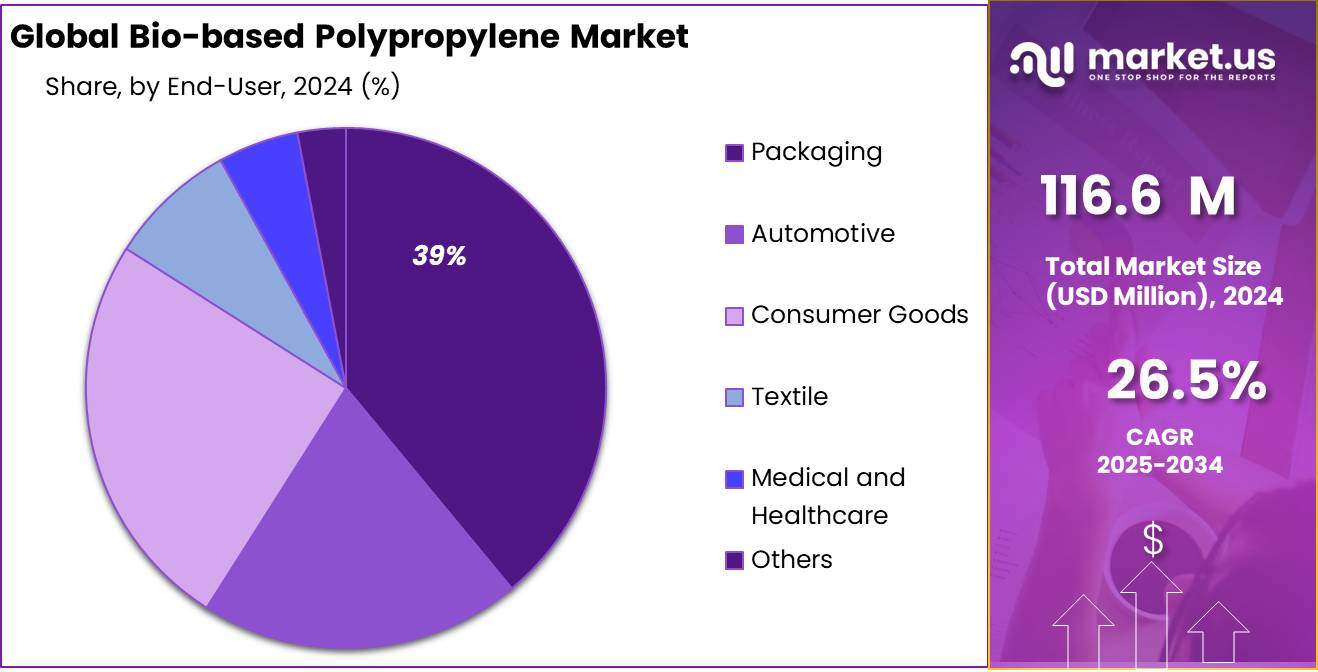
- Packaging held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 39.7% share of the global bio-based polypropylene market.
- North America stands as a dominant force in the global bio-based polypropylene (Bio-PP) market, holding a significant share of 43.2% in 2024, equating to approximately USD 0.4 billion.
By Feedstock Analysis
Sugarcane dominates with 44.8% due to its renewable sourcing and process adaptability.
In 2024, Sugarcane held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 44.8% share of the global bio-based polypropylene market. Its widespread use can be attributed to its renewable nature, well-established agricultural infrastructure, and compatibility with existing fermentation technologies. Sugarcane-based ethanol serves as a primary input in producing propylene, enabling a smoother transition from conventional to bio-based polypropylene production without major changes in processing equipment.
The feedstock’s availability in key regions such as Brazil and India also ensures a stable supply chain, supporting large-scale production. By 2025, sugarcane is expected to maintain its lead, supported by sustainability mandates and increasing investment in circular economy solutions. This continued dominance reflects strong industry preference for sugarcane due to its lower carbon footprint and cost-efficient processing capabilities.
By Production Process Analysis
Melt Mass Polymerization leads with 48.3% due to its efficient and scalable process.
In 2024, Melt Mass Polymerization (MMP) held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 48.3% share of the global bio-based polypropylene market. This method gained preference due to its ability to produce high-quality polymers with consistent molecular weight and fewer impurities. MMP enables a solvent-free and energy-efficient process, aligning well with the sustainability goals of manufacturers transitioning to bio-based alternatives.
Its compatibility with large-scale industrial operations has further strengthened its adoption, especially in regions aiming to reduce environmental impact while maintaining performance standards. By 2025, MMP is expected to retain its lead, driven by advancements in polymerization technology and increasing demand for cleaner production routes in the bio-plastics sector.
By Extrusion Type Analysis
Sheet Extrusion leads with 38.1% thanks to its uniform thickness and cost efficiency.
In 2024, Sheet Extrusion held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.1% share of the bio‑based polypropylene market. Its strength lies in producing uniform sheets rapidly, which are ideal for applications such as packaging panels, thermoformed trays, and protective liners. The process’s scalability and minimal material waste appeal to manufacturers seeking both sustainability and consistent product quality.
Equipment requirements closely mirror those used for conventional polypropylene, enabling smooth technology transfer and faster plant ramp‑up. By 2025, Sheet Extrusion is expected to maintain its leadership, as demand grows for eco‑friendly packaging solutions and architectural components that combine durability with lower environmental impact.
By End-user Analysis
Packaging dominates with 39.7% due to strong demand for sustainable material alternatives.
In 2024, Packaging held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 39.7% share of the global bio-based polypropylene market. The rising shift toward eco-friendly packaging materials—especially for food, beverages, and personal care products—has significantly increased the use of bio-based polypropylene in this segment.
Its lightweight nature, durability, and compatibility with existing molding and extrusion processes make it ideal for producing films, containers, and caps. Retailers and manufacturers are also under growing pressure to reduce plastic waste, which is driving the adoption of bio-based alternatives. By 2025, packaging is expected to continue leading this market, supported by government regulations, brand sustainability commitments, and consumer preference for greener packaging choices.
Key Market Segments
By Feedstock
- Sugarcane
- Com Starch
- Cellulose
- Lignocellulosic Biomass
By Production Process
- Melt Mass Polymerization (MMP)
- Solution Polymerization
- Gas Phase Polymerization
By Extrusion Type
- Sheet Extrusion
- Film Extrusion
- Pipe Extrusion
By End-user
- Packaging
- Automotive
- Consumer Goods
- Textile
- Medical and Healthcare
- Others
Emerging Trends
Integration of Artificial Intelligence in Bio-Based Polypropylene Production
A significant trend shaping the bio-based polypropylene (Bio-PP) market is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and automation technologies into production processes. This technological advancement is enhancing manufacturing efficiency, reducing costs, and improving product quality, thereby accelerating the adoption of Bio-PP across various industries. In North America, for instance, AI-driven analytics are employed to optimize catalyst efficiency, predict feedstock behavior, and fine-tune reaction parameters, resulting in more cost-effective large-scale production.
The implementation of AI in Bio-PP production also facilitates real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, minimizing downtime and enhancing operational reliability. Furthermore, AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets to identify patterns and optimize production schedules, leading to increased throughput and reduced waste. These improvements not only make Bio-PP more competitive with traditional polypropylene but also contribute to the overall sustainability of the manufacturing process.
Government initiatives are playing a crucial role in supporting the integration of AI in Bio-PP production. In the United States, for example, the Department of Energy has invested in projects that explore the use of AI and machine learning to optimize bio-based polymer production processes. Such investments are fostering innovation and facilitating the commercialization of advanced manufacturing techniques.
Drivers
Government Policies and Initiatives Driving the Bio-Based Polypropylene Market
Government policies and initiatives are pivotal in accelerating the adoption of bio-based polypropylene (Bio-PP), a sustainable alternative to conventional polypropylene. These measures aim to reduce plastic waste, lower carbon footprints, and promote the use of renewable materials across various industries.
In Europe, the European Union’s Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation mandates that all packaging placed on the market by 2030 must be recyclable. This regulation is prompting manufacturers to adopt materials like Bio-PP, which retain the same recycling codes as their fossil-based counterparts, ensuring compliance with recycling standards. Additionally, the EU’s Circular Economy Action Plan encourages the use of recycled and bio-based materials, further boosting the demand for Bio-PP.
In North America, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) supports initiatives that promote the use of sustainable materials through grants and funding programs. These programs assist companies in developing and commercializing bio-based products, including Bio-PP. Such support is crucial for companies looking to transition from traditional plastics to more sustainable alternatives.
Furthermore, countries like India are implementing policies that encourage the use of biodegradable and bio-based materials. The Indian government’s focus on reducing plastic waste has led to the promotion of alternatives like Bio-PP in packaging and other applications. These policies are creating a conducive environment for the growth of the Bio-PP market in the region.
Restraints
High Production Costs: A Barrier to Bio-Based Polypropylene Adoption
One of the primary challenges hindering the widespread adoption of bio-based polypropylene (Bio-PP) is its higher production cost compared to conventional polypropylene. This cost disparity arises from several factors, including the price of renewable feedstocks, specialized processing technologies, and limited economies of scale.
Bio-PP is typically produced from renewable resources such as sugarcane, corn, and vegetable oils. These feedstocks are often more expensive than the petroleum-based raw materials used for traditional polypropylene. Additionally, the production processes for Bio-PP can be more complex and energy-intensive, further increasing costs. For instance, the fossil fuel energy required to produce a kilogram of polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA), a biodegradable bioplastic, is estimated to be between 50.4 and 59.0 megajoules per kilogram, which is higher than that of conventional plastics .
The higher production costs of Bio-PP can make it less competitive in price-sensitive markets, such as packaging and automotive industries, where cost is a significant factor in material selection. This economic barrier can slow the transition from traditional plastics to more sustainable alternatives.
However, ongoing research and technological advancements aim to reduce these costs. Innovations in feedstock sourcing, such as utilizing waste biomass and algae, and improvements in production processes are expected to make Bio-PP more cost-competitive in the future. Additionally, supportive government policies and incentives can help offset some of the cost disadvantages associated with Bio-PP production.
Opportunity
Government Support and Policy Initiatives Fueling Bio-Based Polypropylene Growth
Government policies and initiatives are pivotal in accelerating the adoption of bio-based polypropylene (Bio-PP), a sustainable alternative to traditional polypropylene. These measures aim to reduce plastic waste, lower carbon footprints, and promote the use of renewable materials across various industries.
In Europe, the European Union’s Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation mandates that all packaging placed on the market by 2030 must be recyclable. This regulation is prompting manufacturers to adopt materials like Bio-PP, which retain the same recycling codes as their fossil-based counterparts, ensuring compliance with recycling standards. Additionally, the EU’s Circular Economy Action Plan encourages the use of recycled and bio-based materials, further boosting the demand for Bio-PP.
In North America, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) supports initiatives that promote the use of sustainable materials through grants and funding programs. These programs assist companies in developing and commercializing bio-based products, including Bio-PP. Such support is crucial for companies looking to transition from traditional plastics to more sustainable alternatives.
Furthermore, countries like India are implementing policies that encourage the use of biodegradable and bio-based materials. The Indian government’s focus on reducing plastic waste has led to the promotion of alternatives like Bio-PP in packaging and other applications. These policies are creating a conducive environment for the growth of the Bio-PP market in the region.
Regional Insights
North America dominates with a 43.2% share, generating USD 0.4 billion in 2024.
North America stands as a dominant force in the global bio-based polypropylene (Bio-PP) market, holding a significant share of 43.2% in 2024, equating to approximately USD 0.4 billion in market value. This leadership is primarily driven by robust demand across key industries such as automotive, packaging, and consumer goods, all of which are increasingly prioritizing sustainable materials.
The region’s growth trajectory is further supported by favorable government policies and incentives aimed at promoting sustainable practices. For instance, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has been instrumental in encouraging the adoption of eco-friendly materials through various programs and grants. Additionally, advancements in production technologies and the availability of renewable feedstocks have contributed to the economic viability of Bio-PP in North America.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Braskem is a global leader in bio-based polypropylene production, known for its sugarcane-based Green Polyethylene and polypropylene initiatives. Headquartered in Brazil, the company operates one of the world’s largest bio-polymer plants. It has invested heavily in sustainable materials, with ongoing projects to expand bio-based PP capacity in North America. Braskem is actively collaborating with partners to develop scalable renewable propylene technologies, aligning with net-zero emission goals and advancing circular economy solutions.
Japan-based Mitsui Chemicals is a key innovator in bio-based polypropylene, leveraging its expertise in green chemistry and sustainable manufacturing. The company has developed biomass-based propylene using bio-ethanol and integrated this into polypropylene production. Mitsui actively collaborates with firms like Toyota Tsusho to supply bio-based resins for automotive and industrial applications. With its “Blue Value” initiative, the company focuses on products that contribute to environmental preservation, aiming to expand its global footprint in the bioplastics market.
CITRONIQ, a U.S.-based startup, focuses exclusively on carbon-negative bio-based polypropylene. It plans to establish large-scale manufacturing plants in North America using renewable and waste carbon feedstocks. The company’s approach targets full lifecycle sustainability by integrating carbon capture, green hydrogen, and renewable energy. CITRONIQ’s strategic partnership with Lummus Technology enhances its process efficiency and scalability. Positioned as a disruptor, CITRONIQ aims to deliver industrial volumes of low-carbon polypropylene to major sectors such as packaging, automotive, and medical devices.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Braskem
- LyondellBasell Industries N.V.
- Mitsui Chemicals, Inc.
- FKUR
- CITRONIQ, LLC.
- Borealis AG.
- SABIC
- Total Energies
- Borouge
- Beaulieu International Group
- INEOS
- ORLEN Group
- Mitsubishi Chemical Group Corporation
- Avient Corporation
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024, Citroniq, LLC strengthened its foothold in the bio‑based polypropylene sector, securing USD 12 million in Series A funding—led by a major energy technology firm, alongside Lummus Technology Ventures and the State of Nebraska—to support design and engineering of its first commercial facility in Nebraska.
In 2024, LyondellBasell Industries N.V. significantly advanced its position in the bio‑based polypropylene sector by producing and marketing over 203,000 metric tons of recycled and renewable-based polymers, marking a 65% year‑over‑year increase in its Circular & Low Carbon Solutions (CLCS) portfolio.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 116.6 Mn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 1223.5 Mn CAGR (2025-2034) 26.5% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Feedstock (Sugarcane, Com Starch, Cellulose, Lignocellulosic Biomass), By Production Process (Melt Mass Polymerization (MMP), Solution Polymerization, Gas Phase Polymerization), By Extrusion Type (Sheet Extrusion, Film Extrusion, Pipe Extrusion), By End-user (Packaging, Automotive, Consumer Goods, Textile, Medical and Healthcare, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Braskem, LyondellBasell Industries N.V., Mitsui Chemicals, Inc., FKUR, CITRONIQ, LLC., Borealis AG., SABIC, Total Energies, Borouge, Beaulieu International Group, INEOS, ORLEN Group, Mitsubishi Chemical Group Corporation, Avient Corporation Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Bio-based Polypropylene MarketPublished date: July 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Bio-based Polypropylene MarketPublished date: July 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Braskem
- LyondellBasell Industries N.V.
- Mitsui Chemicals, Inc.
- FKUR
- CITRONIQ, LLC.
- Borealis AG.
- SABIC
- Total Energies
- Borouge
- Beaulieu International Group
- INEOS
- ORLEN Group
- Mitsubishi Chemical Group Corporation
- Avient Corporation










