Global Fuel Cell Powertrain Market By Component(Fuel Cell Systems, Battery Systems, Drive Systems, Hydrogen Storage Systems, Others), By Drive Type(Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD), Front-Wheel Drive (FWD), All-Wheel Drive (AWD)), By Vehicle Type(Passenger Vehicles, Light Commercial Vehicles (LCVs), Buses, Trucks), By Power Output(250kW), By Region, and Key Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2024-2033
- Published date: April 2024
- Report ID: 73372
- Number of Pages: 242
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
The global Fuel Cell Powertrain Market size is expected to be worth around USD 93679 Million by 2033, from USD 481.4 Million in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 69.4% during the forecast period from 2023 to 2033.
Fuel Cell Powertrain Market refers to the segment of the global market encompassing all activities, products, and services related to the development, manufacturing, and sale of powertrains powered by fuel cells for various types of vehicles.
A fuel cell powertrain utilizes hydrogen or another fuel to generate electricity through a chemical process within a fuel cell, which then powers the vehicle’s electric motor(s). This market segment is distinguished by its focus on innovative, clean energy solutions for transportation, aiming to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependency on fossil fuels.
Key components of the fuel cell powertrain include the fuel cell stack (where the chemical reaction occurs), hydrogen storage tanks, power electronics, electric motors, and transmission systems. The market for fuel cell powertrains is driven by factors such as advancements in fuel cell technology, governmental policies and incentives promoting clean energy, and growing environmental awareness among consumers.
Market reports on the fuel cell powertrain sector typically cover aspects such as market size, growth projections, technological innovations, regulatory landscape, competitive analysis, and potential barriers to entry. The adoption of fuel cell technology in the transportation sector, including in passenger vehicles, commercial trucks, buses, and even non-road vehicles like forklifts and trains, signifies a transformative shift towards more sustainable and efficient energy use.
In essence, the Fuel Cell Powertrain Market is a critical component of the broader move towards electrification in transportation, representing a growing industry focused on leveraging hydrogen and fuel cell technologies to achieve cleaner, more efficient mobility solutions.
Key Takeaways
- Market Growth: Fuel cell powertrain market projected to reach USD 93,679 million by 2033, growing at 69.4% CAGR from 2023’s USD 481.4 million.
- Component Dominance: Fuel cell systems hold 44.2% market share, followed by battery and drive systems, driving vehicle efficiency.
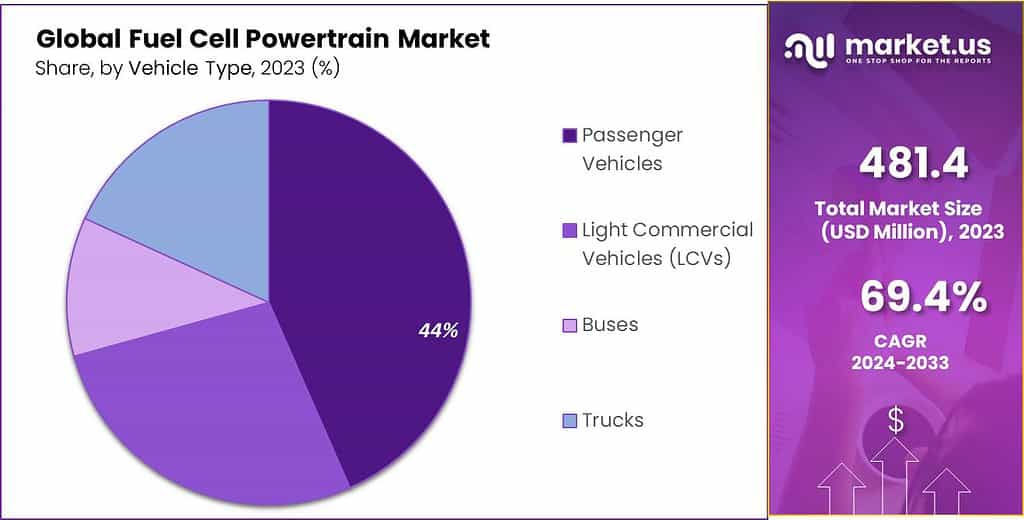
- Vehicle Type: Passenger vehicles dominate with 47.3% market share, followed by Light Commercial Vehicles (LCVs) and buses.
- Power Output Segment: <150 kW segment holds 49.3% market share, catering to diverse vehicle needs.
- By 2024, the number of hydrogen refueling stations in Europe is projected to reach over 1,000, with Germany, France, and the UK leading the way.
- In 2023, the European Union announced a €5.4 billion investment in the development of hydrogen technologies, including fuel cell powertrains.
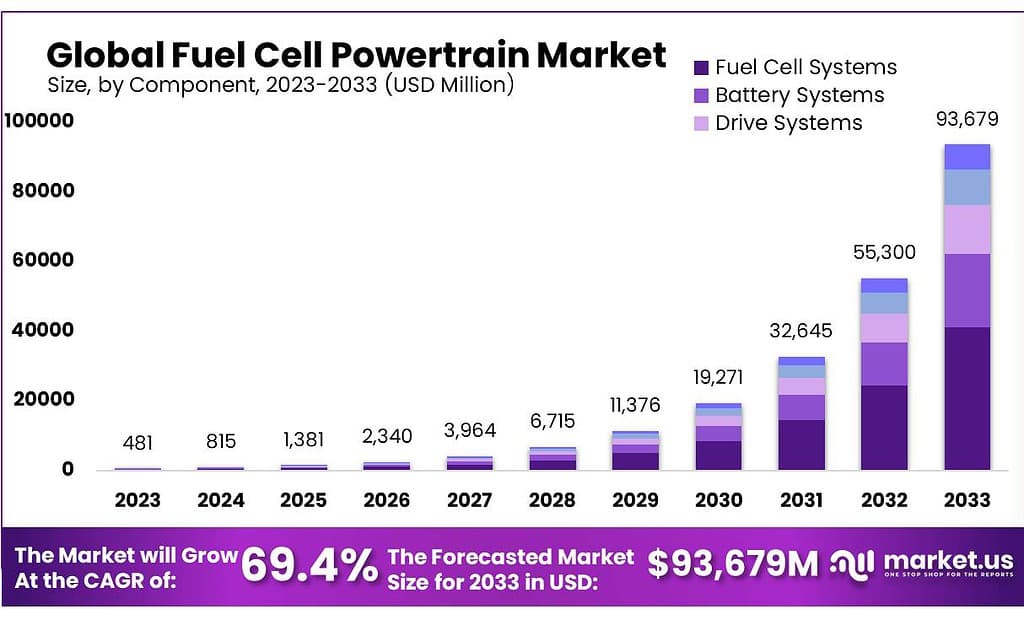
By Component
In 2024, Fuel Cell Systems held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 44.2% share. This segment’s leadership can be attributed to the core role fuel cells play in generating electricity directly from hydrogen, marking them as essential for the powertrain’s functionality. Advancements in fuel cell efficiency and durability have further bolstered their market presence.
Battery Systems, as a vital complementary component, accounted for a significant portion of the market. These systems store electrical energy produced by fuel cells for later use, enhancing vehicle range and efficiency. The push for higher energy density and faster charging solutions has driven innovation in this area.
Drive Systems, encompassing electric motors and transmission units, also claimed a notable market share. Their importance lies in converting electrical energy into mechanical power, directly influencing vehicle performance. Technological improvements aimed at increasing power output and reducing weight have been key growth factors.
Hydrogen Storage Systems are critical for fuel cell vehicles, offering the means to store hydrogen fuel safely and efficiently. Innovations in storage technologies, aimed at increasing capacity and reducing refueling times, have supported this segment’s growth. This component’s market share is reflective of the ongoing efforts to make hydrogen a viable fuel option for wider adoption.
Other components, including power electronics and control systems, although capturing a smaller share, play crucial roles in the operation and efficiency of fuel cell powertrains. These elements ensure the seamless integration of all powertrain components, contributing to the system’s overall performance and reliability.
By Drive Type
In 2024, the All-Wheel Drive (AWD) segment led the Fuel Cell Powertrain Market by drive type, capturing a significant market share. The preference for AWD in fuel cell vehicles is attributed to its enhanced traction and stability across various driving conditions, making it a popular choice for consumers seeking safety and performance. This drive type’s adaptability to both urban and off-road settings has further solidified its market dominance.
Rear-wheel drive (RWD) configurations, known for their traditional appeal and performance characteristics, maintained a strong presence in the market. RWD offers benefits in terms of handling and acceleration, appealing to a segment of consumers and manufacturers focused on performance-oriented vehicles. Despite facing competition from more technologically advanced drive types, the RWD segment continues to hold its ground, supported by ongoing advancements in fuel cell technology that enhance vehicle dynamics.
Front-wheel drive (FWD) systems, typically favored for their cost-effectiveness and simplicity, also accounted for a notable share of the market. FWD vehicles are often highlighted for their efficiency and space-saving design, which aligns well with the compact nature of many fuel cell systems. This drive type remains a practical choice for consumers prioritizing economy and reliability in their vehicles.
Each drive type within the Fuel Cell Powertrain Market caters to different consumer preferences and requirements, showcasing the diversity and adaptability of fuel cell technology in the automotive industry. As the market evolves, the balance between performance, cost, and technological innovation will continue to shape the competitive landscape of these segments.
By Vehicle Type
In 2024, Passenger Vehicles held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 47.3% share. This segment’s leadership is driven by the increasing consumer demand for clean, sustainable personal transportation solutions. The adoption of fuel cell technology in passenger vehicles is further propelled by advancements in fuel cell efficiency, government incentives, and growing environmental awareness, making them a preferred choice for eco-conscious consumers.
Light Commercial Vehicles (LCVs) also marked a significant presence in the market. LCVs, essential for urban logistics and transportation, benefited from the integration of fuel cell powertrains, offering enhanced range and payload capacity without emissions. The push towards reducing urban pollution and noise levels has made fuel cell LCVs an attractive option for businesses aiming to green their operations.
Buses equipped with fuel cell powertrains captured a substantial market share, driven by the need for clean public transportation systems. The adoption of fuel cell buses is supported by their ability to operate over long distances without emissions, meeting the demand for sustainable urban mobility solutions. Governmental policies promoting clean energy and public transport infrastructure development have further bolstered this segment.
Trucks, including heavy-duty vehicles, also adopted fuel cell technology, aiming to reduce carbon emissions in freight and logistics. The fuel cell trucks segment, although smaller in comparison, is crucial for achieving low-carbon transportation networks. The development of hydrogen refueling infrastructure and technological advancements in hydrogen storage and fuel cell efficiency are key factors supporting the growth of this segment.
Each vehicle type within the Fuel Cell Powertrain Market addresses unique challenges and opportunities in the transition towards sustainable transportation. With ongoing technological advancements and supportive regulatory frameworks, the market is poised for continued growth across all segments.
By Power Output
In 2024, the <150 kW segment held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 49.3% share. This segment’s prominence is largely due to its suitability for a wide range of passenger vehicles and light commercial vehicles, where moderate power output meets the needs for daily commuting and light-duty tasks. The popularity of this power output range is also bolstered by its efficiency and cost-effectiveness, appealing to a broad consumer base seeking reliable and sustainable transportation solutions without the need for high power outputs.
The 150-250 kW segment, serving a critical role for vehicles requiring higher power, such as certain light commercial vehicles, buses, and trucks, secured a significant portion of the market. Vehicles within this power output range benefit from enhanced performance capabilities while maintaining efficient fuel usage. This segment meets the needs of commercial transportation and service providers looking for a balance between power and sustainability, making it an attractive option for businesses aiming to reduce their carbon footprint without compromising on vehicle performance.
Lastly, the >250 kW segment catered to the niche market of heavy-duty trucks and high-performance vehicles. Although smaller in market share, this segment is crucial for applications demanding high power output for heavy transport and specialized operations. The adoption of fuel cell powertrains in this segment demonstrates the versatility of hydrogen fuel technology, capable of meeting even the most demanding power requirements. Despite the challenges of higher costs and the need for more robust infrastructure, the >250 kW segment is poised for growth, driven by advancements in fuel cell efficiency and the expanding network of hydrogen refueling stations.
Each power output segment within the Fuel Cell Powertrain Market caters to different segments of the transportation sector, from personal mobility to heavy-duty logistics, showcasing the adaptability and potential of fuel cell technology to transform the automotive landscape towards a more sustainable future.
Key Market Segments
By Component
- Fuel Cell Systems
- Battery Systems
- Drive Systems
- Hydrogen Storage Systems
- Others
By Drive Type
- Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD)
- Front-Wheel Drive (FWD)
- All-Wheel Drive (AWD)
By Vehicle Type
- Passenger Vehicles
- Light Commercial Vehicles (LCVs)
- Buses
- Trucks
By Power Output
- <150 kW
- 150-250 kW
- >250kW
Drivers
Government Incentives and Supportive Policies
One of the most significant drivers propelling the Fuel Cell Powertrain Market forward is the comprehensive range of government incentives and supportive policies implemented worldwide. These initiatives are aimed at accelerating the adoption of clean and sustainable transportation solutions, among which fuel cell technology stands out due to its potential to drastically reduce carbon emissions and reliance on fossil fuels.
Governments across the globe have recognized the pivotal role that fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) can play in achieving long-term environmental goals and are therefore deploying a variety of strategies to encourage both manufacturers and consumers to embrace this technology.
Financial incentives such as tax rebates, grants, and subsidies for the purchase of FCVs and the development of hydrogen fuel infrastructure have significantly lowered the barriers to entry for both supply and demand sides of the market. For example, consumers benefit from lower upfront costs when purchasing FCVs, making them more competitive with conventional and other electric vehicles. On the manufacturing side, companies receive financial support for research and development (R&D) activities, which fuels innovation and reduces the cost of fuel cell production over time.
Beyond direct financial support, governments are also establishing strict environmental regulations and emissions targets that necessitate the adoption of cleaner transportation technologies. These regulations often come with penalties for non-compliance, further motivating automakers to accelerate the development and deployment of FCVs. Additionally, the creation of low-emission zones in urban areas and the commitment to convert public transportation fleets to zero-emission vehicles are concrete examples of policy measures that directly boost the demand for fuel cell powertrains.
Infrastructure development is another crucial area where governmental policies are making a substantial impact. The establishment of hydrogen refueling stations is essential for the widespread adoption of FCVs. Recognizing this, many governments are investing in or subsidizing the expansion of hydrogen refueling networks, thereby addressing one of the most significant hurdles to consumer acceptance of fuel cell technology. These efforts are complemented by policies aimed at increasing the production, storage, and distribution of green hydrogen, further enhancing the sustainability profile of FCVs.
The synergy of financial incentives, regulatory frameworks, and infrastructure development initiatives under government auspices not only fosters a conducive environment for the growth of the Fuel Cell Powertrain Market but also signals to investors, companies, and consumers alike that fuel cell technology is a viable and supported path towards cleaner transportation. As these policies continue to evolve and expand, they will further reduce the total cost of ownership of FCVs, enhance the operational efficiency of fuel cell powertrains, and solidify the market’s growth trajectory.
Restraints
High Initial Costs and Infrastructure Challenges
A significant restraint facing the Fuel Cell Powertrain Market is the high initial costs associated with fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) and the related hydrogen infrastructure development. This challenge encompasses both the manufacturing costs of the vehicles themselves and the broader ecosystem needed to support their operation, including hydrogen production, storage, and distribution systems, as well as refueling stations.
These factors collectively contribute to a higher total cost of ownership compared to conventional internal combustion engine vehicles and even other electric vehicles (EVs), which can deter both consumers and businesses from adopting this technology.
The manufacturing costs of fuel cell systems are intrinsically higher due to the sophisticated materials and technologies required. Platinum, for example, serves as a critical catalyst within fuel cell stacks but is expensive and contributes to the overall cost.
Furthermore, the production processes for these systems are currently less scalable compared to those for traditional automotive manufacturing, resulting in lower economies of scale. While research and development efforts continue to focus on reducing these costs through innovations in materials science and manufacturing techniques, these advancements have yet to fully materialize into substantial cost reductions for end users.
Beyond the vehicle costs, the development of a comprehensive hydrogen infrastructure poses a significant challenge. Hydrogen refueling stations are essential for the widespread adoption of FCVs but require substantial investments to build and operate.
Compared to the more mature infrastructure for gasoline and diesel or the rapidly expanding network for battery electric vehicle charging, hydrogen refueling networks are limited and concentrated in specific regions. This limitation not only affects the practicality and appeal of owning an FCV but also influences the strategic decisions of automakers and energy companies regarding where and how to invest in this market.
Moreover, the production of hydrogen, particularly green hydrogen produced through electrolysis powered by renewable energy, faces its own set of challenges. The costs associated with green hydrogen production are currently higher than those for hydrogen produced from fossil fuels, known as grey hydrogen.
While the latter is more affordable, it does not offer the same environmental benefits, which can undermine the clean energy proposition of FCVs. Transitioning to a more sustainable hydrogen economy requires significant advancements in electrolysis technology, renewable energy capacity, and financial incentives to lower the cost barrier.
The combined effect of these challenges—high vehicle costs, the nascent stage of hydrogen infrastructure, and the complexities of hydrogen production—creates a considerable restraint for the Fuel Cell Powertrain Market. Consumer adoption is hindered by the upfront costs and practical limitations related to refueling and long-distance travel, while businesses face uncertainties regarding the return on investment in fuel cell technology and infrastructure.
Addressing these restraints is critical for the future growth of the Fuel Cell Powertrain Market. Efforts to reduce the costs of fuel cell systems through technological innovation and increased production scale, along with strategic investments in hydrogen infrastructure and policies supporting clean hydrogen production, are essential.
As these challenges are gradually overcome, the market can move toward broader adoption of fuel cell technology, offering a sustainable and efficient alternative to traditional transportation fuels and contributing to global efforts to reduce carbon emissions. The path forward involves a coordinated approach by industry stakeholders, governments, and research institutions to unlock the full potential of fuel cell powertrains as a cornerstone of the clean energy transition.
Opportunity
Expansion into Heavy-Duty and Industrial Transportation
A major opportunity for the Fuel Cell Powertrain Market lies in its potential expansion into the heavy-duty and industrial transportation sectors. This segment, encompassing trucks, buses, maritime vessels, and even trains, represents a significant portion of global transportation and is a critical area for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving air quality. Fuel cell technology, with its unique advantages of high energy efficiency and the capability for rapid refueling, is ideally positioned to meet the demanding requirements of these applications, offering a clean, viable alternative to diesel-powered vehicles and equipment.
Heavy-duty trucks, responsible for a substantial share of freight transport, face increasing regulatory pressures to reduce emissions, particularly in urban areas and along heavily trafficked corridors. Fuel cell powertrains, offering comparable range and load capacities to diesel engines without the associated emissions, present a compelling solution. The adoption of fuel cell technology in this sector can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of logistics and supply chains, contributing to global sustainability goals.
Similarly, buses powered by fuel cells are gaining traction as cities around the world strive to decrease urban pollution and transition to zero-emission public transportation systems. Fuel cell buses can operate for longer distances than their battery electric counterparts without the need for lengthy recharging times, making them an attractive option for busy urban transit networks and long-distance routes alike.
In the maritime sector, fuel cell technology offers a promising pathway to decarbonize shipping and recreational boating, industries traditionally reliant on heavy fuel oils. Fuel cells can provide a scalable power solution for vessels of various sizes, from small passenger ferries to large cargo ships, significantly reducing marine pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
Furthermore, the rail industry, with its extensive networks and predictable routes, presents another opportunity for the integration of fuel cell technology. Fuel cell-powered trains can replace diesel locomotives, especially on non-electrified tracks, offering a clean alternative that eliminates direct emissions and reduces noise levels, enhancing the sustainability of rail transportation.
The expansion of the Fuel Cell Powertrain Market into these heavy-duty and industrial sectors is not without its challenges, particularly concerning the development of suitable hydrogen infrastructure and the need for technological advancements to increase the durability and efficiency of fuel cell systems. However, the potential environmental and economic benefits are driving increased investment and innovation in this area. Governments and industry players are beginning to collaborate on pilot projects and initiatives to demonstrate the feasibility and advantages of fuel cell technology in heavy-duty transportation, setting the stage for wider adoption.
Moreover, the growing emphasis on green hydrogen as a key component of the global energy transition adds momentum to the opportunity for fuel cell powertrains in heavy-duty and industrial applications. As the production of green hydrogen becomes more cost-effective and scalable, thanks to advances in renewable energy technologies and electrolysis, the economic case for fuel cell transportation solutions will strengthen further.
Trends
Integration of Renewable Energy for Hydrogen Production
A defining trend shaping the Fuel Cell Powertrain Market is the integration of renewable energy sources for the production of green hydrogen. This approach not only enhances the environmental benefits of fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) by reducing their overall carbon footprint but also aligns with global efforts to transition towards a more sustainable and renewable energy-dominated future. As the demand for cleaner transportation solutions grows, the synergy between renewable energy and hydrogen production has become increasingly critical, driving innovation and investment in the fuel cell sector.
The traditional method of hydrogen production, primarily through natural gas reforming, presents a challenge to the environmental credentials of FCVs due to the associated carbon emissions. In contrast, green hydrogen, produced via electrolysis powered by renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, and hydroelectric power, offers a truly zero-emission alternative. The push towards green hydrogen is being fueled by the rapid expansion of renewable energy capacity worldwide, coupled with advancements in electrolysis technology that are making the process more efficient and cost-effective.
The integration of renewable energy into hydrogen production has several key implications for the Fuel Cell Powertrain Market. Firstly, it addresses one of the major criticisms of fuel cell technology—its reliance on hydrogen produced from fossil fuels—by providing a path to truly clean transportation. Secondly, it creates a direct link between the growth of the renewable energy sector and the expansion of the fuel cell market, as increased renewable capacity directly translates to greater potential for green hydrogen production.
Moreover, this trend is fostering innovative business models and partnerships across the energy, automotive, and technology sectors. Energy companies are investing in large-scale electrolysis projects located near renewable energy sources, while automakers are exploring ways to integrate hydrogen fuel cell technology into their future mobility solutions. Governments are also playing a crucial role by implementing policies that support both renewable energy expansion and the development of hydrogen infrastructure, such as funding for electrolysis projects, tax incentives for renewable energy investments, and goals for hydrogen-powered public transportation fleets.
Another aspect of this trend is the development of decentralized hydrogen production facilities, which can directly harness local renewable energy sources to produce hydrogen near the point of use, reducing transportation and storage costs. This approach has the potential to significantly improve the efficiency of the hydrogen supply chain and make fuel cell technology more accessible and attractive for a range of applications, from passenger vehicles to industrial equipment.
However, the integration of renewable energy for hydrogen production also presents challenges, including the need for significant investments in infrastructure and technology, the management of intermittent renewable energy supplies, and the scaling of electrolysis capacity to meet demand. Despite these challenges, the momentum behind renewable energy and green hydrogen is strong, driven by technological advancements, declining costs, and increasing recognition of the need to address climate change.
Regional Analysis
North America Emerges as a Leading Market in the Global Fuel Cell Powertrain Sector
In 2023, North America claimed a 39% share of the global fuel cell powertrain market. The region, with the United States at the forefront, is recognized for its high adoption rate of electric and zero-emission vehicles, which includes those powered by fuel cell technology. The significant interest in clean transportation solutions within North America is propelled by an increased awareness of environmental issues and the urgent need for sustainable mobility options.
The awareness among North American consumers and businesses regarding the environmental impact of transportation has led to a surge in investment in cleaner, alternative propulsion systems like fuel cell powertrains. These investments are aimed at addressing critical environmental challenges such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions and dependency on fossil fuels. The informed populace is thus more inclined to support and adopt vehicles equipped with fuel cell technology, driving demand in the market.
Furthermore, North America is home to a sophisticated ecosystem supporting the development and deployment of fuel cell technology, including a robust network of research institutions, regulatory bodies, and a mature automotive industry. This ecosystem facilitates the rapid development, testing, and commercialization of fuel cell powertrains, supported by both public and private sector investments in research and development. The presence of numerous leading fuel cell technology companies in the region, many of which are pioneering innovations in the field, reinforces North America’s position as a key player in the global market.
This confluence of high consumer interest, a supportive regulatory environment, and cutting-edge technological advancements makes North America one of the most lucrative markets for the fuel cell powertrain industry. As awareness and demand continue to grow, the region is poised to maintain and potentially increase its market share, driving forward the adoption of fuel cell vehicles and contributing significantly to the global transition towards sustainable transportation solutions.
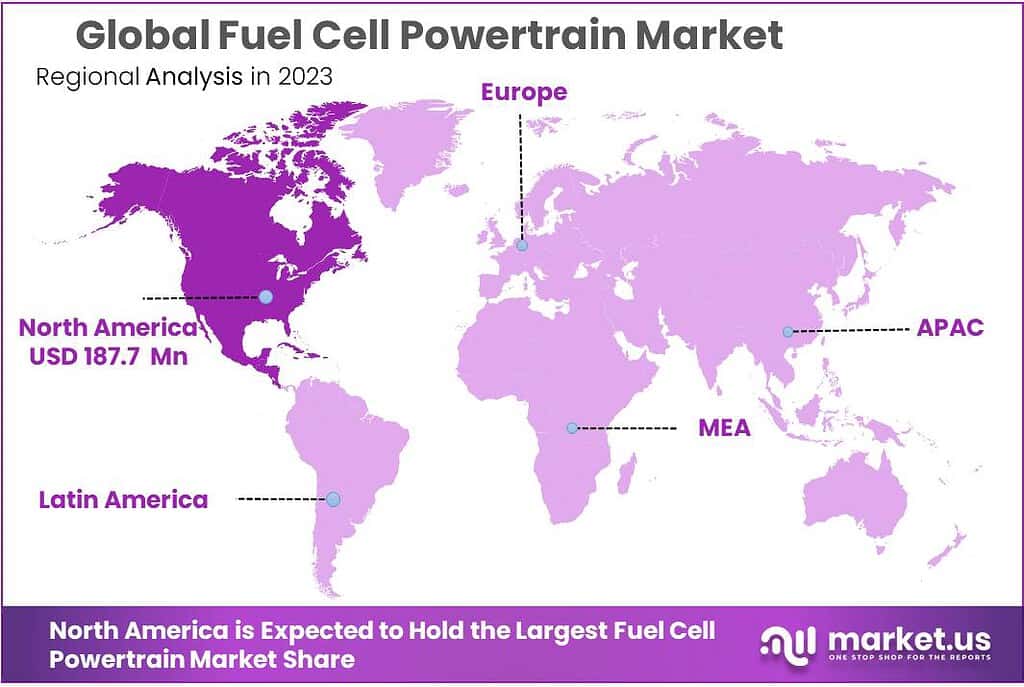
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- The US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia & CIS
- Rest of Europe
- APAC
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- ASEAN
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
The Fuel Cell Powertrain Market is characterized by the presence of several key players who are pivotal in shaping the industry’s trajectory through innovation, strategic partnerships, and a focus on sustainability.
These companies are at the forefront of developing and commercializing fuel cell technology for transportation, contributing to the global shift towards cleaner energy solutions. Below is an analysis of some of the key players in the market, highlighting their strategies, product offerings, and market positions.
Market Key Players
- AVID Technology Ltd.
- Ballard Power Systems
- Brown Machine Group
- Ceres Power
- Cummins Inc.
- Delphi Technologies
- Denso Corporation
- ITM Power Manufacturers
- Robert Bosch
- Bloom Energy
- SFC Energy
Recent Development
In 2024, Ballard received a follow-on order from Canadian Pacific Kansas City (CPKC) rail for 12 fuel cell engines, aimed at bolstering CPKC’s fleet of hydrogen-powered locomotives for regular switching and local freight services.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2023) USD 481.4 Mn Forecast Revenue (2033) USD 93679 Mn CAGR (2024-2033) 69.4% Base Year for Estimation 2023 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2024-2033 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, COVID-19 Impact, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Component(Fuel Cell Systems, Battery Systems, Drive Systems, Hydrogen Storage Systems, Others), By Drive Type(Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD), Front-Wheel Drive (FWD), All-Wheel Drive (AWD)), By Vehicle Type(Passenger Vehicles, Light Commercial Vehicles (LCVs), Buses, Trucks), By Power Output(<150 kW, 150-250 kW, >250kW) Regional Analysis North America – The US & Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia & CIS, Rest of Europe; APAC– China, Japan, South Korea, India, ASEAN & Rest of APAC; Latin America– Brazil, Mexico & Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa– GCC, South Africa, & Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape AVID Technology Ltd., Ballard Power Systems, Brown Machine Group, Ceres Power, Cummins Inc., Delphi Technologies, Denso Corporation, ITM Power Manufacturers, Robert Bosch, Bloom Energy, SFC Energy Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the Size of Fuel Cell Powertrain Market?Fuel Cell Powertrain Market size is expected to be worth around USD 93679 Million by 2033, from USD 481.4 Million in 2023
What CAGR is projected for the Fuel Cell Powertrain Market?The Fuel Cell Powertrain Market is expected to grow at 69.4% CAGR (2023-2032).Name the major industry players in the Fuel Cell Powertrain Market?AVID Technology Ltd., Ballard Power Systems, Brown Machine Group, Ceres Power, Cummins Inc., Delphi Technologies, Denso Corporation, ITM Power Manufacturers, Robert Bosch, Bloom Energy, SFC Energy
 Fuel Cell Powertrain MarketPublished date: April 2024add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Fuel Cell Powertrain MarketPublished date: April 2024add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- AVID Technology Ltd.
- Ballard Power Systems
- Brown Machine Group
- Ceres Power
- Cummins Inc.
- Delphi Technologies
- Denso Corporation
- ITM Power Manufacturers
- Robert Bosch
- Bloom Energy
- SFC Energy










