Global Electric Ship Market By Type(Fully Electric, Hybrid), By Mode of Operation(Fully Autonomous, Semi-Autonomous), By Power Output(7,560 kW), By Ship Type(Commercial Ship, Passenger Ship) By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends, and Forecast 2024-2033
- Published date: May 2023
- Report ID: 54507
- Number of Pages: 304
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
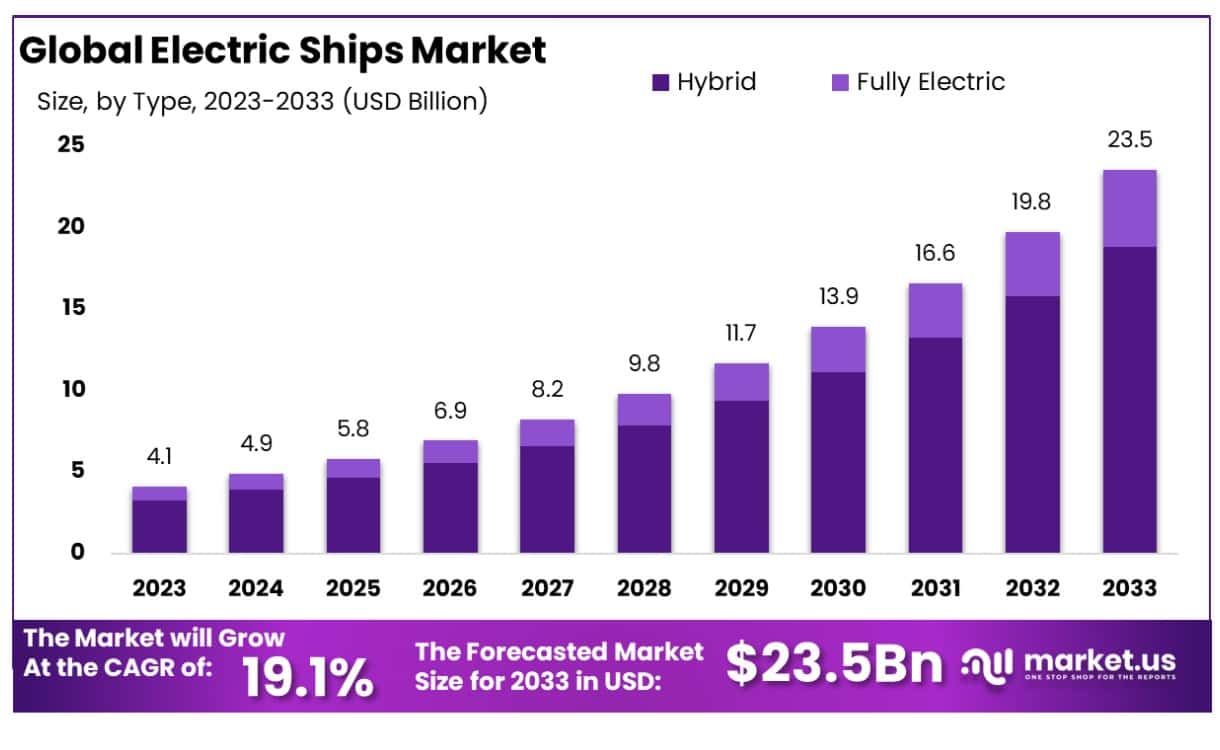
The Global Electric Ship Market size is expected to be worth around USD 23.5 Billion by 2033, From USD 4.1 Billion by 2023, growing at a CAGR of 19.1% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
The Electric Ship Market is a dynamic and rapidly evolving segment within the maritime industry, characterized by the adoption of electric propulsion systems in naval and commercial vessels. This market is driven by the increasing emphasis on reducing carbon emissions, enhancing fuel efficiency, and minimizing the environmental impact of maritime operations.
As global regulations tighten around ship emissions, the demand for electric ships, including battery-operated vessels and hybrid models, is surging. Key stakeholders include shipbuilders, maritime technology firms, and regulatory bodies, working collaboratively to innovate and implement electric propulsion technologies. The market’s growth is propelled by advancements in battery technology, renewable energy integration, and the maritime industry’s commitment to sustainability.
The global shift towards reducing carbon footprints and fuel waste has propelled the demand for electric-powered maritime ships, fostering market expansion. Shipbuilders are increasingly focused on mitigating the noise produced by marine vessel engine systems, aligning with environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), transportation accounted for over 29% of all greenhouse gas emissions in the United States in 2023, highlighting the urgent need for sustainable alternatives in the sector.
Government initiatives aimed at lowering carbon emissions, including incentives for electric-powered cargo ships, are expected to drive future market growth. Additionally, the adoption of diesel engine generators (Gensets) or electric generators enhances ship efficiency under heavy loads, consuming less fuel compared to traditional internal combustion engines. This trend is further reinforced by transportation and logistics service providers’ efforts to reduce operational costs, incentivizing the adoption of electric propulsion systems.
Electric propulsion motors, characterized by their lack of direct connection to prime movers, minimize vibrations and enhance system performance compared to conventional propulsion engines. Moreover, the compact nature of electric propulsion systems equipment allows for efficient space utilization, potentially increasing revenue opportunities for ship operators.
The surge in demand for hybrid and electric propulsion systems extends across various commercial ship categories, including cruise vessels, ferryboats, cargo ships, and container ships. Notably, ship owners from Norway, the US, Greece, China, and France are actively involved in retrofitting their current ship fleets with advanced technologies such as hybrid and electric systems, further driving market growth and innovation in the electric ship industry.
Key Takeaways
- Market Growth: Electric Ships Market was valued at USD 4.1 Billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 23.5 Billion in 2033, at a CAGR of 19.01%
- Segmentation Insights:
- By Type Analysis: Hybrid models hold a dominant market position, capturing more than an 80% share.
- By Mode of Operation Analysis: Semi-autonomous vessels held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 90% share
- By Power Output Analysis: The 75 kW-745kW segment held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 45% share.
- By Ship Type Analysis: The commercial Ship segment held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 75% share.
- Regional Dominance: Europe emerges as the dominating region, holding a substantial 36.5% market share
Driving Factors
Reducing Carbon Emissions: A Catalyst for Sustainable Maritime Operations
The global initiative to reduce carbon emissions is a significant driver for the Electric Ship Market. As international regulatory bodies impose stricter emissions standards, the maritime industry is under increasing pressure to adopt cleaner energy sources. Electric ships, which emit zero greenhouse gases during operation, offer a compelling solution to this challenge. By transitioning to electric propulsion, the maritime sector can significantly reduce its environmental footprint, aligning with global sustainability goals. This shift is not merely regulatory compliance but a strategic move towards future-proofing maritime operations against evolving environmental policies.
Advances in Energy Storage Systems: Enabling Longer Voyages
The development and enhancement of energy storage systems, particularly lithium-ion batteries, have been pivotal in the electric ship market’s growth. Advances in battery technology have led to higher energy densities, longer lifespans, and faster charging times, making electric propulsion increasingly viable for longer maritime routes. As energy storage capabilities continue to improve, the operational range of electric vessels expands, making them competitive alternatives to traditional fossil-fueled ships. This technological progression underpins the market’s expansion, as it addresses one of the primary limitations of electric ships: their previously limited range and endurance.
Increased Adoption of Hybrid and Fully Electric Vessels: A Market Transformation
The adoption of hybrid and fully electric vessels is surging across various maritime sectors, including commercial, passenger, and defense fleets. This shift is driven by the dual objectives of reducing operational costs and complying with environmental regulations. Hybrid vessels, which combine conventional engines with electric propulsion, offer flexibility and reduced emissions, while fully electric ships eliminate fuel costs and carbon emissions. The increased interest and investment in these technologies by leading maritime nations and corporations underscore a transformative phase in the industry, bolstering the market growth.
Increasing Demand: The Economic and Environmental Imperative
The increasing demand for electric ships is propelled by both economic and environmental imperatives. On the economic front, the long-term cost savings on fuel and maintenance make electric and hybrid vessels financially attractive. Environmentally, the push towards decarbonization in transportation aligns with broader climate change mitigation efforts. Additionally, the growing awareness and demand for sustainable practices from consumers and businesses alike fuel this trend. As these economic and environmental drivers converge, they create a robust demand for electric maritime solutions, further accelerating the Electric Ship Market’s growth.
Restraining Factors
Technological Challenges: Impediment to Seamless Market Expansion
Technological hurdles play a significant role in restraining the Electric Ship Market’s growth. The integration of advanced electric propulsion systems into maritime vessels presents complex engineering challenges, including the optimization of energy efficiency and the management of power distribution systems. These challenges necessitate continuous research and development efforts, which can slow market progress. Additionally, the nascent nature of some electric propulsion technologies means that reliability and performance standards are still evolving, potentially deterring widespread adoption among commercial operators concerned with operational continuity and safety.
Infrastructure and Charging Infrastructure: A Bottleneck in Market Scalability
The underdeveloped state of maritime charging infrastructure significantly hinders the Electric Ship Market’s expansion. The availability of charging stations is limited, particularly in remote or less developed ports, posing a challenge to the operational range and feasibility of electric ships. This scarcity of charging points restricts the routes electric vessels can undertake, impacting the attractiveness of electric ships for commercial use. Moreover, the existing infrastructure cannot often support rapid charging of large vessels, extending turnaround times and reducing operational efficiency.
High Cost of Electric Vessels: A Barrier to Adoption
The initial investment required for electric ships is considerably higher than that for traditional fossil fuel-powered vessels, primarily due to the costs associated with advanced battery technologies and electric propulsion systems. This financial barrier can deter shipowners and maritime operators from transitioning to electric solutions, particularly in a market characterized by tight margins and high competition. Although operational costs over the vessel’s lifespan may be lower, due to reduced fuel and maintenance expenses, the upfront capital required can limit market growth by restricting the pool of potential buyers.
Limited Range: Curbing Operational Flexibility
The limited range of electric ships, constrained by current battery technology, poses a significant challenge to the market’s growth. This limitation affects the operational flexibility and utility of electric vessels, making them less suitable for long-haul journeys or operations in areas with sparse charging infrastructure. While suitable for short-sea shipping and inland waterways, the range limitation requires operators to carefully plan routes and charging stops, potentially complicating logistics and increasing transit times compared to traditional vessels.
By Type Analysis
The electric Ship Market was markedly segmented into two primary categories: Fully Electric and Hybrid vessels, with Hybrid models holding a dominant market position, capturing more than an 80% share. This substantial market share is attributed to the hybrid vessels’ ability to combine traditional internal combustion engines with electric propulsion systems. This dual approach offers enhanced fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and the flexibility to operate in areas with limited charging infrastructure, making them an attractive option for many maritime operators seeking to balance environmental concerns with operational practicality.
The Hybrid segment’s dominance in the market underscores the maritime industry’s cautious yet strategic approach to electrification. Operators favor hybrid ships for their versatility, allowing for longer voyages than fully electric counterparts and providing a reliable transition technology towards full electrification. The ability to switch between fuel types reduces reliance on ports with electric charging facilities, which are still in the early stages of development globally. This segment’s growth reflects a pragmatic adoption of green technologies, where immediate operational needs and environmental benefits are balanced.
Although the Fully Electric segment held a smaller portion of the market in 2023, its growth potential is significant, particularly in niche applications and short-sea shipping routes. These vessels are propelled exclusively by electric power, drawing energy from onboard batteries or other energy storage devices. They represent the pinnacle of maritime environmental sustainability efforts, eliminating direct emissions and significantly reducing noise pollution. The development of a more robust charging infrastructure and advancements in battery technology are expected to enhance the operational viability of fully electric ships, driving their adoption rate upward in the coming years.
By Mode of Operation Analysis
Semi-autonomous vessels held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 90% share in the Electric Ship Market. This segment’s commanding lead can be attributed to the advanced integration of semi-autonomous technologies that enhance operational efficiency, safety, and navigational accuracy without completely removing human oversight. Semi-autonomous ships incorporate systems for automated navigation, collision detection, and route optimization, which significantly reduce the potential for human error and operational costs. These advancements have accelerated the adoption of semi-autonomous vessels across various maritime activities, including cargo transport, surveillance, and environmental monitoring.
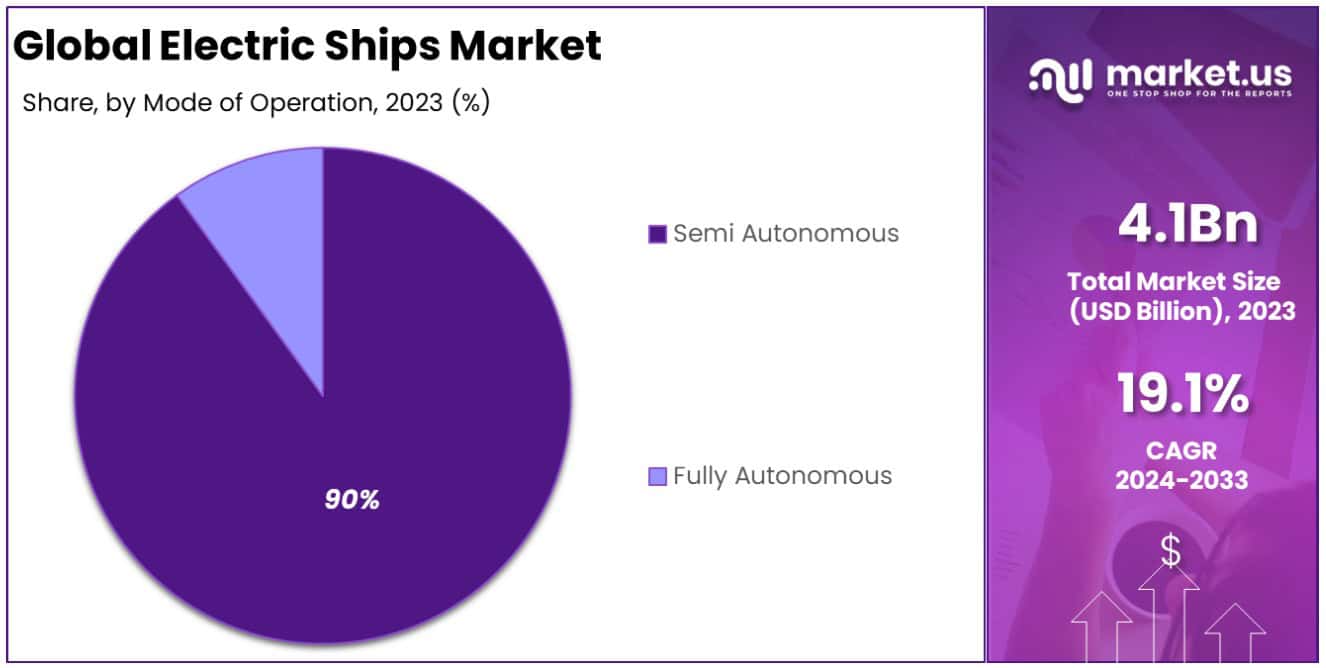
Conversely, Fully Autonomous ships, despite their transformative potential, accounted for a smaller portion of the market. The slower uptake is primarily due to the current regulatory, technological, and safety challenges associated with fully autonomous operations. Comprehensive international regulations governing fully autonomous maritime operations are still under development, creating uncertainty and hesitancy among potential adopters. Furthermore, the technological infrastructure required for fully autonomous operations, including sophisticated sensors, AI algorithms, and reliable communication systems, demands significant investment in research, development, and testing to ensure safety and reliability.
The disparity in market share between Semi-Autonomous and Fully Autonomous vessels underscores the maritime industry’s cautious approach toward full automation. While there is a clear interest in leveraging automation technology to improve efficiency and safety, the sector prioritizes incremental advancements within the framework of existing regulations and operational practices. As technological and regulatory landscapes evolve, the share of Fully Autonomous vessels is expected to grow, driven by continuous improvements in autonomous navigation systems and a gradual resolution of current barriers. However, in the near term, Semi-Autonomous ships will likely continue to dominate the Electric Ship Market, benefiting from their ability to offer immediate operational improvements while navigating the complexities of transitioning towards full autonomy.
By Power Output Analysis
The 75 kW-745kW segment held a dominant market position within the Electric Ship Market, capturing more than a 45% share. This segment’s prominence is attributed to its wide applicability across a variety of vessel types, including small to medium-sized commercial ships, luxury yachts, and certain specialized vessels. The power range offered by this segment is particularly suited to operators looking for a balance between operational efficiency and the benefits of electrification, such as reduced emissions and lower operating costs.
The <75 kW segment, catering primarily to small boats and auxiliary systems, marked its significance in niche applications. Although smaller in market share, this segment demonstrates the versatility of electric propulsion systems in enhancing energy efficiency for a broad spectrum of maritime operations.
Conversely, the 746 kW-7,560 kW segment addresses the needs of larger vessels requiring more significant power outputs for propulsion and onboard systems. Despite its lower market share compared to the 75 kW-745kW segment, its role is critical in pushing the boundaries of electric ship capabilities, showcasing the potential for electrification in larger commercial and industrial vessels.
The >7,560 kW segment, although capturing the smallest market share, highlights the ambitious end of the market where electrification efforts are focused on the most demanding applications. This includes large commercial vessels and specialized ships that require extensive power for propulsion. The development and growth of this segment are crucial for the long-term transformation of the shipping industry towards sustainability.
By Ship Type Analysis
The commercial Ship segment held a dominant market position within the Electric Ship Market, capturing more than a 75% share. This significant market share underscores the pivotal role of commercial vessels in adopting electric propulsion technologies, driven by increasing regulatory pressures to reduce carbon emissions, operational cost benefits, and the rising demand for sustainable shipping solutions. Commercial ships, including cargo carriers, tankers, and container ships, have been at the forefront of this transition, leveraging electric and hybrid technologies to enhance energy efficiency and comply with stringent environmental standards.
The Passenger Ship segment, while smaller in comparison, also demonstrated notable growth, reflecting an increasing consumer demand for environmentally friendly travel options. This segment encompasses ferries, cruise ships, and leisure boats, where the adoption of electric propulsion systems not only contributes to reducing emissions but also enhances the passenger experience by minimizing noise and vibrations. The growth in this segment is fueled by the tourism industry’s shift towards sustainability and the development of urban waterways as a green alternative for public transportation.
The dominance of the Commercial Ship segment in 2023 can be attributed to the sheer volume of global trade relying on maritime transport, compelling the industry to innovate and adopt cleaner energy sources. Additionally, the economic benefits of reduced fuel consumption and lower maintenance costs associated with electric propulsion systems have further bolstered the segment’s growth.
Key Market Segments
By Type
- Fully Electric
- Hybrid
By Mode of Operation
- Fully Autonomous
- Semi-Autonomous
By Power Output
- <75 kW
- 75 kW-745kW
- 746 kW-7,560 kW
- >7,560 kW
By Ship Type
- Commercial Ship
- Passenger Ship
Growth Opportunities
Government Regulations Driving Compliance and Innovation:
Regulatory frameworks instituted by governments worldwide act as a significant catalyst for the Electric Ship Market. Stricter emission standards and incentives for green shipping solutions push shipowners and operators towards electric and hybrid vessels. These regulations not only mandate compliance but also encourage technological advancements, making electric ships more viable and attractive. The International Maritime Organization’s (IMO) ambition to halve greenhouse gas emissions from shipping by 2050 exemplifies such policy-driven momentum, fostering an environment ripe for investment and development in electric propulsion technologies.
Public Awareness Elevating Market Demand:
Enhanced public consciousness regarding environmental issues amplifies the demand for sustainable transportation solutions. This heightened awareness influences consumer preferences and, by extension, the operational choices of commercial entities, including those in maritime logistics and cruise operations. The shift towards eco-friendly vessels is seen as not only a regulatory compliance strategy but also a competitive advantage, driving the market’s expansion.
Increased Adoption Demonstrating Market Viability:
The uptick in the adoption of electric and hybrid ships showcases the market’s viability and growth potential. As technological advancements lower operational costs and improve efficiency, the value proposition of electric ships becomes increasingly compelling. Early adopters in niche markets, such as short-sea shipping and ferries, provide valuable case studies demonstrating the operational and environmental benefits of electric propulsion, setting a precedent for broader industry uptake.
Latest Trends
The Electric Ship Market is poised for significant expansion, underscored by the convergence of technological advancements, evolving regulatory landscapes, and a marked shift in industry stakeholders’ operational preferences. Central to this growth trajectory is the growing demand for electric ships, spurred by the maritime industry’s urgent need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and operate more sustainably. This demand is further amplified by stringent environmental regulations globally, pushing shipowners and operators towards cleaner, electric alternatives. As a result, the market is witnessing a substantial increase in investments aimed at developing electric and hybrid vessels capable of meeting these new standards without compromising operational efficiency.
Advancements in energy storage systems represent another pivotal element driving the market forward. The development of more efficient, durable, and cost-effective battery technologies has significantly enhanced the operational range and reliability of electric ships, making them a more viable option for a broader range of maritime applications. This technological progress not only facilitates the construction of new electric vessels but also opens avenues for retrofitting existing fleets. Retrofitting, in particular, offers a pragmatic pathway for shipowners to comply with environmental regulations and benefit from lower operational costs associated with electric propulsion, without the need for substantial capital investment in new ships.
Collectively, these dynamics underscore a market at the cusp of transformation. The synergy between increased demand, technological innovation, and the strategic retrofitting of fleets heralds a new era for the maritime industry, one that promises enhanced sustainability and operational efficiency. As stakeholders continue to navigate these changes, the Electric Ship Market is expected to witness robust growth, setting a new standard for maritime transport in the years to come.
Regional Analysis
Europe emerges as the dominating region, holding a substantial 36.5% market share
The Electric Ship Market exhibits a diverse regional landscape, characterized by varying degrees of adoption and development across North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa, and Latin America. Europe emerges as the dominating region, holding a substantial 36.5% market share, driven by stringent environmental regulations, robust maritime infrastructure, and significant investments in green shipping technologies. The region’s leadership underscores its commitment to sustainable maritime transport, bolstered by initiatives such as the European Green Deal, which aims to make Europe the first climate-neutral continent by 2050.
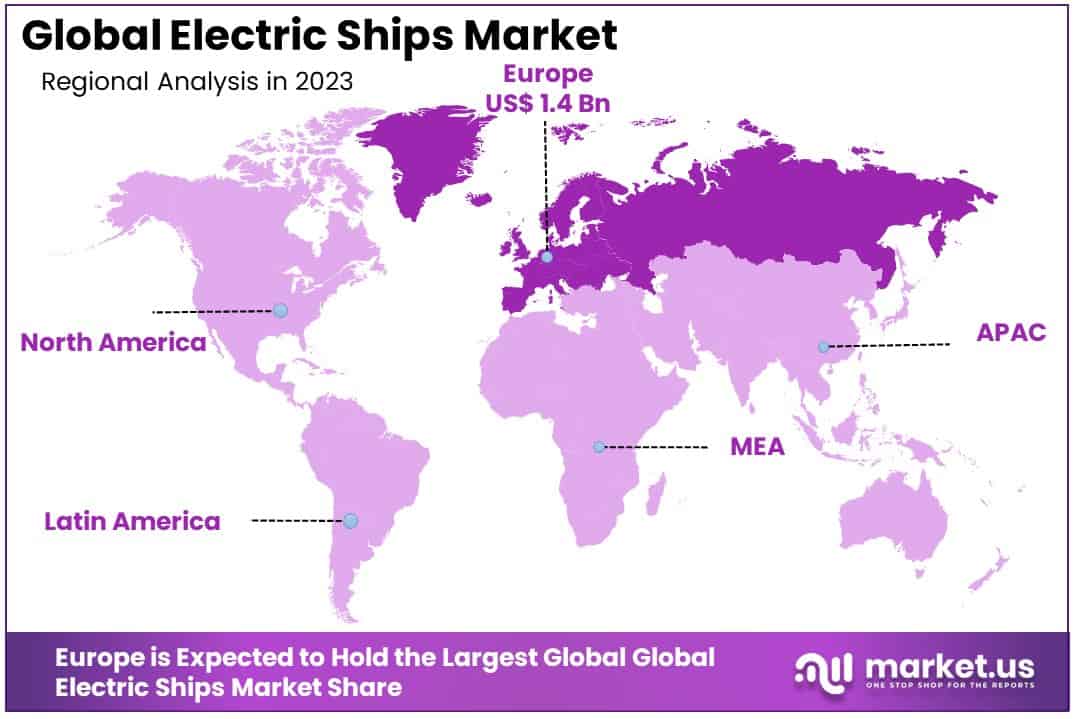
North America, with its advanced technological ecosystem and strong regulatory framework, also shows promising growth in the electric ship sector. The region benefits from governmental support and a growing awareness of environmental sustainability among consumers and businesses alike.
Asia Pacific is witnessing rapid growth, fueled by the expansion of maritime trade, increasing environmental concerns, and governmental incentives in countries like China and South Korea. This region’s focus on innovation and shipbuilding expertise positions it as a key player in the electric ship market.
Meanwhile, the Middle East & Africa, and Latin America are gradually entering the market, driven by emerging regulatory pressures and the potential for renewable energy integration. While these regions currently hold smaller market shares, their strategic maritime locations and growing interest in sustainable development present untapped opportunities for market expansion.
Europe’s leadership, underscored by its significant market share, highlights a broader global trend towards electrification in maritime transport, signaling a shift towards sustainability across the globe.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- The US
- Canada
- Mexico
- Western Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Portugal
- Ireland
- Austria
- Switzerland
- Benelux
- Nordic
- Rest of Western Europe
- Eastern Europe
- Russia
- Poland
- The Czech Republic
- Greece
- Rest of Eastern Europe
- APAC
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia & New Zealand
- Indonesia
- Malaysia
- Philippines
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Colombia
- Chile
- Argentina
- Costa Rica
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- Algeria
- Egypt
- Israel
- Kuwait
- Nigeria
- Saudi Arabia
- South Africa
- Turkey
- United Arab Emirates
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
The electric ship industry is propelled forward by the innovative contributions of key players such as Boesch Motorboote AG, Bureau Veritas, Siemens, KONGSBERG, Brodrene Aa, Wartsila, ABB Group, and Norwegian Electric Systems.
Boesch Motorboote AG, known for its proficiency in electric propulsion systems, particularly in motorboats, caters to the leisure and recreational boating sector, highlighting the versatility of electric solutions beyond commercial shipping. Bureau Veritas, a leading classification society, ensures compliance with maritime regulations and safety standards, instilling trust in the reliability and performance of electric vessels.
Siemens, a major provider of electric propulsion systems, contributes to the market’s advancement with innovative technologies aimed at enhancing maritime transportation efficiency and sustainability.
KONGSBERG specializes in autonomous and electric propulsion systems, addressing various vessel types’ electrification needs, from ferries to offshore vessels. Brodrene Aa stands out for its expertise in designing and manufacturing high-speed electric ferries, catering to the growing demand for emission-free transportation in the ferry sector. Wartsila, another prominent player, offers a comprehensive range of marine propulsion systems, including electric and hybrid solutions, supporting the transition to sustainable shipping practices.
ABB Group’s expertise in electric power and automation technologies provides integrated solutions for electric propulsion, energy storage, and vessel automation, optimizing electric ship performance and efficiency. Norwegian Electric Systems’ focus on customized electric propulsion solutions aligns with the industry’s evolving needs, offering tailored options for various maritime sectors seeking emission-reducing alternatives. Together, these companies drive innovation, promote sustainability, and shape the future of electric shipping worldwide.
Market Key Players
- BoeschMotorboote
- Bureau Veritas
- Siemens
- KONGSBERG
- Brodrene Aa
- Wartsila
- ABB Group
- Norwegian Electric Systems
- HOLLAND SHIPYARDS GROUP
- Corvus Energy
Recent Development
- In Sept 2023 Wartsila will provide the main propulsion system along with an array of other systems and equipment for two amphibious 110-meter transport vessels to be built by the Chilean Navy. The order was made through Astilleros y Maestranzas de la Armada (Asmar) Astilleros y Maestranzas de la Armada (A state-owned shipyard that will build these vessels.
- In May 2023, Kongsberg Maritime (KONGSBERG) will provide a set of equipment for a brand new ship called SDO-SuRS (Special and Diving Operations Submarine Rescue Ship) to be constructed in T.Mariotti, the Italian Shipyard T.Mariotti to build the Marina Militare Italiana (The Italian Navy).
- In March 2023 when the local subsidiary of GE in India signed a contract in partnership with Cochin Shipyard to provide a complete digital solution package to increase the performance of the marine gas turbines LM2500 which provide power to the Indian Navy’s first Indigenous Aircraft Carrier-1 (IAC-1) Vikrant and was officially launched in August 2022.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2023) USD 4.1 Billion Forecast Revenue (2033) USD 23.5 Billion CAGR (2024-2033) 19.1% Base Year for Estimation 2023 Historic Period 2018-2023 Forecast Period 2024-2033 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Type(Fully Electric, Hybrid), By Mode of Operation(Fully Autonomous, Semi-Autonomous), By Power Output(<75 kW, 75 kW-745kW, 746 kW-7,560 kW, >7,560 kW), By Ship Type(Commercial Ship, Passenger Ship) Regional Analysis North America – The US, Canada, & Mexico; Western Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Portugal, Ireland, Austria, Switzerland, Benelux, Nordic, & Rest of Western Europe; Eastern Europe – Russia, Poland, The Czech Republic, Greece, & Rest of Eastern Europe; APAC – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia & New Zealand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, & Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Colombia, Chile, Argentina, Costa Rica, & Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – Algeria, Egypt, Israel, Kuwait, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, & Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Boesch Motorboote AG, Bureau Veritas, Siemens, KONGSBERG, Brodrene Aa, Wartsila, ABB Group, Norwegian Electric Systems, HOLLAND SHIPYARDS GROUP, Corvus Energy Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the projected CAGR at which the Electric Ship market is expected to grow?The Electric Ship market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 11.5% (2023-2032).
List the segments encompassed in this report on the Electric Ship market?Market.US has segmented the Pigment Dispersion market by geography (North America, Europe, APAC, South America, and the Middle East and Africa). By Power Source Type, Fully Electric, Hybrid, The market has been segmented into <75 kW, 75-745 kW, 746-7,560 kW, >7,560 Kw, By Power Output. the market has been further divided into Semi-Autonomous, Fully By Autonomous level. The market has been segmented into Commercial Vessels, Defense Vessels, and Special Vessels, By Vessel Type.
List the key industry players of the Electric Ship market?Canadian Electric Boat Company, Corvus Energy Ltd., Yara Birkeland, Duffy Electric Boat, General Dynamics (Electric Boat Market), Kongsberg Gruppen ASA, and Other Key Players engaged in the Electric Ship market.
Which region is more appealing for vendors employed in the Electric Ship market?Europe accounted for the highest revenue share at 35%. Therefore, the Electric Ship industry in APAC is expected to garner significant business opportunities over the forecast period.
Name the key areas of business for Electric Ship?U.S., Canada, U.K,. Germany, France, Nordic Countries China, India, Japan, South Korea, Brazil, and Mexico are key areas of operation for the Electric Ship Market.
Which segment accounts for the greatest market share in the Electric Ship industry?Concerning the Electric Ship industry, vendors can expect to leverage greater prospective business opportunities through the hybrid segment, as this area of interest accounts for the largest market share.
 Global Electric Ships MarketPublished date: May 2023add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Global Electric Ships MarketPublished date: May 2023add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- BoeschMotorboote
- Bureau Veritas
- Canadian Electric Boat Company
- Corvus Energy Ltd.
- Yara Birkeland
- Duffy Electric Boat
- General Dynamics (Electric Boat)
- Kongsberg Gruppen ASA
- Eco Marine Power Co. Ltd.
- Marine Power Co. Ltd.
- Norwegian Electric Systems
- Other Key Players










