Global Cross Laminated Timber Market By Product(Adhesive Bonded, Mechanically Fastened), By Application(Residential, Institutional, Commercial, Others), By End-Use(Structural, Non-Structural) , By Region, and Key Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2024-2033
- Published date: May 2024
- Report ID: 119669
- Number of Pages: 240
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
The global Cross Laminated Timber Market size is expected to be worth around USD 5.0 billion by 2033, from USD 1.3 billion in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 14.4% during the forecast period from 2023 to 2033.
Cross Laminated Timber (CLT) is an innovative engineered wood product that has revolutionized modern construction practices. It consists of several layers of solid lumber boards, arranged crosswise and bonded together with adhesives or mechanical fasteners, forming a sturdy and dimensionally stable panel. The cross-lamination technique enhances the structural integrity and load-bearing capacity of the timber, making it a versatile choice for various construction applications.
The CLT market has been expanding rapidly due to its numerous advantages over traditional building materials like concrete and steel. One of the key drivers of this growth is the sustainability aspect of CLT. Being a renewable resource, CLT offers a lower carbon footprint, aligning with the global shift towards green building practices and reducing environmental impact. Its ability to sequester carbon further enhances its appeal as an eco-friendly construction material.
In addition to its environmental benefits, CLT is favored for its construction efficiency. The prefabricated nature of CLT panels allows for faster assembly on-site, reducing labor costs and construction timelines. This efficiency is particularly advantageous in urban settings where speed and minimal disruption are critical. Furthermore, CLT provides design flexibility, enabling architects to explore innovative and aesthetically pleasing structures that are difficult to achieve with conventional materials.
The market for CLT is segmented into various applications, including residential, commercial, institutional, and industrial buildings, each contributing to its overall growth. Despite its many benefits, the market faces challenges such as high initial costs and regulatory hurdles related to building codes. However, ongoing advancements in timber engineering and increasing awareness of sustainable construction practices are expected to drive continued growth in the CLT market. As the construction industry increasingly embraces eco-friendly materials, CLT is poised to play a significant role in the future of sustainable building solutions.
Key Takeaways
- Market Size: Expected to reach USD 5.0 billion by 2033, growing at a 14.4% CAGR from 2023.
- Dominant Market Segment (2023): Residential (44.1%) market share in 2023.
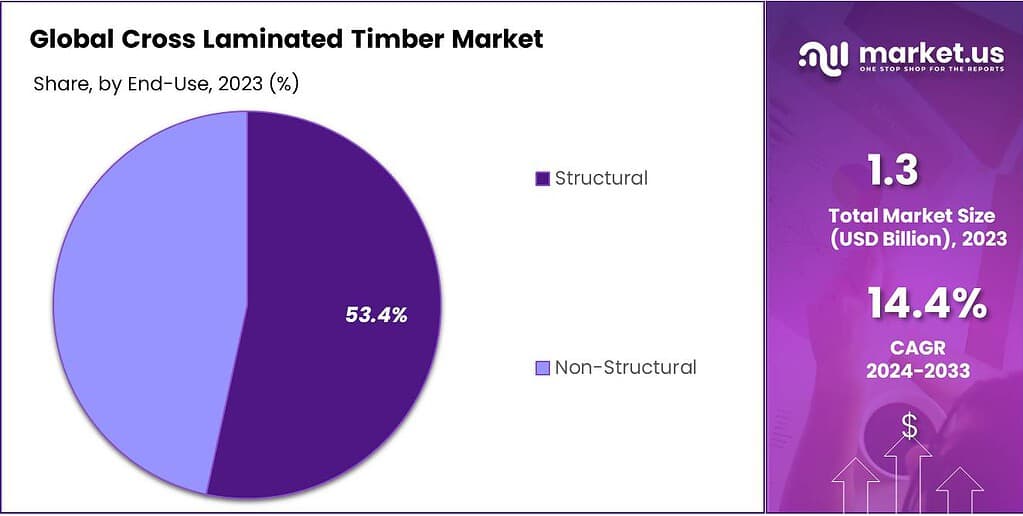
- Structural CLT Market Share (2023): 53.4% market share in 2023.
- Application Dominance: The residential sector leads with a 44.1% market share in 2023.
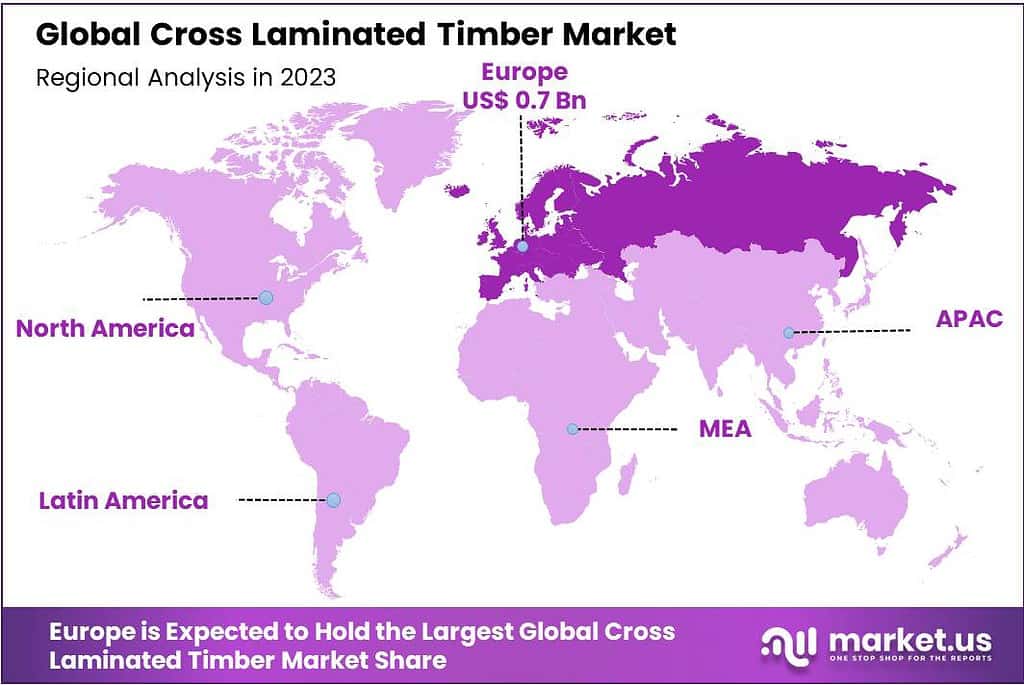
- Europe is set to maintain its leading position in projected to capture a substantial market share of 54.7% by 2023.
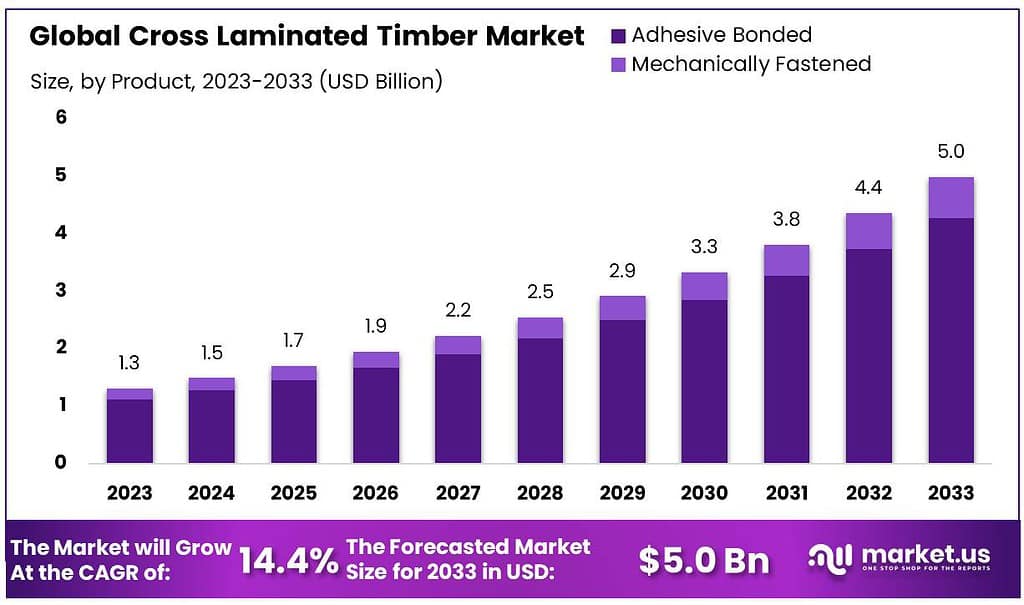
By Product
Adhesive Bonded CLT: In 2023, Adhesive CLT held a dominant market position, capturing more than an 85.6% share. This segment’s dominance is attributed to its widespread use in the construction industry due to its superior bonding strength and stability. Adhesive bonded CLT panels are favored for their uniformity and enhanced load-bearing capacity.
These characteristics make them ideal for a wide range of applications, including residential and commercial buildings. The ease of manufacturing and the ability to produce large panels efficiently contribute to the segment’s significant market share. Additionally, advancements in adhesive technologies have improved the durability and environmental performance of these panels, further boosting their market acceptance.
Mechanically Fastened CLT: Mechanically Fastened CLT, while less dominant, is gaining traction, particularly in regions with stringent environmental regulations. This segment is preferred for its minimal use of synthetic adhesives, making it an eco-friendly option. Mechanically fastened panels are typically joined using metal fasteners, screws, or nails, which can be advantageous in applications requiring disassembly or recycling.
This method offers flexibility in design and construction, catering to specific architectural needs. Although it currently holds a smaller market share, increasing awareness of sustainable building practices and the growing demand for recyclable materials are expected to drive growth in this segment. The market for mechanically fastened CLT is poised to expand as innovations in fastening techniques and materials continue to evolve.
By Application
Residential: In 2023, the Residential sector held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 44.1% share. This leadership is driven by the rising demand for sustainable and energy-efficient housing solutions. CLT is increasingly popular in residential construction due to its excellent insulation properties and quick installation.
Homebuilders favor CLT for its ability to reduce construction time and costs while providing a strong, durable structure. The aesthetic appeal of exposed timber surfaces also adds to its attractiveness for residential projects, enhancing the market growth in this segment.
Institutional: The Institutional segment accounted for a significant portion of the CLT market, driven by the construction of schools, hospitals, and government buildings. Institutions prefer CLT for its fire resistance, acoustic performance, and environmental benefits.
The use of CLT in this segment is supported by increasing investments in sustainable public infrastructure. Its ability to create large, open spaces without internal supports makes it ideal for educational and healthcare facilities. This segment is expected to grow as more institutions adopt green building practices.
Commercial: The Commercial sector, including office buildings, retail spaces, and hotels, is rapidly adopting CLT. This segment benefits from CLT’s ability to meet aesthetic and structural requirements while reducing construction times.
Commercial developers are drawn to CLT for its strength, versatility, and environmental credentials. The trend towards sustainable and eco-friendly commercial spaces is a key driver for this segment. As awareness of CLT’s benefits grows, its use in commercial construction is expected to increase, contributing to market expansion.
By End-Use
Structural: In 2023, Structural applications held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 53.4% share. This segment’s dominance is due to CLT’s strength and versatility, making it ideal for load-bearing walls, floors, and roofs. Builders and architects prefer CLT for its ability to support large spans and heavy loads, which is crucial for structural components.
The growing trend towards sustainable construction has also boosted its use in structural applications, as CLT offers both environmental benefits and structural integrity. Its ease of installation and efficiency in reducing construction time further enhance its appeal in this segment.
Non-Structural: Non-structural applications of CLT, though smaller in market share, are gaining momentum. This segment includes interior walls, partitions, and decorative elements. CLT’s aesthetic appeal and acoustic properties make it popular for creating visually pleasing and functional spaces. The flexibility of CLT in design and its lightweight nature are key factors driving its use in non-structural applications.
As the demand for sustainable and eco-friendly building materials increases, the non-structural segment is expected to grow, leveraging CLT’s versatility and environmental benefits. This segment’s expansion is supported by innovations in design and a growing focus on sustainable interior solutions.
Market Key Segments
By Product
- Adhesive Bonded
- Mechanically Fastened
By Application
- Residential
- Institutional
- Commercial
- Others
By End-Use
- Structural
- Non-Structural
Drivers
Sustainability and Environmental Benefits Driving the Cross-Laminated Timber Market
One of the major drivers of the Cross Laminated Timber (CLT) market is its sustainability and environmental benefits. In an era where environmental consciousness is increasingly influencing construction practices, CLT stands out as a beacon of sustainable development. This innovative material is derived from renewable resources, primarily fast-growing softwoods, which are harvested and replanted in managed forests, ensuring a continuous supply without depleting natural reserves.
The ability of CLT to act as a carbon sink is particularly significant. During the growth phase, trees absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it in their biomass. When these trees are harvested and processed into CLT, the carbon remains sequestered in the timber, effectively reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This characteristic aligns with global efforts to combat climate change and reduce carbon footprints, making CLT an attractive option for eco-conscious builders and developers.
Moreover, the production process of CLT is relatively low in energy consumption compared to traditional building materials like steel and concrete. The manufacturing of concrete and steel is highly energy-intensive, contributing significantly to global carbon emissions. In contrast, the production of CLT involves sawing, drying, and gluing timber, processes that require considerably less energy and result in lower carbon emissions. This energy efficiency not only reduces the overall environmental impact but also enhances the appeal of CLT as a cost-effective and sustainable building material.
The sustainable attributes of CLT extend beyond its production and carbon sequestration capabilities. CLT panels offer excellent thermal insulation properties, which contribute to energy efficiency in buildings. The natural insulating qualities of wood help maintain stable indoor temperatures, reducing the need for heating and cooling systems and, consequently, lowering energy consumption. This energy efficiency translates into cost savings for building owners and operators, further bolstering the attractiveness of CLT in the construction industry.
Additionally, the use of CLT can significantly reduce construction waste. Traditional construction methods often involve substantial on-site cutting and shaping of materials, leading to considerable waste. In contrast, CLT panels are prefabricated to precise specifications in a controlled factory environment, minimizing waste and ensuring efficient use of resources. The reduction in construction waste not only lowers disposal costs but also lessens the environmental impact associated with landfill use.
Another compelling aspect of CLT’s sustainability is its role in promoting healthier indoor environments. Wood is a natural material that does not emit harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs), unlike some synthetic building materials. The use of CLT can improve indoor air quality, contributing to healthier living and working conditions.
This benefit is particularly relevant in the context of green building certifications, such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method), which prioritize indoor environmental quality and sustainability. The aesthetic appeal of CLT also plays a role in its market growth, supporting biophilic design principles that integrate natural elements into built environments.
The warm, natural appearance of exposed timber can create visually appealing and psychologically beneficial spaces, enhancing occupants’ well-being and connection to nature. This aesthetic quality, combined with the environmental benefits, makes CLT a preferred choice for designers and architects aiming to create sustainable and pleasant living and working spaces.
Restraints
High Initial Costs as a Major Restraint for the Cross-Laminated Timber Market
One of the significant restraints impacting the Cross Laminated Timber (CLT) market is the high initial costs associated with its use. While CLT offers numerous benefits, including sustainability, efficiency, and design flexibility, the upfront investment required for CLT construction can be considerably higher than traditional building materials such as concrete and steel. This cost factor is a critical consideration for builders, developers, and stakeholders in the construction industry, potentially limiting the widespread adoption of CLT despite its advantages.
The high initial costs of CLT are primarily driven by several factors, including material costs, manufacturing processes, and the need for specialized expertise. The raw materials used in CLT, typically high-quality softwood timber, must meet stringent standards to ensure the structural integrity and performance of the final product. This requirement for high-grade timber can lead to increased material costs compared to other construction materials that do not require such specific quality standards.
Additionally, the manufacturing process for CLT involves sophisticated machinery and technology to ensure precise cutting, layering, and bonding of the timber boards. The investment in advanced equipment and technology adds to the overall production costs, making CLT panels more expensive to produce. Furthermore, the manufacturing facilities for CLT are often less widespread than those for traditional materials, leading to higher logistics and transportation costs, especially for projects located far from production sites.
The need for specialized expertise in designing and constructing with CLT also contributes to the high initial costs. Architects, engineers, and builders must be trained in the unique properties and handling requirements of CLT to effectively integrate it into building designs and construction processes. This specialized knowledge and training can increase project costs, as it may involve additional time, resources, and consultation fees. The relative novelty of CLT in some regions also means that there may be fewer experienced professionals available, further driving up costs due to the need for specialized skills and expertise.
Moreover, the high initial costs of CLT can be exacerbated by regulatory and approval processes. Building codes and regulations related to the use of CLT can vary significantly across different regions and countries. In areas where CLT is not yet widely recognized or where specific codes and standards for CLT are not well established, obtaining approvals and permits can be a complex and costly process. Developers may need to invest additional time and resources to navigate these regulatory hurdles, further increasing the overall cost of CLT projects.
The higher initial investment required for CLT can also impact the financial planning and budgeting for construction projects. Developers and builders may need to secure more substantial financing or allocate larger budgets upfront, which can be challenging, especially for smaller firms or projects with tight financial constraints. The higher upfront costs can also impact the perceived return on investment (ROI) for CLT projects, making it a less attractive option for some developers who may prioritize cost-efficiency and quicker financial returns.
Despite these cost challenges, it is essential to consider the long-term benefits and potential cost savings associated with CLT. While the initial investment may be higher, CLT can offer significant advantages in terms of construction speed, energy efficiency, and reduced maintenance costs over the building’s lifecycle. The prefabrication and ease of assembly of CLT panels can lead to shorter construction times, reducing labor costs and minimizing project delays. Additionally, the excellent thermal insulation properties of CLT can result in lower energy costs for heating and cooling, providing ongoing savings for building owners and operators.
Opportunity
Rising Demand for Sustainable and Green Buildings as a Major Opportunity for the Cross Laminated Timber Market
The rising demand for sustainable and green buildings presents a significant opportunity for the Cross Laminated Timber (CLT) market. As global awareness of environmental issues and climate change intensifies, there is a growing emphasis on reducing the carbon footprint of buildings and adopting eco-friendly construction practices. This trend is driving the adoption of CLT, which is renowned for its sustainability credentials and environmental benefits, positioning it as a key material in the future of green building initiatives.
One of the primary factors contributing to this opportunity is the increasing implementation of green building standards and certifications, such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design), BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method), and others. These standards encourage the use of sustainable materials and construction practices that reduce energy consumption, minimize waste, and enhance the overall environmental performance of buildings.
CLT, being a renewable resource with excellent thermal insulation properties, aligns perfectly with these criteria. Its use in construction can significantly contribute to achieving higher green building ratings, making it an attractive choice for developers and builders aiming to meet stringent environmental standards.
Furthermore, the push for net-zero carbon buildings is gaining momentum worldwide. Governments, corporations, and environmental organizations are increasingly setting ambitious targets to achieve net-zero carbon emissions in the building sector by specific deadlines, often around 2050. CLT’s ability to sequester carbon during the growth phase of the trees and its relatively low embodied energy compared to traditional construction materials like concrete and steel make it an ideal candidate for net-zero carbon building projects. By incorporating CLT into building designs, developers can significantly reduce the overall carbon footprint of their projects, helping them to meet these critical environmental targets.
The construction industry’s shift towards circular economy principles also underscores the opportunity for CLT. The circular economy focuses on designing out waste and pollution, keeping products and materials in use, and regenerating natural systems. CLT’s prefabrication process minimizes construction waste, and its durability and adaptability make it suitable for reuse and recycling at the end of a building’s lifecycle. These attributes align with the principles of the circular economy, making CLT a valuable component in sustainable construction strategies aimed at reducing waste and promoting resource efficiency.
Another aspect driving the opportunity for CLT is the increasing consumer and corporate demand for sustainable and eco-friendly buildings. As environmental awareness grows, consumers are becoming more conscious of the environmental impact of the buildings they live and work in. This shift in consumer preferences is influencing real estate developers and corporations to prioritize sustainable construction methods and materials. Buildings constructed with CLT not only meet these sustainability demands but also offer aesthetic appeal and a connection to nature, enhancing their marketability and appeal to environmentally conscious buyers and tenants.
Additionally, the trend towards urbanization and the need for efficient, sustainable housing solutions in densely populated areas provide a substantial opportunity for CLT. Urban areas are increasingly seeking construction methods that offer speed, efficiency, and minimal environmental impact. CLT’s prefabricated nature allows for rapid construction and reduced on-site labor, making it well-suited for urban projects where time and space are often limited. Its lightweight properties also make it ideal for vertical extensions and infill projects, addressing the challenges of space constraints in urban environments.
Technological advancements and innovations in CLT production and construction techniques further enhance this opportunity. Advances in digital design tools, automation, and prefabrication technologies are making CLT more accessible and cost-effective, broadening its application range and appeal. These innovations are reducing production costs, improving efficiency, and enabling more complex and customized designs, thereby expanding the potential use cases for CLT in various building types and sectors.
Trends
Integration of Digital Design and Prefabrication Technologies as a Major Trend in the Cross Laminated Timber Market
A significant trend shaping the Cross Laminated Timber (CLT) market is the integration of digital design and prefabrication technologies. This trend is revolutionizing the construction industry by enhancing the efficiency, precision, and scalability of CLT-based projects. The synergy between advanced digital tools and prefabrication techniques is propelling CLT to the forefront of modern construction practices, offering substantial benefits in terms of speed, cost-effectiveness, and design flexibility.
Digital design technologies, including Building Information Modeling (BIM), 3D modeling, and computer-aided design (CAD), are transforming the way CLT structures are conceptualized and executed. BIM, in particular, plays a crucial role in the CLT market by providing a comprehensive digital representation of a building’s physical and functional characteristics.
This technology facilitates detailed planning, visualization, and simulation of CLT projects, enabling architects and engineers to optimize designs, detect potential issues early, and enhance coordination among various stakeholders. By integrating BIM with CLT construction, project teams can achieve greater accuracy in material estimation, reduce waste, and streamline the construction process.
The adoption of 3D modeling and CAD software further complements the use of CLT by enabling precise design and customization of timber panels. These tools allow for the creation of complex geometries and intricate architectural details that are difficult to achieve with traditional construction methods. The ability to digitally model and adjust designs in real time enhances the flexibility and creativity of CLT projects, making it possible to produce bespoke solutions tailored to specific architectural visions and client requirements. This level of customization is particularly valuable in high-end residential, commercial, and institutional projects, where unique design elements can significantly enhance the aesthetic and functional appeal of the building.
Prefabrication technologies are also playing a pivotal role in advancing the CLT market. The prefabrication process involves manufacturing CLT panels in a controlled factory environment, where they are precisely cut, assembled, and treated before being transported to the construction site. This method offers several advantages, including improved quality control, reduced construction time, and minimized on-site labor. The controlled factory setting ensures that CLT panels are produced to exact specifications, enhancing their structural integrity and performance. Additionally, the prefabrication process reduces the risk of weather-related delays and site disruptions, contributing to more predictable project timelines and costs.
The integration of digital design and prefabrication technologies is particularly advantageous in addressing the challenges of urban construction. In densely populated urban areas, construction projects often face constraints related to space, noise, and disruption. The use of prefabricated CLT panels mitigates these challenges by allowing for rapid assembly and installation on-site, significantly reducing construction noise and minimizing the impact on surrounding communities. This efficiency is critical in urban settings where minimizing disruption is a key consideration for developers and city planners.
Moreover, the combination of digital design and prefabrication enhances the sustainability credentials of CLT projects. The precision and efficiency of these technologies contribute to a reduction in material waste, lower energy consumption during production, and decreased transportation emissions due to fewer deliveries and shorter construction times. These sustainability benefits align with the growing emphasis on eco-friendly building practices and contribute to the overall appeal of CLT as a green construction material.
The trend towards integrating digital design and prefabrication technologies is also fostering innovation in the CLT market. Advances in automation, robotics, and smart manufacturing are further enhancing the capabilities of prefabrication processes, enabling the production of more complex and large-scale CLT structures. For example, robotic cutting and assembly systems can achieve higher precision and speed, while smart manufacturing technologies can optimize production workflows and resource utilization. These innovations are expanding the potential applications of CLT and driving its adoption across a wider range of building types and sectors.
Regional Analysis
Europe is set to maintain its leading position in the global Cross Laminated Timber (CLT) market, projected to capture a substantial market share of 54.7% by 2023. This dominance is attributed to Europe’s proactive implementation of stringent environmental regulations and its strong commitment to sustainable building practices.
European governments have been instrumental in promoting initiatives aimed at reducing carbon emissions and enhancing energy efficiency across various sectors, including construction. These initiatives serve as a model for international standards, highlighting the crucial role of CLT in achieving ambitious environmental goals. Regulatory support from European authorities has significantly increased the demand for CLT solutions, positioning them as essential components in Europe’s strategy to address emissions across industries.
The integration of CLT in European markets exemplifies a balanced approach, preserving the region’s rich architectural heritage while embracing innovative sustainable solutions. This strategy ensures that construction projects can thrive while simultaneously reducing their carbon footprint, underscoring the versatility and critical importance of CLT technologies in modern building systems.
Moreover, Europe’s dedication to sustainability has spurred significant advancements in research and development within the CLT sector. These advancements have resulted in the development of more efficient, durable, and eco-friendly CLT solutions, reinforcing Europe’s leadership in promoting greener construction alternatives globally. The region’s pioneering efforts not only enhance the performance of CLT technologies but also establish Europe as a leading innovator and a global benchmark for best practices in the industry.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- The US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia & CIS
- Rest of Europe
- APAC
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- ASEAN
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
The Cross Laminated Timber (CLT) market is characterized by the presence of several key players who are driving innovation, production, and market expansion. Prominent companies such as Stora Enso, Binderholz, KLH Massivholz, Mayr-Melnhof Holz, and HASSLACHER Group are at the forefront of the industry. These companies have established themselves as leaders through their extensive experience, robust production capabilities, and commitment to sustainability.
Market Key Players
- Stora Enso Oyj
- Mayr-Melnhof Holz Holding AG
- Binderholz GmbH
- XLam
- Sterling Company
- Schilliger Holz AG
- KLH Massivholz GmbH
- B&K Structures
- Eugen Decker & WebMan
- Structurlam Mass Timber Corporation
- SmartLam NA
- MEIKEN LAMWOOD Corp
Recent Developments
January 2023, Stora Enso reported that the new Ždírec site had successfully ramped up production, meeting the growing demand for sustainable building materials in Europe
January 2023, the plant had ramped up its production capabilities, with an annual capacity of approximately 140,000 cubic meters of CLT. This expansion aligns with Mayr-Melnhof Holz’s strategic focus on sustainability and innovation, positioning the company as a leading player in the CLT market.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2022) USD 1.3 Bn Forecast Revenue (2032) USD 5 Bn CAGR (2023-2032) 14.4% Base Year for Estimation 2022 Historic Period 2017-2022 Forecast Period 2023-2032 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, COVID-19 Impact, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Product(Adhesive Bonded, Mechanically Fastened), By Application(Residential, Institutional, Commercial, Others), By End-Use(Structural, Non-Structural) Regional Analysis North America – The US & Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia & CIS, Rest of Europe; APAC- China, Japan, South Korea, India, ASEAN & Rest of APAC; Latin America- Brazil, Mexico & Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa- GCC, South Africa, &Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Stora Enso Oyj, Mayr-Melnhof Holz Holding AG, Binderholz GmbH, XLam, Sterling Company, Schilliger Holz AG, KLH Massivholz GmbH, B&K Structures, Eugen Decker & WebMan, Structurlam Mass Timber Corporation, SmartLam NA, MEIKEN LAMWOOD Corp Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the Size of Cross Laminated Timber Market?Cross Laminated Timber Market size is expected to be worth around USD 5.0 billion by 2033, from USD 1.3 billion in 2023
What CAGR is projected for the Cross Laminated Timber Market?The Cross Laminated Timber Market is expected to grow at 14.4% CAGR (2023-2033).Name the major industry players in the Cross Laminated Timber Market?Stora Enso Oyj, Mayr-Melnhof Holz Holding AG, Binderholz GmbH, XLam, Sterling Company, Schilliger Holz AG, KLH Massivholz GmbH, B&K Structures, Eugen Decker & WebMan, Structurlam Mass Timber Corporation, SmartLam NA, MEIKEN LAMWOOD Corp
 Cross Laminated Timber MarketPublished date: May 2024add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Cross Laminated Timber MarketPublished date: May 2024add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Stora Enso Oyj
- Mayr-Melnhof Holz Holding AG
- Binderholz GmbH
- XLam
- Sterling Company
- Schilliger Holz AG
- KLH Massivholz GmbH
- B&K Structures
- Eugen Decker & WebMan
- Structurlam Mass Timber Corporation
- SmartLam NA
- MEIKEN LAMWOOD Corp









