Global Cellular Confinement System Market Size, Share, Growth Analysis By Material (High-Density Polyethylene, Polypropylene, Polyester, Others), By Application (Load Support, Channel And Slope Protection, Green Roofs And Vegetation Growth, Retention of Walls, Others), By End User (Construction And Infrastructure, Mining And Energy, Military And Defense, Water Management, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Nov 2025
- Report ID: 167574
- Number of Pages: 247
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
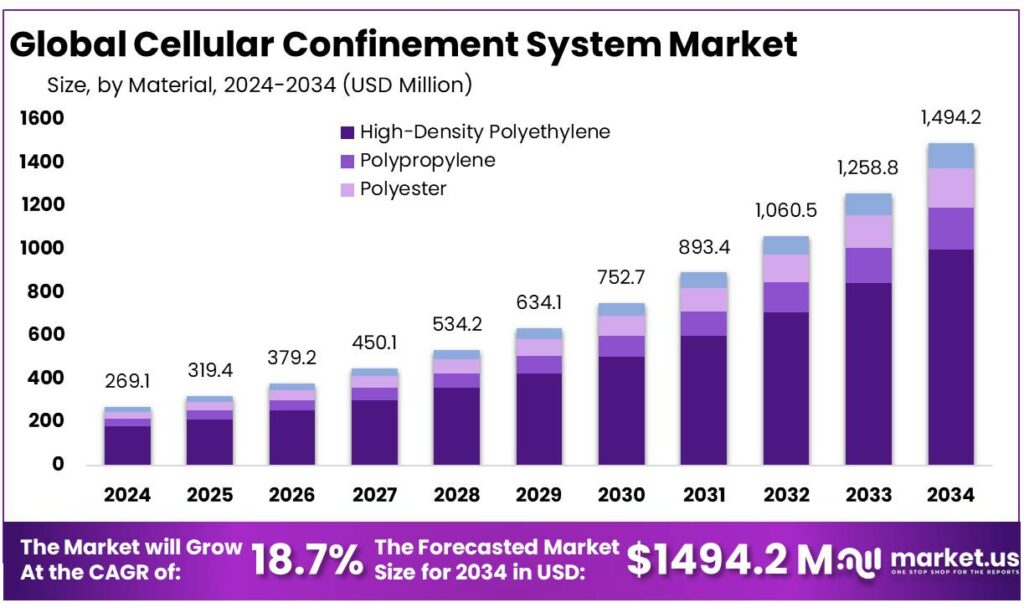
The Global Cellular Confinement System Market size is expected to be worth around USD 1494.2 Million by 2034, from USD 269.1 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 18.7% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North America held a dominan market position, capturing more than a 42.9% share, holding USD 456.7 Million revenue.
Cellular confinement systems (CCS), or geocells, are three-dimensional honeycomb structures, typically made from HDPE or advanced polymer alloys, that confine granular or soil infill to improve load-bearing capacity, control erosion, and stabilize slopes and embankments. Originally developed for military load-support applications, they are now widely used in roads, railways, ports, pipelines, mining and urban landscaping, where they allow thinner pavement structures and the use of marginal or recycled infill.
From an industrial perspective, CCS sit at the intersection of geotechnical engineering and sustainable infrastructure. Global infrastructure investment needs are estimated at about USD 94 trillion between 2016 and 2040 just to keep pace with economic and demographic change, underlining the magnitude of ground-improvement demand where CCS can play a role. Other analyses point to infrastructure requirements rising to roughly USD 106 trillion by 2040, reinforcing the scale of long-term opportunity across transport, energy and water projects.
Transport expansion is a direct volume driver. The United States alone operates nearly 6.6 million kilometres of roads, the largest network in the world, and emerging economies are rapidly building new corridors to close connectivity gaps. As road and rail projects push into soft soils, coastal zones and hilly terrain, CCS offer a lighter, faster and often lower-carbon alternative to traditional crushed-stone and reinforced concrete sections, while maintaining performance and service life.
Energy-transition investments create another strong demand vector. The International Energy Agency (IEA) reports that renewable capacity additions grew by about 50% in 2023, reaching almost 510 GW, with solar PV contributing roughly three-quarters of new capacity. Under existing policies, global renewable capacity is forecast to reach around 7,300 GW by 2028, significantly above today’s installed base, driving a wave of new solar parks, wind farms and associated grid infrastructure that require access roads, crane pads, embankments and drainage, all attractive applications for CCS.
Government initiatives in large emerging markets further support CCS adoption. India’s Ministry of New and Renewable Energy expects non-fossil power capacity to reach about 300 GW, with more than 40 GW of additional projects in advanced stages, implying extensive civil works for foundations, internal roads and transmission corridors where geocells can reduce material use. Separately, the World Bank estimates that India will need around USD 2.4 trillion in urban infrastructure investment by 2050, highlighting enormous potential for cost-effective ground stabilization in metros, BRT systems, urban roads and storm-water channels.
Key Takeaways
- Cellular Confinement System Market size is expected to be worth around USD 1494.2 Million by 2034, from USD 269.1 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 18.7%.
- High-Density Polyethylene held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 67.2% share.
- Centralized held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 45.8% share of the Cellular Confinement System market.
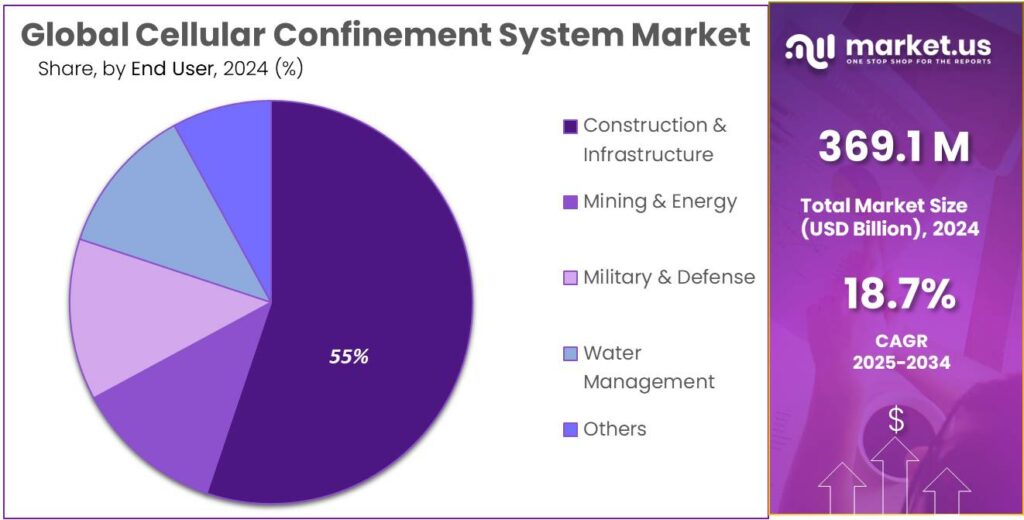
- Construction & Infrastructure held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 55.4% share of the Cellular Confinement System market.
By Material Analysis
High-Density Polyethylene dominates with a 67.2% share owing to its durability and cost-effectiveness.
In 2024, High-Density Polyethylene held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 67.2% share of the Cellular Confinement System market by material; this leadership was supported by HDPE’s proven tensile strength, resistance to chemical and UV degradation, and low life-cycle maintenance requirements, which made it the preferred choice for road subgrade reinforcement, slope protection and channel lining.
Adoption was further facilitated by the material’s ease of installation—panels could be rapidly expanded and infilled on site—resulting in shorter project schedules and lower installation labour costs compared with alternative materials. Performance advantages were complemented by growing specification in public works and infrastructure tender documents, where long-term durability and predictable engineering behaviour were prioritized.
By Application Analysis
Load Support dominates with 45.8% due to its proven ability to boost bearing capacity and extend pavement life.
In 2024, Centralized held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 45.8% share of the Cellular Confinement System market by application for load support, and this leadership was underpinned by the material’s capacity to distribute wheel loads, reduce rutting, and lower subgrade settlement in both new-build and rehabilitation projects. Specification was driven by project owners and designers who prioritized long-term performance and lower whole-life costs; as a result, CCS solutions were increasingly selected for heavy-traffic roadways, rail approach slabs and temporary construction access where improved load-bearing performance was required.
Installation efficiencies were noted in contracts where rapid on-site expansion and infill procedures reduced schedule risk, and engineering teams reported predictable structural behaviour that simplified design checks and reduced contingency allowances.
By End User Analysis
Construction & Infrastructure leads with 55.4% as large-scale projects continue to adopt CCS for stability and long-term durability.
In 2024, Construction & Infrastructure held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 55.4% share of the Cellular Confinement System market by end user, and this strong lead was supported by the growing use of CCS in highways, embankments, retaining structures and public works where improved soil stability and erosion resistance were required. The segment benefited from steady government investment in transport networks, urban expansion and flood-protection works, where CCS offered predictable engineering performance and reduced material consumption compared with traditional reinforcement techniques.
Contractors and design firms continued to favour these systems because they helped stabilize weak subgrades, lower maintenance costs and extend pavement life, making them suitable for both new-build and rehabilitation projects.
Key Market Segments
By Material
- High-Density Polyethylene
- Polypropylene
- Polyester
- Others
By Application
- Load Support
- Channel & Slope Protection
- Green Roofs & Vegetation Growth
- Retention of Walls
- Others
By End User
- Construction & Infrastructure
- Mining & Energy
- Military & Defense
- Water Management
- Others
Emerging Trends
Nature-Based, Food-System-Friendly Design Is Redefining Cellular Confinement Systems
A clear new trend in cellular confinement systems (CCS) is how engineers now use them as part of wider, nature-based solutions for farms, irrigation and food logistics, rather than only as “road technology.” The focus is shifting from pure load-bearing to protecting soil, managing water gently and fitting into climate-resilient food systems that governments and donors are trying hard to build.
Water stress is one reason this trend is gaining speed. UNESCO’s 2024 World Water Development Report notes that agriculture already accounts for roughly 70% of global freshwater withdrawals, leaving less than 30% for industry and households. FAO adds that in the last 30 years food production has more than doubled, while agriculture still uses about 70% of withdrawals. This combination of higher output and tight water budgets is pushing planners toward solutions that stabilise canals, on-farm reservoirs and drainage lines with minimal concrete. CCS, filled with local soil or gravel and often vegetated, fits that requirement.
Food loss numbers add another layer to this trend. FAO’s State of Food and Agriculture 2019 shows around 14% of the world’s food is lost after harvest and before retail, worth about USD 400 billion each year. A large part of this happens because roads flood, storage yards get muddy, or drainage fails during storms. Designers are therefore using CCS not only on highways but around packing sheds, cold stores and collection centres to keep surfaces firm and well-drained, which directly supports national food-loss reduction strategies.
Land degradation and restoration targets are also steering CCS toward food-linked, nature-based applications. UN desertification briefings warn that as much as 1.5 billion hectares of land may need to be restored by 2030 to achieve a land-degradation-neutral world, and that a “trillion-dollar land restoration economy” is emerging. A G20-backed assessment estimates that restoring over 1 billion hectares could generate USD 1.5–2.0 trillion in economic value. In this context, CCS are increasingly specified for terraces, check dams, field access roads and gullies, because they stabilise earthworks while allowing vegetation to come back.
Drivers
Protecting Farmland and Food Supply Drives Cellular Confinement System Demand
One of the strongest forces behind the growing use of cellular confinement systems (CCS) is the urgent need to protect farmland and food-supply infrastructure as land degradation worsens. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) estimates that human-induced soil degradation now affects about 34% of agricultural land, equal to 1.66 billion hectares, while over 95% of our food still comes from land-based production. In this context, CCS become a practical tool to stabilise slopes, farm tracks, irrigation channels and storage yards, reducing erosion and keeping land productive.
Food demand trends make this structural risk even more pressing. FAO projections indicate that feeding the world in 2050 will require raising global food production by about 60–70% compared with the mid-2000s. Meeting that growth while losing fertile land to erosion, salinity and compaction is not realistic. Infrastructure that protects topsoil, stabilises embankments and keeps rural roads passable in wet seasons becomes strategically important. CCS allows the use of local or recycled infill while maintaining bearing capacity, which is attractive for low-budget agricultural and food-logistics projects.
Rural livelihoods add another layer to this driver. The World Bank notes that agriculture can help improve incomes and food security for about 80% of the world’s poor, who live mainly in rural areas and work in farming. In India, government data show that roughly 65% of the population lives in rural areas and 47% depends on agriculture for livelihood. For such countries, any disruption to farm access roads, small irrigation dams or grain-storage yards can quickly translate into food and income losses. CCS improves the durability of these assets without requiring thick concrete slabs, aligning with rural development and cost-control priorities.
Government and multilateral initiatives on land restoration also support CCS adoption. At the UN Convention to Combat Desertification’s COP16, countries reaffirmed a global target to restore 1 billion hectares of degraded land by 2030, including about 250 million hectares of agricultural land, with more than USD 12 billion pledged for drought and land-degradation resilience and USD 282 million committed by the Global Environment Facility to a food-systems programme.
Restraints
Limited Finance for Rural Food Infrastructure Holds Back Cellular Confinement Systems
A big brake on wider use of cellular confinement systems (CCS) is money. CCS work very well for stabilising farm roads, irrigation banks and storage yards, but most of the people who would benefit the most – small farmers and rural communities – work with very tight budgets. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) estimates there are more than 608 million family farms worldwide, managing around 70–80% of global farmland and producing roughly 80% of food by value.
FAO and World Bank data show how fragmented and cash-constrained this base really is. Detailed research finds that about 84% of the world’s 570 million farms are smaller than 2 hectares, and these smallholdings work only around 12% of all agricultural land while producing roughly 35% of the world’s food. Many of these farmers are also among the poorest people globally, which means they tend to patch up earth tracks and canals with local labour rather than invest in engineered CCS layers, geotextiles or professional installation.
The climate-finance gap makes things harder. A 2024 report from Climate Policy Initiative estimates that agrifood systems need about USD 1.1 trillion in climate-related finance every year, while current plans in countries’ climate pledges add up to only about USD 201.5 billion a year – a gap of almost USD 1 trillion. The UN Environment Programme also warns that developing countries will need USD 310–365 billion annually for climate adaptation by the mid-2030s, but public adaptation finance in 2023 was only around USD 26 billion, just 12–14% of what is required.
Opportunity
Climate-Resilient Food and Water Infrastructure Creates Big Openings for Cellular Confinement Systems
One of the clearest growth opportunities for cellular confinement systems (CCS) lies in building climate-resilient infrastructure that keeps food systems running—from field to market. As global demand for food rises and land and water pressures intensify, countries need smarter ways to stabilize farm roads, canals, storage yards and agro-logistics hubs. CCS, with its lightweight honeycomb structure and ability to use local infill, fits naturally into this new generation of low-impact rural and peri-urban infrastructure.
Food demand alone sets a powerful backdrop. FAO’s long-term outlook suggests that feeding about 9.1 billion people in 2050 will require raising overall food production by roughly 70% compared with 2005/07 levels. A separate meta-analysis in Nature Food finds global food demand could increase by 35–56% between 2010 and 2050. Meeting this extra demand requires not only better seeds and practices but also reliable physical infrastructure that allows farmers to move inputs and crops in all seasons—an area where CCS can add real value.
Land restoration targets open another door. The UN Convention to Combat Desertification notes that countries have pledged to restore about 1 billion hectares of degraded land by 2030, including around 250 million hectares of farmland The wider climate agenda talks about restoring up to 1.5 billion hectares and building a “trillion-dollar land restoration economy” by 2030. These hectares will need terraces, check dams, feeder roads, spillways and drainage channels. CCS offers an opportunity to deliver these structures quickly with less concrete, while allowing vegetation to take root.
Rural access is another large, under-served space. A World Bank update on the Rural Access Index estimates that about 73% of the global population lives within 2 km of an all-season road, leaving hundreds of millions still poorly connected. For food systems, missing or low-quality roads mean higher transport costs and more losses. CCS allows engineers to upgrade earth tracks into all-weather farm-to-market roads using thinner granular layers and local soils, which can be critical where budgets are tight.
Regional Insights
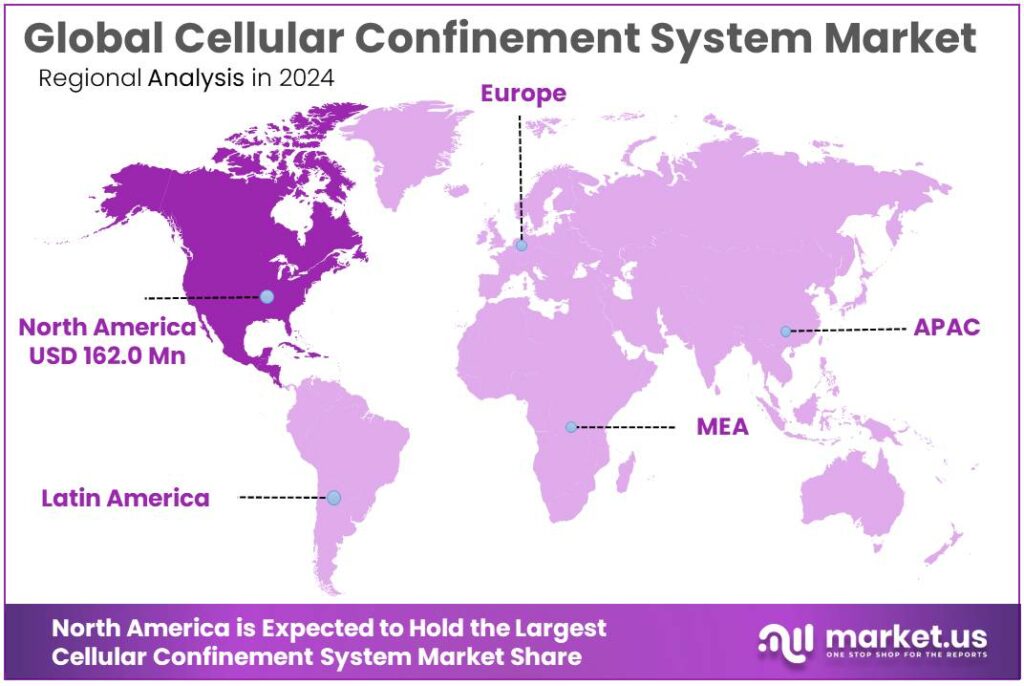
North America Leads the Cellular Confinement System Market with a 43.90% Share Worth USD 162.0 Million
In 2024, North America held a dominant position in the Cellular Confinement System (CCS) market, capturing around 43.90% share, valued at roughly USD 162.0 million, supported by its large infrastructure base and strong focus on sustainable construction. The United States alone operates about 6.6 million km of roads, the largest road network globally, creating continuous demand for geotechnical solutions to reinforce pavements, slopes, and drainage structures.
Regional governments are also ramping up climate-resilient infrastructure spending; for example, the U.S. Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act earmarks over USD 110 billion for roads, bridges, and major projects, encouraging the use of advanced stabilization systems such as geocells to extend asset life and reduce maintenance. At the same time, Canada’s Investing in Canada infrastructure plan targets more than CAD 180 billion over 12 years across public transit, green infrastructure, and trade-supporting corridors, further widening the addressable base for CCS in roadbeds, rail lines, ports, and energy corridors.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Strata Systems is recognized for engineered geogrid and cellular confinement solutions widely used in reinforced earth structures, slope stabilization, and pavement applications. The company focuses on performance-based designs, offering geocell technology optimized for load distribution and long-term soil confinement. With a strong presence across transportation, mining, and commercial infrastructure sectors, Strata integrates engineering support, testing, and customization. Its collaborations with installers and government agencies support expanding adoption of sustainable and cost-efficient ground-reinforcement systems in complex soil environments.
PRS Geo-Technologies is known for its Neoloy®-based geocell systems engineered to improve resilience, durability, and load-bearing strength in challenging ground conditions. The company focuses on innovation driven by polymer science and field validation, positioning its solutions for applications such as roads, embankments, container yards, and military infrastructure. With an international footprint and strong technical engagement, PRS emphasizes lifecycle value, sustainability benefits, and long-term performance compared to conventional stabilization materials like granular layers or reinforced concrete.
Presto Geosystems is a key provider of geocell products for soil stabilization, stormwater management, and erosion control across commercial, public, and environmental projects. The company leverages decades of experience supporting engineers with design tools, case studies, and project support. Presto’s solutions are used in infrastructure, energy, and environmental remediation sectors to enhance ground performance, protect slopes, and extend pavement life. The company also emphasizes environmentally conscious designs, enabling vegetation growth and reduced material consumption in civil construction workflows.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Strata Systems
- PRS Geo-Technologies
- Presto Geosystems
- Terram Geosynthesis
- BOSTD Geosynthesis Qingdao
- GEO Products, LLC.
- Huifeng Geosynthesis
- SABK International
- Admir Technologies
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024, Strata Systems: StrataWeb® geocell was widely specified for load support, slope protection and channel lining owing to its textured HDPE construction and proven field performance; product variants with cell depths of 75, 100, 150, and 200 mm were routinely used to match engineering requirements.
In 2024 Presto Geosystems: published specification was copyrighted to Reynolds Presto Products, Inc. (© 2024), confirming current product standards and material properties for design teams.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 269.1 Mn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 1494.2 Mn CAGR (2025-2034) 18.7% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Material (High-Density Polyethylene, Polypropylene, Polyester, Others), By Application (Load Support, Channel And Slope Protection, Green Roofs And Vegetation Growth, Retention of Walls, Others), By End User (Construction And Infrastructure, Mining And Energy, Military And Defense, Water Management, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Strata Systems, PRS Geo-Technologies, Presto Geosystems, Terram Geosynthesis, BOSTD Geosynthesis Qingdao, GEO Products, LLC., Huifeng Geosynthesis, SABK International, Admir Technologies Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Cellular Confinement System MarketPublished date: Nov 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Cellular Confinement System MarketPublished date: Nov 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Strata Systems
- PRS Geo-Technologies
- Presto Geosystems
- Terram Geosynthesis
- BOSTD Geosynthesis Qingdao
- GEO Products, LLC.
- Huifeng Geosynthesis
- SABK International
- Admir Technologies










