Global Biomass Pellets Market Size, Share, And Business Benefits By Source (Agricultural Residue and Waste, Forest and Wood Waste, Virgin Lumber, Food Waste, Energy Crops, Others), By Application (Heating, Power Generation, Others), By Region, and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends, and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: November 2025
- Report ID: 164626
- Number of Pages: 364
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
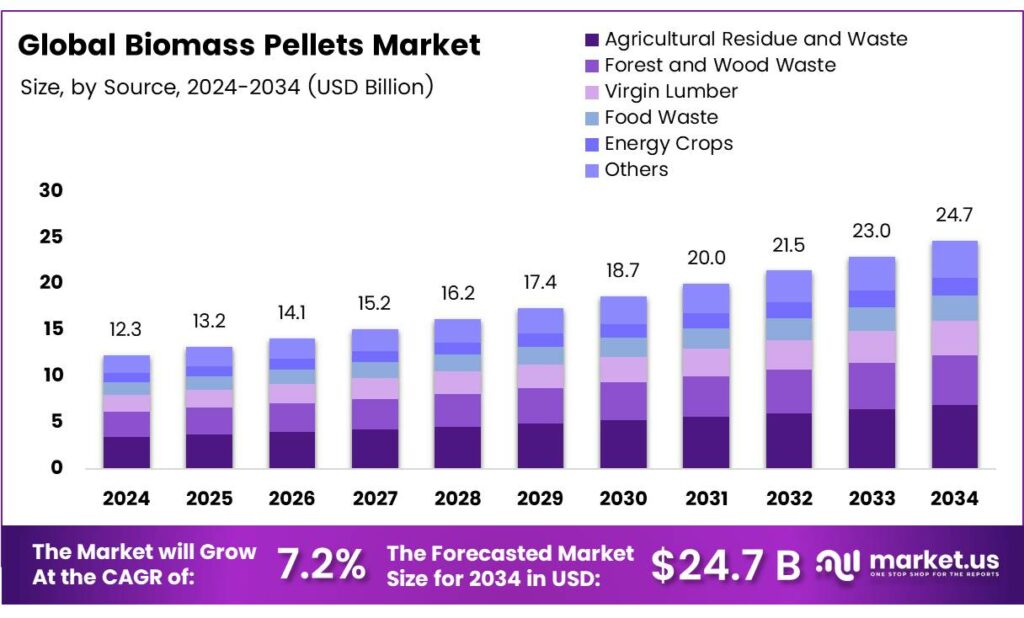
The Global Biomass Pellets Market size is expected to be worth around USD 24.7 billion by 2034, from USD 12.3 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 7.2% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
Biomass pellets are small, cylindrical, and condensed forms of organic material derived from renewable sources, serving as a sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuels. They play a significant role in addressing energy and environmental challenges by providing an efficient biofuel option. Defined as compacted objects made from biomass fuel such as wood sawdust or peat under high pressure, these pellets rely on the natural lignin in the biomass as a binding agent, eliminating the need for additional chemicals or binders.
Energy requirements and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions for producing one tonne of wood pellets, using natural gas as a heat source, vary by stage. Drying consumes 93 MJ/tonne with 11.51 kg CO₂-equiv/tonne emissions, representing a 5% contribution, while drying with heat requires 2880 MJ/tonne and 147.23 kg CO₂-equiv/tonne, accounting for a 69% contribution. Hammermilling uses 120 MJ/tonne and emits 14.85 kgCO₂-equiv/tonne (7%), pelletizing 270 MJ/tonne and 33.41 kgCO₂-equiv/tonne (16%), cooling 6 MJ/tonne and 0.74 kgCO₂-equiv/tonne (0%), and auxiliary power 43 MJ/tonne and 5.32 kgCO₂-equiv/tonne (2%).
The production process of biomass pellets involves several key steps. It begins with the collection of feedstock, gathering suitable organic materials such as wood chips, sawdust, straw, corn stalks, or other residues. The material is then dried to reduce moisture content and enhance combustion efficiency. Next, size reduction is achieved through chippers or grinders to ensure uniform particle size. Pelletization follows, where the processed material is compressed under high pressure in a pellet mill to form cylindrical pellets.
- In Portugal, the solid biofuels market has been developing, with eleven pellet production plants in operation and a biomass consumption of about 1.77 million tonnes. The Portuguese Pellet Association, production reached 690,000 tonnes, an 8% increase, while domestic consumption rose 41% to 73,000 tonnes. Installed capacity was 904,000 tonnes, with plans for new plants to boost annual production capacity to 1,240,000 tonnes.
Additional smaller plants also contribute, though with reduced biomass consumption. Globally, the biomass pellets market is forecasted to grow significantly due to increasing environmental awareness, health concerns, and government initiatives to preserve and conserve natural ecosystems. Densification of biomass into durable pellets effectively meets raw material needs for biofuel production.
Key Takeaways
- The Global Biomass Pellets Market is projected to reach USD 24.7 billion by 2034, growing from USD 12.3 billion in 2024 at a CAGR of 7.2%.
- Agricultural Residue & Waste dominated the By Source segment in 2024 with a 38.5% share, driven by increased conversion of crop leftovers into pellets.
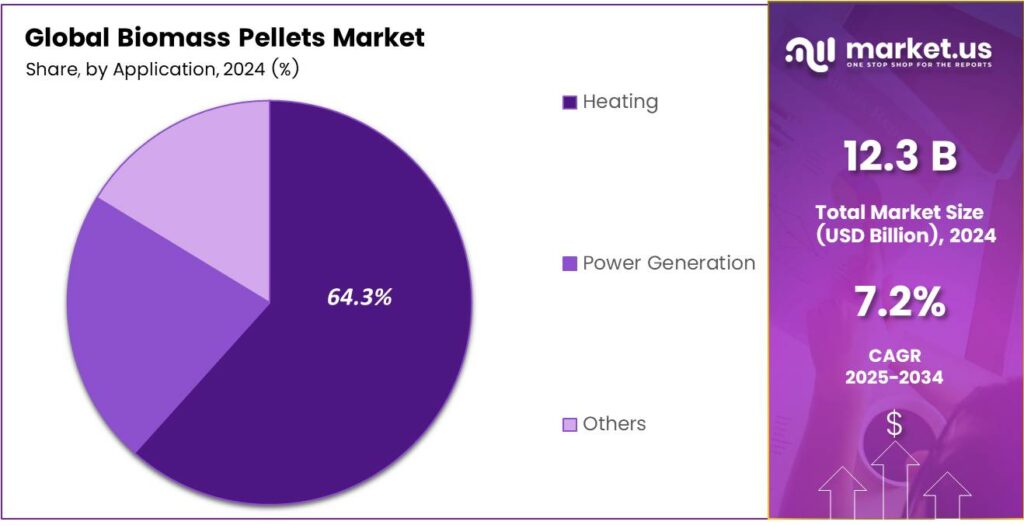
- Heating applications led the By Application segment with a 64.3% share in 2024, reflecting strong residential and commercial heating demand.
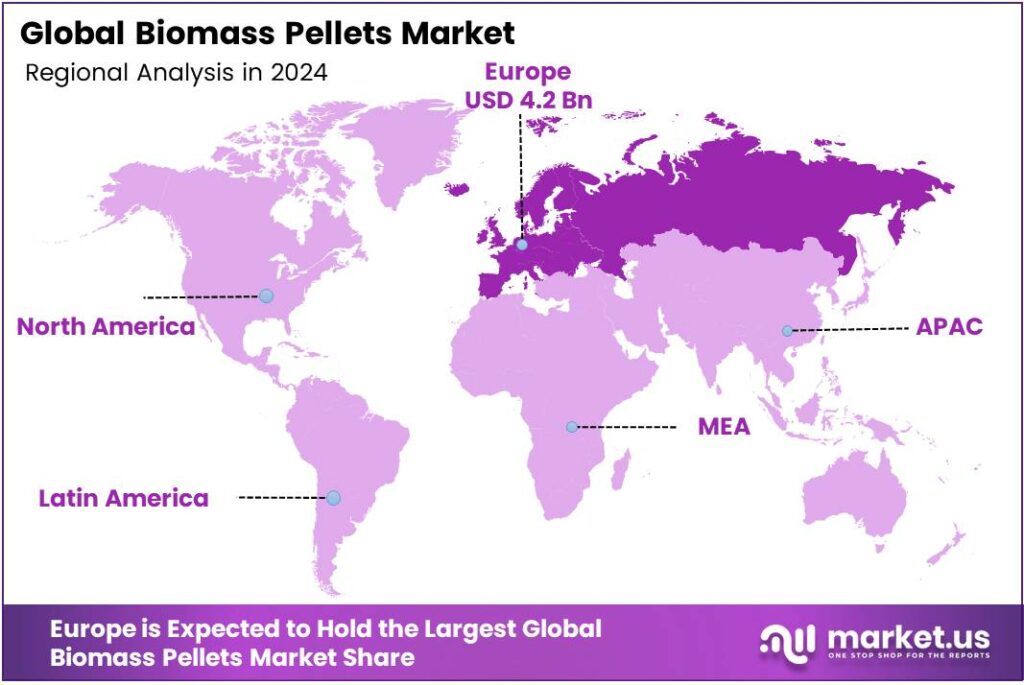
- Europe emerged as the leading regional market, commanding a 34.9% share (USD 4.2 billion) due to the EU’s Renewable Energy Directive and strict emission norms.
By Source Analysis
Agricultural Residue and Waste dominate with 38.5% due to its abundant availability from crop yields and cost-effective recycling.
In 2024, Agricultural Residue and Waste held a dominant market position in the By Source Analysis segment of the Biomass Pellets Market, with a 38.5% share. Farmers harvest vast crops, generating tons of leftovers like straw and husks. These residues transform easily into pellets, reducing farm waste effectively. Industries favor them for sustainability, as they cut disposal costs while fueling green energy needs. This segment surges ahead, driven by rising eco-policies worldwide.
Forest and Wood Waste emerges as a key player next. Logging operations yield sawdust and branches in plenty. Manufacturers collect these by-products swiftly, turning them into high-energy pellets. This approach supports forest management, preventing uncontrolled burns that harm the air. Demand grows as buyers seek reliable, carbon-neutral fuels from nature’s scraps, boosting market efficiency.
Virgin Lumber contributes steadily too. Freshly cut trees provide premium wood for pelletizing. Though pricier, it ensures top-quality density and burn rate. Builders and power plants prefer it for consistent performance. Yet, sustainability concerns push innovators toward recycled options, slowly shifting focus while maintaining its niche role in premium segments.
By Application Analysis
Heating dominates with 64.3% due to its essential role in residential and commercial warmth solutions.
In 2024, Heating held a dominant market position in the By Application Analysis segment of the Biomass Pellets Market, with a 64.3% share. Homes and offices burn these pellets in stoves for cozy warmth. They replace fossil fuels cleanly, slashing emissions during cold seasons. Governments incentivize adoption through subsidies, making heating affordable and eco-friendly.
Power Generation gains momentum rapidly. Utilities co-fire pellets in coal plants, easing the green transition. Large-scale facilities generate electricity reliably, supporting grids amid renewable pushes. Investments pour in as countries target net-zero goals, enhancing pellet use for stable power output without heavy infrastructure overhauls.
Others encompass diverse uses like animal bedding. Farms spread pellets for absorbent, odor-free stalls, improving livestock health. Industries experiment in niche applications, from ceramics to biofuels. Though smaller, this segment innovates quietly, expanding pellet versatility and opening new revenue streams beyond core energy roles.
Key Market Segments
By Source
- Agricultural Residue and Waste
- Forest and Wood Waste
- Virgin Lumber
- Food Waste
- Energy Crops
- Others
By Application
- Heating
- Power Generation
- Others
Emerging Trends
Shift towards large-scale co-firing of biomass pellets in coal plants
One of the most significant emerging trends in the biomass pellets sector is the increasing adoption of the co-firing of agro-residue-based biomass pellets with coal in thermal power plants. In India, for example, the Ministry of Power revised its biomass policy, mandating that coal-fired thermal power plants must co-fire 5% biomass pellets from FY 2024-25, rising to 7% from FY 2025-26.
- This trend reflects a broader global push for utilising biomass pellets as a bridge fuel, enabling existing coal infrastructure to transition towards lower-carbon operation. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), modern bioenergy (which includes pelletised biomass) already accounts for over 6% of global energy supply and nearly 55% of renewable energy excluding traditional biomass use.
In India, the techno-economic study on biomass-pellet-based power estimated a potential of 35 GW of pellet-based capacity, driven by available surplus agricultural and forestry residues. Farmers or rural aggregators collect crop residues, which otherwise might be burnt; pellet manufacturers convert those residues into a standardised fuel; thermal plants blend these pellets with coal, reducing emissions and giving new livelihood streams in rural economies.
Drivers
Surplus biomass feedstock availability from agriculture
A major driver for the biomass-pellet industry is the large surplus of agricultural and forestry residues available in many countries, which provides feedstock for pellet production at relatively competitive cost. In India, studies estimate that there were about 242 million tonnes (Mt) of surplus biomass from agriculture/forestry/wasteland, expected to rise to 281 Mt.
This large feedstock base is critical because pellet manufacture demands a reliable supply of raw material; the more abundant the surplus feedstock, the lower the cost and the more stable the economics of pellet plants. In India’s Unlocking India’s Bioenergy Potential commentary by the IEA, modern bioenergy is identified as expanding rapidly and capable of meeting growing demand, with employment and rural income benefits.
From a human perspective, this driver unlocks value where previously residues may have been burnt in-field, creating air pollution and loss of value. By diverting residues into pellet supply chains, farmers gain new income, local pellet plants create jobs, and power plants receive a renewable fuel that helps decarbonise their operations.
Restraints
Supply-chain and cost competition with coal
Despite the promise, a key restraint for the biomass-pellet sector is the supply-chain complexity and cost competitiveness when compared to coal. One study in India found that while the surplus biomass is large, the cost of transporting raw material, pelletising it estimated at ₹4,473/tonne, and delivering it to a power plant drives up the cost of electricity generation via pellet-based systems.
- The levelised cost was estimated at ₹8.35/kWh, higher than coal‐based generation under many circumstances. Each step adds cost, logistics risk, quality issues (moisture, ash content), and timing challenges (seasonality of harvests). The power plant side also must adjust handling and combustion systems to permit co-firing with biomass pellets, which can require minor retrofits and quality assurance.
Thermal power plants had carried out co-firing (using about 164,976 tonnes of agro-residue-based biomass till then). The pace remains modest given the target scale. Thus—even though feedstock is available—the economics often remain unfavourable compared to cheap coal, making financial viability tricky. Unless costs fall, logistics improve, and biomass pellets achieve parity, this restraint will slow large-scale adoption.
Opportunity
Industrial heat and non-power applications are expanding pellet demand
An emerging opportunity for biomass pellets lies in industrial heat applications and non-power sectors, beyond traditional power generation. The standardised, high-density nature of pellets (cylindrical, 6–12 mm diameter) makes them well-suited for industrial boilers, process heat, district heating, and combined heat and power (CHP) plants.
- A factsheet by World Bioenergy Association noted that around 22 million tonnes of pellets were produced globally 20% annual growth, and agricultural by-product pellets are increasingly used. In human terms, this opportunity means pellet manufacturers are not limited to supplying big power stations—they can serve brick kilns, paper and board plants, sugar mill cogeneration, and even export markets.
In countries like India, where policies such as the SAMARTH Mission recognise agro-residue-based pellet co-firing and manufacturing support, these non-power applications present scalable routes. The opportunity is especially strong in regions with agricultural residues, local pellet plants, and heat‐demanding industries nearby. With proper aggregators, logistics, and policy incentives, pellets can capture this growth segment.
Regional Analysis
Europe leads with a 34.9% share and a USD 4.2 Billion market value.
Europe stands as the dominant force in the global biomass pellets market, accounting for a commanding 34.9% share, which translates to a substantial market value of approximately USD 4.2 billion. This preeminent position is fundamentally driven by the European Union’s stringent regulatory framework and ambitious climate targets, notably the Renewable Energy Directive.
The region’s well-established industrial and residential heating sectors are primary consumers, utilizing pellets for co-firing in power plants and in automated heating systems for residential and commercial buildings. Countries like the United Kingdom, Germany, Denmark, and Sweden are at the forefront of this adoption, supported by robust government subsidies, carbon pricing mechanisms, and a strong societal push for energy security and decarbonization.
The demand is further bifurcated between industrial-grade pellets, largely consumed for power generation, and premium-grade pellets for residential heating. While the market is mature, it continues to exhibit growth, fueled by the ongoing phase-out of fossil fuel-based systems and the need for sustainable, baseload renewable power to complement intermittent sources like wind and solar.
However, the market is not without challenges, including supply chain dependencies on North American imports and price volatility. Despite this, Europe’s well-defined policy landscape and deep-seated commitment to a green transition ensure its continued dominance as the epicenter of global biomass pellet consumption and innovation for the foreseeable future.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Enviva, Inc. is a dominant force, primarily supplying utility customers in Europe and Asia. The company operates numerous large-scale plants and deep-water export terminals, creating a robust, integrated supply chain. Its focus is on displacing coal in power generation to meet global decarbonization goals. However, its scale and reliance on forestry feedstocks place it under significant scrutiny regarding sustainable sourcing practices and carbon accounting.
Fram Fuels is a major distributor and supplier of biomass fuels across the UK and Ireland, rather than a primary manufacturer. The company’s strength lies in its logistics network and supply chain management, sourcing high-quality wood pellets and chips for domestic, commercial, and industrial clients. By focusing on reliable delivery and customer service for heating solutions.
JP Green Fuels is a significant manufacturer and supplier of certified wood pellets and briquettes. The company controls its production process, sourcing sustainable waste wood to create efficient, low-moisture fuels primarily for the domestic heating sector. Its integrated model—from sourcing to manufacturing and distribution—allows for strict quality control and a reliable supply of bagged fuels.
Top Key Players in the Market
- Enviva, Inc.
- Fram Fuels
- JP Green Fuels
- Buhler AG
- Ecostan Biofuel
- Sumitomo Corporation
- Forest Energy Corporation,
- Drax Group plc
Recent Developments
- In 2024, Enviva, Inc., the world’s largest producer of industrial wood pellets, faced significant turbulence in the biomass sector but marked a pivotal recovery. The company successfully emerged from Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection, positioning itself for sustainable growth through optimized operations and enhanced market leadership.
- In 2024, Fram Fuels, a North American-focused supplier of premium wood pellet fuels made from southern pine, has prioritized cost-effective production and sustainability certifications with limited public developments. The company maintains its role as a key player in industrial and domestic pellets.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 12.3 Billion Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 24.7 Billion CAGR (2025-2034) 7.2% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Source (Agricultural Residue and Waste, Forest and Wood Waste, Virgin Lumber, Food Waste, Energy Crops, Others), By Application (Heating, Power Generation, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Enviva, Inc., Fram Fuels, JP Green Fuels, Buhler AG, Ecostan Biofuel, Sumitomo Corporation, Forest Energy Corporation, Drax Group plc Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited Users and Printable PDF)  Biomass Pellets MarketPublished date: November 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Biomass Pellets MarketPublished date: November 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Enviva, Inc.
- Fram Fuels
- JP Green Fuels
- Buhler AG
- Ecostan Biofuel
- Sumitomo Corporation
- Forest Energy Corporation,
- Drax Group plc










