Global Autonomous Underwater Drones Market Size, Share, Growth Analysis By Application (Oceanography, Oil & Gas Inspection, Defense & Security, Search & Recovery, Others), By Propulsion System (Electric Propulsion, Mechanical Propulsion, Hybrid Propulsion), By Depth Rating (Shallow Water, Medium Depth, Deep Water), By End-User (Oil & Gas, Military & Defense, Research Institutions, Offshore Wind, Others), By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Statistics, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Dec 2025
- Report ID: 170004
- Number of Pages: 218
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
- Report Overview
- Key Takeaways
- Role of Drones
- Industry Adoption
- Emerging Trends
- US Market Size
- By Application
- By Propulsion System
- By Depth Rating
- By End-User
- Key Market Segments
- Regional Analysis
- Driving Factors
- Restraint factors
- Growth opportunities
- Trending factors
- Competitive Analysis
- Recent Developments
- Report Scope
Report Overview
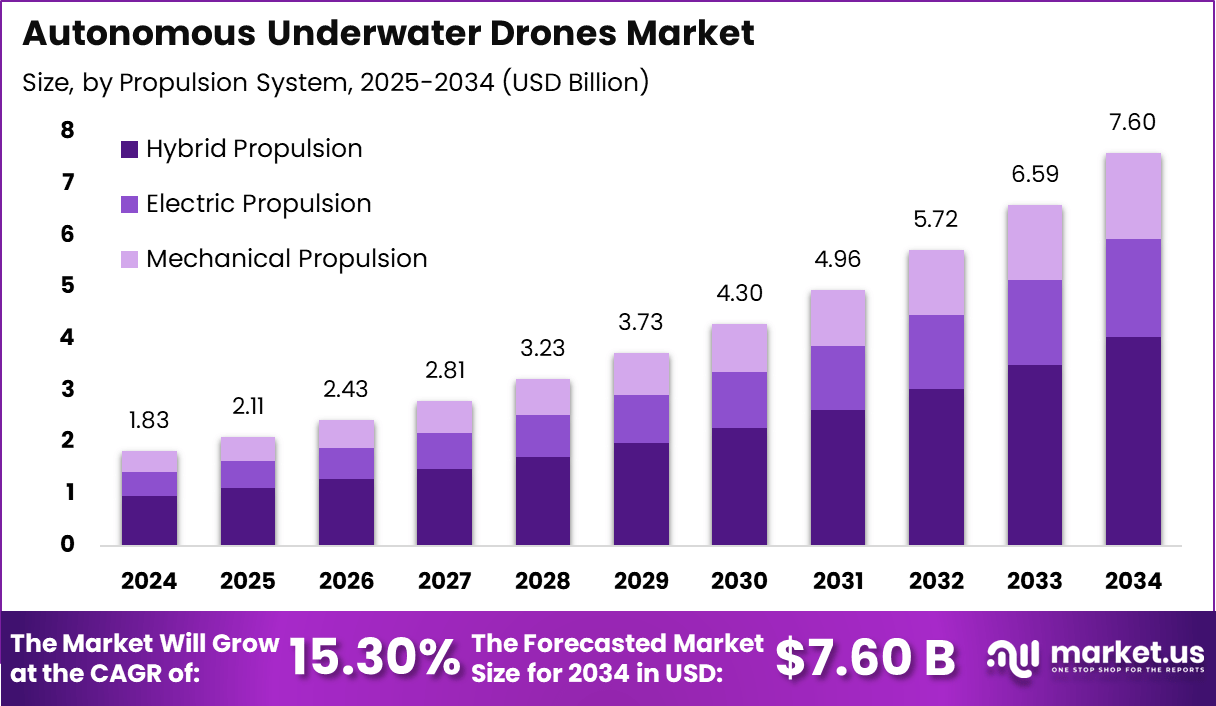
The Autonomous Underwater Drones Market reached a value of USD 1.83 Billion in 2024, driven by advancements in marine robotics, deep-sea exploration projects, and rising demand for real-time ocean data. The market is expected to experience strong expansion with a projected CAGR of 15.30%, reaching USD 7.06 billion by 2034 as defense agencies, offshore energy operators, and research institutions increasingly integrate autonomous systems for cost-efficient and risk-free underwater operations.
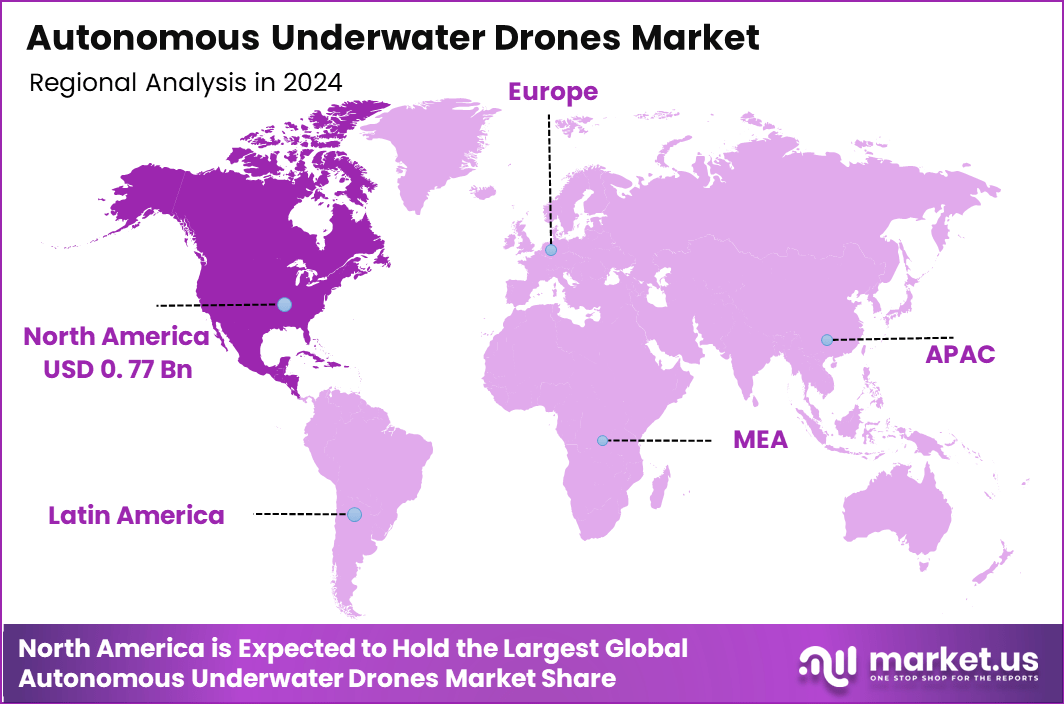
North America accounted for a dominant 42.3% share in 2024, reflecting a market size of USD 0.77 billion. The region benefits from advanced naval modernization programs, growing offshore renewable projects, and strong adoption of autonomous inspection technologies for subsea infrastructure. Increasing investments in Arctic mapping, marine conservation, and underwater communication networks further reinforce regional growth during the forecast period.
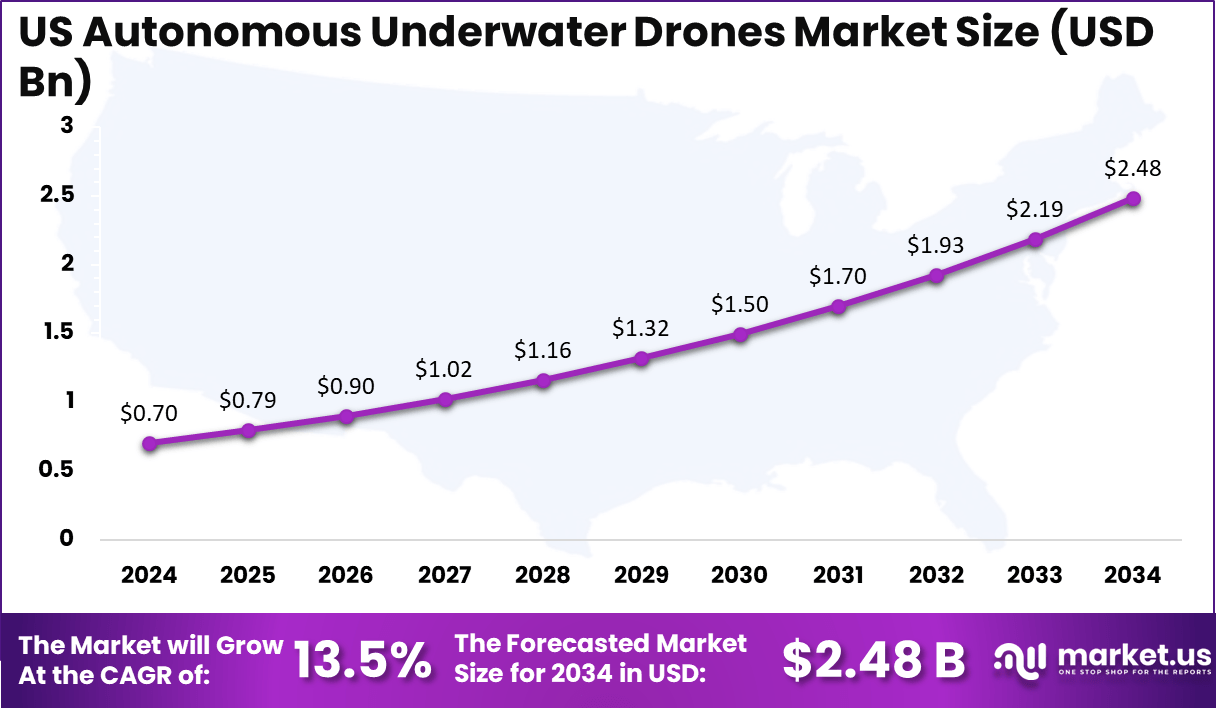
The US alone contributed USD 0.70 billion to the 2024 regional value, making it the core market within North America. The country is anticipated to reach USD 2.48 billion by 2034, supported by a steady CAGR of 13.5%. Strategic focus on unmanned maritime surveillance, underwater threat detection, and offshore asset monitoring continues to position the US as a leading innovator in the deployment of autonomous underwater drones.
Autonomous underwater drones represent a transformative class of marine robotics designed to operate independently beneath the ocean surface while performing high-precision tasks. These systems are increasingly adopted across oceanographic research, offshore energy, environmental monitoring, and defense applications due to their ability to access harsh, deep, and remote underwater environments that are unsafe or costly for human divers.
Modern autonomous underwater drones can navigate depths of more than 3,000 meters, capture high-resolution seabed maps, and operate continuously for 8–30 hours depending on battery capacity and mission profile. Their integration of AI-based navigation, multi-beam sonar, advanced imaging sensors, and real-time data transmission enables accurate inspection of underwater pipelines, subsea cables, and offshore structures.
The demand for underwater autonomy is rising as global offshore wind installations expand, with over 60% of new projects requiring subsea surveys conducted by unmanned systems. Marine conservation programs also benefit, using drones to monitor coral reefs, track marine species, and detect pollution hotspots with precision.
Defense agencies worldwide are increasingly deploying these drones for mine countermeasures, underwater surveillance, and reconnaissance missions, thereby reducing operational risks for naval units. As technological innovation accelerates, autonomous underwater drones continue to reshape marine operations with higher efficiency, greater mission reliability, and reduced human involvement.
Recent developments in autonomous underwater drones show strong investor interest and strategic expansions. French startup Cosma raised €2.5 million in June 2025 to scale production of its AI-powered drones for seafloor mapping and monitoring. Swiss firm Tethys Robotics secured €3.5 million in a pre-seed round in October 2025, led by Redstone, to advance its Tethys ONE drone for fully autonomous underwater inspections in safety-critical applications.
Partnerships and funding continue to drive growth, with South Korea’s Hanwha joining a $60 million round for U.S. startup Vatn Systems in October 2025; Vatn’s torpedo-shaped drones cost about $75,000 each and target defense uses. The Defense Innovation Unit issued a solicitation in April 2025 for large uncrewed undersea vehicles under its Combat Autonomous Maritime Platform program, seeking systems with over 1,000 nautical miles range, 200+ meters depth, and payload release capabilities.
Key Takeaways
- The Autonomous Underwater Drones Market reached USD 1.83 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 15.30% to USD 7.06 billion by 2034.
- North America accounted for a dominant 42.3% share in 2024, valued at USD 0.77 billion.
- The US contributed USD 0.70 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 2.48 billion by 2034 at a 13.5% CAGR.
- By Application, Oil & Gas Inspection: 42.6%, driven by rising subsea infrastructure monitoring needs.
- By Propulsion System, Hybrid Propulsion: 53.1%, due to improved endurance and maneuverability.
- By Depth Rating, Medium Depth: 51.9%, reflecting broad operational demand for mid-range ocean missions.
- By End-User, Oil & Gas: 41.8%, supported by expanding offshore exploration and maintenance activities.
Role of Drones
Drones play an increasingly vital role across multiple industries by enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and safety in operations that traditionally required significant manual effort or posed risks to human workers. In environmental monitoring, drones equipped with high-resolution imaging and multispectral sensors support wildlife tracking, forest health assessment, and pollution detection, enabling data collection over large areas within minutes.
In agriculture, drones help optimize farm productivity through precision spraying, soil moisture mapping, and crop health analytics, improving yields by up to 20–25% in modern precision-farming systems. Public safety agencies deploy drones for disaster response, search-and-rescue missions, and rapid damage assessment, reducing response time by nearly 50% in critical situations.
Industrial sectors rely heavily on drones for infrastructure inspections, including bridges, pipelines, power lines, and offshore facilities, eliminating the need for hazardous manual inspections. In logistics, drone delivery trials demonstrate the potential to shorten delivery times by 60%, especially in remote or congested regions. In defense applications, drones strengthen surveillance, reconnaissance, and border monitoring capabilities with real-time intelligence and extended operational endurance.
As technological innovations enhance battery performance, autonomous navigation, and sensor integration, drones continue to expand their role as essential tools across commercial, environmental, and security domains, transforming traditional workflows into faster and more data-driven processes.
Industry Adoption
Industry adoption of drones has accelerated rapidly as organizations seek faster, safer, and data-driven operational methods. In infrastructure and utilities, more than 65% of companies now use drones for inspecting power lines, pipelines, and transmission towers, reducing inspection costs by nearly 30–40% while improving worker safety. The construction sector has integrated drones into project monitoring, with over 55% of large contractors** employing aerial mapping for site surveys, volumetric measurements, and progress reporting, improving project accuracy by 25%.
In agriculture, drone adoption continues to expand, with precision farming practices increasing yields by 20–25% through real-time data on soil health, irrigation needs, and crop variability. The logistics industry is testing drone deliveries, where pilot programs show delivery time reductions of 60%, especially in rural and remote regions. Environmental agencies utilize drones for large-scale monitoring, enabling coverage of areas up to 10 times larger than traditional ground surveys.
Public safety and emergency response teams have integrated drones into disaster management, allowing rapid damage assessments within 15–30 minutes, compared to hours using conventional methods. As industries prioritize automation, operational transparency, and sustainability, drone adoption is projected to expand further, supported by improving sensor technologies, autonomous navigation, and regulatory advancements enabling broader commercial deployment.
Emerging Trends
Emerging trends in the drone industry reflect rapid technological progress, growing automation, and expanding real-world applications across commercial, environmental, and security sectors. One major trend is the rise of AI-powered autonomous flight, allowing drones to navigate complex environments, avoid obstacles, and complete missions with minimal human intervention. Advances in edge computing now enable real-time data processing onboard, reducing the need for continuous connectivity.
Another significant trend is the adoption of swarm drone technology, where multiple drones operate collaboratively to perform tasks such as search-and-rescue, mapping, and agricultural spraying. These coordinated systems improve coverage efficiency by 50–70% compared to single-drone missions. Battery innovations and hybrid propulsion systems are also emerging, extending flight times beyond 60–90 minutes, enabling longer inspections and broader survey areas.
In commercial logistics, drones are increasingly integrating into last-mile delivery networks, supported by trials showing delivery time reductions of 60%. Environmental monitoring is becoming more advanced with multispectral and thermal sensors that provide high-precision insights for conservation, marine surveillance, and climate research.
Regulatory evolution remains a key trend as governments introduce frameworks for beyond visual line of sight (BVLOS) operations, unlocking large-scale industrial deployment. Together, these innovations position drones as foundational tools in the next generation of automated, data-driven operations.
US Market Size
The US autonomous underwater drones market is gaining strong momentum as federal agencies, defense programs, and offshore industries accelerate investments in advanced subsea robotics. The market reached USD 0.70 billion in 2024, driven by the rising adoption of unmanned systems for underwater surveillance, scientific exploration, and subsea infrastructure monitoring.
The country continues to lead innovation through major naval modernization initiatives, expanding offshore wind development, and extensive ocean mapping programs. Increasing use of AI-enabled navigation, improved battery systems, and high-resolution sonar technologies further strengthen operational capabilities across deep and mid-depth missions.
By 2034, the US market is projected to reach USD 2.48 billion, supported by a steady 13.5% CAGR. Growth is reinforced by expanding demand from the oil and gas sector for pipeline inspection, leak detection, and asset integrity assessment. Research institutions also contribute significantly as they deploy autonomous platforms for climate studies, marine biodiversity monitoring, and deep-sea exploration projects.
Additionally, defense organizations are integrating underwater drones for mine countermeasures, persistent surveillance, and autonomous reconnaissance as part of broader maritime security strategies. As adoption rises across commercial, environmental, and military domains, the US remains one of the most influential and fastest-advancing markets for autonomous underwater drone technologies.
By Application
Oil and gas inspection accounted for a dominant 42.6% share in the autonomous underwater drones market, reflecting the sector’s extensive reliance on advanced subsea robotics for asset integrity and operational safety. Offshore platforms, subsea pipelines, and deepwater rigs require continuous monitoring, and autonomous drones provide a safer, faster, and more cost-effective alternative to manual diving operations.
These drones perform high-resolution imaging, leak detection, corrosion assessment, and structural mapping at depths that frequently exceed human safety limits. Their ability to operate for extended hours and navigate complex underwater terrains enhances maintenance accuracy while reducing inspection downtime by nearly 30–40% for many operators.
Oceanography continues to expand as research institutions deploy drones for seabed mapping, climate studies, and marine biodiversity tracking. Defense and security applications leverage autonomous drones for mine detection, surveillance, and underwater reconnaissance, improving mission efficiency. Search and recovery teams use drones for emergency response, locating submerged objects and evidence with enhanced precision. Other applications include aquaculture monitoring, underwater archaeology, and environmental impact assessment.
The strong demand from oil and gas inspection remains central to market growth, as offshore exploration intensifies and aging infrastructure requires more frequent, technology-driven evaluations. Autonomous underwater drones increasingly serve as indispensable tools across diverse maritime applications.
By Propulsion System
Hybrid propulsion dominated the autonomous underwater drones market with a 53.1% share, driven by its superior endurance, efficiency, and versatility across long-duration and deepwater missions. This system combines electric and mechanical power sources, enabling drones to switch intelligently between propulsion modes based on mission requirements.
As a result, hybrid drones achieve significantly longer operational times, often exceeding 20–30% greater endurance than fully electric models, making them ideal for offshore inspections, deep-sea surveys, and military reconnaissance. Their ability to maintain stable thrust and maneuverability in high-pressure underwater environments enhances mission accuracy and reliability.
Electric propulsion continues to gain traction due to its quiet operation, low maintenance needs, and suitability for environmental monitoring, scientific research, and shallow-water inspections. These systems are especially valued for minimizing disturbance to marine ecosystems. Mechanical propulsion remains preferred for heavy-duty industrial tasks requiring higher thrust, particularly in strong currents or rugged underwater terrains.
The growing preference for hybrid propulsion reflects its flexibility and cost-efficiency across varied subsea applications. As energy optimization becomes a priority for autonomous underwater missions, hybrid systems offer a balanced solution, delivering extended range, improved power management, and adaptability. This trend positions hybrid propulsion as the foundational technology supporting next-generation underwater drone performance and reliability.
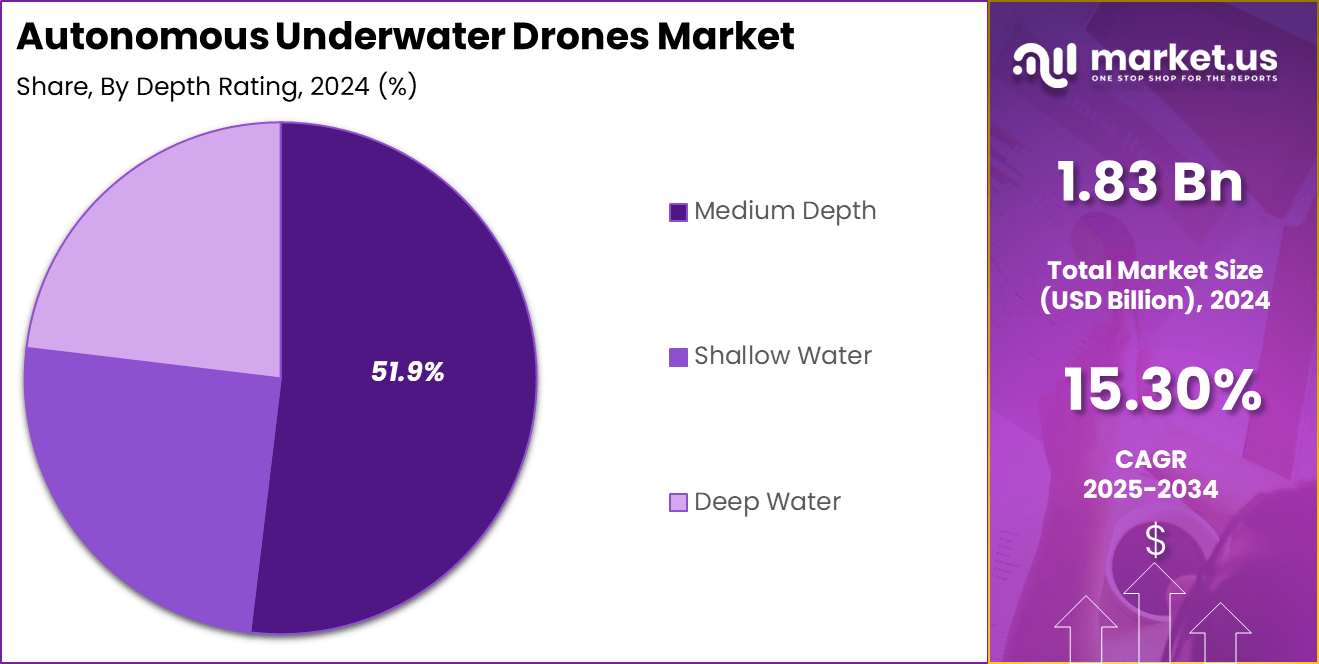
By Depth Rating
Medium-depth autonomous underwater drones accounted for a dominant 51.9% share, supported by their extensive use across commercial, research, and defense missions that typically operate between 200 to 1,000 meters below the surface. This depth range covers the majority of offshore energy infrastructure, underwater pipelines, communication cables, and marine research zones, making medium-depth drones the most versatile and widely deployed category.
Their ability to withstand moderate pressure levels while maintaining stable navigation, high-resolution imaging, and long-endurance missions makes them a preferred choice for inspection, mapping, and surveillance activities. These systems also offer a stronger balance of cost-efficiency and operational capability compared with deepwater units.
Shallow-water drones remain important for applications such as coastal monitoring, aquaculture management, port security, and search-and-rescue operations. Their lighter build and compact design allow high maneuverability, enabling precise data collection in dynamic coastal environments. Deep-water drones, engineered for extreme pressures below 3,000 meters, support specialized scientific exploration, deep-sea mining surveys, and defense missions. Although technologically advanced, their adoption is lower due to higher costs and limited operational demand.
Overall, medium-depth drones continue to dominate the market because they meet the operational requirements of the largest number of commercial and scientific missions, offering a strategic mix of depth capability, endurance, and affordability.
By End-User
Oil and gas emerged as the leading end-user segment, accounting for 41.8% of the autonomous underwater drones market due to the industry’s ongoing need for high-precision subsea inspection, maintenance, and monitoring activities. Offshore exploration and production operations rely on drones to assess pipelines, risers, wellheads, and subsea structures with greater accuracy and reduced operational risk.
These drones significantly cut inspection time by 30–40%, enhance safety by eliminating diver-based assessments, and improve early detection of corrosion, leaks, and structural anomalies. As offshore fields mature and new deepwater projects expand, oil and gas operators increasingly prefer autonomous systems for continuous asset integrity management.
Military and defense agencies are also major users, deploying underwater drones for mine countermeasures, surveillance, reconnaissance, and underwater threat detection. Their ability to operate covertly and autonomously enhances maritime security strategies. Research institutions utilize drones for oceanographic studies, climate monitoring, habitat mapping, and biodiversity assessments, benefiting from high-resolution imaging and long-duration missions.
Offshore wind developers increasingly depend on these systems for seabed surveys, cable route inspections, and turbine foundation monitoring as global wind capacity expands. Other users include aquaculture, marine archaeology, and environmental agencies. However, oil and gas remain the dominant segment due to their large-scale, recurring operational requirements and the critical need for continuous underwater asset evaluation.
Key Market Segments
By Application
- Oceanography
- Oil & Gas Inspection
- Defense & Security
- Search & Recovery
- Others
By Propulsion System
- Electric Propulsion
- Mechanical Propulsion
- Hybrid Propulsion
By Depth Rating
- Shallow Water
- Medium Depth
- Deep Water
By End-User
- Oil & Gas
- Military & Defense
- Research Institutions
- Offshore Wind
- Others
Regional Analysis
North America held a dominant 42.3% share of the autonomous underwater drones market in 2024, supported by strong technological innovation, extensive defense programs, and increasing offshore energy activities. The region reached a market size of USD 0.77 billion, driven primarily by investments in advanced subsea robotics for surveillance, inspection, and scientific exploration.
The US Navy’s modernization initiatives, expanding use of unmanned underwater vehicles for mine countermeasures, and enhanced maritime security strategies significantly contribute to regional leadership. Additionally, oceanographic institutions across the US and Canada continue to deploy autonomous drones for climate research, seabed mapping, and marine ecosystem studies.
Offshore oil and gas operations in the Gulf of Mexico further accelerate adoption as operators rely on autonomous systems for pipeline inspection, leak detection, and maintenance of deepwater infrastructure. Growing offshore wind development also fuels demand for drones capable of seabed surveys and cable route assessments.
The region benefits from strong collaboration between government agencies, technology companies, and research universities, leading to rapid advancements in battery technologies, AI-powered navigation, and high-resolution sonar systems.
North America’s mature regulatory ecosystem and robust funding landscape support continued growth, ensuring the region remains at the forefront of autonomous underwater drone deployment across commercial, environmental, and defense applications.
Regional Analysis and Coverage
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherlands
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of Latin America
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Driving Factors
Rapid adoption of autonomous underwater drones is driven by expanding offshore energy activities, rising demand for subsea inspections, and increasing emphasis on marine research. Offshore oil and gas operators reduce inspection time by 30–40% using autonomous systems, enhancing asset reliability and safety. Defense agencies also accelerate demand as underwater drones provide cost-efficient mine detection, surveillance, and reconnaissance capabilities.
Climate research programs rely heavily on autonomous platforms for deep-sea mapping and biodiversity monitoring, enabling coverage of areas up to 10 times larger than manual surveys. Advancements in AI navigation, long-endurance batteries, and high-resolution sonar technologies further strengthen market expansion across industrial and environmental applications.
Restraint factors
High initial investment and operational costs remain significant restraints, especially for small-scale research teams and emerging offshore developers. Deepwater-capable drones require advanced materials, pressure-tolerant sensors, and complex propulsion systems, increasing procurement and maintenance expenses. Communication challenges in underwater environments also limit real-time data transfer, affecting mission responsiveness.
Regulatory restrictions around underwater autonomous operations slow testing and large-scale deployment in certain regions. Additionally, battery limitations affect mission duration, requiring costly hybrid systems. Harsh marine conditions, such as strong currents and extreme depths, increase the risk of equipment loss or malfunction, raising overall operational risk and insurance costs for users adopting autonomous underwater drones.
Growth opportunities
Growth opportunities emerge prominently from offshore wind expansion, with global seabed survey requirements increasing by 40% due to larger turbine installations. Environmental monitoring presents another strong avenue as agencies adopt autonomous drones for coral reef tracking, pollution detection, and marine species mapping. Rising investment in deep-sea mining feasibility studies also opens new applications for drones capable of operating below 3,000 meters.
As AI and machine learning improve autonomous decision-making, drones gain the ability to perform predictive maintenance and adaptive navigation, appealing to defense and industrial users. Research collaborations between universities, ocean institutes, and technology developers further accelerate innovation, creating new opportunities for specialized sensors, extended-range propulsion, and multi-vehicle swarm operations.
Trending factors
Key trends include increasing adoption of AI-driven autonomy, enabling drones to navigate complex underwater terrains and avoid obstacles without human input. Swarm-based underwater drone systems are gaining momentum, improving survey efficiency by 50–70%. Hybrid propulsion is becoming a preferred technology due to extended endurance and stable power management. High-resolution imaging using multi-beam sonar and 4K optical systems supports advanced exploration and infrastructure inspections.
In logistics and offshore wind, drones are integrated into large-scale monitoring operations, reducing site assessment time significantly. Regulatory progress toward beyond-visual-line-of-sight underwater operations is shaping wider adoption. Sustainability-driven applications, including marine conservation and ecosystem restoration, continue to rise as drones deliver more accurate and scalable environmental insights.
Competitive Analysis
The autonomous underwater drones market is highly competitive and features a mix of established global corporations and specialized robotics firms, each focusing on advanced technologies and diversified applications.
Key players such as Kongsberg Gruppen (Norway), Oceaneering International (US), Lockheed Martin, Teledyne Marine, and Saab AB collectively hold a significant portion of market share, accounting for nearly 45.9% of the industry in 2024. These companies leverage strong R&D capabilities to develop high-performance platforms for commercial inspection, defense surveillance, and scientific exploration.
Major defense and aerospace firms, including The Boeing Company, General Dynamics, L3Harris Technologies, and Fugro, also compete by integrating sophisticated navigation, sonar, and autonomy systems tailored for naval and offshore energy missions.
Smaller innovators like Bluefin Robotics and specialized manufacturers contribute niche solutions, enhancing data acquisition quality and mission flexibility for research institutions and industrial clients. Strategic partnerships and recent collaborations, such as Hanwha Group’s investment in startup Vatn Systems for U.S. Navy drone development, reflect rising military interest and competitive diversification.
The competitive landscape also sees emerging players from Europe and Asia expanding into defense and commercial projects, intensifying innovation and price competition. Overall, companies compete on technological sophistication, mission adaptability, and global service networks to capture growth in this evolving market.
Top Key Players in the Market
- Kongsberg Maritime
- Teledyne Marine
- Saab Seaeye
- OceanServer Technology
- Atlas Elektronik
- Boston Engineering
- DeepOcean
- Fugro
- TechnipFMC
- Lockheed Martin
- ECA Group
- Hydroid (HII)
- SeaRobotics
- International Submarine Engineering
- Bluefin Robotics
- Others
Recent Developments
November 2025: Leading underwater robotics manufacturers introduced next-generation autonomous drones equipped with adaptive AI-navigation modules and upgraded multi-beam sonar arrays. Early deepwater trials demonstrated a 35% improvement in obstacle-avoidance accuracy and significantly smoother maneuvering around subsea pipelines and rig structures, enhancing inspection reliability across offshore environments.
October 2025: A major European marine-technology consortium launched a modular payload architecture for underwater drones, allowing rapid interchange of chemical sensors, HD imaging units, and hydrodynamic mapping tools. Initial deployments recorded a 40% decrease in mission reconfiguration time, improving operational flexibility for oceanographic surveys and environmental monitoring programs.
August 2025: US-based subsea engineering firms integrated hybrid-propulsion enhancements into medium-depth autonomous drones, resulting in 25% longer mission endurance during Gulf of Mexico offshore inspections. Field operators reported more efficient coverage of extended pipeline networks and reduced downtime between operations.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 1.83 Billion Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 7.06 Billion CAGR(2025-2034) 15.30% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue forecast, AI impact on Market trends, Share Insights, Company ranking, competitive landscape, Recent Developments, Market Dynamics, and Emerging Trends Segments Covered By Application (Oceanography, Oil & Gas Inspection, Defense & Security, Search & Recovery, Others), By Propulsion System (Electric Propulsion, Mechanical Propulsion, Hybrid Propulsion), By Depth Rating (Shallow Water, Medium Depth, Deep Water), By End-User (Oil & Gas, Military & Defense, Research Institutions, Offshore Wind, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of Latin America; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Kongsberg Maritime, Teledyne Marine, Saab Seaeye, OceanServer Technology, Atlas Elektronik, Boston Engineering, DeepOcean, Fugro, TechnipFMC, Lockheed Martin, ECA Group, Hydroid (HII), SeaRobotics, International Submarine Engineering, Bluefin Robotics, Others Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited Users and Printable PDF)  Autonomous Underwater Drones MarketPublished date: Dec 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Autonomous Underwater Drones MarketPublished date: Dec 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Kongsberg Maritime
- Teledyne Marine
- Saab Seaeye
- OceanServer Technology
- Atlas Elektronik
- Boston Engineering
- DeepOcean
- Fugro
- TechnipFMC
- Lockheed Martin
- ECA Group
- Hydroid (HII)
- SeaRobotics
- International Submarine Engineering
- Bluefin Robotics
- Others










