Global 5G Infrastructure Market Size, Share, Trends Analysis Report By Component (Hardware (Radio Access Network (RAN), Core Network, Others), Services), By Spectrum(Sub-6 GHz, mmWave), By Network Architecture(Standalone, Non-standalone), By Vertical(Manufacturing, Automotive and Transportation, Enterprise/Corporate, Energy & Utilities, Healthcare/Hospitals, Smart Cities, Others), Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2024-2033
- Published date: March 2025
- Report ID: 132771
- Number of Pages: 383
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
- Report Overview
- Key Takeaways
- APAC 5G Infrastructure Market Size
- Component Analysis
- Spectrum Analysis
- Network Architecture Analysis
- Vertical Industry Analysis
- Key Market Segments
- Driver
- Restraint
- Opportunity
- Challenge
- Growth Factors
- Emerging Trends
- Business Benefits
- Key Player Analysis
- Recent Developments
- Report Scope
Report Overview
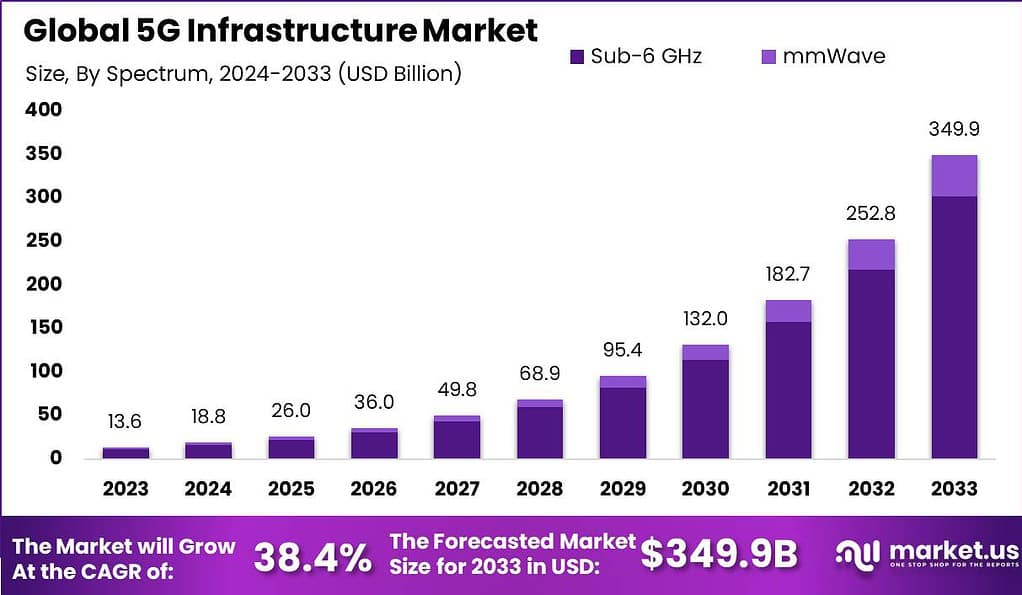
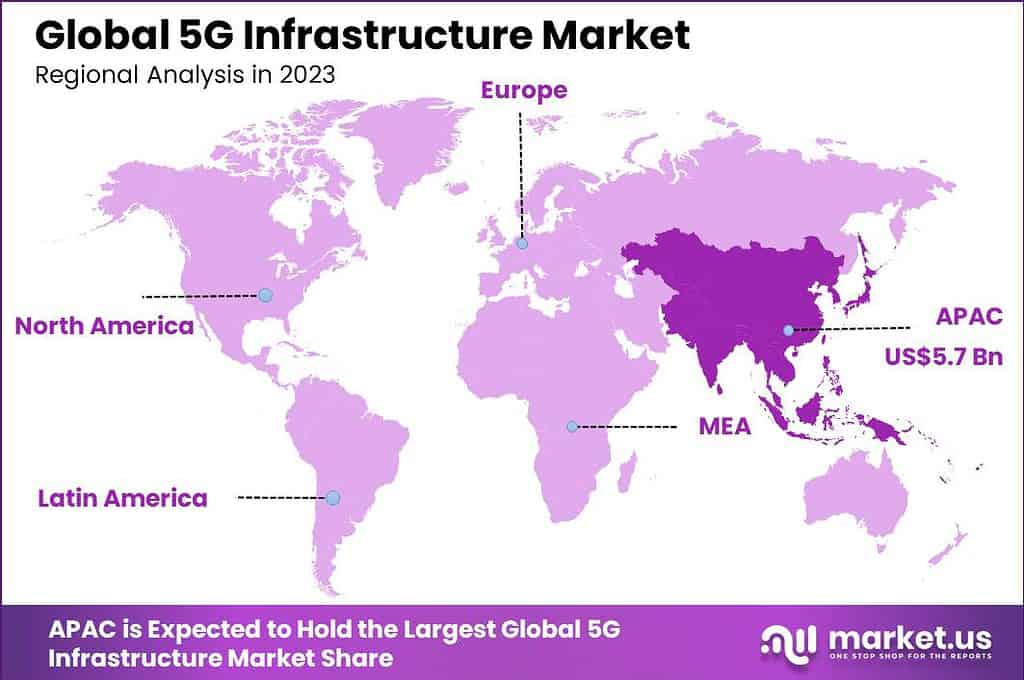
The Global 5G Infrastructure Market size is expected to be worth around USD 349.9 Billion By 2033, from USD 13.6 billion in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 38.4% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033. In 2023, APAC held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 42.1% share, holding USD 5.7 billion revenue.
5G infrastructure represents the next-generation backbone of telecommunications, aiming to dramatically enhance data transmission speeds and connectivity. This technology uses advanced antennas, new frequencies, and upgraded cellular networks to facilitate faster and more reliable internet services. The core of 5G involves extensive fiber optics, advanced networking technologies, and the deployment of small cells that provide expansive network coverage and capacity.
The 5G infrastructure market is expanding as the demand for high-speed internet and the growth of data-intensive applications in sectors such as autonomous vehicles, IoT, and smart cities continue to rise. This market includes the development and deployment of various 5G components like antennas, chipsets, and routers, which are critical for supporting the data transmission capabilities of the network.
The primary catalysts for the growth of the 5G infrastructure market include the expanding implementation of machine-to-machine and IoT connections, and a surge in demand for mobile data services. These elements are necessitated by a broad spectrum of industries adopting digital and automated solutions, which rely on robust and speedy internet connectivity.
Market demand for 5G infrastructure is robust, particularly in regions with high technology adoption rates such as North America and Asia-Pacific. This demand is propelled by the growing need for infrastructure capable of supporting high-speed, low-latency applications across various sectors including automotive, industrial, and healthcare, where real-time data transfer is crucial.
For instance, as highlighted by Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson in their Mobile Data Traffic Outlook report, the scope of mobile data usage across the globe is experiencing an impressive surge. At the close of 2023, the total monthly mobile data traffic globally (excluding fixed wireless access) stood at 130 EB (Exabytes). Looking forward, this figure is projected to substantially rise, tripling to an estimated 403 EB per month by the year 2029.
Significant technological advancements in 5G include the development of massive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) antennas, advanced beamforming techniques, and the deployment of small cells that enhance coverage and network efficiency. The evolution of network infrastructure to support standalone 5G networks, which operate independently of existing 4G networks, is also a notable advancement. These technologies are pivotal for achieving the high-speed, high-capacity goals set forth by 5G standards.
5G technology opens vast opportunities for enhancing network services that cater to advanced applications such as smart cities, autonomous driving, and telemedicine, all of which require uninterrupted high-speed internet. Additionally, government initiatives across various countries to fund and support the expansion of 5G technologies further amplify these opportunities, making it an attractive sector for investment.
Key Takeaways
- The Global 5G Infrastructure Market is projected to grow significantly in the coming years. It is expected to reach a valuation of USD 349.9 billion by 2033, up from USD 13.6 billion in 2023, achieving a robust CAGR of 38.4% during the forecast period (2024–2033).
- APAC emerged as the market leader in 2023, holding over 42.1% of the global share, with revenues amounting to USD 5.7 billion. This dominance is attributed to the region’s rapid technological advancements and government initiatives supporting 5G deployment.
- The Hardware segment commanded the market in 2023, capturing more than 80.5% of the market share. This includes components such as antennas, small cells, and radio access networks, driven by widespread infrastructure upgrades.
- Within the frequency bands, the Sub-6 GHz segment led the market, holding a remarkable 86.3% share in 2023. Its dominance stems from its widespread use in urban and suburban networks due to its balance of speed and coverage.
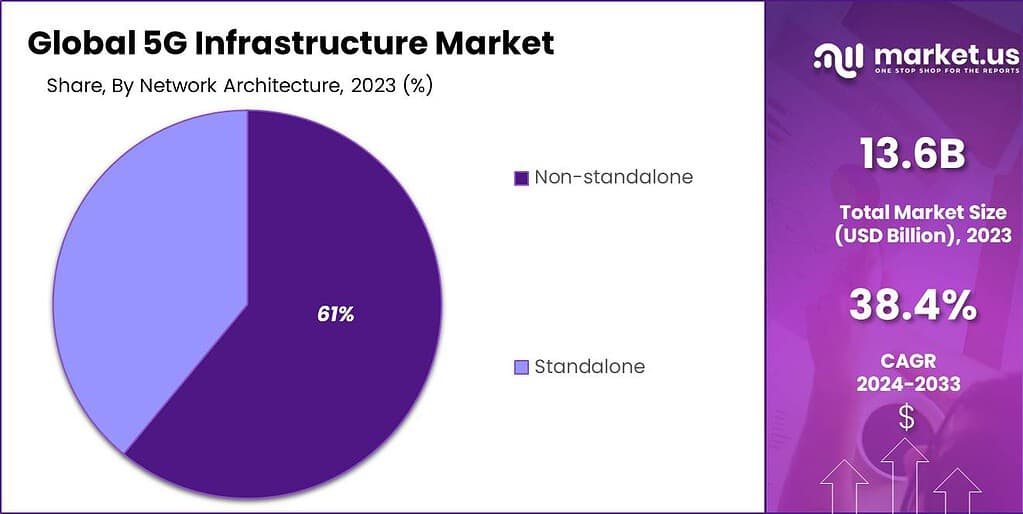
- The Non-Standalone (NSA) architecture was the top deployment mode in 2023, securing more than a 61% share. This architecture enables faster rollouts by integrating 5G with existing 4G LTE infrastructure.
- The Manufacturing sector stood out as the leading industry vertical, accounting for 23.8% of the market share in 2023. The adoption of 5G in manufacturing supports smart factories, automation, and real-time monitoring, boosting operational efficiencies.
APAC 5G Infrastructure Market Size
In 2023, APAC held a dominant market position in the 5G infrastructure market, capturing more than a 42.1% share, with revenues amounting to USD 5.7 billion. This leading position can be attributed to several strategic and economic factors that have accelerated the deployment and adoption of 5G technologies across the region.
APAC’s leadership in the 5G infrastructure market is largely driven by the aggressive expansion policies of key regional economies like China, South Korea, and Japan. These countries have made substantial investments in 5G technology as part of their national agendas to boost technological innovation and economic growth. China, in particular, has rapidly built out its 5G network, with tens of thousands of 5G base stations already operational, serving as a model for rapid deployment.
For instance, as of October 2023, China has significantly advanced its 5G network by deploying over 3.19 million 5G base stations across the country. This massive infrastructure development is aimed at spearheading the digital and intelligent transformation of China’s real economy. The deployment density is impressive, with around 22.6 5G stations for every 10,000 residents, showcasing China’s commitment to widespread 5G accessibility and integration.
Furthermore, the region benefits from a robust manufacturing sector that produces a significant portion of the world’s telecommunications equipment. This has facilitated easier access to 5G components at a lower cost, which, in turn, has sped up 5G infrastructure development. Additionally, the presence of major telecommunications companies and technology innovators in the region, who are continuously pushing for advanced applications of 5G technology, adds to the momentum.
According to the GSM Association, China is set to invest approximately $184 billion in 5G infrastructure by 2025, aiming to lead the global 5G market. This substantial investment underscores China’s commitment to advancing its digital economy and enhancing connectivity nationwide. In Japan, the 5G landscape is evolving rapidly. In May 2023, Ericsson and KDDI collaborated to deploy the country’s first underground 5G base stations, known as vault base stations.
The high rate of technological adoption among APAC’s consumer base also plays a crucial role. With a large, tech-savvy population keen on adopting the latest technologies, there is a strong consumer demand for high-speed internet and mobile services, which further drives the deployment of 5G networks. This demand is complemented by burgeoning sectors like e-commerce, smart cities, and digital healthcare, which leverage 5G for enhanced services and connectivity.
Component Analysis
In 2023, the Hardware segment held a dominant market position within the 5G Infrastructure sector, capturing more than an 80.5% share. This substantial market share can be attributed to the critical role that hardware components like Radio Access Networks (RAN) and Core Networks play in the deployment and operation of 5G technologies.
RAN components are essential for establishing and maintaining the connection between user devices and the core network, facilitating the high-speed, low-latency communication that 5G promises. Meanwhile, the Core Network is vital for routing and managing network traffic efficiently, enabling new functionalities like network slicing and edge computing which are pivotal for advanced 5G applications.
The prominence of the Hardware segment is further underscored by ongoing global investments in building out 5G networks to support increasing volumes of data traffic and to cater to the expansion of IoT devices. Countries and companies are heavily investing in this infrastructure to not only enhance current telecommunication capabilities but to also lay the groundwork for future innovations such as smart cities and autonomous systems, which rely heavily on reliable and robust network connections.
Additionally, advancements in hardware technology, such as the development of more sophisticated and miniaturized RAN components and the implementation of new core network technologies, continue to drive the segment’s growth. These advancements are making it possible to deploy 5G networks more broadly and at lower costs, further fueling the expansion of this market segment.
The critical need for robust, scalable, and efficient network infrastructure to handle the anticipated growth in 5G network traffic and services ensures that the Hardware segment will likely maintain its dominance. As the backbone of 5G networks, the ongoing evolution and enhancement of hardware components are essential for enabling the full spectrum of 5G capabilities, thus sustaining the high market share and continuing the segment’s growth trajectory.
Spectrum Analysis
In 2023, the Sub-6 GHz segment held a dominant market position in the 5G Infrastructure market, capturing more than an 86.3% share. This commanding presence is largely due to its widespread adoption facilitated by the spectrum’s ability to cover larger areas and penetrate buildings more effectively than higher frequency bands.
The Sub-6 GHz range is versatile, supporting a wide range of applications from mobile broadband to industrial IoT, which require broad coverage and reliable connectivity. Its compatibility with existing mobile frequencies has allowed for quicker and more cost-effective network upgrades, a significant factor for its widespread deployment, especially in regions with existing LTE infrastructure.
Furthermore, the Sub-6 GHz band is crucial for providing the foundation for nationwide 5G coverage, essential for reaching rural and suburban areas where high-speed connectivity is increasingly demanded. Its ability to carry signals over long distances without substantial loss of data integrity makes it a practical choice for operators aiming to offer enhanced mobile broadband services across expansive geographical areas.
Technological advancements in antenna design and signal processing have also enhanced the capabilities of Sub-6 GHz frequencies, enabling them to handle more data and support more simultaneous connections. This improvement is vital for accommodating the exponential increase in devices connecting to the internet, driven by the growth of smart devices and the IoT.
Overall, the robust performance and versatility of the Sub-6 GHz spectrum ensure its continued dominance in the 5G infrastructure market, as it remains pivotal in providing widespread, reliable 5G access. Its role is expected to be foundational as new 5G applications and services continue to evolve and demand for connectivity extends into more areas.
Network Architecture Analysis
In 2023, the Non-Standalone (NSA) segment held a dominant market position in the 5G infrastructure market, capturing more than a 61% share. This segment’s leadership stems from its practical and cost-effective approach to deploying 5G technologies, leveraging existing 4G LTE infrastructure. By utilizing current network architecture, telecom operators can introduce 5G services more rapidly and at a lower initial cost compared to a standalone setup, which requires a completely new infrastructure.
The NSA architecture is particularly advantageous during the transitional period from 4G to 5G. It allows for the simultaneous use of 4G and 5G technologies, where 5G NR (New Radio) is used for data throughput while the existing 4G networks manage non-data tasks such as signaling and connection. This dual connectivity enhances the overall network performance by boosting data speeds and reducing latency without the need for widespread hardware updates.
Moreover, the NSA setup is ideal for areas where full 5G coverage is not yet feasible or economically viable. It enables service providers to offer enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) services that improve consumer experiences with faster internet speeds, supporting the growing demand for high-bandwidth applications such as streaming, gaming, and augmented reality.
The dominance of the NSA architecture is likely to persist in the near term as more regions and providers initiate their transition to 5G. Its ability to deliver immediate improvements in network performance and user experience with a balanced investment makes it an attractive option for many telecom operators. As the global 5G landscape evolves, the NSA segment’s role as a critical pathway to broader 5G adoption is expected to remain substantial, underscored by ongoing enhancements and integration with existing telecom infrastructures.
Vertical Industry Analysis
In 2023, the Manufacturing segment held a dominant market position in the 5G infrastructure market, capturing more than a 23.8% share. This substantial market presence is primarily attributed to the critical role that 5G technology plays in enabling Industry 4.0, which focuses on automation, real-time data exchange, and improved manufacturing processes through advanced technologies like AI and IoT.
The integration of 5G in manufacturing settings allows for the establishment of smart factories, where machinery and equipment are interconnected seamlessly, facilitating automated and highly efficient production processes. This connectivity not only boosts operational efficiency but also enhances the flexibility and scalability of manufacturing operations, allowing factories to swiftly adjust to new production requirements and market demands.
For instance, GSMA Intelligence projects a remarkable expansion in the adoption of 5G technology globally. By the end of 2025, the number of 5G connections is expected to reach around 2 billion, doubling from the count at the end of 2023. This surge is spurred by the launch of 5G networks in over 30 new countries throughout 2023, including multiple locations within Asia and Africa which are setting up their first 5G networks this year.
Moreover, 5G’s ultra-reliable, low-latency communications are pivotal for mission-critical applications in manufacturing, such as remote control of heavy machinery, real-time monitoring of industrial processes, and predictive maintenance of equipment. These applications reduce downtime and maintenance costs, significantly improving overall productivity and safety in the manufacturing environment.
The sustained dominance of the Manufacturing segment in the 5G infrastructure market is driven by the ongoing push towards digital transformation in the industry. As manufacturers continue to invest in digital technologies to remain competitive, the role of 5G infrastructure in supporting these advanced applications becomes increasingly indispensable.
Key Market Segments
By Component
- Hardware
- Radio Access Network (RAN)
- Core Network
- Others
- Services
By Spectrum
- Sub-6 GHz
- mmWave
By Network Architecture
- Standalone
- Non-standalone
By Vertical Industry
- Manufacturing
- Automotive and Transportation
- Enterprise/Corporate
- Energy & Utilities
- Healthcare/Hospitals
- Smart Cities
- Others
Key Regions and Countries
North America
- US
- Canada
Europe
- Germany
- UK
- Spain
- Austria
- Rest of Europe
Asia-Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Thailand
- Rest of Asia-Pacific
Latin America
- Brazil
Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- United Arab Emirates
Driver
Increasing Demand for High-Speed Connectivity
The primary driver of the 5G Infrastructure market is the escalating demand for high-speed, low-latency internet connectivity, which is crucial for supporting advanced applications such as the Internet of Things (IoT), autonomous vehicles, and augmented reality.
As industries and consumers alike seek faster data transfer rates to support real-time communication and large data transfers, 5G technology is becoming indispensable. This demand is especially pronounced in urban areas and among sectors that rely heavily on real-time data, such as entertainment and telecommunication, to improve user experiences and operational efficiencies.
Restraint
High Initial Capital Expenditure
One significant restraint in the 5G Infrastructure market is the high initial capital required for the deployment of network architecture and spectrum acquisition. Establishing a comprehensive 5G network involves substantial investments in new base stations, small cells, and the acquisition of suitable spectrum bands through auctions, which can pose financial challenges for service providers.
This financial burden is compounded by the need to ensure comprehensive coverage and network density to deliver the promised speeds and connectivity of 5G, making the financial outlay a major hurdle for many operators.
Opportunity
Expansion into New Geographical and Industrial Markets
There is a considerable opportunity for the expansion of 5G infrastructure into new geographical regions and industrial applications. As countries and regions that are currently underserved in terms of high-speed internet begin to upgrade their capabilities, there is potential for significant growth in the 5G infrastructure space.
Additionally, industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and automotive are increasingly implementing IoT and smart technologies that require reliable and fast internet connections, thereby driving further expansion of 5G networks into these new verticals.
Challenge
Technological and Infrastructure Compatibility
A major challenge facing the rollout of 5G infrastructure is ensuring compatibility with existing technologies and infrastructure. As 5G requires a denser network of antennas and more sophisticated hardware, integrating these requirements with current systems can be complex and costly.
Additionally, there is the challenge of ensuring that the new 5G networks can coexist with existing 3G and 4G networks during the transitional period. This requires careful planning and execution to avoid service disruptions and to manage the technological integration smoothly.
Growth Factors
The 5G infrastructure market is poised for substantial growth, driven by the accelerating need for high-speed mobile broadband services and the proliferation of machine-to-machine (M2M) and Internet of Things (IoT) connections.
Over 80 billion devices are projected to be connected to the Internet by 2025, according to a study published by Forbes. This highlights the immense growth of IoT technology and its transformative impact across industries. Key sectors like manufacturing, smart cities, logistics, healthcare, and automotive are set to benefit significantly from enhanced connectivity and automation
As digital transformation initiatives across various sectors pick up pace, the demand for more efficient, high-capacity wireless communication networks grows. This is particularly evident in urban areas where the density of users and devices necessitates robust connectivity to support an array of applications from smart city infrastructure to immersive media experiences and remote real-time operations.
Emerging Trends
Emerging trends in the 5G market include the rapid deployment of small cells, which are crucial for extending the coverage and capacity of 5G networks, especially in densely populated areas. The integration of advanced technologies like network functions virtualization (NFV) and software-defined networking (SDN) is also reshaping the landscape.
These technologies offer greater network agility and efficiency, facilitating easier scaling and management of network resources. Another significant trend is the rise of edge computing, which moves data processing closer to the end-user, dramatically reducing latency and enhancing the performance of applications that rely on real-time data.
Business Benefits
The deployment of 5G infrastructure brings several business benefits, such as enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) that supports higher data-rate and lower-latency communications. This is crucial for businesses relying on cloud computing and IoT technologies, where rapid, reliable data transmission can significantly optimize operations and customer experiences.
For industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and automotive, 5G enables the implementation of connected machinery and devices, autonomous systems, and advanced remote operations, leading to increased productivity and reduced operational costs. Additionally, 5G opens up new avenues for service expansion and innovative business models, particularly in areas like virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and ultra-HD video content delivery.
Key Player Analysis
The 5G infrastructure market is characterized by the presence of several key players who are instrumental in the deployment and advancement of 5G networks globally. Prominent among these are Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd., Ericsson, Nokia Corporation, ZTE Corporation, and Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd.
Ericsson Ericsson has consistently demonstrated leadership in the 5G infrastructure sector, marked by its strategic partnerships and technological advancements. In 2023, Ericsson was recognized for its high performance in network solutions for 5G. The company’s significant R&D investments over the years have fortified its market presence, particularly outside China, where it commands a substantial market share.
Huawei Huawei remains a powerhouse in the global 5G market, driven by its extensive R&D initiatives and broad product portfolio. Despite facing regulatory challenges in various markets, Huawei’s technological prowess in network equipment provides a strong foundation for its 5G infrastructure services. The company’s focus on developing end-to-end 5G solutions has been instrumental in its ability to secure a leading role in the market.
Nokia Nokia is another key player making substantial contributions to the 5G infrastructure market, with a strong focus on the research and development of 5G technologies. The company’s comprehensive approach spans various components of 5G technology, including RAN, core networks, and transport solutions.
Top Key Players in the Market
- Cisco Systems Inc.
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP
- Mavenir Systems Inc.
- NEC Corporation
- Nokia Corporation
- Oracle Corporation
- Qualcomm Technologies Inc.
- Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
- ZTE Corporation
- Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd
- Qucell Networks Co. Ltd
- Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd
- Airspan Networks Inc.
- CommScope Holding Company Inc.
- Other Key Players
Recent Developments
- In November 2024, Nokia acquired the world’s largest API hub and marketplace from U.S. company Rapid. This strategic move aims to enhance revenues from Nokia’s 5G and 4G networks by enabling clients to better integrate their networks and collaborate with developers. In June 2024, Nokia announced plans to acquire networking company Infinera for $2.3 billion, aiming to strengthen its network infrastructure business.
- In June 2024, T-Mobile announced plans to acquire US Cellular for $4.4 billion, aiming to enhance its 5G network reach, particularly in rural areas, and offer more value-packed plans to customers.
- In June 2023, Vodafone announced a merger with Three UK to create one of Europe’s leading 5G networks. The Competition and Markets Authority provisionally approved the £18 billion merger in November 2024, contingent upon significant network investments and customer protections.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2023) USD 13.6 Bn Forecast Revenue (2033) USD 349.9 Bn CAGR (2024-2033) 38.4% Largest Market APAC Base Year for Estimation 2023 Historic Period 2019-2022 Forecast Period 2024-2033 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Component (Hardware (Radio Access Network (RAN), Core Network, Others), Services), By Spectrum(Sub-6 GHz, mmWave), By Network Architecture(Standalone, Non-standalone), By Vertical(Manufacturing, Automotive and Transportation, Enterprise/Corporate, Energy & Utilities, Healthcare/Hospitals, Smart Cities, Others) Regional Analysis North America (US, Canada), Europe (Germany, UK, Spain, Austria, Rest of Europe), Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Thailand, Rest of Asia-Pacific), Latin America (Brazil), Middle East & Africa(South Africa, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates) Competitive Landscape Cisco Systems Inc., Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP, Mavenir Systems Inc., NEC Corporation, Nokia Corporation, Oracle Corporation, Qualcomm Technologies Inc., Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson, ZTE Corporation, Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd, Qucell Networks Co. Ltd, Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd, Airspan Networks Inc., CommScope Holding Company Inc., Other Key Players Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Cisco Systems Inc.
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP
- Mavenir Systems Inc.
- NEC Corporation
- Nokia Corporation
- Oracle Corporation
- Qualcomm Technologies Inc.
- Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
- ZTE Corporation
- Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd
- Qucell Networks Co. Ltd
- Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd
- Airspan Networks Inc.
- CommScope Holding Company Inc.
- Other Key Players













