Global Zinc Sulphate Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Type (Anhydrous, Monohydrate, Hexahydrate, Heptahydrate), By Applications (Micronutrient, Nutritional Supplements, Preservative, Etching and Engraving, Others), By End-use (Agriculture, Animal Nutrition, Food and Nutrition, Water Treatment, Mining, Pharmaceutical, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends, and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: July 2025
- Report ID: 153863
- Number of Pages: 277
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
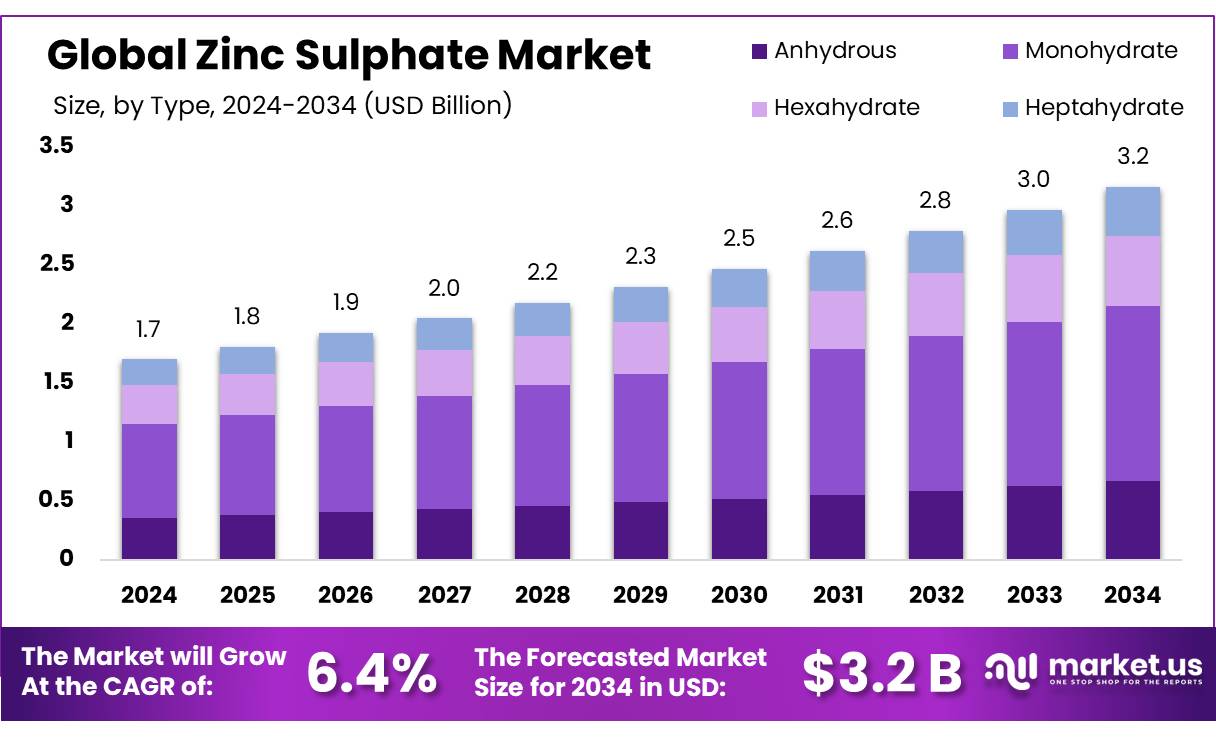
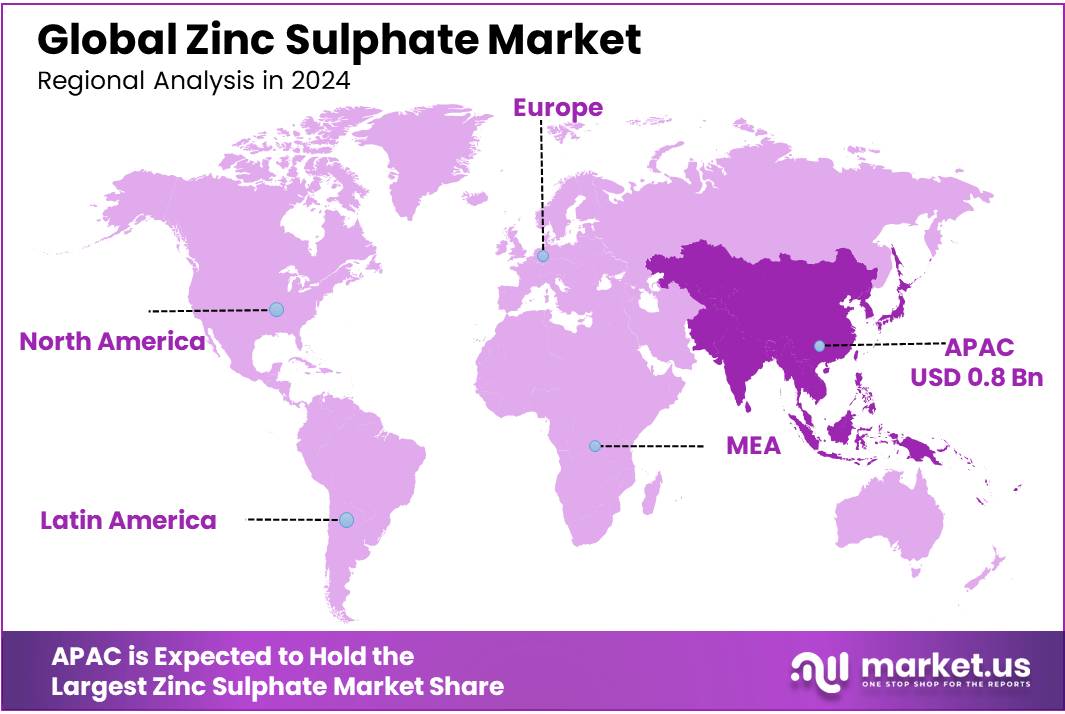
The Global Zinc Sulphate Market size is expected to be worth around USD 3.2 Billion by 2034, from USD 1.7 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 6.4% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, Asia Pacific (APAC) held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 47.3% share, holding USD 0.8 Billion revenue.
Zinc Sulphate Concentrates (ZSC) are integral to various industrial applications, including agriculture, pharmaceuticals, water treatment, and chemical manufacturing. These compounds, primarily produced through the leaching of zinc-bearing ores or secondary zinc sources, are essential for addressing micronutrient deficiencies in soils and plants.
In India, the zinc industry is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand across multiple sectors. The country’s zinc consumption is notably lower than the global average, with per capita consumption at approximately 0.5 kg, compared to China’s 5.0 kg and the global average of 1.9 kg. This disparity indicates substantial potential for growth in the Indian market. Hindustan Zinc Limited, a leading producer, operates several smelters with advanced technologies such as Roast Leach Electro-winning (RLE) and Ausmelt, enabling efficient production of zinc and its derivatives. For instance, the Chanderiya Lead-Zinc Smelter has a capacity of 525,000 tonnes per annum of zinc.
The demand for zinc sulphate concentrates is poised for growth, fueled by the expanding agricultural sector, which is projected to reach USD 24 billion by 2025. The adoption of zinc-based fertilizers is increasing to address soil deficiencies and improve crop yields. Moreover, the pharmaceutical industry’s reliance on zinc supplements for treating deficiencies further bolsters the market. Technological advancements and environmental considerations are also driving the development of more efficient and sustainable production methods for zinc sulphate concentrates.
Key Takeaways
- The Zinc Sulphate Market is expected to grow from USD 1.7 billion in 2024 to around USD 3.2 billion by 2034, registering a CAGR of 6.4%.
- Monohydrate held the leading market position, accounting for more than 47.8% of the global share.
- The Micronutrient segment dominated the market, contributing over 41.2% of the total market share.
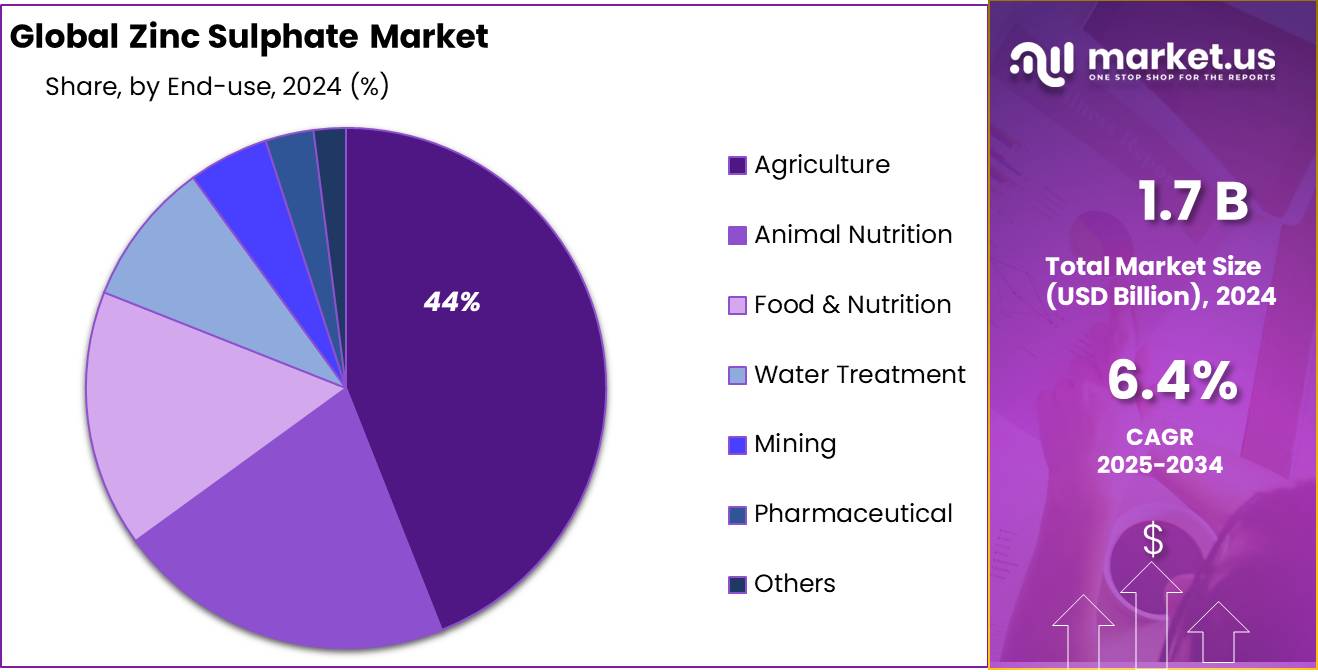
- Agriculture was the dominant application area, with more than 44.9% share in the global market.
- The Asia Pacific (APAC) region led the market, capturing 47.3% of the global share and reaching a value of approximately USD 0.8 billion.
By Type Analysis
Monohydrate Zinc Sulphate dominates with 47.8% share due to its wide agricultural use
In 2024, Monohydrate held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 47.8% share in the global zinc sulphate market by type. Its high solubility, effectiveness in correcting zinc deficiency in soils, and cost-efficiency have driven widespread adoption, particularly in agricultural applications. Farmers across Asia and Africa prefer monohydrate zinc sulphate due to its ease of handling and suitability for soil application and foliar sprays.
This variant is commonly used in micronutrient fertilizers for crops such as rice, wheat, and maize. The growing focus on soil health management by national governments—especially in India and China—has further supported demand for monohydrate forms. In 2025, the segment is expected to maintain its lead, as awareness around balanced fertilization practices continues to rise. With expansion in public fertilizer subsidy programs and increasing penetration in smallholder farming, monohydrate zinc sulphate is projected to see sustained volume growth in the coming years.
By Applications Analysis
Micronutrient application leads with 41.2% share due to strong crop nutrition demand
In 2024, Micronutrient held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 41.2% share in the global zinc sulphate market by application. This segment’s growth is mainly driven by the rising need to correct zinc deficiency in crops, which directly affects yield and food quality. Zinc sulphate is widely used as a key micronutrient in fertilizers to enhance soil fertility and plant metabolism. Countries such as India and China have introduced national soil health programs that promote the use of micronutrients like zinc to improve crop productivity.
Small and marginal farmers are increasingly using zinc-based supplements for staple crops like rice, wheat, and maize. In 2025, the demand for zinc sulphate as a micronutrient is expected to remain strong, supported by government subsidies, educational outreach on nutrient management, and expansion of modern farming practices. The consistent need for high-yield agriculture to meet growing food demand is likely to keep micronutrient applications at the forefront of zinc sulphate usage globally.
By End-use Analysis
Agriculture leads with 44.9% share owing to high demand for zinc-based fertilizers
In 2024, Agriculture held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 44.9% share in the global zinc sulphate market by end-use. The dominance of this segment is largely driven by the widespread use of zinc sulphate as a micronutrient fertilizer in crop production. Zinc deficiency is a common issue in many agricultural soils, especially in regions across Asia and Africa. To address this, governments and agricultural agencies have promoted zinc-enriched fertilizers to improve crop yield and food quality.
Farmers increasingly rely on zinc sulphate to support the growth of cereals, pulses, and oilseeds, particularly in zinc-deficient areas. In 2025, agriculture is expected to maintain its leading role in zinc sulphate consumption, supported by national soil health programs, rising awareness among growers, and the push for higher agricultural productivity. The strong link between zinc nutrition and crop output continues to position agriculture as the most influential sector in the zinc sulphate market.
Key Market Segments
By Type
- Anhydrous
- Monohydrate
- Hexahydrate
- Heptahydrate
By Applications
- Micronutrient
- Nutritional Supplements
- Preservative
- Etching & Engraving
- Others
By End-use
- Agriculture
- Animal Nutrition
- Food & Nutrition
- Water Treatment
- Mining
- Pharmaceutical
- Others
Emerging Trends
Integration of Zinc Sulphate in Biofortification and Sustainable Agriculture
A notable trend in the Zinc Sulphate Concentrate (ZSC) industry is its increasing role in biofortification and sustainable agricultural practices. Biofortification involves enhancing the nutritional quality of food crops through agronomic practices, including the application of micronutrient fertilizers like zinc sulfate. This approach aims to address widespread micronutrient deficiencies in populations, particularly in developing regions.
In India, the government has recognized the importance of micronutrients in agriculture and has implemented various initiatives to promote their use. The Nutrient Based Subsidy (NBS) Scheme, for instance, provides subsidies on fertilizers, including zinc and boron, to encourage balanced fertilization and improve soil health. Despite these efforts, challenges remain in achieving widespread adoption due to factors such as inconsistent quality of fertilizers and limited awareness among farmers.
The application of zinc sulfate in biofortification has shown promising results. Field trials conducted by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) have demonstrated that the application of zinc sulfate-based formulations can improve maize yields by an average of 18%, highlighting the potential of zinc fertilizers in enhancing crop productivity and nutritional quality.
Drivers
Addressing Soil Zinc Deficiency through Government Initiatives
One of the primary drivers for the increased use of Zinc Sulphate Concentrates (ZSC) in India is the widespread deficiency of zinc in soils, which significantly impacts agricultural productivity. According to data from the Indian government’s Soil Health Card (SHC) program, approximately 39% of Indian soils are deficient in zinc, with variations across states ranging from 2% to 67%. This deficiency leads to reduced crop yields and nutritional quality, posing a challenge to food security.
In response to this issue, the Indian government has implemented several initiatives to promote the use of zinc-based fertilizers. Under the National Food Security Mission (NFSM), the government provides an additional subsidy of ₹500 per hectare for the application of micronutrients, including zinc fertilizers, to encourage their use among farmers . Additionally, the Nutrient Based Subsidy (NBS) Scheme, initiated in 2010, offers subsidies on fertilizers, including zinc sulfate, to make them more affordable for farmers .
These government-backed programs have led to a significant increase in the adoption of zinc sulfate fertilizers.
- For instance, in Andhra Pradesh, the state’s initiative to provide zinc sulfate at subsidized rates has resulted in the sale of nearly 14,000 metric tons of Zinc Sulfate 21%, covering approximately 300,000 hectares of agricultural land in a single year . This widespread application has not only improved soil health but also enhanced crop yields, demonstrating the effectiveness of such government interventions.
Restraints
High Production Costs and Supply Chain Challenges
One of the significant challenges hindering the growth of the Zinc Sulphate Concentrate (ZSC) industry in India is the high production cost, primarily driven by the fluctuating prices of raw materials and energy inputs. The cost of zinc, a critical raw material, is subject to global market dynamics, leading to price volatility. For instance, in August 2024, zinc sulphate prices in India’s domestic market were on the higher side due to persistent inquiries from the downstream agrochemical sector and rising costs from upstream zinc oxide . This volatility poses a challenge for manufacturers in maintaining consistent pricing and profitability.
The Indian government’s initiatives, such as the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for the chemical sector, aim to bolster domestic production capabilities and reduce import dependency. However, the high production costs associated with ZSC may impede the full realization of these objectives. To address this, there is a need for targeted policy interventions that focus on reducing input costs, promoting energy efficiency, and supporting technological advancements in the manufacturing processes of ZSC.
The demand for ZSC in India is on the rise, the high production costs and associated supply chain challenges remain significant restraining factors. Addressing these issues through strategic policy measures and industry innovations is crucial for the sustainable growth and competitiveness of the ZSC industry in India.
Opportunity
Expansion of Micronutrient Fertilizer Usage in Agriculture
A significant growth opportunity for the Zinc Sulphate Concentrate (ZSC) industry in India lies in the increased adoption of micronutrient fertilizers, particularly zinc sulfate, within the agricultural sector. This shift is driven by the recognition of widespread zinc deficiencies in Indian soils and the subsequent impact on crop yields and nutritional quality.
According to the Indian government’s Soil Health Card (SHC) program, approximately 39% of Indian soils are deficient in zinc, with variations across states ranging from 2% to 67% . This deficiency leads to reduced crop yields and nutritional quality, posing a challenge to food security. In response, the government has implemented several initiatives to promote the use of zinc-based fertilizers. Under the National Food Security Mission (NFSM), the government provides an additional subsidy of ₹500 per hectare for the application of micronutrients, including zinc fertilizers, to encourage their use among farmers.
These government-backed programs have led to a significant increase in the adoption of zinc sulfate fertilizers. For instance, in Andhra Pradesh, the state’s initiative to provide zinc sulfate at subsidized rates has resulted in the sale of nearly 14,000 metric tons of Zinc Sulfate 21%, covering approximately 300,000 hectares of agricultural land in a single year. This widespread application has not only improved soil health but also enhanced crop yields, demonstrating the effectiveness of such government interventions.
Furthermore, the government’s focus on soil health and micronutrient management has led to increased awareness among farmers about the importance of zinc in agriculture. Educational campaigns, workshops, and the distribution of Soil Health Cards have empowered farmers with knowledge to make informed decisions about fertilizer use, leading to more sustainable agricultural practices.
Regional Insights
Asia Pacific dominates with 47.3% share, valued at USD 0.8 billion in 2024
In 2024, the Asia Pacific (APAC) region held a dominant position in the global zinc sulphate market, accounting for 47.3% of the total market share and reaching a value of approximately USD 0.8 billion. This leadership is primarily attributed to the region’s large-scale agricultural activities, high prevalence of zinc-deficient soils, and strong government support for micronutrient fertilizer use. Countries such as India, China, Bangladesh, and Indonesia represent the major consumption hubs, where zinc sulphate is widely applied as a key input in crop nutrition programs targeting rice, wheat, and maize production.
India, in particular, has implemented extensive soil health initiatives under government-backed schemes like the “Soil Health Card” program, which promotes the balanced use of fertilizers, including zinc sulphate, to address micronutrient deficiencies. In China, agricultural policies continue to support the use of zinc-enriched fertilizers in grain-producing provinces, reinforcing steady demand. Additionally, the expanding animal feed industry in Southeast Asia has also contributed to the uptake of zinc sulphate as a nutritional additive.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Balaji Chemicals, based in Mumbai, India, specializes in manufacturing high-purity solvents, including HPLC-grade solvents. Their offerings cater to pharmaceutical, laboratory, and industrial applications, ensuring compliance with stringent quality standards. The company emphasizes innovation and quality control to meet the evolving needs of the chemical industry. Their product range includes solvents like methanol, acetone, and isopropanol, which are crucial for various analytical and synthesis processes.
Changsha Haolin Chemicals Co., Ltd., located in Changsha, China, manufactures a range of chemical products, including zinc sulfate, manganese sulfate, and sodium metabisulfite. With an annual production capacity of 10,000 tons, the company caters to industries such as agriculture, water treatment, and chemical manufacturing. Their focus on quality and customer satisfaction has established them as a reliable supplier in the chemical industry.
Clean Agro, based in Bangladesh, is a leading manufacturer of agricultural chemicals, including fertilizers, pesticides, and micronutrient supplements. Their product portfolio aims to enhance crop yield and quality, addressing the nutritional needs of plants. The company focuses on sustainable agriculture by providing solutions that promote soil health and reduce environmental impact. Clean Agro’s commitment to innovation and quality has made it a trusted name in the agricultural sector.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Balaji Chemicals
- Bohigh Group
- Changhsa Haolin Chemicals Co., Ltd
- China Bohigh
- Clean Agro
- FUJI KASEI CO., LTD.
- GRILLO-Werke AG
- Oasis Fine Chem
- Old Bridge Minerals Inc.
- Prakash Chemicals
- Redox
- Rongqing Chemical Co. Ltd
- Saba Chemical GmbH
- Tianjin Topfert Agrochemical Co
Recent Industry Developments
In FY2024, BSCL received environmental clearance for a ₹750 crore greenfield project in Solapur, Maharashtra, aimed at producing specialty chemicals like Hydrogen Cyanide (HCN), Sodium Cyanide (NaCN), and Ethylene Diamine Tetra Acetic Acid (EDTA).
In 2024 China Bohigh, maintained its position as China’s top zinc sulfate producer, with an annual production capacity of 120,000 metric tons. Their products are widely used across various sectors, including agriculture, animal nutrition, and industrial applications such as water treatment and rubber manufacturing.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 1.7 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 3.2 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 6.4% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Type (Anhydrous, Monohydrate, Hexahydrate, Heptahydrate), By Applications (Micronutrient, Nutritional Supplements, Preservative, Etching and Engraving, Others), By End-use (Agriculture, Animal Nutrition, Food and Nutrition, Water Treatment, Mining, Pharmaceutical, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Balaji Chemicals, Bohigh Group, Changhsa Haolin Chemicals Co., Ltd, China Bohigh, Clean Agro, FUJI KASEI CO., LTD., GRILLO-Werke AG, Oasis Fine Chem, Old Bridge Minerals Inc., Prakash Chemicals, Redox, Rongqing Chemical Co. Ltd, Saba Chemical GmbH, Tianjin Topfert Agrochemical Co Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Balaji Chemicals
- Bohigh Group
- Changhsa Haolin Chemicals Co., Ltd
- China Bohigh
- Clean Agro
- FUJI KASEI CO., LTD.
- GRILLO-Werke AG
- Oasis Fine Chem
- Old Bridge Minerals Inc.
- Prakash Chemicals
- Redox
- Rongqing Chemical Co. Ltd
- Saba Chemical GmbH
- Tianjin Topfert Agrochemical Co










