Global Term Repurchase Agreements Market Size, Share Report By Participant (Banks, Non-Banking Financial Institutions, Government Entities, Others), By Application (Liquidity Management, Collateralized Borrowing, Short-Term Funding, Others), By End-User (Institutional Investors, Corporates, Government Agencies, Others), By Regional Analysis, Global Trends and Opportunity, Future Outlook By 2025-2034
- Published date: Dec. 2025
- Report ID: 169016
- Number of Pages: 268
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
- Report Overview
- Key Takeaway
- Role of Generative AI
- Investment and Business Benefits
- U.S. Market Size
- Participant Analysis
- Application Analysis
- End-User Analysis
- Emerging Trends
- Growth Factors
- Key Market Segments
- Drivers
- Restraint
- Opportunities
- Challenges
- Key Players Analysis
- Future Outlook
- Recent Developments
- Report Scope
Report Overview
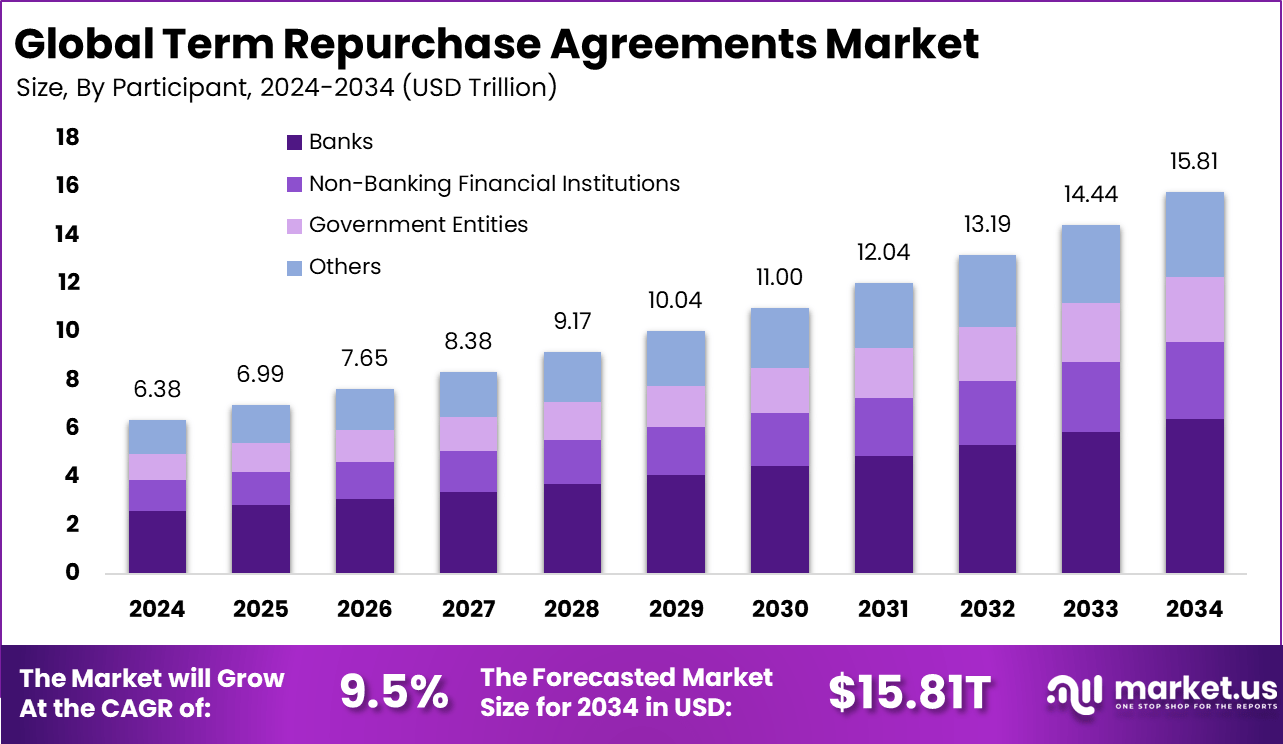
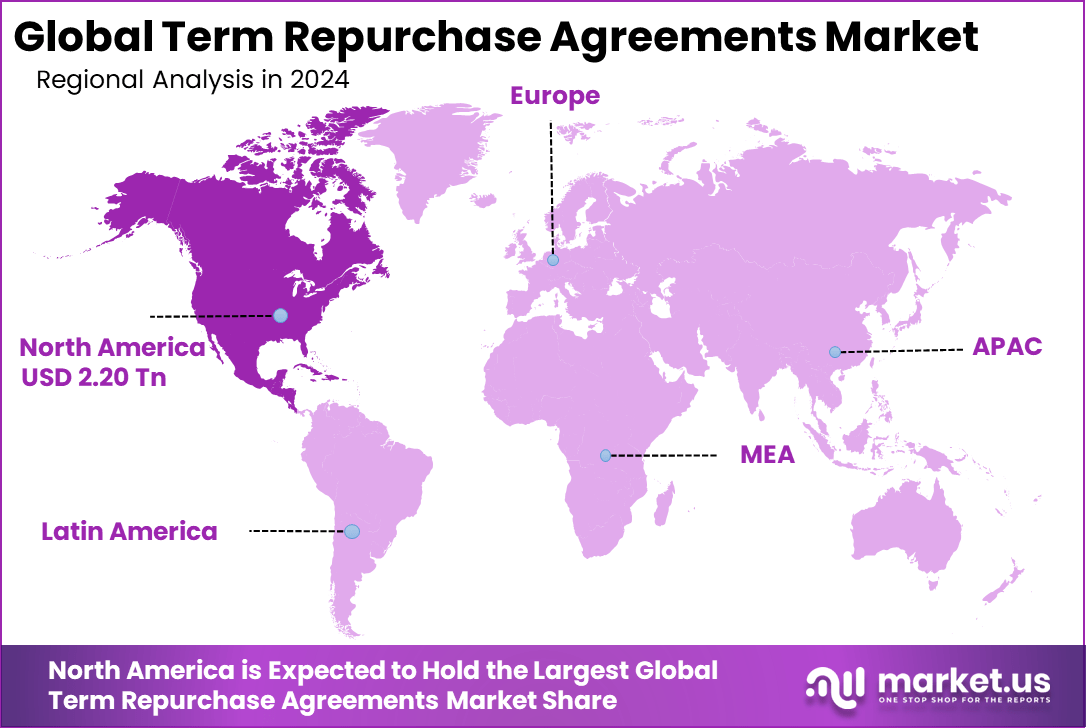
The Global Term Repurchase Agreements Market size is expected to be worth around USD 15.81 trillion by 2034, from USD 6.38 trillion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 9.5% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 34.5% share, holding USD 2.20 trillion in revenue.
The term repurchase agreements market has expanded as financial institutions increasingly rely on secured funding to support balance sheet operations over defined periods. Growth reflects rising trading volumes in the short term funding ecosystem, greater preference for collateral backed liquidity, and heightened focus on predictable financing. Term repos now serve as a key liquidity instrument for banks, dealers and institutional investors seeking stable funding rather than overnight borrowing.
The main factors driving term repurchase agreements stem from the need for quick access to cash and short-term funding. Banks use them to manage daily liquidity and meet reserve requirements, while government debt issuance encourages higher demand since market participants need funds to purchase these securities. Many term repos back dealers who handle bond inventories without committing excess capital.
The market for Term Repurchase Agreements is driven by banks and dealers needing quick cash against safe securities like government bonds. These deals let firms cover short-term gaps in funding without selling assets outright, keeping operations smooth during busy periods. Central banks use them, too, to adjust the money supply and support lending when reserves tighten.
For instance, in July 2025, Morgan Stanley kicked off a fresh $20 billion share repurchase program after passing Fed stress tests, while growing its overnight and open repo books as rivals pulled back. This flexibility in repo funding underscores the firm’s strength in managing term repo exposures amid market shifts.
Key Takeaway
- The banks segment accounted for 40.6% in 2024, showing that traditional financial institutions remain the core participants in term repo operations.
- Liquidity management represented 35.5%, highlighting how repo structures continue to support short-term funding stability for large market players.
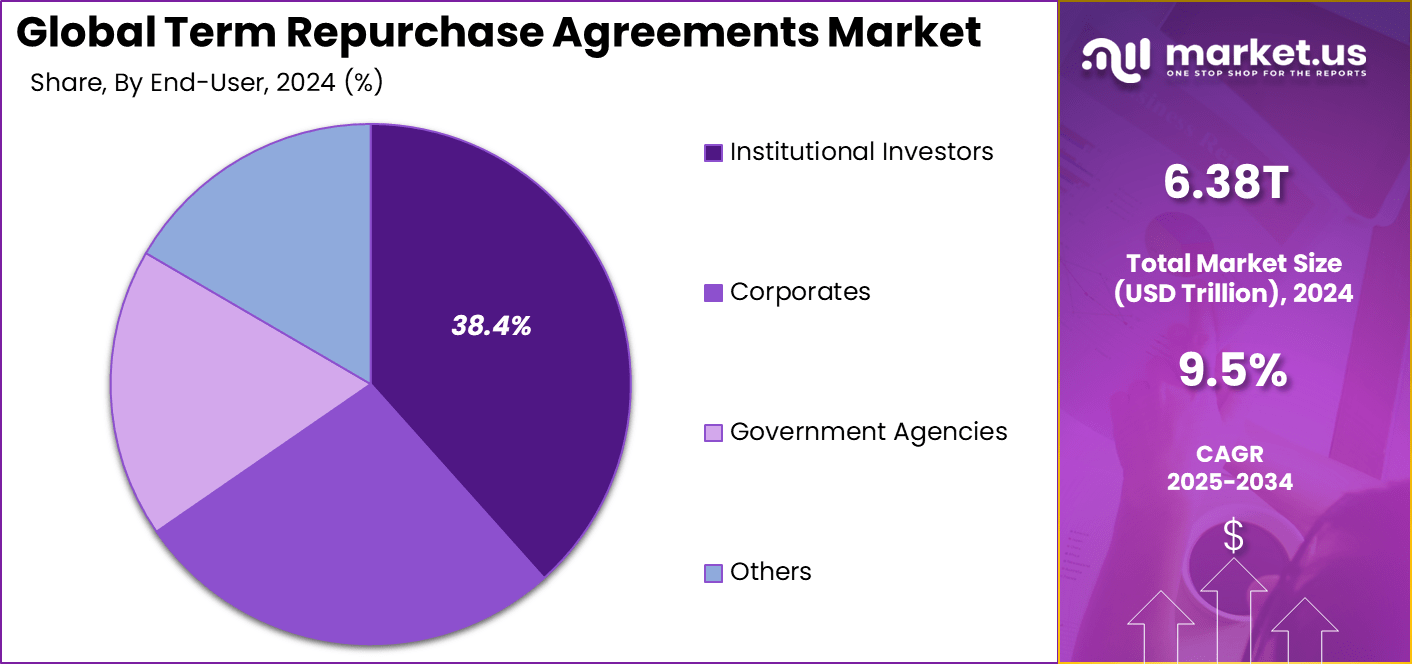
- Institutional investors held 38.4%, reflecting growing reliance on secured lending to optimize portfolio liquidity and reduce counterparty risk.
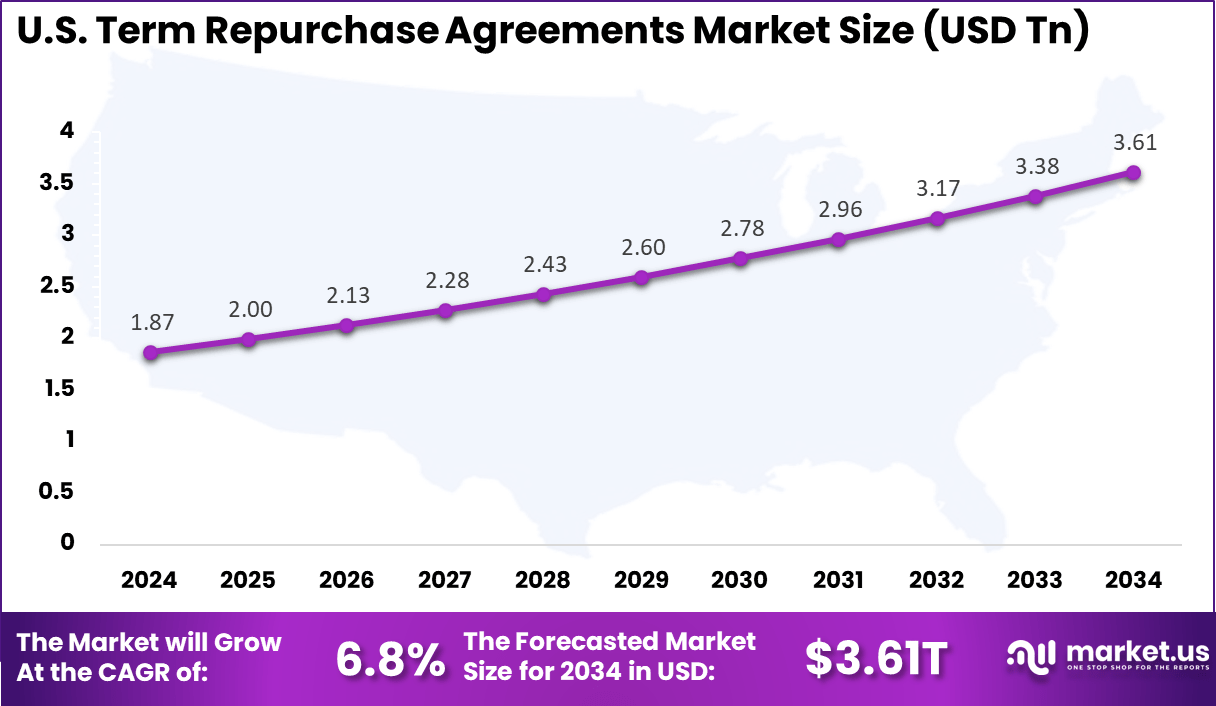
- The U.S. market reached USD 1.87 trillion in 2024 with a 6.8% CAGR, indicating strong activity in secured financing across money markets.
- North America captured 34.5%, supported by a deep repo ecosystem and mature financial infrastructure.
Role of Generative AI
Generative AI steps into term repurchase agreements by pulling together data fast from various sources, letting traders spot the best deals without hours of manual checks. Tools built on this tech now handle up to 70% more queries per day in treasury operations, cutting down errors that used to slow things down. This shift makes the process feel less like guesswork and more like having a sharp assistant always on call.
Accuracy jumps too when these AI systems learn from past repo contracts, extracting key terms like rates and dates with 85% better precision than older methods. Banks find it easier to check compliance and adjust positions on the fly, especially during busy market hours. Over time, this builds trust in handling bigger volumes without the usual headaches.
Investment and Business Benefits
Investment opportunities in term repurchase agreements attract investors looking for low-risk, short-term yield enhancement. Reverse repos allow market participants to earn interest while holding top-quality collateral, often government securities. The growing supply of sovereign debt worldwide creates more space for funding dealers and institutional investors via repo markets.
Investors designing automated trading strategies can exploit repo rate differentials and collateral selection to enhance returns. Overall, repos serve as a flexible tool for portfolio risk management and short-term investment diversification. Term repurchase agreements help businesses optimize liquidity and capital efficiency.
Borrowers can free up cash without selling assets permanently, smoothing out operational cash flow. The use of high-quality collateral enables firms to secure funds at lower costs than unsecured borrowing would demand. Lenders enjoy the benefit of collateral protection and portfolio diversification with easy access to funds when needed. For many companies, repos improve balance sheet management by aligning funding with short-term obligations and regulatory reserve requirements, thus reducing financial risk.
U.S. Market Size
The market for Term Repurchase Agreements within the U.S. is growing tremendously and is currently valued at USD 1.87 trillion, the market has a projected CAGR of 6.8%. The market is growing due to rising demand from hedge funds and asset managers for leverage in basis trades, which boosts borrowing volumes.
Increased Treasury issuance creates more collateral supply, drawing banks and dealers into matched-book intermediation to channel cash from investors to borrowers. Regulatory shifts toward repo clearing and quantitative tightening also lift activity by improving efficiency and dealer balance sheet use.
For instance, in October 2025, State Street executed live trades on its peer-to-peer repo platform supporting both overnight and term repurchase agreements between buy-side firms, with State Street guaranteeing qualifying trades. Headquartered in Boston, this innovation extends U.S. leadership in repo infrastructure by enhancing buy-side liquidity access and collateral flexibility.
In 2024, North America held a dominant market position in the Global Term Repurchase Agreements Market, capturing more than a 34.5% share, holding USD 2.20 trillion in revenue. This strength stems from deep, liquid financial markets supported by a high volume of government debt issuances supplying ample collateral.
Advanced clearing systems and regulatory frameworks in the region promote trust and efficiency in repo trading. Additionally, active participation from major banks, dealers, and institutional investors drives large volumes, making North America a central hub for short-term secured funding globally.
For instance, in July 2025, Morgan Stanley authorized a new $20 billion common share repurchase program following Federal Reserve stress tests, highlighting its strong capital position and active engagement in repo markets, where it grew overnight and open repo obligations significantly while rivals shifted to term repos. This reflects North American banks’ dominance in managing liquidity through sophisticated repo strategies.
Participant Analysis
In 2024, The Banks segment held a dominant market position, capturing a 40.6% share of the Global Term Repurchase Agreements Market. They rely on these short-term deals to cover daily cash shortfalls while holding onto their bond portfolios. This approach lets them keep trading active without forced sales during tight funding periods.
Their strong credit standing draws lenders who see banks as reliable partners in these trades. Banks often borrow to build up securities stock or meet daily reserve targets set by regulators. This steady demand from banks helps keep the overall repo market running smoothly.
For Instance, in August 2025, Bank of America took part in a $12.5 billion term repo for Mexico’s Pemex. The deal involved U.S. Treasuries as collateral for long-term financing. This highlights banks’ funding of large energy projects. Their involvement stabilized the borrower’s cash flow.
Application Analysis
In 2024, the Liquidity Management segment held a dominant market position, capturing a 35.5% share of the Global Term Repurchase Agreements Market. Companies and funds use these setups to bridge brief cash needs with the safety of pledged collateral. The quick turnaround makes it a practical choice for handling everyday fund flows.
Players park surplus funds in repos to pick up modest returns over short holds like overnight or a few days. Central banks step in to adjust money availability and calm stressed conditions. Such use grows sharper when markets face unexpected pressures.
For instance, in October 2025, Goldman Sachs forecasted RBI rate cuts tied to repo policy easing. They noted fast repo adjustments outside crisis times to aid credit flow. This view underscores the role of managing liquidity for central banks. It helps steady market funding rates.
End-User Analysis
In 2024, The Institutional Investors segment held a dominant market position, capturing a 38.4% share of the Global Term Repurchase Agreements Market. Groups like pension funds and insurers deploy spare cash here for secure short-term holds that fit their liquidity rules. The collateral focus keeps risks low on these quick placements.
They lean toward repos backed by prime assets such as government bonds for that extra safety layer. These users boost market turnover by funding dealers in need of cash. Their consistent participation adds real depth to trading flows.
For Instance, in September 2025, Goldman Sachs raised its India outlook linked to repo-driven credit growth. Institutional views see policy repos freeing bank lending capacity. Funds benefit from lower funding costs in such setups. This lifts portfolio returns amid easing.
Emerging Trends
Emerging trends include the growing shift toward digital collateral management, where automated platforms manage asset eligibility and margin requirements. Recent research shows that almost 48% of large financial firms are moving toward end to end digital repo systems to improve transparency and shorten settlement cycles. This transition supports more efficient operations and reduces the risk of collateral mismatches, which remains a common challenge in traditional repo processes.
Another trend shaping the market is the expansion of tri party repo infrastructures, driven by higher demand for centralised collateral handling. Industry data highlights that tri party platforms manage more than 70% of daily collateral allocations in some regions, reflecting stronger reliance on custodians to streamline operations. The increased use of digital dashboards and real time reporting tools reinforces this trend, allowing traders to manage exposures more accurately.
Growth Factors
Growth factors include tighter liquidity regulations, which have encouraged institutions to hold secure funding instruments such as term repos. Global regulatory surveys show that more than 58% of banks increased reliance on collateralised borrowing to meet liquidity coverage obligations. The predictable nature of term repos has supported funding stability, especially during periods of market volatility, and this consistency has increased adoption across key institutions.
Another factor driving expansion is the rise in collateral diversification, with more institutions using high quality securities to optimise funding costs. Reports indicate that collateral reuse practices have grown by nearly 40% in the past few years, which improves liquidity and enhances the efficiency of secured markets. As treasury teams adopt more sophisticated collateral strategies, term repos continue to gain appeal as a dependable funding tool.
Key Market Segments
By Participant
- Banks
- Non-Banking Financial Institutions
- Government Entities
- Others
By Application
- Liquidity Management
- Collateralized Borrowing
- Short-Term Funding
- Others
By End-User
- Institutional Investors
- Corporates
- Government Agencies
- Others
Regional Analysis and Coverage
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherlands
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of Latin America
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Drivers
Rising need for short term liquidity support among financial institutions
The demand for short term liquidity has increased as banks and market participants manage daily funding needs in a more cautious environment. Term repurchase agreements provide predictable funding for several days or weeks, which helps institutions maintain smooth operations without unexpected cash shortages. This reliability strengthens their use in treasury operations, especially when market conditions are tight or interest rate volatility is high.
Central banks have also continued to use term repo facilities to stabilise funding markets. Their actions create confidence and encourage greater activity in term repos as institutions seek efficient and secure liquidity sources. This steady demand helps maintain the growth trajectory of the market.
For instance, in June 2024, J.P. Morgan teamed up with Broadridge to speed up repo settlements using their JPM Coin token on a ledger platform. This lets firms handle cash and securities legs at the same time, making short-term funding quicker for daily needs. Banks gain better control over liquidity with trades settling in minutes instead of days.
Restraint
Sensitivity to interest rate shifts and regulatory constraints
The term repurchase agreements market is highly sensitive to rate movements because the cost of borrowing changes quickly when monetary policy tightens. When short term rates rise, borrowing through term repos becomes more expensive, reducing participation from smaller institutions. Fluctuations in collateral valuations also create uncertainties that can discourage consistent use.
Regulatory frameworks that tighten leverage ratios or collateral requirements further limit the ability of financial institutions to engage freely in repo transactions. Higher compliance costs and reporting rules can reduce flexibility, which slows overall market expansion and keeps some participants on the sidelines.
For instance, in October 2024, Bank of America noted repo rates climbing to 4.86% amid Treasury settlements, with banks holding back on lending due to balance sheet limits. Mid-month cash pulls strained middlemen, hinting at tighter rules curbing how much they can commit. This squeezed funding even as fed funds stayed steady.
Opportunities
Broader adoption of repos for secured financing and collateral optimisation
The growing emphasis on secured financing creates an important opportunity for term repos. As institutions shift from unsecured borrowing to collateral backed transactions, the use of government securities and high quality assets in term repos becomes more attractive. This move supports safer funding practices and increases the role of repos in long term balance sheet planning.
Institutional investors are also exploring more efficient ways to use their collateral portfolios. Term repos offer a structured method to generate short term cash without selling assets. This improves liquidity management and opens new revenue pathways for fund managers and other large asset holders.
For instance, in June 2024, J.P. Morgan’s tie-up with Broadridge brought JPM Coin into repo for atomic settlements across cash and bonds. This opens flexible cycles down to minutes, pulling in more players to cleared trades with less risk. Monthly volumes already top 1 trillion dollars, signaling wider adoption ahead.
Challenges
Operational risks and settlement complexities in multi party transactions
The term repo market faces operational challenges linked to settlement procedures, collateral transfers, and timing mismatches. Even small delays in clearing can create systemic concerns because transactions involve large values and time bound commitments. These operational gaps place pressure on financial institutions to maintain strong risk controls.
A further challenge arises from varying practices across regions and institutions. Differences in collateral standards, settlement cycles, and documentation make cross market transactions more complex. This lack of uniformity limits scalability and increases operational burdens for participants who rely on smooth and predictable settlement flows.
For instance, in October 2024, Bank of America flagged surging overnight repo overwhelming dealers, with rates spiking on high Treasury holdings post-selloffs. Balance sheet strains from collateral calls hit hard at quarter ends, forcing asset cuts. Cash shortages amplified the pressure across the 4 trillion dollar market.
Key Players Analysis
J.P. Morgan, Goldman Sachs, Bank of America, Citigroup, and Morgan Stanley lead the term repurchase agreements market with extensive liquidity networks and strong balance-sheet capacity. Their operations support short- to medium-term funding for institutional investors, broker-dealers, and hedge funds. These firms focus on collateral quality, efficient pricing, and stable term structures.
Barclays, Deutsche Bank, UBS, Credit Suisse, BNP Paribas, HSBC, and Societe Generale strengthen the competitive landscape through active participation in cross-border repo transactions. Their platforms support diverse collateral types, including government securities and high-grade corporate bonds. These institutions prioritize risk management, regulatory alignment, and operational efficiency.
Wells Fargo, Nomura, Mizuho, SMBC, Royal Bank of Canada, ING, State Street, BNY Mellon, and other participants broaden the market with custodial repo services, triparty arrangements, and specialized collateral programs. Their offerings help asset managers, pension funds, and sovereign institutions optimize cash management and enhance portfolio liquidity. These firms focus on transparency, settlement efficiency, and strong collateral governance.
Top Key Players in the Market
- J.P. Morgan
- Goldman Sachs
- Bank of America
- Citigroup
- Morgan Stanley
- Barclays
- Deutsche Bank
- UBS
- Credit Suisse
- BNP Paribas
- HSBC
- Societe Generale
- Wells Fargo
- Nomura Holdings
- Mizuho Financial Group
- Sumitomo Mitsui Banking Corporation (SMBC)
- Royal Bank of Canada (RBC)
- ING Group
- State Street Corporation
- BNY Mellon
- Others
Future Outlook
The future outlook suggests sustained growth as financial institutions strengthen their liquidity frameworks and adopt more advanced digital systems. The combination of AI powered analytics, automated settlement, and broader regulatory alignment is expected to improve transparency and reduce operational risks.
As markets move toward faster settlement cycles and more structured collateral reporting, term repurchase agreements are positioned to play a central role in funding operations across banks, asset managers, and institutional investors.
New opportunities lie in:
- AI driven collateral optimisation platforms
- Digital repo settlement solutions
- Real time liquidity forecasting tools
- Tokenised collateral ecosystems
- Market intelligence platforms for repo risk monitoring
Recent Developments
- In April 2025, Bank of America announced the redemption of €1.25 billion principal amount of its senior notes due in 2026, reflecting ongoing debt management related to its repo and securities financing operations. This action is part of its broader capital strategy to optimize funding costs while maintaining liquidity in the term repurchase agreements market.
- In August 2025, Pemex closed a $12.5 billion repo and securities lending transaction involving Bank of America, Citigroup, and J.P. Morgan. The sizable repo deal demonstrates the use of term repurchase agreements in large-scale sovereign-backed financing, with scheduled amortizations through August 2030, reflecting the long-term nature of some repo market instruments.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 6.3 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 15.8 Bn CAGR(2025-2034) 9.5% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue forecast, AI impact on Market trends, Share Insights, Company ranking, competitive landscape, Recent Developments, Market Dynamics and Emerging Trends Segments Covered By Participant (Banks, Non-Banking Financial Institutions, Government Entities, Others), By Application (Liquidity Management, Collateralized Borrowing, Short-Term Funding, Others), By End-User (Institutional Investors, Corporates, Government Agencies, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of Latin America; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape J.P. Morgan, Goldman Sachs, Bank of America, Citigroup, Morgan Stanley, Barclays, Deutsche Bank, UBS, Credit Suisse, BNP Paribas, HSBC, Societe Generale, Wells Fargo, Nomura Holdings, Mizuho Financial Group, Sumitomo Mitsui Banking Corporation (SMBC), Royal Bank of Canada (RBC), ING Group, State Street Corporation, BNY Mellon, Others Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three license to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Term Repurchase Agreements MarketPublished date: Dec. 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Term Repurchase Agreements MarketPublished date: Dec. 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- J.P. Morgan
- Goldman Sachs
- Bank of America
- Citigroup
- Morgan Stanley
- Barclays
- Deutsche Bank
- UBS
- Credit Suisse
- BNP Paribas
- HSBC
- Societe Generale
- Wells Fargo
- Nomura Holdings
- Mizuho Financial Group
- Sumitomo Mitsui Banking Corporation (SMBC)
- Royal Bank of Canada (RBC)
- ING Group
- State Street Corporation
- BNY Mellon
- Others










