Global Tamarind Gum Derivatives Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Type (Carboxymethyl Tamarind Gum (CMT), Hydroxypropyl Tamarind Gum (HPTG), Oxidized Tamarind Gum, Others), By End Use (Food Manufacturers, Textile Processors, Cosmetics Companies, Pharmaceutical Firms, Specialty Chemical Producers, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Jan 2026
- Report ID: 172698
- Number of Pages: 236
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
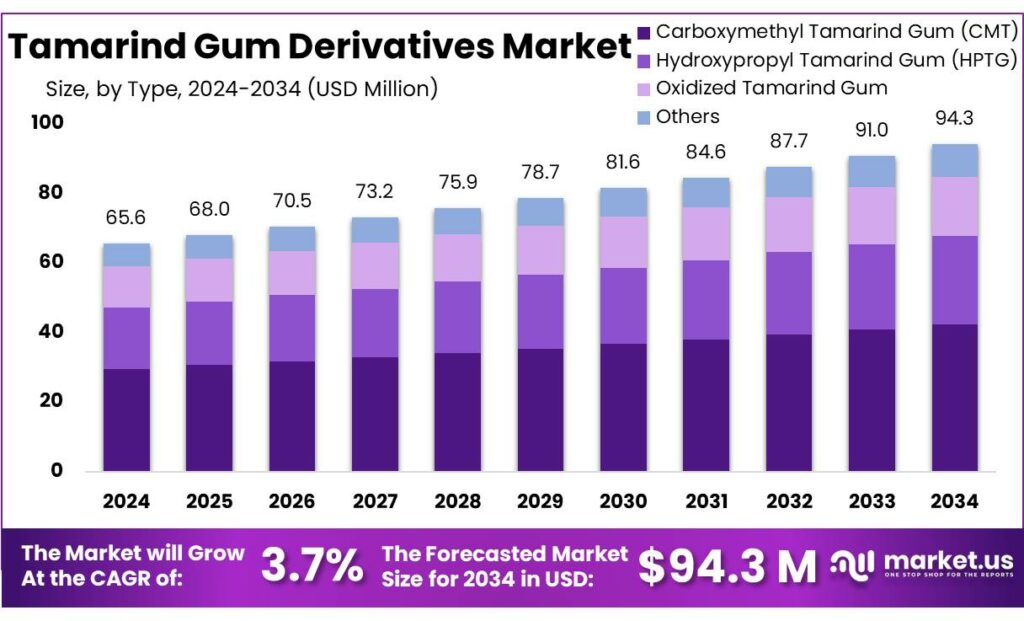
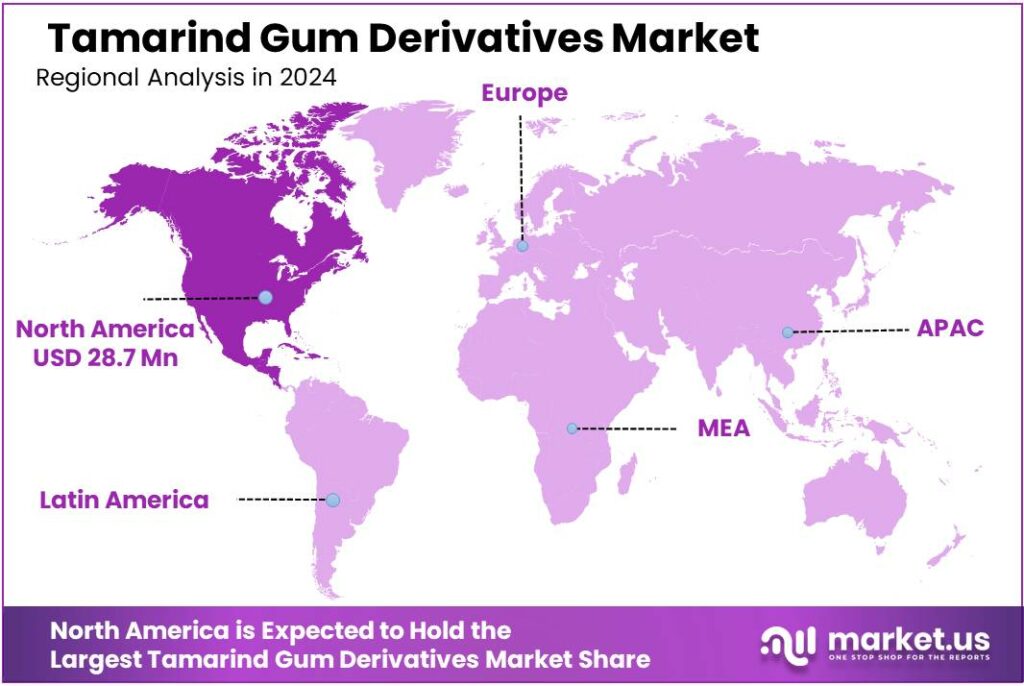
The Global Tamarind Gum Derivatives Market size is expected to be worth around USD 94.3 Million by 2034, from USD 65.6 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 3.7% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024 North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.8% share, holding USD 28.7 Million in revenue.
Tamarind gum derivatives are industrial hydrocolloids made largely from tamarind seed—processed into tamarind seed polysaccharide (TSP / INS 437) and related modified grades used to control viscosity, suspension, mouthfeel, and stability in formulated products. Their value proposition is rooted in feedstock efficiency: the tamarind pod is typically ~25–40% seed, creating a meaningful by-product stream for ingredient recovery rather than disposal.
From an industrial scenario standpoint, food and beverage remains the most regulation-driven demand center. Under the Codex General Standard for Food Additives (GSFA), tamarind seed polysaccharide (INS 437) sits in Table 3, meaning it is permitted across many foods at GMP levels, which materially de-risks adoption for exporters supplying multi-market formulations.
Key driving factors therefore cluster around formulation consistency in mass food manufacturing, “plant-derived” texture systems that can support cleaner label positioning versus some synthetic stabilizer systems, and waste-to-value economics by upgrading seed streams into higher-margin ingredients. In India specifically, policy support for organized processing capacity also reinforces ingredient pull-through: the Government of India’s MoFPI PLISFPI carries an outlay of ₹10,900 crore and had 171 applicants enrolled, improving the investment climate for scalable processing, quality systems, and export-ready manufacturing practices that indirectly benefit hydrocolloid supply chains.
Commercial demand is being pulled by formulation pressure to deliver stable textures with fewer “synthetic-sounding” additives, plus operational needs for tolerance to acids, salts, and thermal steps. The U.S. FDA GRAS Notice 503 covers tamarind seed polysaccharide used as a thickener/stabilizer/emulsifier/ gelling agent; it was filed on Mar 5, 2014 and closed on Aug 12, 2014, which de-risks adoption for multinational food portfolios. In the USDA technical review, intended use levels are cited across categories at 0.2–1.5% of product composition, showing that relatively low inclusion rates can deliver measurable rheology outcomes—an attractive lever when brands are also managing cost-in-use and label space.
Commercial pull is reinforced by the size and volatility of global food supply chains, where formulation efficiency and ingredient performance matter. FAO reports global production of primary crops at 9.9 billion tonnes in 2023, indicating the scale of raw inputs feeding processed and formulated foods where hydrocolloids are routinely used to manage texture and shelf stability. On the demand-and-cost side, the FAO Food Price Index averaged 125.1 points in November 2025, highlighting persistent pricing pressure that incentivizes processors to optimize yield, reduce waste, and stabilize quality.
Key Takeaways
- Tamarind Gum Derivatives Market size is expected to be worth around USD 94.3 Million by 2034, from USD 65.6 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 3.7%.
- Carboxymethyl Tamarind Gum (CMT) held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 45.8% share.
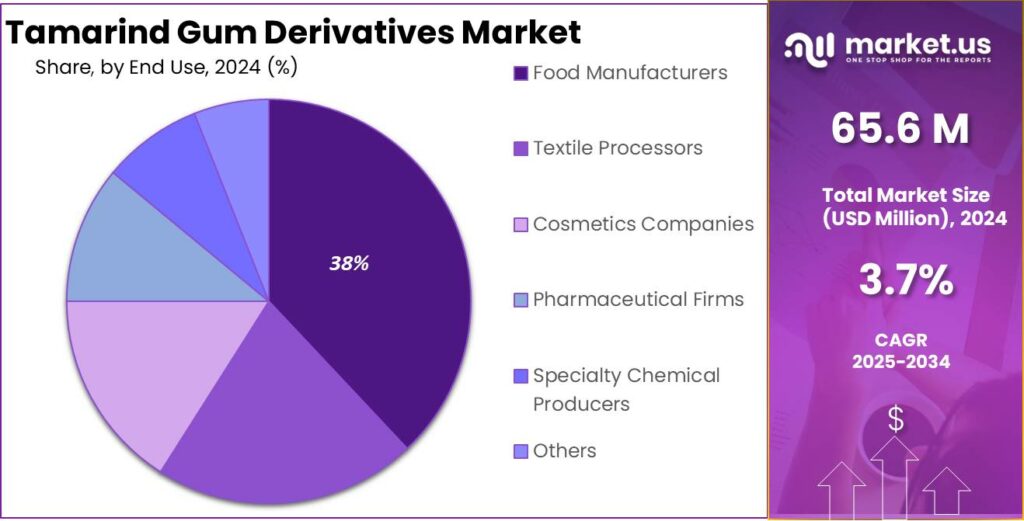
- Food Manufacturers held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.5% share.
- North America region emerged as a dominant market for tamarind gum derivatives, capturing 43.8% share and generating around USD 28.7 million.
By Type Analysis
Carboxymethyl tamarind gum leads with a 45.8% share, supported by its wide industrial usability and stable performance.
In 2024, Carboxymethyl Tamarind Gum (CMT) held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 45.8% share in the tamarind gum derivatives market, mainly due to its strong thickening, binding, and stabilizing properties across multiple end-use industries. CMT was widely used in food processing, pharmaceuticals, textiles, and personal care applications, where consistent viscosity and water solubility are critical. During 2024, demand remained steady as manufacturers preferred CMT for its natural origin and functional reliability in clean-label and eco-friendly formulations.
Moving into 2025, usage continued to expand, supported by increasing preference for plant-based hydrocolloids and biodegradable additives. The segment’s leadership was further reinforced by its cost efficiency, ease of modification, and suitability for both industrial and consumer-grade applications, making CMT a preferred derivative within the tamarind gum value chain.
By End Use Analysis
Food manufacturers lead with a 38.5% share, driven by rising demand for natural thickeners and stabilizers.
In 2024, Food Manufacturers held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.5% share in the tamarind gum derivatives market, supported by the growing use of natural hydrocolloids in processed and packaged foods. Tamarind gum derivatives were widely applied as thickening, gelling, and texturizing agents in sauces, bakery items, confectionery, and ready-to-eat products, where texture stability and shelf-life improvement are essential.
Food producers increasingly favored these derivatives due to their plant-based origin and compatibility with clean-label formulations. Entering 2025, demand remained strong as manufacturers continued to replace synthetic additives with naturally sourced alternatives. The segment’s dominance was reinforced by consistent performance across temperature variations and its ability to enhance mouthfeel, making tamarind gum derivatives a reliable ingredient choice for large-scale food manufacturing operations.
Key Market Segments
By Type
- Carboxymethyl Tamarind Gum (CMT)
- Hydroxypropyl Tamarind Gum (HPTG)
- Oxidized Tamarind Gum
- Others
By End Use
- Food Manufacturers
- Textile Processors
- Cosmetics Companies
- Pharmaceutical Firms
- Specialty Chemical Producers
- Others
Emerging Trends
Shelf-life focused formulation to meet waste targets
A clear latest trend around tamarind gum derivatives is that food makers are putting shelf life and physical stability at the center of formulation decisions, not as a “nice extra,” but as a response to waste targets and tighter factory economics. The reason is straightforward: products are often thrown away because they separate, weep, settle, or look “wrong,” even before safety becomes an issue. The UN Environment Programme estimates that in 2022 the world generated 1.05 billion tonnes of food waste across retail, food service, and households—about 19% of food available to consumers. It also puts the global average at 132 kg per person in 2022, with 60% of waste from households, 28% from food service, and 12% from retail.
Policy is adding momentum, especially in Europe. The European Commission states that the 2025 amendment of the Waste Framework Directive introduced binding food waste reduction targets to reach by 2030. Member States are required to reduce food waste by 10% in processing and manufacturing, and by 30% per capita across retail and consumption, measured against the annual average waste generated between 2021 and 2023.
That is where tamarind gum derivatives increasingly fit into “modern” texture systems. Tamarind seed polysaccharide is already positioned in global food standards as INS 437 under Codex, with use permitted under GMP conditions for relevant food categories. In parallel, the WHO/FAO JECFA database lists an evaluation year of 2017 and an ADI of “not specified,” noting no toxicity concerns in long-term studies that would block normal use.
Cost pressure is reinforcing the trend. FAO reported the Food Price Index averaged 125.1 points in November 2025, showing that ingredient price stress is still part of the operating environment for food producers. In that setting, stability ingredients that protect yield, reduce rework, and prevent customer complaints become easier to justify. In simple terms, the latest trend is a shift from “texture as a sensory feature” to “texture as waste prevention,” and tamarind gum derivatives benefit because they sit at the intersection of recognized standards and practical stability gains.
Drivers
Volatile food costs are pushing smarter, more reliable formulation
One major driving factor for tamarind gum derivatives is the food industry’s need to hold texture and stability steady while ingredient costs and supply conditions keep shifting. When prices swing, processors become less tolerant of batch failures, watery separation, grainy mouthfeel, or short shelf life. The context is real: the FAO Food Price Index averaged 125.1 points in November 2025, showing that price volatility is not a short-term story for manufacturers buying sugar, dairy inputs, oils, and cereals.
The scale of global food throughput strengthens this push for “right-first-time” production. FAO reports that global production of primary crops reached 9.9 billion tonnes in 2023, an indicator of how large the raw-material base is for processed foods, beverages, sauces, bakery items, and ready-to-eat categories that depend on texture systems.
A second layer to this same driving factor is that manufacturers prefer ingredients with clear, recognized use pathways. Tamarind seed polysaccharide is listed in Codex GSFA (INS 437) with use under GMP conditions for relevant food categories, which helps suppliers and buyers align on globally understood specifications and application boundaries. In addition, the WHO/FAO JECFA database records an evaluation year of 2017 for tamarind seed polysaccharide and lists its functional classes as emulsifier, gelling agent, stabilizer, and thickener, which supports confidence when companies scale derivatives for similar functional outcomes.
- Government- and UN-linked outlook data also reinforces why processors keep investing in formulation resilience. FAO’s November 2025 update points to world trade in cereals in 2025/26 rising 3.3% to 500.6 million tonnes, while global cereal stocks are forecast to expand 6.5% to 925.5 million tonnes.
Restraints
Regulatory re-checks and documentation burden can slow adoption
A major restraining factor for tamarind gum derivatives is the compliance workload that comes with selling “one ingredient” into many rulebooks. Food manufacturers like ingredients that behave the same way in every plant and every country. In reality, stabilizers and thickeners often sit under active regulatory review, and that forces suppliers to keep updating data, specs, and dossiers. In the European Union, the European Commission explains that food additives permitted before 20 January 2009 must go through a new risk assessment by EFSA.
EFSA itself signals the size of the task. On its public topic page, EFSA states it has so far re-evaluated more than 70% of the 315 food additives that were approved in the EU before 20 January 2009, and it notes timelines slipped because of the volume of work and requests for extra data. For a buyer, this creates hesitation: procurement teams do not want surprises that trigger relabeling, reformulation, or a second round of internal approvals. Even when an ingredient remains acceptable, the “paperwork risk” can be enough to delay switching from a familiar hydrocolloid to a newer tamarind-based derivative.
This is not about tamarind seed polysaccharide being unknown. In fact, internationally it is well characterized: the JECFA database lists tamarind seed polysaccharide with CAS 39386-78-2, and shows an evaluation year of 2017 with functional classes including emulsifier, gelling agent, stabilizer, and thickener. The restraint comes from the step after that: companies still have to map these global references to local rules, customer standards, and retailer requirements—often country by country.
The compliance challenge becomes sharper because supply chains for tamarind-based inputs sit close to agricultural realities. India is a major hub for tamarind as a crop and spice ingredient, and government-linked industry material highlights the broader scale: India’s total spices production is cited as 511.81 thousand tonnes, across 260.16 thousand hectares, with tamarind listed among key spices. When raw material markets are seasonal and fragmented, users worry about batch-to-batch variation in viscosity and performance—exactly the properties that derivatives are meant to control.
Opportunity
Cutting food waste with longer shelf life and better stability
One major growth opportunity for tamarind gum derivatives sits in a place food companies talk about every day, but rarely celebrate: stopping good food from turning into waste. Governments and global food bodies are now treating waste as a measurable target, not just a “nice-to-fix” issue. The UN’s Sustainable Development Goal 12.3 sets a clear direction: by 2030, the world should halve per-capita global food waste at retail and consumer levels and also reduce losses along supply chains.
The size of the waste problem is also hard to ignore. UNEP’s Food Waste Index Report 2024 estimates that in 2022 the world generated 1.05 billion tonnes of food waste, which equals 19% of food available to consumers. The same reporting highlights a global average of 132 kg per capita wasted in 2022, with households responsible for 60%, food service 28%, and retail 12%. Those numbers explain why companies are investing in “quiet improvements” like better texture systems and stronger stability—because waste often begins with quality loss: separation, weeping, settling, and a product that looks off even when it is still safe.
Supply-chain loss data adds another layer of urgency. FAO’s policy and platform pages summarize that 13.2% of food is lost after harvest and before retail, and then 19% more is wasted at retail, food service, and household levels. FAO has also cited the earlier baseline that around 14% of the world’s food is lost between harvest and retail, valued at about $400 billion per year.
Europe is moving from messaging to enforcement, which can accelerate adoption of ingredients that help prevent waste. The European Commission notes that the 2025 amendment to the Waste Framework Directive introduced binding food waste reduction targets for Member States to achieve by 2030. When targets become binding, food companies operating in those markets tend to harden their internal KPIs, pushing more R&D spend into stability, shelf-life, and packaging/texture combinations that reduce returns and write-offs.
Regional Insights
North America leads with a 43.8% share and USD 28.7 million in 2024, showing strong growth for natural tamarind gum derivatives.
In 2024, the North America region emerged as a dominant market for tamarind gum derivatives, capturing 43.8% share and generating around USD 28.7 million, driven by increasing demand for clean-label and plant-based stabilisers across food, beverage, pharmaceuticals, and personal care sectors. Manufacturers in the United States and Canada intensified the use of tamarind gum derivatives in bakery, confectionery, and dairy alternatives as consumers sought natural thickeners that align with wellness and sustainability trends. Clean-label formulation adoption grew by nearly 20% in food processing, reflecting heightened consumer interest in transparency and ingredient simplicity.
Pharmaceutical and cosmetic segments also reported rising incorporation of these derivatives for natural excipient properties and moisturising functions. The mature retail infrastructure and strong regulatory compliance environment supported broader product availability through supermarkets, speciality ingredient distributors, and online channels, facilitating market access for both domestic and imported tamarind gum derivatives. Challenges such as import dependence and logistical costs resulted in a modest price premium, but did not dampen overall demand momentum.
The regional market sustained positive growth as clean-label initiatives expanded and broader industrial applications emerged, supported by increasing investments in functional ingredient development. North America’s performance was further reinforced by heightened consumer education around the benefits of plant-based hydrocolloids and natural emulsifiers, positioning the region as a key growth engine within the global tamarind gum derivatives landscape.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Chemtotal Labs: Chemtotal Labs operates as a chemicals and speciality excipients supplier, offering tamarind gum derivatives used in food processing, cosmetics, and textile industries. With distribution networks covering over 12 regions by 2024, the company emphasised product quality, competitive pricing, and technical support, enabling formulators to adopt natural hydrocolloid solutions in clean-label and functional ingredient applications.
Wonyoung Industrial: Wonyoung Industrial Co., Ltd. is a South Korea-based manufacturer of gums and cellulose derivatives, including tamarind gum products tailored for food and industrial uses. By 2024, the firm had expanded exports to 20+ markets in Asia, Europe, and the Americas, focusing on product consistency and global partnerships that enhance supply chain reliability for tamarind-based hydrocolloids.
Adachi Group: Adachi Group is a Japan-centred chemicals and food ingredient company providing natural gum derivatives for food manufacturers and industrial applications. With operations in 10+ countries by 2024, the company emphasised research-based product formulations and quality control standards, supporting broad use of tamarind gum and modified derivatives in texture enhancement and stabilisation.
Top Key Players Outlook
- JD Gums & Chemicals
- Chemtotal Labs
- Wonyoung Industrial
- Adachi Group
- Lucid Colloids
- Indian Hydrocolloids
- Socius Ingredients
- Shree Krishna Industries
- Altrafine Gums
Recent Industry Developments
Chemtotal Labs Pvt. Ltd., product line lists tamarind gum derivatives such as D.Col – EcoPol XGD, EcoPol XGDD and CMHPTKP, each with specified viscosities and quality measures like 98–99 % passing 100 mesh and moisture limits between 5–8 % as part of standard technical specifications for industrial gum powders.
By 2024, Wonyoung Industrial was recognized in industry listings alongside other key players such as JD Gums & Chemicals and Adachi Group in the global tamarind gum derivatives landscape, showing its presence in a market that is projected to be worth around USD 68.8 million in 2025.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 65.6 Mn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 94.3 Mn CAGR (2025-2034) 3.7% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Type (Carboxymethyl Tamarind Gum (CMT), Hydroxypropyl Tamarind Gum (HPTG), Oxidized Tamarind Gum, Others), By End Use (Food Manufacturers, Textile Processors, Cosmetics Companies, Pharmaceutical Firms, Specialty Chemical Producers, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape JD Gums & Chemicals, Chemtotal Labs, Wonyoung Industrial, Adachi Group, Lucid Colloids, Indian Hydrocolloids, Socius Ingredients, Shree Krishna Industries, Altrafine Gums Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Tamarind Gum Derivatives MarketPublished date: Jan 2026add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Tamarind Gum Derivatives MarketPublished date: Jan 2026add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- JD Gums & Chemicals
- Chemtotal Labs
- Wonyoung Industrial
- Adachi Group
- Lucid Colloids
- Indian Hydrocolloids
- Socius Ingredients
- Shree Krishna Industries
- Altrafine Gums













