Global Synchronizing Systems Market By Component (Hardware, Software, Services ), By Technology (GNSS-based, Network-based Synchronization, Others), By Precision (Phase & Time Synchronization, Frequency Synchronization, Time-of-Day Synchronization), By End-User Industry (Telecommunications, Power & Energy, Others), By Regional Analysis, Global Trends and Opportunity, Future Outlook By 2025-2034
- Published date: Jan. 2026
- Report ID: 172572
- Number of Pages: 389
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
- Report Overview
- Top Market Takeaways
- Drivers Impact Analysis
- Risk Impact Analysis
- Restraint Impact Analysis
- Investor Type Impact Matrix
- Component Analysis
- Technology Analysis
- Precision Analysis
- End-User Industry Analysis
- Investor Type Impact Matrix
- Technology Enablement Analysis
- Key Reasons for Adoption
- Benefits
- Usage
- Emerging Trends
- Growth Factors
- Key Market Segments
- Regional Analysis
- Emerging Trends
- Growth Factors
- Opportunity
- Challenge
- Competitive Analysis
- Future Outlook
- Report Scope
Report Overview
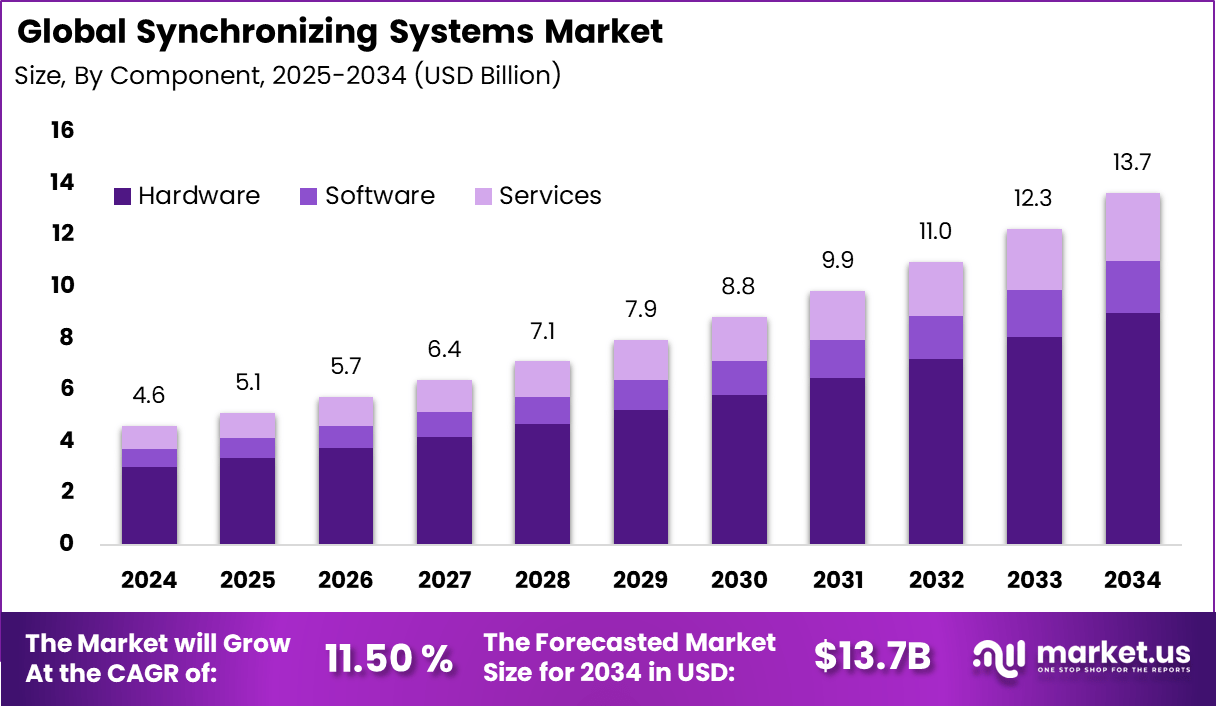
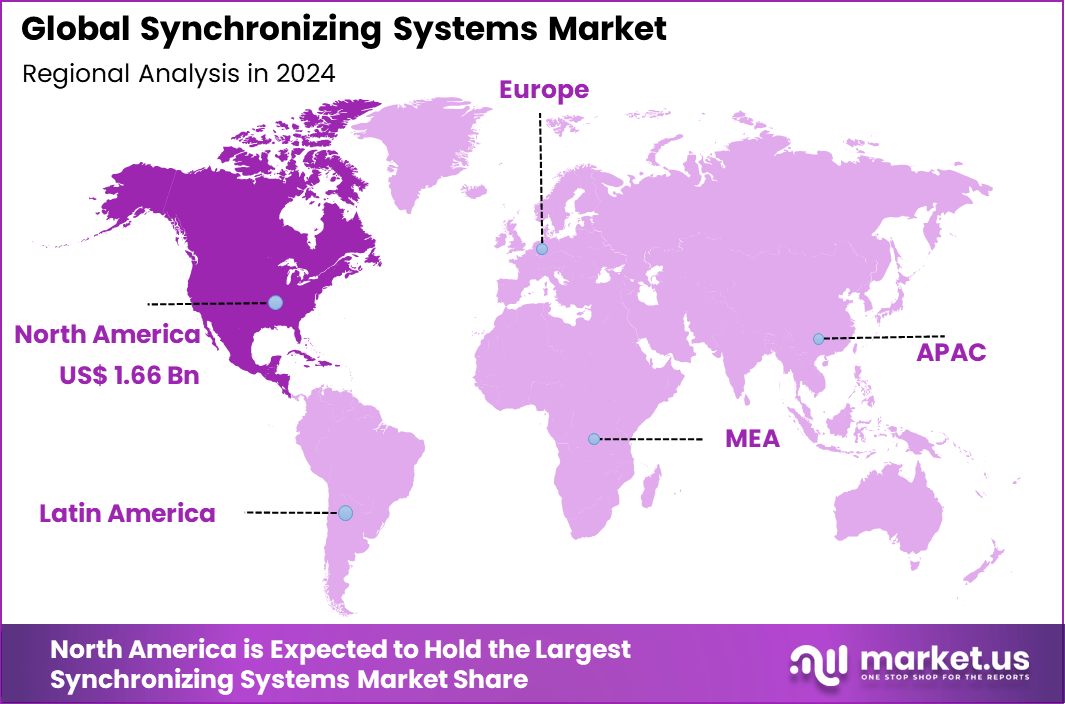
The Global Synchronizing Systems Market generated USD 4.6 billion in 2024 and is predicted to register growth from USD 5.1 billion in 2025 to about USD 13.7 billion by 2034, recording a CAGR of 11.50% throughout the forecast span. In 2024, North America held a dominan market position, capturing more than a 36.3% share, holding USD 1.66 Billion revenue.
The synchronizing systems market refers to solutions that ensure precise coordination of electrical, mechanical, or digital signals across machines, power systems, and networked equipment. These systems are used to align frequency, phase, timing, and voltage between multiple sources or components to enable stable and efficient operation. Synchronizing systems are widely applied in power generation, industrial automation, telecommunications, transportation, and data centers.
Market development has been driven by increasing system complexity and interconnectivity across industries. Modern infrastructure relies on tightly coordinated operations to avoid failures, inefficiencies, or safety risks. Synchronizing systems provide the control and monitoring needed to manage these interactions reliably. As automation and digitalization expand, the importance of accurate synchronization continues to grow.
One major driving factor of the synchronizing systems market is the expansion of distributed power generation and grid interconnection. Power plants, renewable energy sources, and backup generators must be synchronized before connection to electrical grids. Synchronizing systems ensure stable integration by matching critical electrical parameters. This requirement has increased demand across utility and energy sectors.
Demand for synchronizing systems is influenced by rising investments in critical infrastructure and industrial modernization. Industries with continuous operations, such as oil and gas, chemicals, and metals, rely on synchronization to maintain process stability. Even minor timing discrepancies can cause costly downtime in these environments. As uptime becomes a priority, demand for reliable synchronization solutions increases.
Top Market Takeaways
- By component, hardware took 65.7% of the synchronizing systems market, providing clocks, GPS receivers, and timing devices for precise operations.
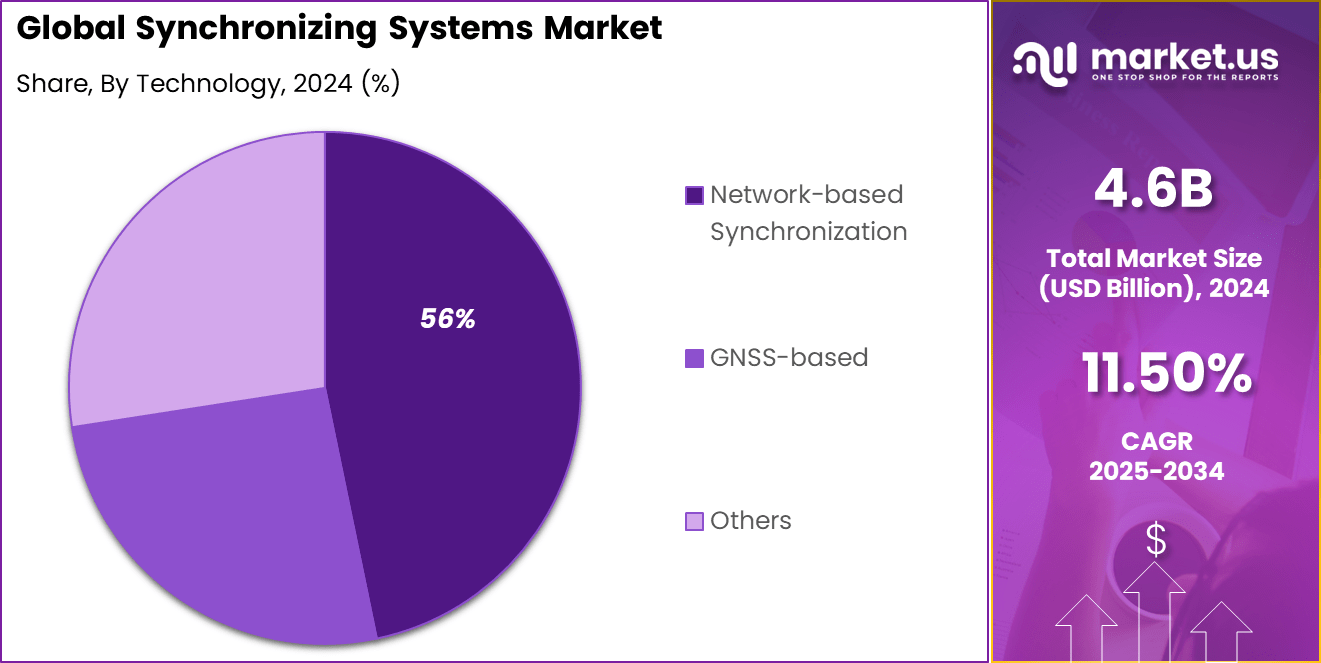
- By technology, network-based solutions held 56.2% share, using PTP and NTP protocols for distributed timing across telecom and data centers.
- By precision, phase and time synchronization captured 52.4%, essential for 5G base stations and financial trading platforms.
- By end-user industry, telecommunications led with 44.9%, driven by 5G rollout needing microsecond accuracy between cell sites.
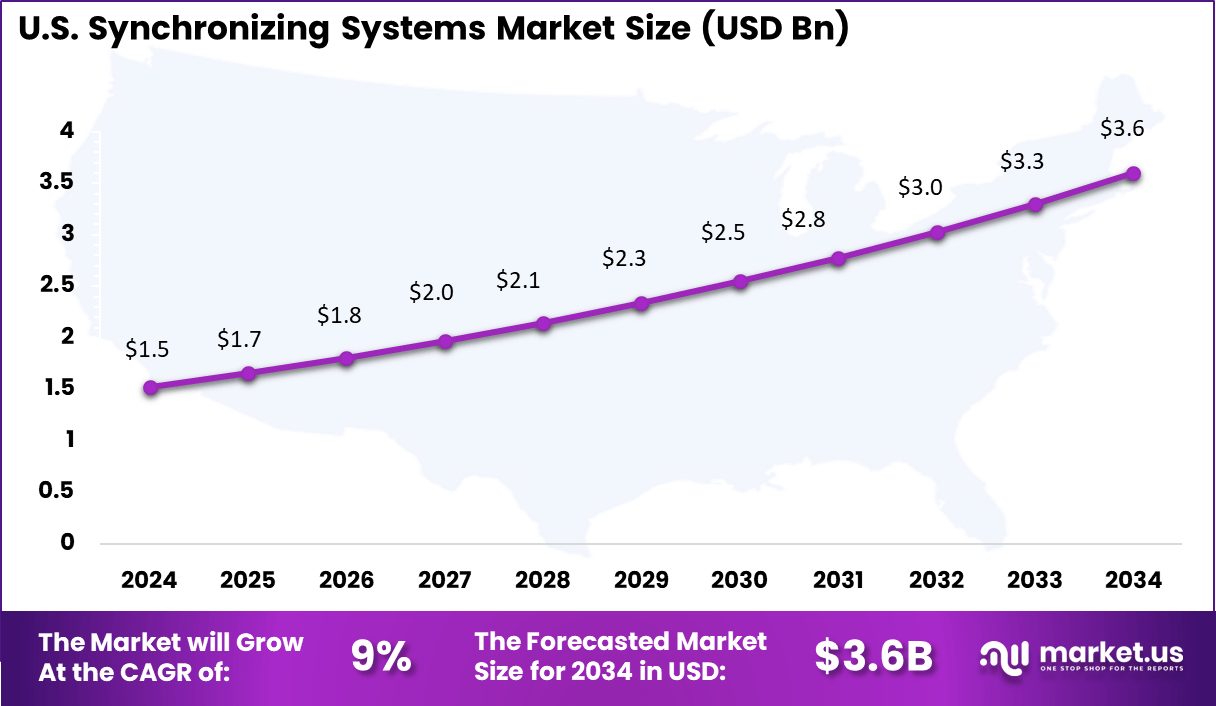
- North America had 36.3% of the global market, with the U.S. at USD 1.52 billion in 2025 and growing at a CAGR of 9%.
Drivers Impact Analysis
Driver Category Key Driver Description Estimated Impact on CAGR (%) Geographic Relevance Impact Timeline Expansion of 5G networks Precise timing for network synchronization ~3.2% North America, Asia Pacific Short Term Growth of data traffic Need for stable and low latency networks ~2.6% Global Short to Mid Term Transition to packet based networks Replacement of legacy timing systems ~2.2% Europe, North America Mid Term Smart grid and utility digitization Time sensitive grid operations ~1.9% North America, Europe Mid Term Financial trading infrastructure Requirement for accurate time stamping ~1.6% Global Long Term Risk Impact Analysis
Risk Category Risk Description Estimated Negative Impact on CAGR (%) Geographic Exposure Risk Timeline Cybersecurity threats Attacks on timing and synchronization signals ~2.7% Global Short Term GNSS dependency risk Vulnerability to signal disruption ~2.1% Global Short to Mid Term Technology obsolescence Rapid evolution of timing standards ~1.7% Global Mid Term High system cost Capital intensive deployments ~1.3% Emerging Markets Short Term Vendor concentration Limited number of certified suppliers ~1.0% Global Long Term Restraint Impact Analysis
Restraint Factor Restraint Description Impact on Market Expansion (%) Most Affected Regions Duration of Impact High installation cost Cost barriers for smaller operators ~2.5% Emerging Markets Short to Mid Term Integration complexity Compatibility with legacy infrastructure ~2.0% Global Mid Term Skilled workforce shortage Limited expertise in timing technologies ~1.6% Global Mid Term Regulatory compliance Sector specific timing standards ~1.2% Europe, North America Long Term Maintenance requirements Ongoing calibration and monitoring ~0.9% Global Long Term Investor Type Impact Matrix
Investor Type Adoption Level Contribution to Market Growth (%) Key Motivation Investment Behavior Telecom operators Very High ~44.9% Network reliability and precision Long term infrastructure investment Utilities and grid operators High ~21% Time sensitive operations Phased upgrades Financial institutions Moderate to High ~15% Regulatory compliant time stamping Selective deployment Government agencies Moderate ~12% National timing resilience Public funding Industrial enterprises Low to Moderate ~7% Operational synchronization Project based adoption Component Analysis
Hardware accounts for 65.7%, highlighting its critical role in synchronizing systems. Physical components such as clocks, timing modules, and synchronization units ensure accurate signal alignment. These components are essential for maintaining system stability across networks. Hardware-based solutions deliver consistent performance in demanding environments. Reliability remains a primary requirement.
The dominance of hardware is driven by the need for precise and continuous synchronization. Many industries rely on dedicated devices for timing accuracy. Hardware solutions operate independently of software limitations. They also support long-term deployment with minimal disruption. This sustains strong demand for hardware components.
Technology Analysis
Network-based technology holds 56.2%, making it the leading synchronization approach. This technology distributes timing signals over communication networks. It supports coordination across geographically distributed systems. Network-based methods reduce the need for isolated timing sources. Efficiency and scalability are key advantages.
Adoption of network-based synchronization is driven by expanding digital infrastructure. Organizations prefer centralized timing distribution. Network-based systems support modern communication standards. They also integrate with existing network architectures. This keeps network-based technology widely adopted.
Precision Analysis
Phase and time synchronization account for 52.4%, reflecting the need for high precision. Accurate phase and time alignment is critical for network performance. These systems ensure minimal signal delay and interference. Precision supports reliable data transmission. Performance consistency remains essential.
Growth in this segment is driven by increasing data traffic. Communication networks require tight synchronization to operate efficiently. Phase and time accuracy support advanced services. Systems with high precision reduce operational errors. This sustains continued adoption.
End-User Industry Analysis
Telecommunications represents 44.9%, making it the leading end-user industry. Telecom networks rely heavily on synchronized timing for operations. Accurate synchronization supports network stability and quality. Timing errors can impact service delivery. Reliability is a core requirement.
Adoption in telecommunications is driven by network expansion and modernization. Operators deploy synchronization systems to support high-speed networks. Precise timing improves signal coordination. Synchronizing systems also support regulatory standards. This keeps telecom as the primary end user.
Investor Type Impact Matrix
Investor Type Adoption Level Contribution to Market Growth (%) Key Motivation Investment Behavior Telecom operators Very High ~44.9% Network reliability and precision Long term infrastructure investment Utilities and grid operators High ~21% Time sensitive operations Phased upgrades Financial institutions Moderate to High ~15% Regulatory compliant time stamping Selective deployment Government agencies Moderate ~12% National timing resilience Public funding Industrial enterprises Low to Moderate ~7% Operational synchronization Project based adoption Technology Enablement Analysis
Technology Layer Enablement Role Impact on Market Growth (%) Adoption Status GNSS based timing Primary global time reference ~3.4% Mature Precision Time Protocol Packet based network synchronization ~2.7% Growing Network time servers Local timing distribution ~2.1% Mature Time sensitive networking Deterministic data delivery ~1.8% Developing Holdover oscillators Resilience during signal loss ~1.5% Growing Key Reasons for Adoption
- Precise timing alignment is required across distributed equipment and control systems.
- Growth in automated and networked operations increases the need for coordinated processes.
- High system reliability is demanded in mission-critical and safety-sensitive environments.
- Integration of digital platforms requires stable and consistent synchronization signals.
- Operational efficiency improves when processes run in a coordinated manner.
Benefits
- Improved system accuracy is achieved through consistent timing and phase alignment.
- Reduced operational errors support stable and predictable performance.
- Enhanced interoperability allows different systems to operate as a single unit.
- Lower downtime is achieved by minimizing timing-related failures.
- Scalable designs support future expansion without major system redesign.
Usage
- Power generation and grid management for phase and frequency coordination.
- Telecommunications networks to maintain signal alignment across infrastructure.
- Industrial automation for synchronized production lines and machinery.
- Transportation systems to coordinate signaling, control, and safety functions.
- Data centers and IT infrastructure to support time-sensitive operations and workloads.
Emerging Trends
Key Trend Description Precision Time Protocol Adoption PTP delivers sub microsecond accuracy for high precision applications in telecom and automation. Synchronous Ethernet Expansion SyncE ensures frequency alignment across Ethernet networks for reliable data flow. GPS Based Enhancements Satellite synchronization supports outdoor networks with global time references. Edge Computing Integration Distributed timing aligns nodes closer to data sources to reduce latency. AI Optimized Algorithms Machine learning improves clock recovery and fault tolerance in complex systems. Growth Factors
Key Factors Impact 5G Network Rollouts Ultra low latency synchronization is required for base stations and fronthaul links. IoT Device Proliferation Growing sensor networks require coordinated and accurate timing. Industrial Automation Rise Smart factories depend on real time synchronization for machine to machine control. Data Center Evolution Cloud and edge environments rely on precise timing for load balancing and system integrity. Automotive System Demands ADAS and V2X communications require robust timing for safety critical functions. Key Market Segments
By Component
- Hardware
- Software
- Services
By Technology
- GNSS-based
- Network-based Synchronization
- Others
By Precision
- Phase and Time Synchronization
- Frequency Synchronization
- Time-of-Day Synchronization
By End-User Industry
- Telecommunications
- Power and Energy
- Financial Services
- Industrial Automation and Transportation
- Government and Defense
- Others
Regional Analysis
North America accounted for 36.3% share, supported by strong demand for precise timing and synchronization across telecommunications, power utilities, data centers, and industrial automation. Synchronizing systems have been widely adopted to ensure accurate coordination of networks, control systems, and critical infrastructure.
Demand has been driven by expansion of high speed communication networks, grid modernization, and increasing reliance on real time data exchange. The regions focus on reliability and uptime has reinforced the importance of accurate synchronization for operational stability.
Regional Driver Comparison
Region Primary Growth Driver Regional Share (%) Regional Value (USD Bn, 2024) Adoption Maturity North America Advanced telecom and financial networks 36.3% USD 1.67 Bn Advanced Europe 5G rollout and power grid modernization 27.8% USD 1.28 Bn Advanced Asia Pacific Rapid mobile infrastructure expansion 24.6% USD 1.13 Bn Developing to Advanced Latin America Telecom network upgrades 6.4% USD 0.29 Bn Developing Middle East and Africa Smart infrastructure projects 4.9% USD 0.23 Bn Early The U.S. market reached USD 1.52 Bn and is projected to grow at a 9.0% CAGR, reflecting steady investment in communication networks and critical infrastructure. Adoption has been particularly strong in telecommunications and energy sectors, where precise timing is essential for network performance and grid protection. Synchronizing systems have helped U.S. operators improve coordination, reduce downtime, and meet regulatory and performance standards.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherlands
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Emerging Trends
In the synchronizing systems market, one clear trend is the wider adoption of network time protocols in distributed digital systems. Organisations are deploying time synchronisation across servers, network devices, industrial controllers, and edge nodes so that all components share a consistent time reference. This shared timing improves coordination, event logging, and sequence integrity across complex environments.
Another emerging trend is the integration of precision timing solutions into wireless and Internet of Things networks. Connected devices in smart factories, telecommunications networks, and sensor arrays increasingly depend on accurate time alignment to support data fusion, coordinated control, and real time decision making. This trend reflects a broader need for synchronisation beyond traditional computing systems into operational technology environments.
Growth Factors
A key growth factor in the synchronizing systems market is the expansion of digital infrastructure that relies on coordinated operations. Services such as financial trading, telecommunications, cloud computing, and industrial automation require precise time alignment to ensure data integrity, system resilience, and seamless interaction between distributed components.
Another important factor supporting growth is the regulatory emphasis on accurate time records for compliance and auditability. Sectors such as finance and critical communications must maintain accurate timestamps to meet legal and reporting standards. Synchronised timing systems help organisations adhere to these requirements by providing reliable, traceable time references.
Opportunity
A strong opportunity exists in the development of synchronisation solutions optimised for multi domain digital ecosystems. As systems spread across cloud, edge, and on premise infrastructure, solutions that can manage consistent time alignment across these environments will be in demand. Providers that simplify cross platform integration can broaden market reach.
Another opportunity lies in enhancing tools that support automated calibration and health monitoring of synchronised systems. Platforms that detect drift, flag discrepancies, and support corrective actions can improve confidence in timing accuracy and reduce manual maintenance tasks.
Challenge
One of the main challenges for the synchronizing systems market is ensuring precision under varying network conditions and load patterns. Network congestion, jitter, and latency can affect the accuracy of time distribution. Solutions must account for these variations and maintain stability under real world conditions.
Another challenge involves balancing performance with cost and complexity. High precision timing systems can require specialised hardware and careful configuration. Delivering reliable synchronisation without imposing excessive cost or operational overhead is essential for adoption across varied organisations.
Competitive Analysis
Siemens AG, ABB Ltd., General Electric Company, and Schneider Electric SE hold a strong position in the synchronizing systems market. Their solutions support power grids, industrial automation, and utility operations. Focus is placed on time accuracy, grid stability, and system reliability. These companies benefit from deep domain expertise. Global project execution capabilities strengthen adoption. Their systems are widely used in substations, transmission networks, and critical infrastructure environments.
Honeywell International Inc., Emerson Electric Co., Rockwell Automation, Inc., and Eaton Corporation plc focus on synchronization for industrial control systems. Their offerings integrate timing, protection, and monitoring functions. Emphasis is placed on operational safety and system resilience. These vendors support oil and gas, manufacturing, and energy sectors. Strong service capabilities improve lifecycle performance. Their solutions help reduce downtime and improve coordination across distributed assets.
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Hitachi, Ltd., Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories, Inc., Woodward, Inc., Larsen & Toubro Limited, Yokogawa Electric Corporation, and OMRON Corporation address specialized synchronization needs. Their strengths include precision timing and protection systems. Regional expertise supports grid modernization. Other players serve niche applications and emerging markets.
Top Key Players in the Market
- Siemens AG
- ABB Ltd.
- General Electric Company
- Schneider Electric SE
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Emerson Electric Co.
- Rockwell Automation, Inc.
- Eaton Corporation plc
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Hitachi, Ltd.
- Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories, Inc. (SEL)
- Woodward, Inc.
- Larsen & Toubro Limited (L&T)
- Yokogawa Electric Corporation
- OMRON Corporation
- Others
Future Outlook
Growth in the Synchronizing Systems market is expected to remain stable as industries focus on reliable power and system coordination. These systems are widely used to align generators, grids, and critical equipment to ensure smooth operation and prevent outages.
Rising investment in distributed energy resources and backup power solutions is supporting steady demand. Over time, smarter control features, remote monitoring, and integration with digital energy management platforms are likely to improve efficiency and operational safety.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 4.6 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 13.7 Bn CAGR(2025-2034) 11.50% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue forecast, AI impact on Market trends, Share Insights, Company ranking, competitive landscape, Recent Developments, Market Dynamics and Emerging Trends Segments Covered By Component (Hardware, Software, Services), By Technology (GNSS-based, Network-based Synchronization,Others), By Precision (Phase & Time Synchronization, Frequency Synchronization, Time-of-Day Synchronization), By End-User Industry (Telecommunications,Power & Energy,Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of Latin America; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Siemens AG, ABB Ltd., General Electric Company, Schneider Electric SE, Honeywell International Inc., Emerson Electric Co., Rockwell Automation, Inc., Eaton Corporation plc, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Hitachi, Ltd., Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories, Inc., Woodward, Inc., Larsen & Toubro Limited, Yokogawa Electric Corporation, OMRON Corporation, Others Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three license to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Synchronizing Systems MarketPublished date: Jan. 2026add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Synchronizing Systems MarketPublished date: Jan. 2026add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Siemens AG
- ABB Ltd.
- General Electric Company
- Schneider Electric SE
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Emerson Electric Co.
- Rockwell Automation, Inc.
- Eaton Corporation plc
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Hitachi, Ltd.
- Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories, Inc. (SEL)
- Woodward, Inc.
- Larsen & Toubro Limited (L&T)
- Yokogawa Electric Corporation
- OMRON Corporation
- Others










