Global Sugar Alcohol Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Type (Mannitol, Sorbitol, Xylitol, Maltitol, Isomalt, Others), By Form (Powder, Liquid), By Application (Food and Drink, Pharmaceuticals, Cosmetics and Personal Care, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Jan 2026
- Report ID: 173383
- Number of Pages: 253
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
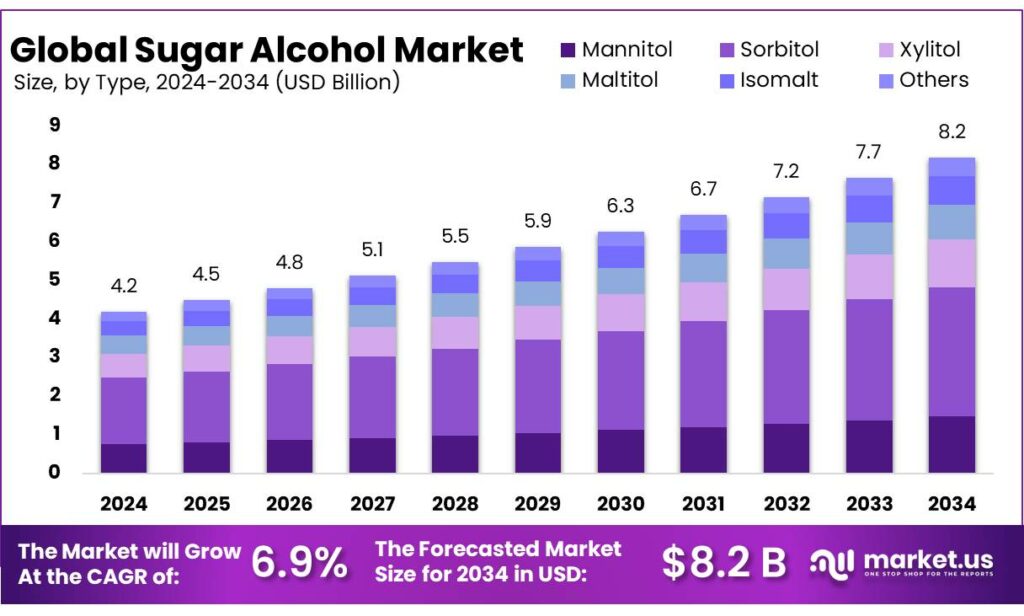
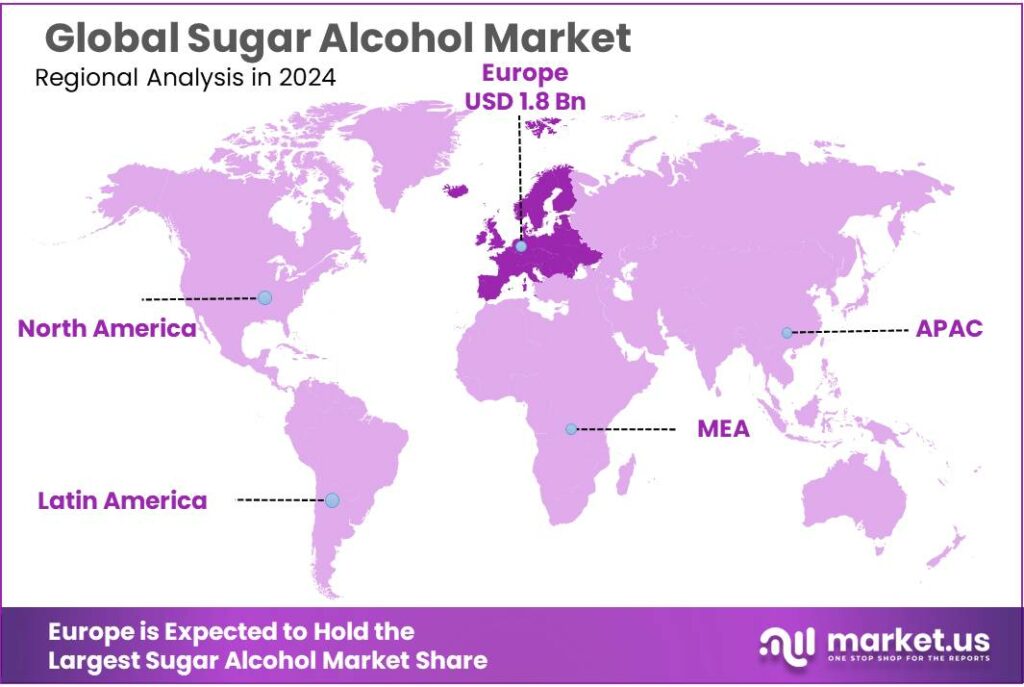
Global Sugar Alcohol Market size is expected to be worth around USD 8.2 Billion by 2034, from USD 4.2 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 6.9% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024 Europe held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.8% share, holding USD 1.8 Billion in revenue.
Sugar alcohols (also called polyols) are sweet-tasting carbohydrates used to replace sucrose in “no added sugar,” reduced-sugar, and sugar-free formulations across confectionery, chewing gum, bakery, dairy-style desserts, tabletop sweeteners, and nutrition products. A key commercial advantage is their lower physiological energy contribution versus sucrose: Codex-aligned energy conversion factors commonly recognize polyols at 10 kJ/g (2.4 kcal/g), compared with carbohydrate at 17 kJ/g (4.0 kcal/g), which supports calorie-reduction positioning in finished foods.
From an industrial scenario standpoint, the sugar alcohol value chain is closely tied to the broader carbohydrate economy (sugar, starch, and syrups). FAO forecasts global sugar consumption at 177.8 million tonnes in 2024/25, reflecting steady demand for sweet-tasting foods even as many brands reformulate. At the same time, global supply-demand balances can tighten: the International Sugar Organization’s August 2024 outlook projected 182.867 million tonnes of consumption versus 179.287 million tonnes of production for 2024/25, implying a deficit of 3.580 million tonnes.
Key driving factors are anchored in nutrition policy, dental/health positioning, and reformulation economics. WHO recommends reducing “free sugars” to less than 10% of total energy intake, and suggests a further reduction below 5%—approximately 25 grams per day—for additional health benefits. In the U.S., the Dietary Guidelines for Americans similarly recommend keeping added sugars below 10% of calories; FDA explains this equals 50 grams per day on a 2,000-calorie diet.
Regulation and public initiatives also shape formulation choices and labeling strategies. In the EU, food products with more than 10% added polyols must carry the statement “excessive consumption may produce laxative effects,” and EU rules highlight the laxative potential that constrains broader beverage use cases. In the U.S., USDA finalized school-meal updates that introduce added-sugars limits, including a dietary specification of less than 10% of calories across the week to be implemented by school year 2027–28—a policy signal that tends to accelerate supplier innovation in sweetening systems.
Key Takeaways
- Sugar Alcohol Market size is expected to be worth around USD 8.2 Billion by 2034, from USD 4.2 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 6.9%.
- Sorbitol held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 41.8% share.
- Powder held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 72.5% share.
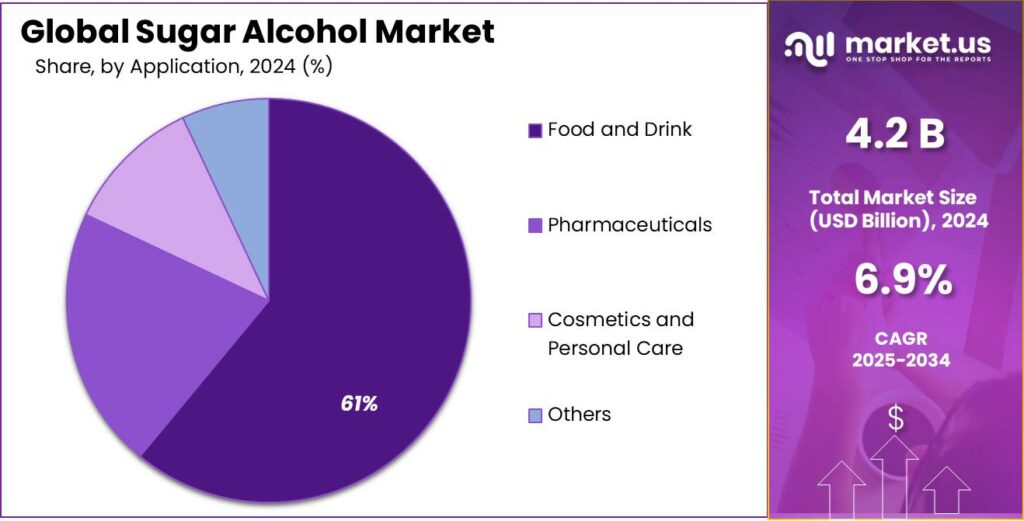
- Food and Drink held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 61.3% share.
- Europe established itself as a leading region in the global sugar alcohol market, with a commanding 43.80% share and approximately USD 1.8 billion.
By Type Analysis
Sorbitol leads the Sugar Alcohol Market with a strong 41.8% share, supported by its wide use and stable demand across industries
In 2024, Sorbitol held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 41.8% share, reflecting its strong acceptance across food, pharmaceutical, and personal care applications. This leadership position was mainly supported by its long-standing use as a sweetener, humectant, and texturizing agent, especially in sugar-free and low-calorie food products. Sorbitol continued to be preferred due to its mild sweetness, good stability, and cost-efficient production compared to other sugar alcohols. In the food industry, its role in confectionery, chewing gum, baked goods, and diabetic-friendly products remained significant, as manufacturers focused on reducing sugar content while maintaining taste and shelf life.
From a pharmaceutical perspective, Sorbitol was widely used in syrups and oral formulations, where it supported taste masking and moisture retention. Moving into 2025, demand for Sorbitol was further supported by rising consumer awareness of sugar reduction and clean-label formulations, particularly in emerging economies. Its versatility, regulatory acceptance, and consistent performance across multiple end-use sectors allowed Sorbitol to maintain its leading position within the sugar alcohol market without major substitution pressure.
By Form Analysis
Powder form dominates the Sugar Alcohol Market with a solid 72.5% share, driven by ease of use and wide industrial adoption
In 2024, Powder held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 72.5% share, mainly due to its strong suitability for large-scale food and pharmaceutical manufacturing. The powder form was widely preferred because it offered better handling, longer shelf life, and precise dosage control compared to liquid alternatives. In food processing, powdered sugar alcohols were extensively used in bakery mixes, confectionery, tabletop sweeteners, and nutritional products, where consistency and uniform blending were critical.
From an operational point of view, manufacturers favored powder as it simplified storage, transportation, and formulation processes, especially in dry-mix applications. During 2025, the demand for powder form continued to remain stable, supported by rising production of sugar-free and reduced-calorie foods across both developed and developing markets. Its compatibility with automated production lines and lower risk of spoilage further strengthened its market presence, allowing the powder segment to retain its leading position within the sugar alcohol market.
By Application Analysis
Food and Drink leads the Sugar Alcohol Market with a strong 61.3% share, supported by rising demand for low-sugar products
In 2024, Food and Drink held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 61.3% share, largely driven by the growing focus on sugar reduction across everyday food and beverage products. Sugar alcohols were widely used in confectionery, chewing gum, baked goods, dairy alternatives, and functional beverages, where they helped lower calorie content while maintaining taste and texture. Their ability to provide sweetness without causing sharp blood sugar spikes made them especially attractive for diabetic-friendly and weight-management products.
During 2025, the segment continued to benefit from increasing consumer awareness of health and nutrition, along with stricter labeling norms related to added sugar. Food and beverage manufacturers increasingly relied on sugar alcohols to reformulate existing products and launch new reduced-sugar options without compromising shelf life or mouthfeel. This consistent demand from high-volume food and drink applications allowed the segment to maintain its leading position within the sugar alcohol market.
Key Market Segments
By Type
- Mannitol
- Sorbitol
- Xylitol
- Maltitol
- Isomalt
- Others
By Form
- Powder
- Liquid
By Application
- Food and Drink
- Pharmaceuticals
- Cosmetics and Personal Care
- Others
Emerging Trends
“Added Sugar Limits” Are Driving Polyol Blend Innovation
A clear latest trend in sugar alcohols (polyols) is the fast move toward blended sweetening systems designed to cut added sugars while keeping the texture people expect. This is happening because public-health targets are now stated in simple numbers that product teams can build around. WHO recommends reducing free sugars to less than 10% of total energy intake and suggests going below 5%, or roughly 25 grams per day, for extra health benefits.
In the U.S., the Nutrition Facts label and federal guidance have made “added sugars” a headline metric, which pushes developers to find solutions that lower that line item without creating a thin mouthfeel. The FDA explains that the Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend limiting added sugars to less than 10% of calories; on a 2,000-calorie diet, that equals 200 calories or 50 grams of added sugars per day.
The most visible proof that sugar reduction is becoming institutional is school food policy, which has started to set numeric limits that suppliers must meet. USDA’s school nutrition updates introduce product-based limits beginning in school year 2025–26 (starting July 1, 2025). Breakfast cereals may have no more than 6 grams of added sugars per dry ounce, yogurt no more than 12 grams per 6 ounces, and flavored milk no more than 10 grams per 8 fluid ounces.
At the same time, the trend is not “use more polyols everywhere.” Instead, it is smarter, lower-dose polyol use with careful portion sizing and clearer consumer communication. In Europe, foods containing more than 10% added polyols must carry the statement “excessive consumption may produce laxative effects.”
Drivers
Sugar-Reduction Policies Are Forcing Reformulation
One major driving factor for sugar alcohols (polyols) is the steady tightening of public-health guidance on sugar, which pushes food and beverage brands to reformulate at scale. The World Health Organization recommends that adults and children reduce “free sugars” to less than 10% of total energy intake, and it suggests going below 5% for extra benefits—roughly 25 grams per day.
In the United States, federal nutrition communication reinforces the same direction and makes it easy for shoppers to compare products. The FDA explains that the Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend keeping calories from added sugars under 10% per day; for a 2,000-calorie diet, that equals 200 calories or 50 grams of added sugars daily. The CDC repeats this <10% guidance and translates 200 calories into about 12 teaspoons of added sugar, which is simple for consumers to visualize.
This is where sugar alcohols become commercially important. Polyols can help lower “added sugars” while still giving sweetness and bulk—two functions that plain high-intensity sweeteners often cannot deliver alone. That functional advantage matters in real manufacturing: gum needs chew, chocolate needs structure, cookies need spread control, and fillings need moisture management.
Government initiatives in institutional food service add another layer of demand. USDA’s updated school meal standards introduce added-sugars limits in phases. Starting in school year 2025–26, there are product-based limits for items that often run high in sugar, such as breakfast cereals, yogurt, and flavored milk. Then, starting in school year 2027–28, USDA states that no more than 10% of weekly calories in school meals can come from added sugars.
Regulatory clarity also shapes how polyols are positioned globally. In the EU, foods containing more than 10% added polyols must include the statement “excessive consumption may produce laxative effects,” which encourages controlled, responsible use and clearer communication.
Restraints
Digestive Tolerance Limits And Mandatory Warnings
A major restraining factor for sugar alcohols (polyols) is simple: many consumers cannot tolerate higher intakes without stomach discomfort, and regulators require clear warnings when products cross certain thresholds. Health Canada notes that sugar alcohols are “poorly taken up” in the gut, and that eating too much can cause gastrointestinal discomfort and laxative effects. This tolerance issue becomes a commercial barrier because it can trigger complaints, reduce repeat purchases, and force brands to cap usage levels—especially in products that people eat in large portions.
Regulatory rules make this restraint visible on-pack, which can reduce consumer acceptance even when the product tastes good. EU consumer information rules state that when foods contain more than 10% added polyols, they must carry the warning “excessive consumption may induce laxative effects.” That threshold matters in real product development because many “sugar-free” confectionery items need high sweetener solids to replace sugar’s bulk. Once a label must carry a laxative warning, some shoppers hesitate, and some retailers become cautious about placement and claims. In short, even when polyols help hit sugar-reduction targets, the warning requirement can weaken the marketing story.
Industry-facing references underline that tolerance thresholds can be reached faster than many consumers expect—particularly with frequent snacking. A widely cited regulatory benchmark is that labels should carry the laxative warning when it is reasonable that daily consumption could exceed 50 g of sorbitol. For mannitol, a similar benchmark is 20 g. These figures are important because they show why polyols are easier to use in small-portion products than in items people may eat in larger quantities. The restraint is not theoretical; it shapes how much of the sweetener system can realistically be polyol-based.
Opportunity
Reformulation Wave In Schools And “Better-For-You” Brands
One major growth opportunity for sugar alcohols (polyols) is the widening, policy-driven shift toward lower-added-sugar foods—especially in high-volume channels where recipes must be compliant, affordable, and familiar. The World Health Organization recommends keeping “free sugars” below 10% of total energy intake and suggests aiming below 5% (about 25 grams per day) for extra health benefits. When global guidance is this numeric and consistent, it becomes a practical target for large manufacturers, not just a wellness message.
Public food programs are turning those targets into procurement reality, which creates a clear lane for ingredients that reduce sugar without breaking taste and texture. In the United States, USDA’s school nutrition updates introduce added-sugars limits starting in school year 2025–26 for specific items that often run high in added sugar, including breakfast cereals, yogurt, and flavored milk. The next step is bigger: starting in school year 2027–28, USDA sets a dietary specification so that no more than 10% of weekly calories in school meals can come from added sugars.
The demand pull is reinforced by the growing health burden linked to diets high in sugar, which continues to steer consumers toward sugar-reduced products. The International Diabetes Federation estimates 589 million adults (ages 20–79) were living with diabetes in 2024, and projects 853 million by 2050. IDF also estimates diabetes drove at least USD 1 trillion in health expenditure and was responsible for 3.4 million deaths in 2024.
Finally, the long-term opportunity is not about eliminating sweetness; it is about changing how sweetness is delivered. The OECD-FAO outlook projects global sugar consumption will expand by 1.2% per year and reach 202 Mt by 2034.
Regional Insights
Europe dominates the Sugar Alcohol Market with 43.80% share and revenue reaching USD 1.8 Bn in 2025 as strong health trends persist
In 2024–2025, Europe established itself as a leading region in the global sugar alcohol market, with a commanding 43.80% share and approximately USD 1.8 billion in revenue by 2025. This strong performance was supported by well-established consumer demand for reduced-sugar and sugar-free products across key national markets such as Germany, the United Kingdom, and France. European consumers remained highly health-aware, prompting food and beverage manufacturers to reformulate products with sugar alcohols to comply with stringent regional nutritional guidelines and clean-label trends.
The regulatory environment in Europe, guided by frameworks from institutions such as the European Food Safety Authority, further reinforced market stability by permitting the use of selected sugar alcohols in a range of food, personal care, and pharmaceutical applications. This regulatory clarity supported broad utilization without major compliance barriers and encouraged innovation within regional ingredient supply chains. In pharmaceuticals, sugar alcohols were extensively used in chewable tablets, cough syrups, and oral care formulations, reinforcing cross-industry demand.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Cargill Inc. is a major global player in the sugar alcohol market, with estimates indicating a 25–30 % market share in 2024 driven by erythritol, xylitol, and sorbitol offerings. The company’s extensive R&D and new product launches for low-calorie and functional food segments strengthen its competitive position worldwide.
Ingredion Incorporated supplies a range of sugar alcohols for reduced-sugar and clean-label products, with an estimated 10–15 % market share by 2024. Its product development emphasizes plant-based and non-GMO sweetener solutions, catering to shifting consumer preferences for health-oriented foods. Strategic partnerships in Asia-Pacific further expand its market penetration.
Archer Daniel Midland Company (ADM) holds a significant position in the global sugar alcohol market, supplying sorbitol and xylitol for food, beverage, and pharmaceutical applications. In 2024, ADM’s integrated refining and distribution network contributed an estimated 20–25 % market share in sugar alcohols, supported by R&D investments and strategic partnerships that strengthen its product portfolio across regions.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Archer Daniel Midland Company
- Associated British Food Plc.
- Atlantic Chemicals Trading GmbH
- Cargill Inc.
- Dupont De Nemours Inc.
- Ingredion Incorporated
- Mitsusrhi Corporation Life Sciences Limited
- Roquette Frères Sa.
- Tate and Lyle Plc.
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024, ABF reported overall group revenue of £20,073 million, with its sugar and ingredients segments contributing significantly to its ingredient supply chain, though sugar alcohol-specific figures are not separately disclosed publicly.
ADM’s capacity for sorbitol production was among the industry’s largest, with an annual output reaching approximately 300,000 metric tons, enabling reliable supply to food and pharmaceutical manufacturers. Its established supply chain and fermentation technologies helped maintain stable volumes despite fluctuating commodity markets.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 4.2 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 8.2 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 6.9% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Type (Mannitol, Sorbitol, Xylitol, Maltitol, Isomalt, Others), By Form (Powder, Liquid), By Application (Food and Drink, Pharmaceuticals, Cosmetics and Personal Care, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Archer Daniel Midland Company, Associated British Food Plc., Atlantic Chemicals Trading GmbH, Cargill Inc., Dupont De Nemours Inc., Ingredion Incorporated, Mitsusrhi Corporation Life Sciences Limited, Roquette Frères Sa., Tate and Lyle Plc. Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Archer Daniel Midland Company
- Associated British Food Plc.
- Atlantic Chemicals Trading GmbH
- Cargill Inc.
- Dupont De Nemours Inc.
- Ingredion Incorporated
- Mitsusrhi Corporation Life Sciences Limited
- Roquette Frères Sa.
- Tate and Lyle Plc.










