Global Space Asset Securitization Market Size, Share Report Analysis By Asset Type (Satellites, Spacecraft, Launch Vehicles, Ground Equipment, Others), By Securitization Structure (Asset-Backed Securities, Mortgage-Backed Securities, Collateralized Debt Obligations, Others), By End-User (Commercial, Government, Defense, Others), By Application (Telecommunications, Earth Observation, Navigation, Space Exploration, Others) , By Regional Analysis, Global Trends and Opportunity, Future Outlook By 2025-2034
- Published date: Dec. 2025
- Report ID: 169752
- Number of Pages: 227
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
- Report Overview
- Key Takeaway
- Role of Generative AI
- Investment and Business Benefits
- U.S. Market Size
- Asset Type Analysis
- Securitization Structure Analysis
- End-User Analysis
- Application Analysis
- Emerging Trends
- Growth Factors
- Key Market Segments
- Drivers
- Restraint
- Opportunities
- Challenges
- Key Players Analysis
- Recent Developments
- Report Scope
Report Overview
The Global Space Asset Securitization Market size is expected to be worth around USD 8.56 billion by 2034, from USD 2.08 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 15.2% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 46.4% share, holding USD 0.96 billion in revenue.
The space asset securitization market has grown as satellite operators and space infrastructure owners seek new ways to raise capital using space based assets as financial instruments. Growth is linked to rising private investment in satellites, launch services and space communications. Securitization allows future cash flows from space assets such as bandwidth usage, data services and lease contracts to be converted into tradable financial products.
The growth of the market can be attributed to high capital requirements in satellite deployment, rising demand for space based communication services and the need for alternative financing methods. Traditional funding methods place heavy pressure on balance sheets. Securitization allows operators to unlock value from existing assets while spreading risk across investors. Long term service contracts in space support more stable cash flow structures.
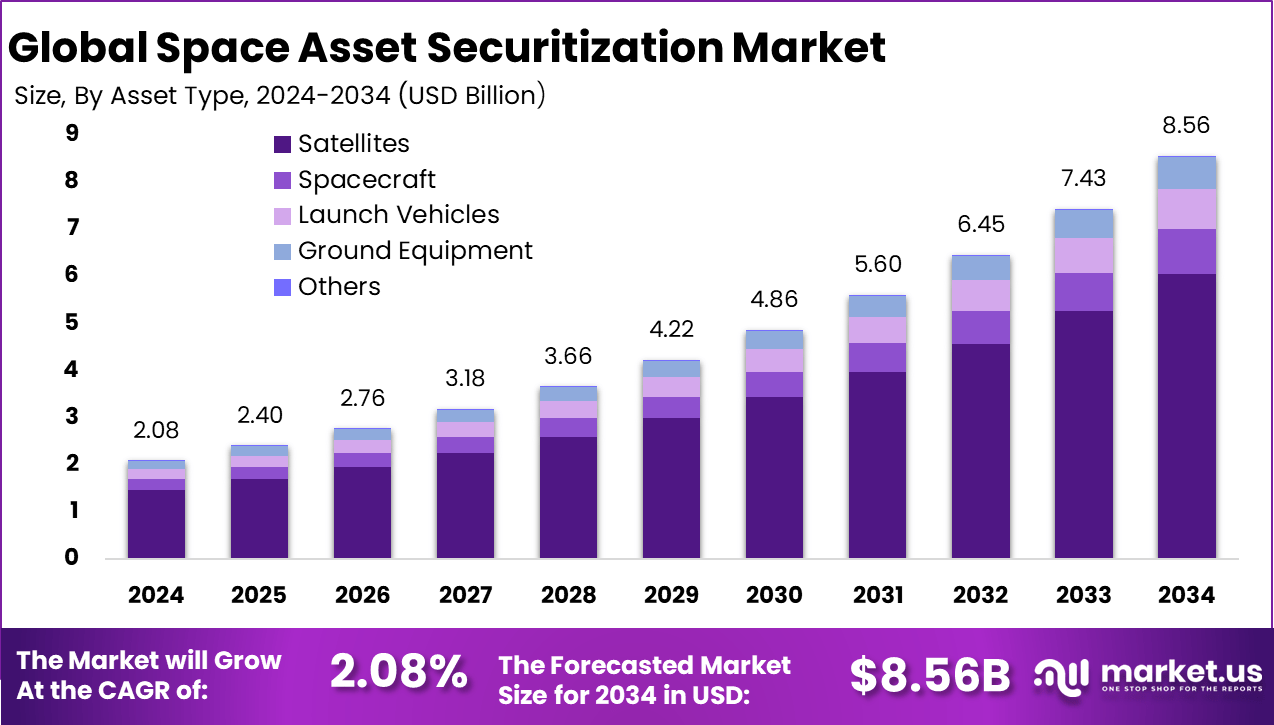
The market for Space Asset Securitization is driven by blockchain and AI tools that track satellites and spacecraft in real time. These technologies create clear records and quick value checks, building investor trust. Companies turn large space projects into shares that funds can easily buy, funding more launches and missions. North America leads this push with strong tech advances from firms like Thales Group. Growth comes as space firms seek cash for satellite networks, cutting fraud and speeding global deals.
Demand is rising across satellite operators, space infrastructure developers, launch service operators and financial institutions involved in structured finance. Companies operating large satellite fleets use securitization to fund expansion without increasing direct debt exposure. Investor interest is also rising due to the long term and recurring nature of space service revenues.
For instance, in September 2025, Planet Labs PBC announced a $300 million private offering of Convertible Senior Notes due 2030, complete with capped call hedges to curb dilution. Backed by strong Earth observation demand, this financing fuels satellite fleet growth and positions Planet as a key player in securitizing daily global imagery data streams.
Key Takeaway
- Satellites dominated with a 70.8% share in 2024, showing that orbiting assets remain the primary collateral base for space-linked financing.
- Asset-backed securities led with a strong 86.5% share, confirming that structured debt remains the preferred securitization method in this market.
- The commercial segment captured 82.2%, indicating that private operators now drive most space asset financing activity.
- Telecommunications accounted for 75.6%, reflecting the heavy use of securitization to fund satellite-based connectivity and data transmission networks.
- The U.S. market reached USD 0.87 billion in 2024 with a steady 13.4% CAGR, showing rising investor confidence in space-linked financial instruments.
- North America held more than 46.4% share, supported by mature capital markets, strong satellite operators, and advanced financial structuring capabilities.
Role of Generative AI
Generative AI speeds up analysis of space asset data, finding hidden patterns in cash flows and hazards quicker than manual reviews. Financial leaders report 70% ramping up investments in this tech, slashing review times through real-time processing of huge datasets.
It creates mock data sets to simulate deal outcomes, sharpening risk checks. In asset handling, it lifts efficiency by 8%, letting teams adjust portfolios on the fly for space securities. This makes funding decisions sharper and faster for operators. Banks lean on these tools for custom risk models tied to satellite lifespans and orbit paths.
Adoption grows as 60% of finance pros see it boosting forecast accuracy in complex fields like space. It automates contract drafting too, cutting errors in securitization papers. Operators use it to predict revenue dips from tech failures, building stronger investor pitches. Hands-on, it feels like having an extra sharp analyst always on call.
Investment and Business Benefits
Bonds backed by satellite leases offer solid entry points. Tokenized shares trade globally for quick access. Revenue from navigation or images spreads bets widely. Protocols ease cross-nation deals as orbits fill fivefold in key areas. Funds tap ongoing fees from space services.
Investors pick income types like signals or scans. Returns are tied to asset uptime stats. Portfolios mix Earth and orbit yields. Liquidity grows with digital tools. Space traffic rise opens more streams. Securitization improves cash flow for quick upgrades. Lenders spread loans into space with low defaults via tracking.
Costs fall through automated trades across operations. Firms reinvest sooner in tech refreshes. Efficiency rises in funding cycles. Operators avoid debt traps on hardware. Banks build diverse books with steady streams. Overall margins lift from faster capital turns. Risks balance with asset values. Growth speeds without equity loss.
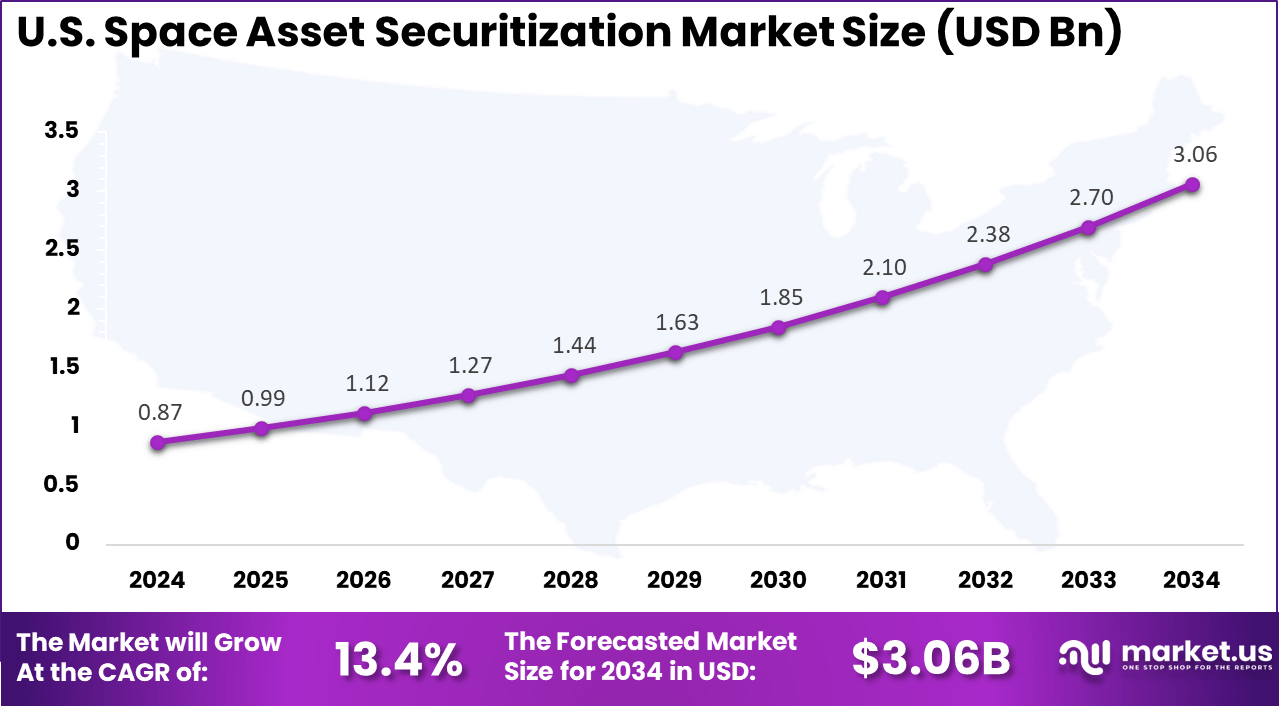
U.S. Market Size
The U.S. market for space asset securitization is valued at USD 0.87 billion and is expanding at a projected CAGR of 13.4%, supported by rising demand for satellite constellations that provide stable telecom and data services. Growth is driven by private operators seeking flexible, asset backed funding models, strong capital markets, and increasing investor confidence in predictable space based cash flows.
For instance, In December 2025, SpaceX reinforced this trend by initiating a secondary share sale targeting an USD 800 billion valuation, highlighting U.S. leadership in innovative space financing and signaling future monetization of space assets through public markets.
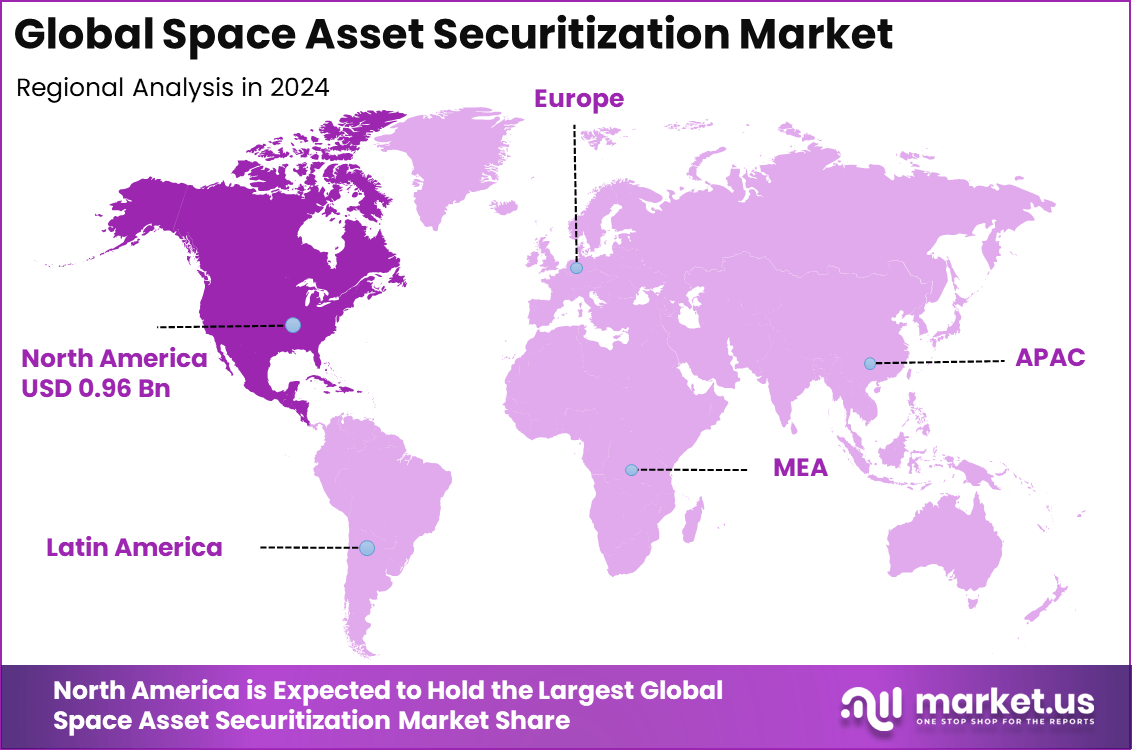
In 2024, North America held a dominant market position in the Global Space Asset Securitization Market, capturing more than a 46.4% share, holding USD 0.96 billion in revenue. This dominance is due to the region’s mature financial systems that support complex asset-backed deals for satellites.
Private space firms thrive here with easy access to investors eager for space revenue streams. Strong regulatory frameworks and high demand for telecom satellites fuel securitization activity. The US leads as a hub for innovative funding tied to orbital assets.
For instance, in December 2025, Iridium Communications Inc. secured a major U.S. Space Force IDIQ contract valued up to $85.8 million, highlighting North American leadership in securitizing satellite communications assets for defense applications. The deal underscores Iridium’s critical role in resilient, secure space-based networks, driving investor confidence with stock gains and sustained dividends.
Asset Type Analysis
In 2024, The Satellites segment held a dominant market position, capturing a 70.8% share of the Global Space Asset Securitization Market. Operators often choose these assets first because they bring in steady revenue from services like data transmission and earth imaging. This reliability draws investors who want stable returns in the growing space field.
Cash flows from satellite contracts make securitization straightforward and appealing for funding new launches or upgrades. The dominance of satellites comes from their proven track record in generating long-term income. Unlike ground equipment, they operate over vast areas and serve multiple clients at once.
Securitization lets owners unlock value without selling the assets outright. This approach supports fleet expansions as space demand rises for communication and monitoring needs. Lenders see lower risks here due to established revenue models.
For Instance, in December 2025, SpaceX advanced satellite asset strategies with a secondary share sale targeting high valuations. This move highlights how satellite fleets drive investor interest through revenue potential. Operators like SpaceX use such financing to scale constellations without full equity dilution.
Securitization Structure Analysis
In 2024, the Asset-Backed Securities segment held a dominant market position, capturing an 86.5% share of the Global Space Asset Securitization Market. These tools bundle future payments from space assets into bonds that attract diverse investors. The direct tie between cash flows and assets reduces worries in this new area. Lenders prefer this structure for its clarity and ability to spread risk across many buyers.
This structure works well because it mirrors traditional finance but fits space assets perfectly. Pooling revenues from satellite leases or service contracts creates predictable payouts. Investors gain access to space growth without owning hardware. Issuers free up capital for innovation while keeping operational control. Over time, this builds trust and scales the market further.
For instance, in November 2025, Eutelsat Communications raised funds through a capital increase advised by major banks. This supports LEO satellite deployments and debt management via structured finance. The approach aligns with asset-backed models by tying proceeds to future satellite income.
End-User Analysis
In 2024, The Commercial segment held a dominant market position, capturing an 82.2% share of the Global Space Asset Securitization Market. Private companies push this forward as they need capital to grow satellite networks and roll out services fast. Securitization avoids heavy debt on balance sheets and fuels quick expansions. Their revenue from connectivity and data apps makes assets ideal for this financing.
Commercial players thrive here due to their focus on profit-driven projects. They securitize to fund everything from broadband satellites to imaging fleets. This method aligns with business goals of scaling without slowing down. Governments step back, letting private initiative lead. This leads to faster innovation and broader access to space tech benefits.
For Instance, in September 2025, EchoStar Corporation pivoted to an asset-light model after spectrum sales and note exchanges. The strategy frees capital for commercial satellite partnerships and growth. This shift emphasizes commercial users’ need for flexible financing options.
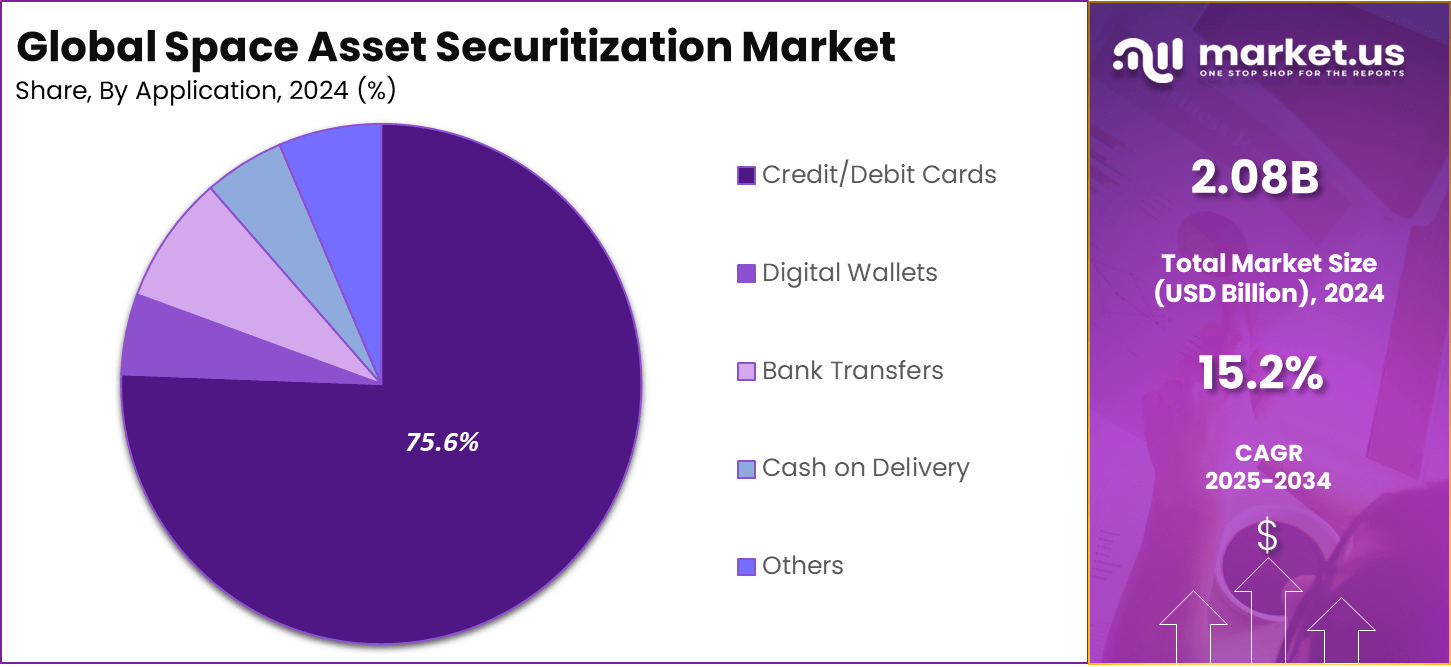
Application Analysis
In 2024, the Telecommunications segment held a dominant market position, capturing a 75.6% share of the Global Space Asset Securitization Market. Global demand for fast networks leans on satellites for coverage in remote spots. Providers securitize to finance builds that match rising data traffic from mobiles and internet users. This keeps services competitive worldwide.
The telecom focus stems from satellites’ role in bridging connectivity gaps. Securitization taps into subscription revenues for steady funding. Operators expand capacity without upfront cash strains. This supports growth in underserved regions and high-demand zones alike. As data needs climb, telecom remains the core driver of asset financing in space.
For instance, in August 2025, OneWeb secured a LEO deal in India through Eutelsat partnerships. The contract expands telecom coverage via satellite broadband in key markets. Financing ties to subscription flows make it ideal for securitization. Telecom applications stay central to asset funding trends.
Emerging Trends
One emerging trend in the space asset securitization market is the growing acceptance of satellites as financeable assets. As satellite technology improves, assets now offer longer operational life and more predictable revenue streams from communication, navigation, and earth observation services. This stability makes it easier for financial institutions to assess asset value and future cash flow. As a result, satellites are increasingly viewed as suitable backing for structured financing arrangements.
Another important trend is progress in legal frameworks that support asset based financing in space activities. International efforts to clarify ownership rights, registration, and enforcement related to space assets are improving confidence among lenders and investors. Clearer rules reduce uncertainty around asset recovery and priority rights. This legal clarity supports wider use of securitization structures linked to space assets.
Growth Factors
A major growth factor is the rapid expansion of commercial space activities. Demand for satellite services continues to rise across telecommunications, weather monitoring, navigation, and defense support. This growth increases the number of operational space assets that can be used as collateral. As the asset base expands, interest in structured financing solutions grows alongside it.
Another growth factor is the high capital requirement of space projects. Building, launching, and operating satellites requires significant upfront investment. Many space companies seek funding methods that reduce reliance on equity dilution or traditional debt. Asset securitization offers an alternative by allowing companies to raise capital using future revenue or asset value. This need for flexible financing supports ongoing growth of the space asset securitization market.
Key Market Segments
By Asset Type
- Satellites
- Spacecraft
- Launch Vehicles
- Ground Equipment
- Others
By Securitization Structure
- Asset-Backed Securities
- Mortgage-Backed Securities
- Collateralized Debt Obligations
- Others
By End-User
- Commercial
- Government
- Defense
- Others
By Application
- Telecommunications
- Earth Observation
- Navigation
- Space Exploration
- Others
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherlands
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Drivers
Tech Boost from Blockchain and AI
Blockchain and AI are reshaping space asset securitization by enabling real time tracking, transparent records, and stronger investor confidence. Blockchain supports secure and immutable transaction histories, while AI based valuation models improve the pricing of complex assets such as satellites, orbital slots, and ground infrastructure. Together, these technologies simplify how space assets are monitored, valued, and packaged into investable financial structures.
This technology combination is expanding investor participation by lowering entry barriers for both institutional and retail investors. Tokenization and smart contracts are being adopted to improve liquidity and create new funding channels for large scale space missions. As a result, capital availability for satellite constellations and launch programs continues to improve, with North America remaining a key hub due to strong fintech capabilities and industry collaboration.
In June 2025, Thales Alenia Space demonstrated this progress by deploying a blockchain network in orbit through the IMAGIN-e mission with 3IPK. The system applies multiple AI models to analyze sensor data in real time, prioritizing critical insights while discarding low value data. Blockchain based verification enhances secure and transparent asset monitoring, supporting future space securitization models.
Restraint
Tough Rules Across Borders
Regulatory fragmentation across countries remains a key challenge for space asset securitization, as varying export controls, data protection rules, and national security requirements increase compliance complexity and costs. These differences limit the ability to standardize securitized assets for cross border trading and create uncertainty around ownership rights, which keeps many investors cautious.
Supply chain instability adds further pressure, with material shortages and geopolitical tensions delaying spacecraft manufacturing and deployment. Financial institutions remain hesitant due to the lack of historical benchmarks for space backed securities, while cybersecurity risks linked to blockchain enabled platforms raise additional concerns. Together, these factors slow securitization activity despite strong technological progress.
In May 2025, Rheinmetall and ICEYE announced plans for a satellite production joint venture under the Rheinmetall Space Cluster, highlighting these barriers. Differences in national data regulations and export controls complicate technology transfer, while geopolitical supply chain risks delay production timelines and reinforce investor uncertainty around international legal frameworks.
Opportunities
Private Cash for Space Growth
The rising flow of private capital is reshaping space asset securitization, as investors seek exposure to high growth space assets through fractional ownership models. Securitized instruments linked to satellites and launch systems are improving liquidity and expanding funding options for space companies. Stronger collaboration between public agencies and private firms is also supporting market confidence and faster execution of capital intensive projects.
New investment areas such as orbital debris management, lunar infrastructure, and in orbit servicing are further widening the opportunity set. Blockchain based platforms are simplifying leasing and secondary trading of space assets, making participation easier for wealth funds and individual investors. This trend is strengthening diversified capital inflows and supporting the next phase of space commercialization across key regions.
In September 2024, Lockheed Martin Ventures led a funding round in Agile Space Industries to expand propulsion technology and mobile payload centers. This investment highlights growing private sector interest in space hardware that can later be structured into securitized assets, reinforcing momentum toward fractional ownership and commercial satellite network expansion.
Challenges
Valuing Rare Space Assets
Valuation remains a major challenge in space asset securitization due to the unique nature of orbital assets and the lack of long term market history. Satellites and spacecraft face uncertain lifespans because of technology degradation, space debris exposure, and harsh operating conditions, making accurate pricing difficult. Inconsistent valuation approaches, combined with high operating costs and specialized insurance requirements, continue to create wide gaps in risk assessment among investors and lenders.
Efforts to build standardized valuation frameworks and improve data transparency are under way, but progress remains slow. Fragmented regulations, limited international coordination, and a shortage of professionals with expertise across both finance and space engineering add to market uncertainty. Supply chain disruptions and cybersecurity risks further complicate confidence in securitized structures.
In May 2025, Northrop Grumman invested USD 50 million in Firefly Aerospace to support development of the Eclipse rocket, highlighting these valuation issues. Delays, cost overruns, and difficulty in pricing early stage launch systems illustrate how uncertainty around asset lifespan and operational risk continues to weigh on investor confidence in space asset securitization.
Key Players Analysis
SpaceX, SES, Intelsat, Eutelsat, and OneWeb lead the space asset securitization market through large satellite fleets that enable predictable cash flows for asset-backed financing. Their revenue is anchored in broadband connectivity, broadcast services, and managed network capacity. These operators support securitization by offering long-term service contracts and stable utilization rates. Rising demand for satellite-based internet and broadcasting continues to strengthen their role in structured space financing.
Iridium Communications, Viasat, Telesat, Planet Labs, and Maxar Technologies strengthen the market with communication and Earth observation assets that generate recurring data and service revenue. Their satellites support mobility services, defense, climate monitoring, and commercial imaging. These companies benefit from subscription-led models that improve asset bankability.
Inmarsat, Hughes Network Systems, EchoStar, Blue Origin, Lockheed Martin, Airbus Defence and Space, Northrop Grumman, and Thales Alenia Space expand the landscape through satellite manufacturing, launch services, and secure government-backed programs. Their involvement improves asset reliability and investor confidence. These players enable risk-sharing structures and long-duration asset financing.
Top Key Players in the Market
- SpaceX
- SES S.A.
- Intelsat S.A.
- Eutelsat Communications
- OneWeb
- Iridium Communications Inc.
- Viasat Inc.
- Telesat
- Planet Labs PBC
- Maxar Technologies
- Inmarsat
- Hughes Network Systems
- EchoStar Corporation
- Blue Origin
- Lockheed Martin
- Airbus Defence and Space
- Northrop Grumman
- Thales Alenia Space
- Others
Recent Developments
- In September 2025, Viasat landed a multi-year contract with the U.S. Space Force to build next-gen space-based encryption tech, securing sensitive data from space-to-ground links. This bolsters protection for high-value satellite assets, making Viasat’s fleet even more bankable for securitization as defense spending pours into resilient space infrastructure.
- In December 2025, SpaceX is eyeing a secondary share sale that could value the company at nearly $800 billion, paving the way for a 2026 IPO while ramping up Starlink launches. With Starlink’s massive constellation generating steady subscription revenue, this positions SpaceX assets as prime candidates for innovative securitization structures blending satellite capacity with broadband cash flows.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 2.08 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 8.56 Bn CAGR(2025-2034) 15.2% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue forecast, AI impact on Market trends, Share Insights, Company ranking, competitive landscape, Recent Developments, Market Dynamics and Emerging Trends Segments Covered By Asset Type (Satellites, Spacecraft, Launch Vehicles, Ground Equipment, Others), By Securitization Structure (Asset-Backed Securities, Mortgage-Backed Securities, Collateralized Debt Obligations, Others), By End-User (Commercial, Government, Defense, Others), By Application (Telecommunications, Earth Observation, Navigation, Space Exploration, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of Latin America; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape SpaceX, SES S.A., Intelsat S.A., Eutelsat Communications, OneWeb, Iridium Communications Inc., Viasat Inc., Telesat, Planet Labs PBC, Maxar Technologies, Inmarsat, Hughes Network Systems, EchoStar Corporation, Blue Origin, Lockheed Martin, Airbus Defence and Space, Northrop Grumman, Thales Alenia Space, Others Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three license to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Space Asset Securitization MarketPublished date: Dec. 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Space Asset Securitization MarketPublished date: Dec. 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- SpaceX
- SES S.A.
- Intelsat S.A.
- Eutelsat Communications
- OneWeb
- Iridium Communications Inc.
- Viasat Inc.
- Telesat
- Planet Labs PBC
- Maxar Technologies
- Inmarsat
- Hughes Network Systems
- EchoStar Corporation
- Blue Origin
- Lockheed Martin
- Airbus Defence and Space
- Northrop Grumman
- Thales Alenia Space
- Others










