Global Smart Grid Network Market Size, Share, Growth Analysis Report By Application (Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI), Transmission, Demand Response, Other Applications), By End-User (Residential, Commercial, Industrial), Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2024-2033
- Published date: November 2024
- Report ID: 132505
- Number of Pages: 248
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
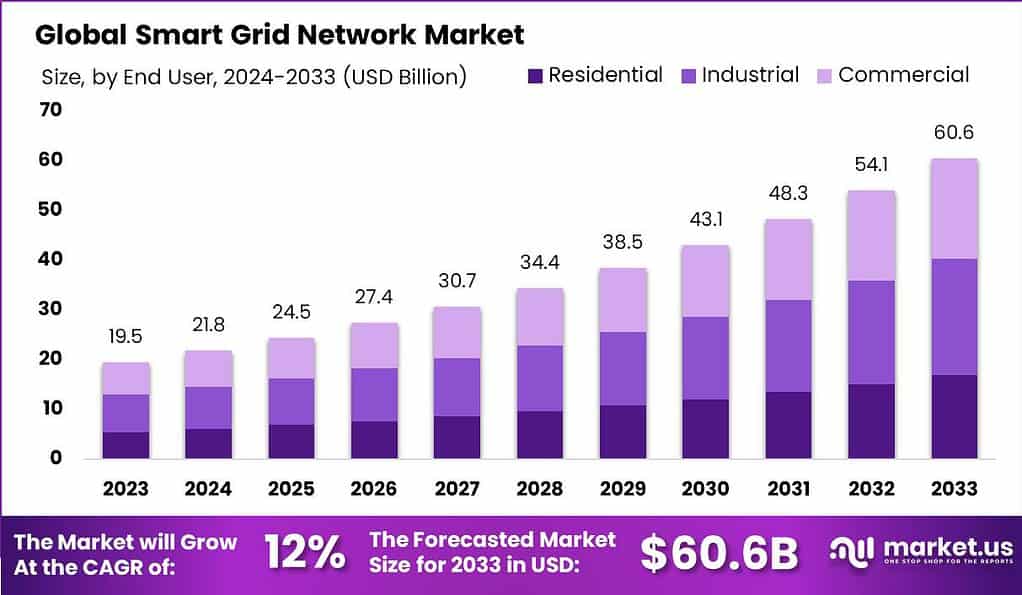
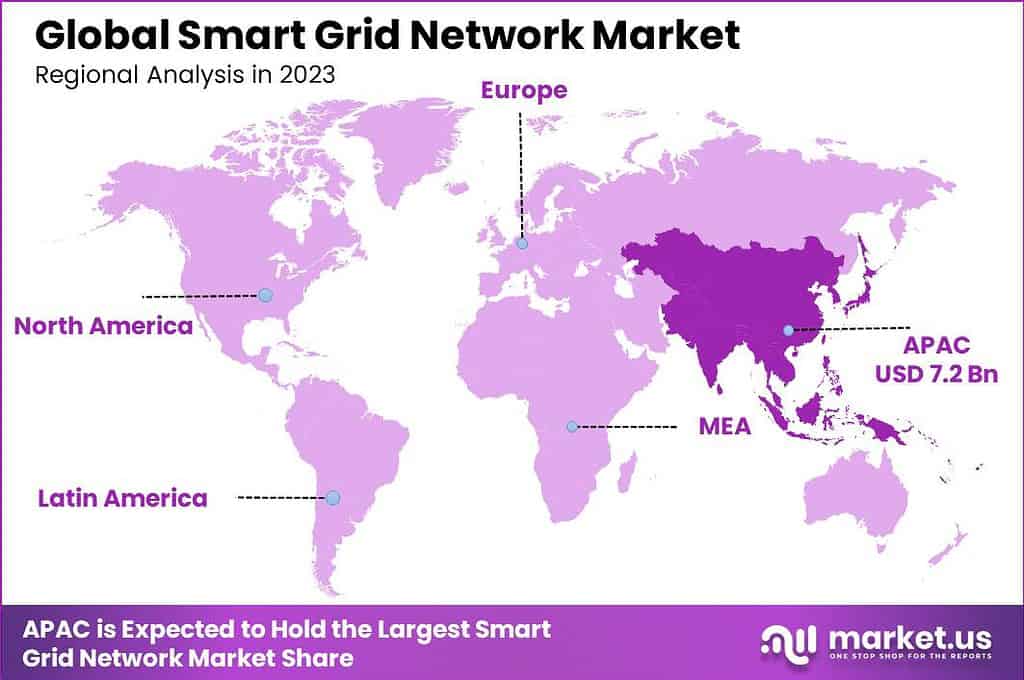
The Global Smart Grid Network Market size is expected to be worth around USD 60.6 Billion By 2033, from USD 19.5 Billion in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 12.00% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033. In 2023, the Asia-Pacific region dominated the smart grid network market, accounting for more than 37.0% of the market share and generating USD 7.2 billion in revenue.
A smart grid network is an advanced electricity supply network that enhances the traditional electricity grid by integrating digital communications technology. This technology allows for real-time management and monitoring of the electricity flow from generators to consumers. Smart grids help to improve the efficiency, reliability, and sustainability of the production and distribution of electricity.
The growth of the smart grid network market is primarily driven by the increasing demand for efficient energy solutions and government initiatives promoting renewable energy. As global energy consumption rises, there is a significant push towards sustainable energy practices. Smart grids play a crucial role in integrating renewable resources, which tend to be more variable and dispersed compared to traditional energy sources.
Furthermore, the growing need for grid reliability and energy efficiency, spurred by the rise in extreme weather events and electricity demand, compels utilities to invest in smart grid technologies. Technological advancements in IoT and AI are also critical, as they enhance grid management capabilities through predictive analytics and real-time decision-making.
The demand for smart grid networks is surging due to growing environmental concerns and the push for clean energy. Governments and energy companies are heavily investing in smart grid technologies to ensure energy efficiency and to reduce carbon footprints. This demand is further propelled by the aging infrastructure of existing power grids, necessitating upgrades to incorporate smart technology solutions.
Smart grid technology has gained significant popularity because of its ability to optimize power consumption and enhance operational performance for utility companies. Consumer awareness regarding the benefits of smart grids, such as reduced power outages, enhanced energy management, and cost savings on utility bills, has also increased their acceptance.
For instance, In January 2023, ABB entered into a strategic partnership with OKTO GRID, a Denmark-based digital solutions provider focusing on electrical assets. This collaboration aims to revolutionize the digitalization of energy grids and extend the lifespan of associated electrical infrastructure. Through their joint efforts, ABB and OKTO GRID are set to modernize aging grid systems, enhancing reliability and delivering consistent energy supplies worldwide.
There are numerous opportunities within the smart grid network market, particularly in developing regions where grid systems are not yet fully developed. The integration of IoT and AI technologies into smart grids presents opportunities for innovation in grid management and maintenance. Also, the ongoing shift towards renewable energy sources offers a significant chance for the expansion and upgrade of grid networks to accommodate new types of energy inputs.
Key Takeaways
- The Global Smart Grid Network Market size is projected to reach approximately USD 60.6 Billion by 2033, growing from USD 19.5 Billion in 2023, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.00% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
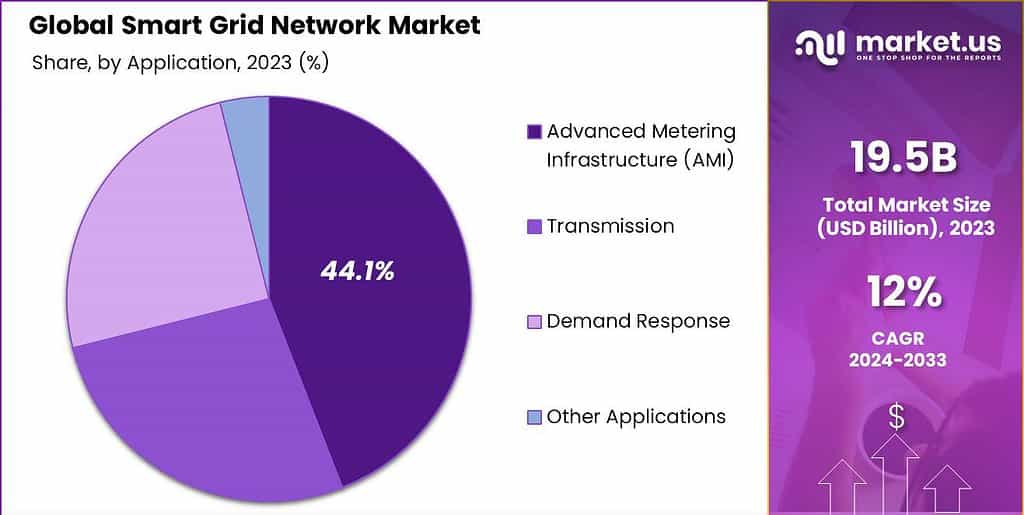
- In 2023, the Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) segment held a dominant position in the market, capturing over 44.1% of the market share.
- The Industrial segment also led the market in 2023, accounting for more than 38.5% of the total market share.
- The Asia-Pacific region dominated the global Smart Grid Network market in 2023, with a market share exceeding 37.0%, and generating revenue of USD 7.2 billion.
Application Analysis
In 2023, the Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) segment held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 44.1% share. This substantial market share is attributed to the significant role that AMI systems play in modernizing energy management networks. These systems enable utilities to automatically collect data on electricity, gas, and water usage in real time.
This facilitates more accurate billing, improved energy consumption management, and the ability to detect outages quickly, which is critical for enhancing operational efficiencies and customer service. The deployment of AMI has been pivotal in driving smarter energy solutions. Utilities are leveraging AMI to implement dynamic pricing models that encourage consumers to adjust their usage patterns in response to real-time changes in energy prices, thereby aiding in peak load management and contributing to energy conservation.
Additionally, AMI systems are integral to the integration of renewable energy sources into the grid, as they provide the critical data needed to balance supply and demand effectively. Furthermore, the surge in smart city initiatives across the globe has spurred the growth of the AMI segment. Cities are adopting smart technologies to enhance their sustainability efforts, with AMI serving as a backbone for these initiatives by ensuring efficient energy usage and reducing carbon footprints.
The ability of AMI to support other smart grid applications like demand response systems and grid optimization further solidifies its position as a key component of the smart grid network. Overall, the dominance of the AMI segment is expected to continue as more utilities and municipalities recognize its benefits in cost reduction, operational efficiency, and enhanced consumer engagement in energy management.
End-User Analysis
In 2023, the Industrial segment held a dominant market position in the smart grid network market, capturing more than a 38.5% share. This leadership is primarily due to the critical need for reliable and efficient power management in industrial operations, which face high energy demands and significant costs associated with downtime and energy inefficiencies.
Industries are increasingly adopting smart grid technologies to enhance their energy consumption patterns and to improve the resilience of their operations against power-related disruptions. The use of smart grid technologies in the industrial sector facilitates greater control over energy usage and costs by employing advanced metering infrastructure (AMI), demand response systems, and grid optimization tools.
These technologies enable industries to reduce peak energy loads, participate in utility demand-response programs, and improve their overall energy efficiency. Moreover, smart grids help industries comply with regulatory standards for energy consumption and carbon emissions, thus not only optimizing operational costs but also bolstering their sustainability initiatives.
Another driver for the adoption of smart grid technologies in the industrial sector is the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, into their energy systems. Smart grids enable a more seamless integration of these variable energy sources, which is essential for maintaining grid stability and ensuring a constant energy supply. This is increasingly important as industries seek to reduce their reliance on fossil fuels and move towards greener alternatives.
Key Market Segments
By Application
- Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI)
- Transmission
- Demand Response
- Other Applications
By End-User
- Residential
- Commercial
- Industrial
Driver
Integration of Renewable Energy Sources
The global shift towards sustainable energy has significantly propelled the adoption of smart grid networks. Traditional power grids, designed for unidirectional electricity flow from centralized power plants, face challenges in accommodating decentralized and intermittent renewable energy sources like solar and wind.
Smart grids, equipped with advanced communication and automation technologies, enable real-time monitoring and management of energy flows, facilitating the seamless integration of renewables into the energy mix.
This integration not only enhances grid reliability and efficiency but also supports environmental goals by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. For instance, countries with high renewable energy penetration have leveraged smart grid technologies to balance supply and demand effectively, ensuring a stable and resilient power supply.
Restraint
High Implementation Costs
Despite the numerous benefits, the deployment of smart grid networks is often hindered by substantial initial investment requirements. Upgrading existing infrastructure to incorporate advanced metering systems, communication networks, and automated control mechanisms demands significant capital expenditure.
Utilities, especially in developing regions, may find it challenging to justify these costs without clear, immediate returns on investment. Additionally, the complexity of integrating new technologies with legacy systems can lead to unforeseen expenses and technical hurdles. While long-term operational savings and efficiency gains are anticipated, the upfront financial burden remains a critical barrier to widespread smart grid adoption.
Opportunity
Advancements in Energy Storage Technologies
The evolution of energy storage solutions presents a significant opportunity for the smart grid network market. Efficient storage systems, such as advanced battery technologies, enable the retention of excess energy generated during periods of low demand, which can be dispatched during peak times or when renewable generation is low.
This capability enhances grid stability and reliability, making it easier to manage the variability associated with renewable energy sources. Moreover, integrating energy storage with smart grids allows for more effective demand response strategies, where consumers can adjust their energy usage in response to real-time price signals or grid needs.
As storage technologies become more cost-effective and scalable, they offer utilities and consumers alike the potential to optimize energy consumption, reduce costs, and contribute to a more resilient and sustainable energy system.
Challenge
Cybersecurity Threats
The digitalization inherent in smart grid networks introduces vulnerabilities to cyberattacks, posing a significant challenge to their deployment and operation. As these grids rely on interconnected devices and communication networks to function, they become potential targets for malicious activities that can disrupt power supply, compromise sensitive data, or damage critical infrastructure.
Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures is essential to protect against such threats. This includes implementing secure communication protocols, regular system monitoring, and rapid response strategies to detect and mitigate potential breaches. The dynamic nature of cyber threats necessitates continuous vigilance and adaptation, requiring utilities to invest in advanced security technologies and workforce training.
Emerging Trends
The evolution of smart grid networks is reshaping how we produce, distribute, and consume electricity. A significant trend is the integration of the Internet of Energy (IoE), which leverages Internet of Things (IoT) devices to enable real-time monitoring and management of energy systems. This connectivity allows for more efficient energy distribution and consumption, enhancing grid reliability and resilience.
Another notable development is the incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) into grid operations. AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of data to predict energy demand, detect faults, and optimize energy flow, leading to reduced operational costs and improved service reliability.
The rise of microgrids is also transforming the energy landscape. These localized grids can operate independently or in conjunction with the main grid, providing communities with greater energy security and the ability to integrate renewable energy sources more effectively.
Additionally, the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, into the grid is becoming more prevalent. This shift not only reduces carbon emissions but also necessitates advanced grid management techniques to handle the variability of these energy sources.
Business Benefits
Implementing smart grid networks offers numerous advantages for businesses and utilities. One of the primary benefits is enhanced operational efficiency. Real-time data collection and analysis enable utilities to monitor energy flow accurately, quickly identify issues, and reduce downtime, leading to cost savings and improved service reliability.
Smart grids also facilitate better demand response management. By providing detailed consumption data, businesses can adjust their energy usage during peak periods, potentially lowering energy costs and contributing to grid stability.Moreover, advanced monitoring systems can detect and address power quality issues promptly, minimizing disruptions that could affect business operations.
The integration of renewable energy sources into smart grids allows businesses to adopt sustainable practices more easily. This not only reduces environmental impact but can also enhance corporate reputation and meet regulatory requirements for sustainability.
Additionally, the adoption of smart grid technologies can lead to new business opportunities. For instance, companies can develop and offer innovative energy management solutions or participate in energy markets through demand response programs, creating new revenue streams.
Regional Analysis
In 2023, APAC held a dominant position in the smart grid network market, capturing more than a 37% share with revenues amounting to USD 7.2 billion. This leadership stems primarily from substantial investments in modernizing power infrastructure to support burgeoning urban populations and rapidly growing industrial sectors.
Countries like China and India are at the forefront, driven by national initiatives that aim to enhance grid reliability and integrate renewable energy sources extensively. China, for instance, has made significant strides with its ambitious plans to increase the use of renewable energy, necessitating advanced grid solutions to manage the variability and distribution challenges associated with solar and wind energies.
Similarly, India’s government has been proactive with initiatives like the National Smart Grid Mission, which aims to implement full-scale smart grid capabilities across the country to improve efficiency and reduce losses in power transmission and distribution. The region’s focus on sustainability and reduction of carbon footprints has further fueled the adoption of smart grid technologies.
This includes efforts to upgrade outdated infrastructure and increase the deployment of smart meters, which are pivotal in managing energy consumption efficiently. As these countries continue to urbanize and industrialize, the demand for more sophisticated and reliable energy solutions is expected to grow, ensuring APAC’s leading role in the global smart grid network market for years to come.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Singapore
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Key Player Analysis
In the competitive landscape of the Smart grid network market, key companies stand out due to their innovative solutions and global reach. Each company brings unique strengths to the table, significantly shaping the industry’s dynamics.
Siemens AG has established itself as a leader in the smart grid industry by offering a wide range of solutions that enhance grid stability and efficiency. Siemens focuses on digital grid solutions that incorporate advanced technologies like AI and IoT to optimize electricity distribution and enable seamless integration of renewable energy sources.
ABB Group is another prominent figure in the smart grid network market, renowned for its robust and efficient energy solutions. ABB’s expertise lies in their comprehensive suite of products and services that cover everything from grid automation to energy management systems.
Schneider Electric SE stands out for its integrated and holistic approach to smart grid technology. Schneider Electric’s solutions are geared towards optimizing energy costs and consumption, which are critical factors for the adoption of smart grid technologies. Their EcoStruxure Grid platform leverages edge control and analytics to enhance grid performance, energy efficiency, and sustainability.
Top Key Players in the Market
- Siemens AG
- ABB Group
- Schneider Electric SE
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Oracle Corporation
- General Electric Company
- Eaton Corporation plc
- Landis+Gyr
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Itron, Inc.
- Other Key Players
Recent Developments
- In 2023, Eaton Corporation plc continued to be a key player in the smart grid market, offering solutions that improve grid reliability and efficiency. Their portfolio includes advanced metering infrastructure and grid automation technologies.
- In June 2024, Landis+Gyr partnered with Itron to integrate their smart grid communication technologies, broadening the options available for utilities in deploying advanced metering systems.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2023) USD 19.5 Bn Forecast Revenue (2033) USD 60.6 Bn CAGR (2024-2033) 12.00% Base Year for Estimation 2023 Historic Period 2019-2022 Forecast Period 2024-2033 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, COVID-19 Impact, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Application (Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI), Transmission, Demand Response, Other Applications), By End-User (Residential, Commercial, Industrial) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Siemens AG, ABB Group, Schneider Electric SE, Cisco Systems,Inc., Oracle Corporation, General Electric Company, Eaton Corporation plc, Landis+Gyr, Honeywell International Inc., Itron,Inc., Other Key Players Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three license to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Smart Grid Network MarketPublished date: November 2024add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Smart Grid Network MarketPublished date: November 2024add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Siemens AG
- ABB Group
- Schneider Electric SE
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Oracle Corporation
- General Electric Company
- Eaton Corporation plc
- Landis+Gyr
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Itron, Inc.
- Other Key Players













