Global Smart Asset Management in Utility Market Size, Share, Statistics Analysis Report By Component (Hardware (Sensors, Smart Meters, Actuators, RFID Devices), Software (Asset Performance Management (APM), Enterprise Asset Management (EAM), Predictive Maintenance Tools), Services (Consulting & Integration, Support & Maintenance, Managed Services))), By Asset Type (Electric Assets (Transformers, Substations, Transmission Lines), Water Assets (Pipelines, Pumps, Water Treatment Plants), Gas Assets (Distribution Pipes, Gas Meters, Storage Tanks)), By Deployment Mode (On-premise, Cloud-based), By Utility Type (Electric Utilities, Water Utilities, Gas Utilities, Combined Utilities (Multi-utility providers)), By Application (Predictive Maintenance, Real-time Asset Monitoring, Lifecycle Management, Work Order Management, Outage Management, Risk Management, Others), By Enterprise Size (Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs), Large Enterprises), Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: May 2025
- Report ID: 148730
- Number of Pages: 337
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
- Report Overview
- Key Takeaways
- Strategy Highlights
- U.S. Market Growth
- Component Analysis
- Asset Type Analysis
- Deployment Mode Analysis
- Utility Type Analysis
- Application Analysis
- Enterprise Size Analysis
- Key Market Segments
- Driver
- Restraint
- Opportunity
- Challenge
- Emerging Trends
- Business Benefits
- Key Player Analysis
- Recent Developments
- Report Scope
Report Overview
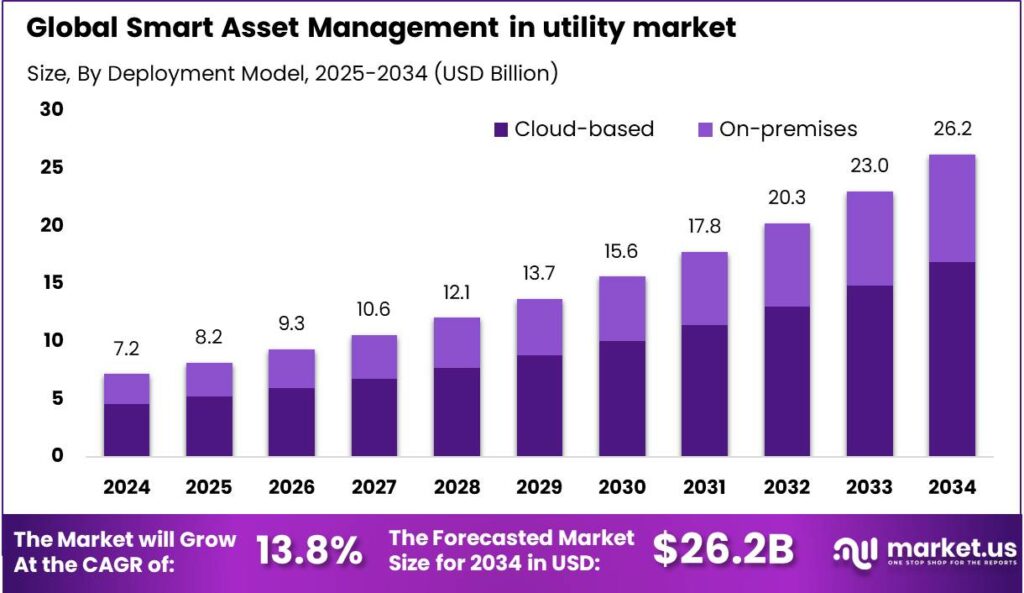
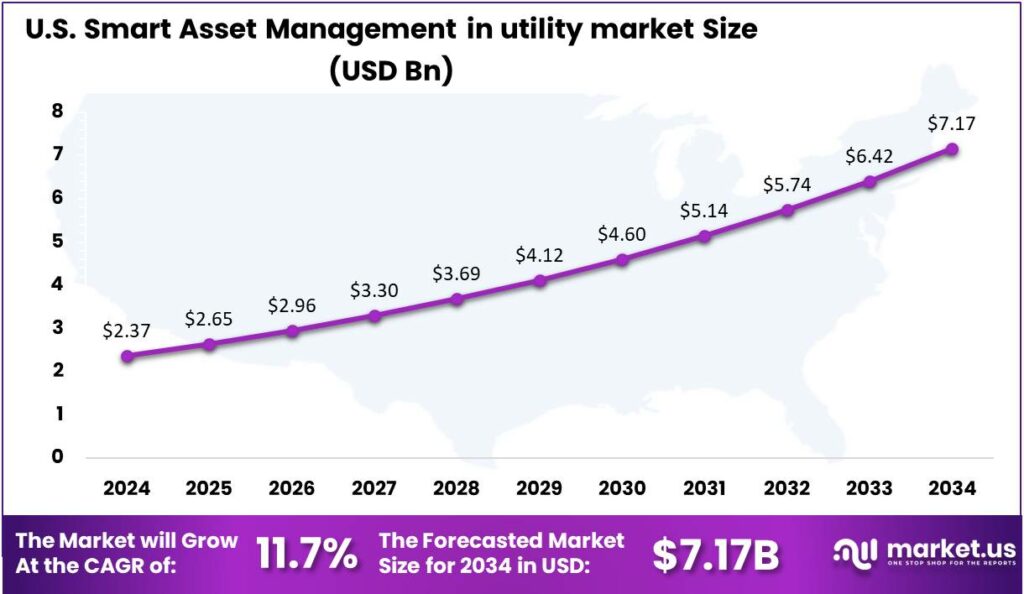
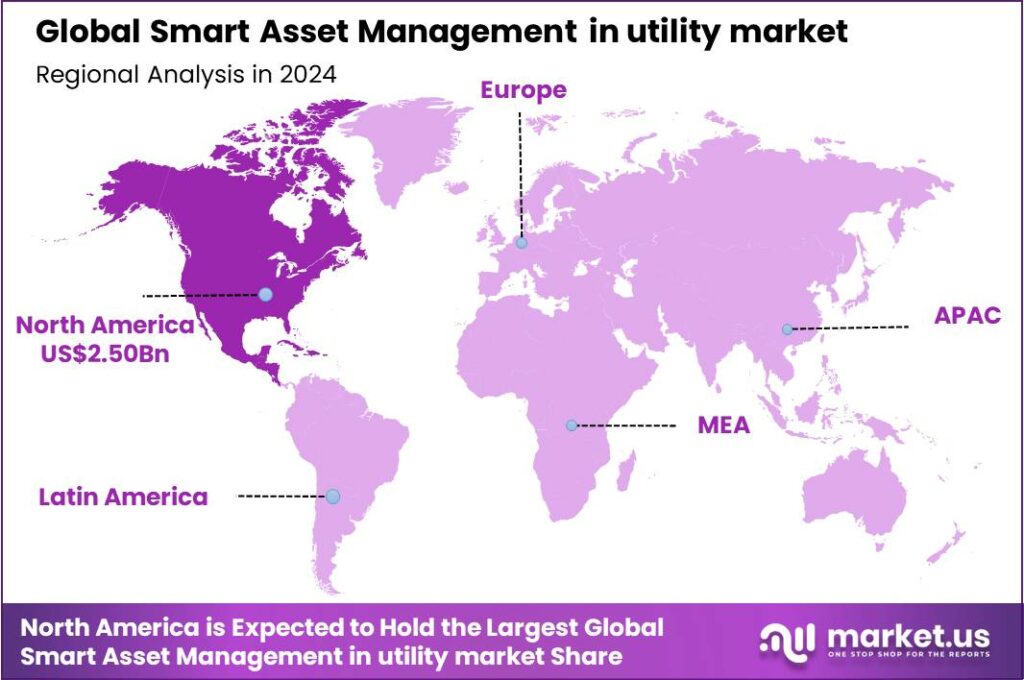
The Smart Asset Management in utility market size is expected to be worth around USD 26.2 Bn By 2034, from USD 7.2 Bn in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 13.80% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North America dominated the market in the utility sector, capturing over 34.8% of the global market share and generating approximately USD 2.50 billion in revenue. The U.S. market was valued at USD 2.37 bn, with a CAGR of 11.7%, driven by increased digitalization of infrastructure.
Smart Asset Management in utilities refers to the strategic approach of overseeing and maintaining physical assets – such as transformers, substations, and distribution lines – using advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and data analytics. This method enables utilities to monitor asset conditions in real-time, predict failures before they occur, and optimize maintenance schedules, thereby enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs.
The primary driver fueling the growth of Smart Asset Management in the utility industry is the aging infrastructure across developed and emerging economies. Aging infrastructure is straining utility reliability and safety, driving demand for intelligent systems that can predict failures in advance. With IoT-enabled sensors and AI-driven analytics, utilities are moving from reactive to condition-based and predictive maintenance strategies.
Technological advancements are central to the increasing adoption of SAM. The integration of IoT devices enables real-time monitoring of asset conditions, while AI and machine learning algorithms facilitate predictive maintenance by analyzing data patterns to forecast potential failures. These technologies collectively enhance decision-making processes, reduce operational risks, and contribute to more sustainable utility operations.
Investing in SAM offers numerous business benefits. Utilities can achieve significant cost savings through optimized maintenance schedules and reduced unplanned outages. Enhanced asset performance leads to improved service quality and customer satisfaction. Moreover, the data-driven insights provided by SAM support strategic planning and resource allocation, enabling utilities to respond more effectively to changing market demands and regulatory requirements.
The regulatory environment also influences the adoption of SAM in utilities. Regulatory bodies increasingly mandate stringent standards for asset performance, reliability, and reporting. SAM systems facilitate compliance by providing accurate and timely data, supporting utilities in meeting these regulatory obligations and avoiding potential penalties.
Several factors significantly impact the implementation of SAM in the utility sector. These include the availability of skilled personnel to manage and interpret complex data systems, the initial investment costs associated with deploying advanced technologies, and the need for organizational change management to integrate new processes. Addressing these factors is essential for the successful adoption and utilization of SAM solutions.
Key Takeaways
- The Global Smart Asset Management in the utility market size is expected to reach USD 26.2 Billion by 2034, growing from USD 7.2 Billion in 2024, at a CAGR of 13.80% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
- In 2024, the Hardware segment held a dominant market position, capturing more than 42% of the share, primarily driven by the widespread deployment of IoT devices, sensors, and smart meters across electric, water, and gas utilities.
- In 2024, the Electric Assets segment maintained a dominant market position in the utility smart asset management landscape, capturing more than 50.6% of the market share.
- In 2024, the cloud-based segment held a dominant position in the smart asset management in utility market, accounting for more than 64.4% of the total market share.
- In 2024, the Electric Utilities segment held a dominant market position, capturing over 48% of the market share in the smart asset management in utility sector.
- In 2024, the Predictive Maintenance segment led the market with a dominant share of more than 22% in the smart asset management in utility market.
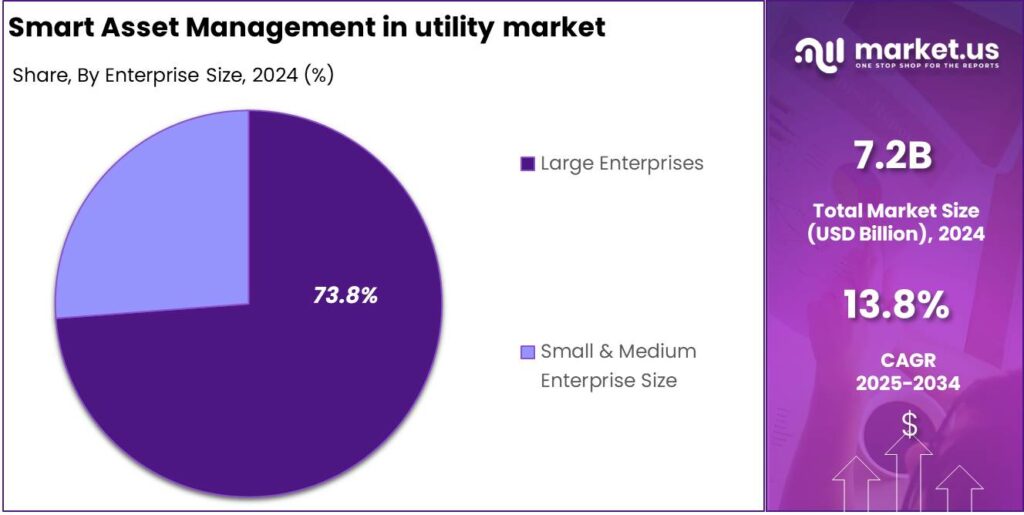
- In 2024, the Large Enterprises segment dominated the market, capturing more than 73.8% of the share in the smart asset management market within the utility sector.
- In 2024, North America held a dominant market position in the smart asset management in the utility sector, capturing over 34.8% of the global market share and generating revenue of approximately USD 2.50 billion.
- In 2024, the U.S. smart asset management market in the utility sector was valued at around USD 2.37 billion, with a CAGR of 11.7%, driven by the increasing digitalization of infrastructure.
Strategy Highlights
Key aspects of Smart Asset Management (SAM) in utilities are centered around enhancing operational efficiency, asset longevity, and regulatory compliance through the use of intelligent technologies. These aspects form the foundation of digital transformation strategies within utility infrastructures:
- One of the core components is real-time asset monitoring, which is enabled by the integration of IoT sensors across utility equipment such as transformers, substations, pipelines, and power grids. These sensors collect continuous data on parameters like temperature, vibration, pressure, and energy flow, allowing early detection of anomalies and failures.
- Another vital aspect is lifecycle asset management, which supports strategic planning from procurement through decommissioning. Smart systems track the performance and degradation of assets, helping utility providers optimize asset replacement cycles and allocate capital more effectively.
- Data integration and analytics also play a critical role, as utility companies often manage thousands of dispersed assets. Advanced analytics platforms consolidate this data into centralized dashboards, offering decision-makers comprehensive visibility into asset health, operational status, and future maintenance needs.
- Cybersecurity and data governance have become increasingly important, as digital asset management exposes infrastructure to cyber threats. Secure data protocols and compliance with standards like NERC CIP ensure the integrity and confidentiality of asset-related data.
- Finally, regulatory compliance and reporting are strengthened under SAM frameworks. With digital tracking and documentation, utilities can more easily demonstrate compliance with energy efficiency mandates, emissions targets, and operational benchmarks set by government agencies, contributing to sustainable and resilient energy systems.
U.S. Market Growth
In 2024, the U.S. smart asset management market in the utility sector was valued at approximately USD 2.37 billion, reflecting the growing digitalization of infrastructure and the increased adoption of intelligent monitoring solutions across power, water, and gas utilities. The market is being propelled by a steady push toward modernizing grid systems, optimizing asset lifecycles, and minimizing unplanned outages.
The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.7% forecasted for the coming years suggests strong momentum in digital transformation across the U.S. utility landscape. This growth can be attributed to several converging factors, including regulatory mandates for grid modernization, the integration of renewable energy sources, and increasing investments in smart grids and digital twins.
Additionally, advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning algorithms, and cloud-based platforms are further expanding the capabilities of asset management systems.These innovations allow for seamless remote data aggregation, real-time condition monitoring, and predictive failure analytics helping utility operators improve efficiency, maintain environmental compliance, and enhance customer satisfaction.
In 2024, North America held a dominant market position in the smart asset management in utility sector, capturing over 34.8% of the global market share and generating revenue of approximately USD 2.50 billion. This leadership is primarily driven by the region’s early adoption of digital utility infrastructure, advanced asset performance management systems, and significant investment in grid modernization programs.
One of the key factors behind North America’s lead is the strong presence of major technology players and utility conglomerates that are at the forefront of innovation. Companies across the U.S. have formed strategic collaborations with AI, IoT, and cloud service providers to enhance real-time asset monitoring and reduce downtime.
North America shows higher adoption of smart meters, automated substations, and GIS-integrated platforms than other regions. This trend is reinforced by strict FERC and NERC regulations, which drive utilities to adopt advanced asset management practices to meet performance and reliability standards.
The North American market leads in smart asset management for utilities, driven by the need for sustainable, resilient operations amid extreme weather and aging grid infrastructure. Utilities are investing in digital twins, AI forecasting, and condition-based maintenance to prevent failures and boost disaster readiness, making the region both the largest and most technologically advanced in this sector.
Component Analysis
In 2024, Hardware segment held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 42% share, primarily due to the widespread deployment of IoT devices, sensors, and smart meters across electric, water, and gas utilities. The growing focus on real-time data acquisition and condition monitoring has made physical devices a foundational layer in the smart asset ecosystem.
Utilities are increasingly embedding sensors and actuators into transmission and distribution assets to continuously track health, usage, and performance, enabling a shift from time-based to condition-based maintenance. This has made hardware components indispensable for utilities aiming to modernize their asset infrastructures.
Rising demand for smart meters, especially in digitally transforming regions, is driving growth in the hardware segment. These devices enable real-time monitoring, detect anomalies, and meet regulatory and consumer demands for transparency, leading utilities to rapidly scale installations.
RFID devices and edge sensors are also playing a critical role in tracking the movement, location, and usage of assets in real-time, especially in power grids and water treatment plants. These devices allow asset tagging and streamline inventory and lifecycle management, which is especially valuable in geographically dispersed utility networks.
Asset Type Analysis
In 2024, the Electric Assets segment held a dominant market position in the utility smart asset management landscape, capturing more than a 50.6% share. This prominence is primarily attributed to the critical nature of electric infrastructure such as transformers, substations, and transmission lines which necessitates continuous monitoring and maintenance to ensure uninterrupted power supply.
The Water Assets segment, encompassing pipelines, pumps, and water treatment plants, has been progressively adopting smart asset management technologies. The implementation of IoT sensors and advanced analytics in this segment aids in leak detection, pressure monitoring, and overall system optimization. These technologies contribute to water conservation efforts and operational efficiency.
Gas Assets, including distribution pipes, gas meters, and storage tanks, are also integrating smart asset management systems to enhance safety and efficiency. The deployment of advanced monitoring tools allows for the early detection of leaks and system anomalies, thereby mitigating risks associated with gas distribution.
The leading position of the Electric Assets segment in the smart asset management market is further reinforced by the increasing demand for reliable electricity, driven by urbanization and the proliferation of digital technologies. Utilities are prioritizing investments in smart grid technologies to enhance resilience and meet regulatory requirements.
Deployment Mode Analysis
In 2024, the cloud-based segment held a dominant position in the smart asset management in utility market, capturing more than 64.4% of the total market share. This leadership is largely due to the growing need among utility providers for scalable, cost-effective, and remotely accessible solutions.
The shift toward cloud-based smart asset management is also being accelerated by the increasing complexity of modern utility networks. With rising integration of renewable energy, distributed energy resources (DERs), and smart grids, utility providers require flexible systems that can handle dynamic operational demands.
Cloud platforms offer utilities the agility to scale up or down based on demand and integrate new data sources quickly. In contrast to traditional on-premise models, which involve time-intensive upgrades and limited interoperability, cloud systems enable continuous innovation through seamless updates and integrations with IoT devices, sensors, and AI modules.
Enhanced security and compliance frameworks have boosted trust in cloud-based systems. With protocols like NERC CIP and ISO/IEC 27001, vendors address data privacy concerns, prompting utilities especially in North America and Europe to shift from legacy systems. Cloud platforms now enable scalable predictive maintenance, asset lifecycle management, and fault detection, significantly improving reliability and efficiency.
Utility Type Analysis
In 2024, Electric Utilities segment held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 48% share in the Smart Asset Management in utility market. This leadership can be attributed to the widespread integration of smart grid technologies, growing investments in electrical infrastructure modernization, and the rising pressure to minimize power outages and transmission losses.
As electricity remains the backbone of industrial and domestic life, utility providers are increasingly deploying smart asset management platforms to monitor transformer health, manage energy flow, and predict faults before they escalate. This demand has been intensified by regulatory mandates pushing for enhanced grid reliability and real-time monitoring of electric assets.
The adoption of AI-powered condition monitoring, predictive maintenance, and digital twin simulation is more prevalent in electric utilities than in other segments. With electric grids becoming increasingly complex due to the influx of distributed energy resources (DERs) such as solar and wind, utility providers are depending on asset intelligence tools to enhance visibility and operational efficiency.
The push for renewable energy integration is driving the need for advanced electric asset management. As grids become decentralized, utilities are adopting centralized systems for real-time analytics, remote diagnostics, and automated decision-making to manage transformer loads, grid balancing, and voltage control, ensuring stability and optimized energy flow.
Application Analysis
In 2024, Predictive Maintenance segment held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 22% share in the Smart Asset Management in utility market. This dominance is primarily driven by the growing need among utility providers to prevent equipment failures before they occur. Utilities face mounting pressure to ensure uninterrupted service, reduce downtime, and control maintenance costs.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning into predictive maintenance systems has further enhanced its adoption. These technologies help utility firms analyze historical data, operational trends, and real-time equipment performance to detect early signs of failure. For instance, transformers, switchgear, and pump stations equipped with condition-monitoring tools can now signal irregularities before a breakdown happens.
Another reason behind the segment’s growth is its alignment with cost optimization strategies. Traditional maintenance approaches often involve high labor costs and result in longer downtimes. Predictive maintenance, in contrast, minimizes these disruptions and ensures that resources are allocated more effectively.
Regulatory pressures on service reliability and infrastructure safety are driving investments in predictive maintenance technologies. With increasing emphasis on asset reliability, particularly in electric and water utilities, predictive maintenance has become a strategic priority, enhancing compliance, service continuity, and reducing operational risk. It is now a key application in smart asset management systems.
Enterprise Size Analysis
In 2024, Large Enterprises segment held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 73.8% share in the smart asset management market within the utility sector. This significant share can be attributed to the large-scale operational needs and complex asset infrastructures managed by utility giants.
Under regulatory pressure to improve asset performance and reduce operational risks, large utilities are increasing investments in asset digitization, including IoT sensors and integrated lifecycle management platforms. End-to-end integration with SCADA systems is essential, and large enterprises, with their IT maturity and digital transformation budgets, are well-positioned to meet this need.
Large enterprises, often operating across electric, gas, and water services, face increased complexity in asset tracking. To manage this, they require unified platforms offering real-time visibility, failure risk alerts, and long-term planning. Due to their organizational readiness and financial capacity, these enterprises are the primary drivers of market demand for robust asset management solutions.
Furthermore, partnerships with technology vendors and participation in smart grid modernization programs have also enabled large enterprises to stay ahead in digital asset management. Strategic collaborations with cloud providers and analytics firms have accelerated AI integration, enabling faster decisions and reduced downtime.
Key Market Segments
By Component
- Hardware
- Sensors
- Smart Meters
- Actuators
- RFID Devices
- Software
- Asset Performance Management (APM)
- Enterprise Asset Management (EAM)
- Predictive Maintenance Tools
- Services
- Consulting & Integration
- Support & Maintenance
- Managed Services
By Asset Type
- Electric Assets
- Transformers
- Substations
- Transmission Lines
- Water Assets
- Pipelines
- Pumps
- Water Treatment Plants
- Gas Assets
- Distribution Pipes
- Gas Meters
- Storage Tanks
By Deployment Mode
- On-premise
- Cloud-based
By Utility Type
- Electric Utilities
- Water Utilities
- Gas Utilities
- Combined Utilities (Multi-utility providers)
By Application
- Predictive Maintenance
- Real-time Asset Monitoring
- Lifecycle Management
- Work Order Management
- Outage Management
- Risk Management
- Others
By Enterprise Size
- Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
- Large Enterprises
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Singapore
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Driver
Enhanced Operational Efficiency through Predictive Maintenance
In the utility sector, the integration of smart asset management systems has significantly improved operational efficiency. By leveraging technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI), utilities can monitor equipment health in real-time.
This continuous monitoring enables predictive maintenance strategies, allowing for the identification of potential issues before they lead to equipment failure. Consequently, maintenance activities can be scheduled proactively, reducing unplanned outages and extending the lifespan of assets. This approach not only ensures a more reliable service delivery but also optimizes resource allocation, leading to cost savings and improved customer satisfaction.
Restraint
High Implementation Costs and Integration Challenges
Despite the benefits, the adoption of smart asset management systems in utilities faces significant barriers, primarily due to high initial investment costs. Implementing these systems requires substantial capital for purchasing advanced sensors, communication infrastructure, and analytics platforms.
Moreover, integrating new technologies with existing legacy systems poses technical challenges, often necessitating additional investments in system upgrades or replacements. These financial and technical hurdles can be particularly daunting for smaller utility companies, potentially delaying or limiting the adoption of smart asset management solutions. For smaller utility companies with limited budgets, this can result in significant operational challenges and hinder their ability to leverage the full potential of smart asset management solutions.
Opportunity
Integration of Renewable Energy Sources
The global shift towards renewable energy presents a significant opportunity for smart asset management in utilities. As utilities incorporate diverse energy sources like solar and wind into the grid, managing these assets becomes increasingly complex.
Smart asset management systems can facilitate this integration by providing real-time data and analytics, enabling utilities to monitor performance, predict maintenance needs, and optimize the operation of renewable assets. This capability not only enhances the efficiency and reliability of renewable energy sources but also supports utilities in meeting sustainability goals and regulatory requirements.
Challenge
Data Security and Cybersecurity Risks
The digitalization of asset management in utilities introduces significant cybersecurity challenges. Smart asset management systems rely on interconnected devices and networks to collect and transmit data, making them vulnerable to cyber threats.
Potential risks include unauthorized access, data breaches, and disruptions to critical infrastructure operations. Ensuring the security of these systems requires robust cybersecurity measures, including encryption, access controls, and continuous monitoring. Addressing these challenges is crucial to protect sensitive data, maintain customer trust, and ensure the reliable operation of utility services.
Cybercriminals can exploit vulnerabilities in smart asset management systems to disrupt operations, steal data, or damage infrastructure. Utilities, especially in critical sectors, face increased risks of attacks like ransomware or data breaches, leading to financial losses, reputational harm, and regulatory penalties.
Emerging Trends
One significant trend is the adoption of AI-driven predictive maintenance. AI algorithms analyze data from sensors to forecast equipment failures, allowing utilities to perform maintenance proactively, thus reducing downtime and extending asset life .
IoT-enabled devices are increasingly used for real-time asset monitoring, enabling timely interventions and efficient resource allocation. Meanwhile, blockchain technology enhances data security and transparency in asset management by creating immutable records of transactions and maintenance, ensuring data integrity and fostering trust.
Furthermore, the integration of digital twins virtual replicas of physical assets allows for advanced simulations and scenario planning. Utilities can test various operational strategies in a risk-free environment, leading to more informed decision-making .
Business Benefits
Smart Asset Management enables utilities to monitor equipment health in real-time, allowing for early detection of potential issues. This proactive approach reduces unexpected breakdowns and extends the lifespan of assets. By addressing problems before they escalate, utilities can maintain consistent service delivery.
SAM systems collect and analyze vast amounts of data from various assets, providing utilities with actionable insights. These insights support informed decision-making regarding asset investments, replacements, and upgrades. Data-driven strategies lead to better resource allocation and long-term planning.
SAM provides accurate and up-to-date records of asset conditions and maintenance activities, facilitating compliance with regulatory requirements. Automated reporting ensures timely documentation submission, reducing compliance risks and building trust with stakeholders and regulators.
Key Player Analysis
Smart asset management leverages digital technologies like IoT and predictive analytics to monitor and optimize asset performance. It helps utilities improve efficiency, prevent failures, and manage asset lifecycles, supporting the shift towards clean energy and sustainable infrastructure.
ABB Ltd. is a global leader in electrification and automation, providing innovative smart asset management solutions to the utility industry. ABB’s digital solutions integrate real-time data analytics, cloud services, and predictive maintenance to help utilities monitor and manage critical assets like transformers and circuit breakers.
Siemens AG is another major player in the utility sector, known for its advanced digital solutions in asset management. With a strong emphasis on innovation, Siemens integrates AI, IoT, and machine learning into their smart asset management systems. Their solutions are designed to optimize asset performance, increase operational efficiency, and reduce costs for utility companies.
General Electric (GE Digital) brings a wealth of experience and expertise in industrial automation, focusing on the digital transformation of utility asset management. GE Digital’s solutions, such as Asset Performance Management (APM) and advanced analytics, are built to improve asset reliability, reduce operational costs, and enhance safety.
Top Key Players in the Market
- ABB Ltd.
- Siemens AG
- General Electric (GE Digital)
- IBM Corporation
- Schneider Electric
- Hitachi Energy
- Bentley Systems
- SAP SE
- Oracle Corporation
- Emerson Electric Co.
- Itron Inc.
- Trimble Inc.
- Uptake Technologies
- Others
Recent Developments
- In October 2024, IBM acquired Prescinto, a renewable energy asset performance management platform. This acquisition enhances the capabilities of IBM’s Maximo Application Suite, allowing clients to monitor renewable energy assets in near real-time.
- In August 2024, Aptean, a global provider of enterprise software, expanded its reach by acquiring SSG Insight, a UK-based company known for its smart Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) solutions. This move strengthens Aptean’s cloud-based EAM offerings, which are designed for asset-intensive industries including utilities.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 7.2 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 26.2 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 13.8% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue forecast, AI impact on market trends, Share Insights, Company ranking, competitive landscape, Recent Developments, Market Dynamics and Emerging Trends Segments Covered By Component (Hardware (Sensors, Smart Meters, Actuators, RFID Devices), Software (Asset Performance Management (APM), Enterprise Asset Management (EAM), Predictive Maintenance Tools), Services (Consulting & Integration, Support & Maintenance, Managed Services)), By Asset Type (Electric Assets (Transformers, Substations, Transmission Lines), Water Assets (Pipelines, Pumps, Water Treatment Plants), Gas Assets (Distribution Pipes, Gas Meters, Storage Tanks)), By Deployment Mode (On-premise, Cloud-based), By Utility Type (Electric Utilities, Water Utilities, Gas Utilities, Combined Utilities (Multi-utility providers)), By Application (Predictive Maintenance, Real-time Asset Monitoring, Lifecycle Management, Work Order Management, Outage Management, Risk Management, Others), By Enterprise Size (Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs), Large Enterprises) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape ABB Ltd., Siemens AG, General Electric (GE Digital), IBM Corporation, Schneider Electric, Hitachi Energy, Bentley Systems, SAP SE, Oracle Corporation, Emerson Electric Co., Itron Inc., Trimble Inc., Uptake Technologies, Others Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three license to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Smart Asset Management in Utility MarketPublished date: May 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Smart Asset Management in Utility MarketPublished date: May 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- ABB Ltd.
- Siemens AG
- General Electric (GE Digital)
- IBM Corporation
- Schneider Electric
- Hitachi Energy
- Bentley Systems
- SAP SE
- Oracle Corporation
- Emerson Electric Co.
- Itron Inc.
- Trimble Inc.
- Uptake Technologies
- Others













