Global Psychedelic Mushrooms Market By Form (Fresh/Whole, Dried, Processed), By Product Type (Psilocybe, Gymnopilus, Panaeolus), By Application (De-addiction, Anxiety Relief, Depression Relief, Recreational, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Feb 2026
- Report ID: 177587
- Number of Pages: 288
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
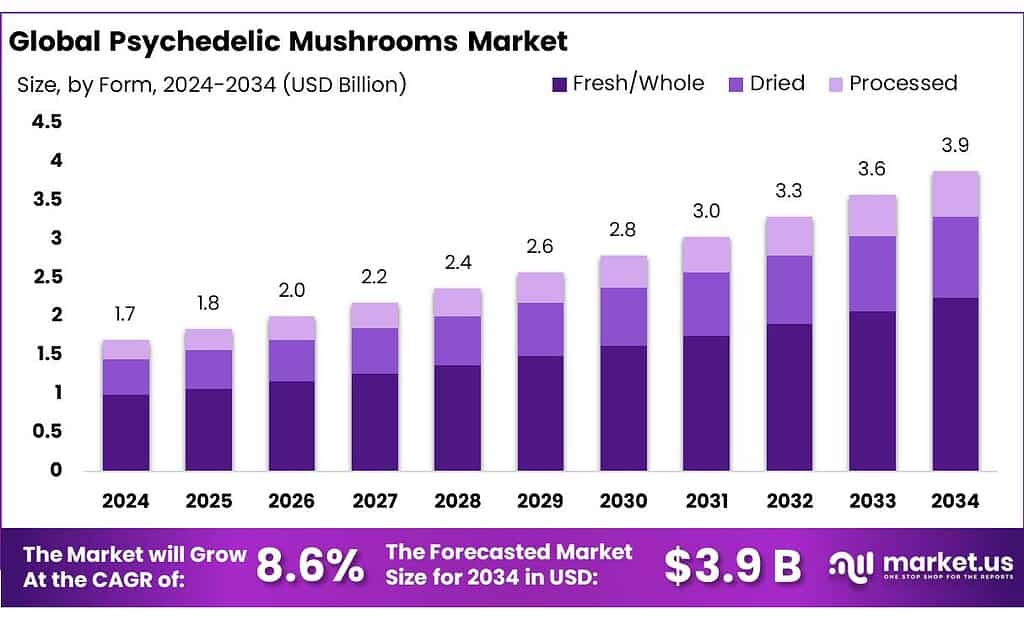
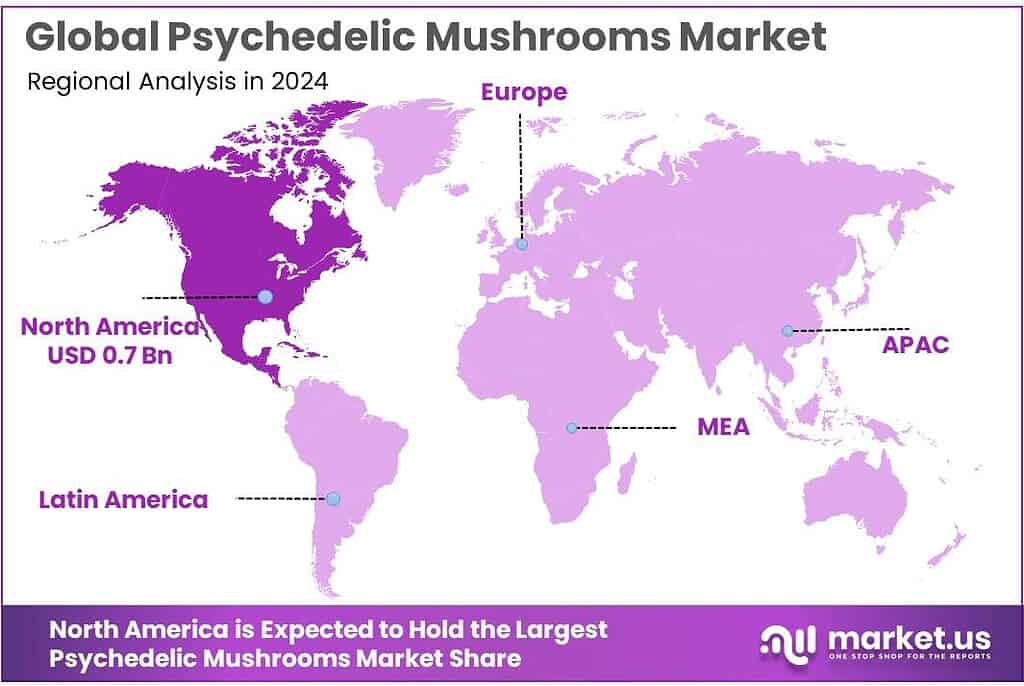
The Global Psychedelic Mushrooms Market is expected to be worth around USD 3.9 Billion by 2034, up from USD 1.7 Billion in 2024, and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.6% from 2025 to 2034. The North America segment maintained 46.8%, supporting a Psychedelic Mushrooms value of USD 0.7 Bn.
Psychedelic mushrooms—most commonly referring to Psilocybe species that naturally contain psilocybin—sit at the intersection of controlled-substance regulation, clinical drug development, and tightly supervised adult-access service models. In parallel, the broader “mushroom economy” provides useful industrial context: global production of mushrooms and truffles reached 44,207,117 tonnes in 2021. In the U.S. alone, the 2023–2024 commercial mushroom crop totaled 659 million pounds with an all-mushroom value of sales of $1.09 billion, illustrating the scale and sophistication of adjacent edible-fungi infrastructure that psychedelic operators often borrow from.
Industrially, the current scenario is best described as a “regulated medical + regulated services + illicit legacy” structure. On the medical side, companies and academic groups are building GMP-grade supply chains aligned with pharmaceutical expectations. Regulatory signaling has been a key catalyst: the U.S. FDA granted Breakthrough Therapy designation (Oct 2018) to a psilocybin therapy program for treatment-resistant depression. The FDA also granted Breakthrough Therapy designation (2019) to Usona’s psilocybin IND pathway for major depressive disorder.
Demand-side momentum is being shaped by measured increases in adult use and policy experimentation. In the U.S., RAND estimates ~8 million American adults used psilocybin in 2023, with 3.1% reporting past-year use and ~12% reporting lifetime use. This consumer reality is feeding investment in harm-reduction education, testing infrastructure, and service design—while also raising compliance expectations around traceability, potency consistency, and adverse-event protocols.
Government initiatives are now creating “test-bed” markets that indirectly accelerate industrial learning. In Australia, the Therapeutic Goods Administration announced (Feb 2023) rescheduling changes that took effect 1 July 2023, enabling prescribing pathways limited to authorised psychiatrists under defined controls. In the U.S., Oregon’s regulated psilocybin services program has moved beyond pilots into a visible micro-industry: as of early Feb 2026, official counts show 11 manufacturers, 1 testing laboratory, 23 service centers, 389 licensed facilitators, and 935 worker permits issued.
Key Takeaways
- Psychedelic Mushrooms Market is expected to be worth around USD 3.9 Billion by 2034, up from USD 1.7 Billion in 2024, and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.6%.
- Fresh/Whole held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 58.2% share.
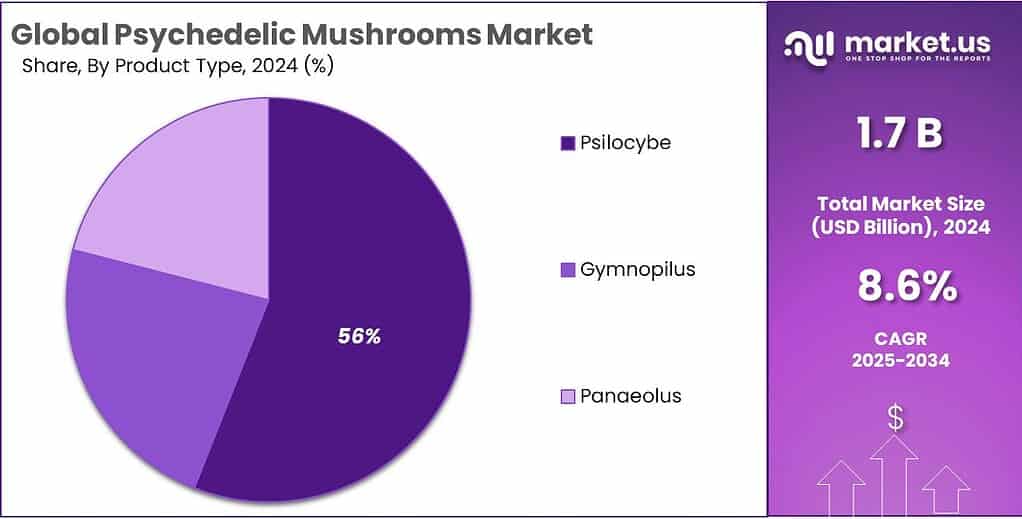
- Psilocybe held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 56.1% share.
- De-addiction held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.3% share.
- North America is the dominating region in the psychedelic mushrooms market, accounting for 46.8% and reaching 0.7 Bn.
By Form Analysis
Fresh/Whole leads the Psychedelic Mushrooms Market with 58.2% share in 2024, supported by cultivation ease and consumer preference
In 2024, Fresh/Whole held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 58.2% share. This strong position reflects how most psychedelic mushroom activity—especially in early regulated and decriminalized regions—continues to rely on whole fruiting bodies rather than processed formats. Fresh or dried whole mushrooms are easier to cultivate, require minimal post-harvest processing, and align with traditional usage practices. Licensed cultivation facilities in select regulated markets have largely focused on standardized growing, harvesting, and drying protocols instead of complex extraction systems, which naturally supports higher volumes in whole form.
By Product Type Analysis
Psilocybe dominates with 56.1% share driven by therapeutic research and regulated adoption
In 2024, Psilocybe held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 56.1% share. This leadership reflects the strong scientific and regulatory focus on Psilocybe species, particularly due to their natural psilocybin content and long history of documented use. Most clinical research programs and therapeutic frameworks have centered around Psilocybe varieties, making them the primary raw material in legally supervised environments. As regulatory clarity continued to improve in 2024, licensed producers and research institutions largely prioritized Psilocybe cultivation because of its established compound profile and standardized growing methods.
By Application Analysis
De-addiction leads application segment with 38.3% share as treatment demand rises
In 2024, De-addiction held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.3% share. This strong share reflects the growing interest in psychedelic-assisted therapy as a potential support tool for substance use disorders. Research institutions and supervised service programs have increasingly explored the role of psychedelic mushrooms in helping individuals address alcohol dependency, nicotine addiction, and other substance-related challenges. The focus has shifted from recreational narratives toward structured therapeutic environments where controlled administration and guided sessions are central to treatment models.
Key Market Segments
By Form
- Fresh/Whole
- Dried
- Processed
By Product Type
- Psilocybe
- Gymnopilus
- Panaeolus
By Application
- De-addiction
- Anxiety Relief
- Depression Relief
- Recreational
- Others
Emerging Trends
Growing Conversations Around Therapeutic Use and Broader Acceptance Reflect a Major Trend in Psychedelic Mushrooms
One of the most significant and current trends in the psychedelic mushrooms space is the increasing public and professional conversation around therapeutic use, especially for mental health and addiction support. This trend isn’t built overnight — it is rooted in real human need. Around the world, millions of people live with depression, anxiety, or addiction, and many have struggled to find lasting relief through traditional treatments.
- According to the World Health Organization (WHO), more than 332 million people lived with depression in 2021, and suicide claimed approximately 727,000 lives that same year. These numbers shine a stark light on how urgently new treatment ideas are needed.
This trend shows up in the real world as well. States like Oregon have built out regulatory systems for supervised psilocybin services, and by the end of 2024 had licensed 345 facilitators, 31 service centers, 11 manufacturers, and 1 testing laboratory, along with 724 worker permits and 22 approved training programs. While these numbers may seem modest compared with mainstream food production, they represent a tangible maturation of an industry once informal and decentralized.
A key part of this trend is that conversations around therapeutic use are no longer confined to medical journals or specialized conferences. Mainstream media, professional associations, and even some health insurers are beginning to discuss the possibilities — always with caution, but with growing seriousness. People are not just curious; they are hopeful. Many clinicians who have worked with trauma and addiction for decades express a desire for new tools that can help patients who haven’t found relief elsewhere.
The edible mushroom sector illustrates how public perception can evolve over time. Global production of mushrooms and truffles reached 48,335,996 tonnes in 2022, showing that mushrooms as a category already have mainstream food value and global acceptance.
Drivers
Rising mental-health and addiction burden is pushing regulated psychedelic care forward
One major driving factor for the psychedelic mushrooms industry is the growing pressure on health systems to find better options for depression and addiction, combined with governments slowly opening regulated pathways for supervised use. In real terms, the need is large and visible. The World Health Organization reports that approximately 332 million people worldwide have depression, and it also notes that 727,000 people died by suicide in 2021—numbers that keep mental health near the top of public-health agendas.
On the addiction side, the demand signal is equally strong. In the United States alone, the National Center for Health Statistics (CDC) reports 79,384 drug overdose deaths in 2024. Even with recent declines, this is still a very high national burden, and it keeps policymakers, hospitals, and community programs looking for new tools that can work alongside existing treatments.
This pressure is helping move psychedelic mushrooms from a fringe topic into structured pilot programs and regulated service models. Oregon is a practical example of how demand, policy, and industry capacity connect. Oregon’s official “2024: Year in Review” for its psilocybin services program lists the licensed ecosystem that existed by the end of 2024: 345 licensed facilitators, 31 licensed service centers, 11 licensed manufacturers, and 1 licensed laboratory, plus 724 worker permits and 22 approved training programs. Those figures matter because they show a real supply chain forming around supervised access—training, compliance, manufacturing, testing, and service delivery—rather than informal trade.
Another reason this driving factor has momentum is that the industry can borrow proven operational knowledge from the mainstream mushroom sector, which already runs industrial cultivation, drying, packaging, cold-chain handling, and quality controls. In the food industry, the infrastructure is mature and measurable. The USDA National Agricultural Statistics Service reported that the value of sales for the 2023–2024 United States mushroom crop was $1.09 billion, and it tracks production, pricing, and volume annually through grower surveys.
Restraints
Strict regulatory controls and federal illegality continue to limit full market expansion
One major restraining factor for the psychedelic mushrooms industry is the continued federal classification of psilocybin as a Schedule I substance in many countries, especially in the United States. Under the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA), psilocybin remains listed as a Schedule I drug, meaning it is defined as having a high potential for abuse and no currently accepted medical use at the federal level. This classification creates significant barriers for cultivation, interstate commerce, banking access, insurance coverage, and large-scale food or agricultural integration.
Even though certain states have introduced regulated service models, the federal status restricts national commercialization. For example, Oregon’s regulated psilocybin program operates under state law, but it does not override federal drug policy. According to Oregon’s official 2024 review, by the end of 2024 the state had licensed 31 service centers, 11 manufacturers, and 1 laboratory, but all operations must remain within state boundaries. This geographic limitation prevents broader supply chain expansion across states and limits the development of large centralized production hubs.
Another layer of restraint comes from the cost and compliance burden required to operate legally in approved jurisdictions. Licensing, facility upgrades, security systems, lab testing, staff training, and documentation requirements significantly increase operational expenses compared to traditional mushroom farming.
To understand the contrast, it helps to look at the established edible mushroom industry. The USDA reported that the U.S. mushroom crop value reached $1.09 billion in 2023–2024, supported by established distribution networks, food safety frameworks, and interstate commerce. Psychedelic mushrooms, however, cannot tap into this broader food distribution system due to their controlled classification. This separation prevents operators from leveraging economies of scale already available in the food mushroom sector.
Public health concerns also shape regulation. According to the World Health Organization, approximately 727,000 people died by suicide in 2021, highlighting the seriousness of mental health treatment needs. Governments remain cautious when approving alternative therapies, especially substances with psychoactive effects, which slows the pace of broad legalization despite clinical interest.
Opportunity
Expanding clinical acceptance and government support unlocks fresh growth opportunities in psychedelic mushrooms
A major growth opportunity for the psychedelic mushrooms industry lies in increasing clinical acceptance and supportive government moves toward regulated therapeutic use. As mental health challenges continue to grow worldwide, policymakers and health authorities are cautiously exploring new ways to address conditions such as depression, PTSD, and addiction. One clear example of this shift is found in Australia, where the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) approved the prescribing of psilocybin for treatment-resistant depression and MDMA for PTSD, starting from 1 July 2023.
Such clinical acceptance expands the potential landscape for psychedelic mushroom applications. It enables licensed psychiatrists and mental health professionals to administer evidence-based treatment more widely, within approved frameworks. This moves the conversation from informal or underground use toward validated healthcare routes, which can attract clinical partnerships, funding, and careful monitoring. The mainstream medical system’s involvement can also reduce stigma and increase patient confidence in trying these therapies when traditional treatments have failed.
Another piece of evidence showing rising interest in regulated psychedelic therapy is the growing number of active clinical trials. While comprehensive global datasets are still emerging, sources note that there are over 100 active psilocybin trials exploring its therapeutic potential for issues like depression and other psychiatric disorders.
Looking at the broader mushroom and fungi ecosystem also highlights the opportunity. The edible mushroom sector has shown massive global production increases over decades: production expanded more than five-fold since 2000, reaching around 44 million metric tons worldwide by 2023, with projections to exceed 50 million metric tons by 2025.
Regional Insights
North America dominates with 46.8% share and a 0.7 Bn value, powered by regulated access pilots and high unmet mental-health need
North America is the dominating region in the psychedelic mushrooms market, accounting for 46.8% and reaching 0.7 Bn in value, largely because the region combines early policy experimentation with a deep clinical and research base. Demand-side pressure is clear in the United States, where the National Institute of Mental Health estimates 21.0 million adults experienced at least one major depressive episode—a scale that keeps health systems looking for more effective, supervised treatment options beyond standard pathways.
On the public-health side, addiction continues to shape policy urgency and treatment innovation. The CDC’s National Center for Health Statistics reports the official number of U.S. drug overdose deaths in 2024 was 79,384, reinforcing why new models for de-addiction support are gaining attention across healthcare and community settings.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Numinus runs a clinic-led model focused on psychedelic-assisted care delivery and training. In Q2 fiscal 2025, it reported total revenue of $1,512,435 and ended the quarter with cash and cash equivalents of $705,631, showing how scaling patient services is closely tied to liquidity and cost control in a regulated care setting.
ATAI Life Sciences operates a multi-program mental health pipeline across psychedelics and other modalities. As of Dec 31, 2024, it reported $72.3 million in cash, cash equivalents, restricted cash, and short-term securities; the same filings detail components including $17.5 million cash and cash equivalents, $10.0 million restricted cash, and $44.8 million short-term securities.
PharmaTher is a specialty life-sciences company centered on ketamine programs, with some psychedelic-adjacent development history. In the three months ended Aug 31, 2024, it reported cash, end of period: $1,801,550 and a quarterly net loss of $380,162, reflecting a small-company profile where runway and disciplined spend strongly shape execution pace.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Compass Pathways
- ATAI Life Sciences
- Numinus Wellness
- Field Trip Health
- PharmaTher Holdings
- Revive Therapeutics
- Havn Life Sciences
- Algernon Pharmaceuticals
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024, Numinus Wellness highlighted real service throughput and research activity: it delivered 17,661 client appointments, supported 15 clinical trials at Cedar Clinical Research, and said enrollment in its training programs doubled to over 1,400 learners.
In 2024, ATAI Life Sciences ended the year with $72.3 million in cash, cash equivalents, restricted cash and short-term securities and reported $55.5 million in full-year R&D spend, showing it is still in an investment phase rather than a commercial one.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 1.7 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 3.9 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 8.6% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Form (Fresh/Whole, Dried, Processed), By Product Type (Psilocybe, Gymnopilus, Panaeolus), By Application (De-addiction, Anxiety Relief, Depression Relief, Recreational, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Compass Pathways, ATAI Life Sciences, Numinus Wellness, Field Trip Health, PharmaTher Holdings, Revive Therapeutics, Havn Life Sciences, Algernon Pharmaceuticals Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Psychedelic Mushrooms MarketPublished date: Feb 2026add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Psychedelic Mushrooms MarketPublished date: Feb 2026add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Compass Pathways
- ATAI Life Sciences
- Numinus Wellness
- Field Trip Health
- PharmaTher Holdings
- Revive Therapeutics
- Havn Life Sciences
- Algernon Pharmaceuticals










