Global Polymer Solar Cells Market By Junction Type (Bulk Heterojunction, Single Layer, Bilayer, Multi-Junction, Others), By Technique (Printing Technique, Coating Technique), By Application (Bipv, Consumer Electronics, Automotive, Defense, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends, and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: June 2025
- Report ID: 151196
- Number of Pages: 234
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
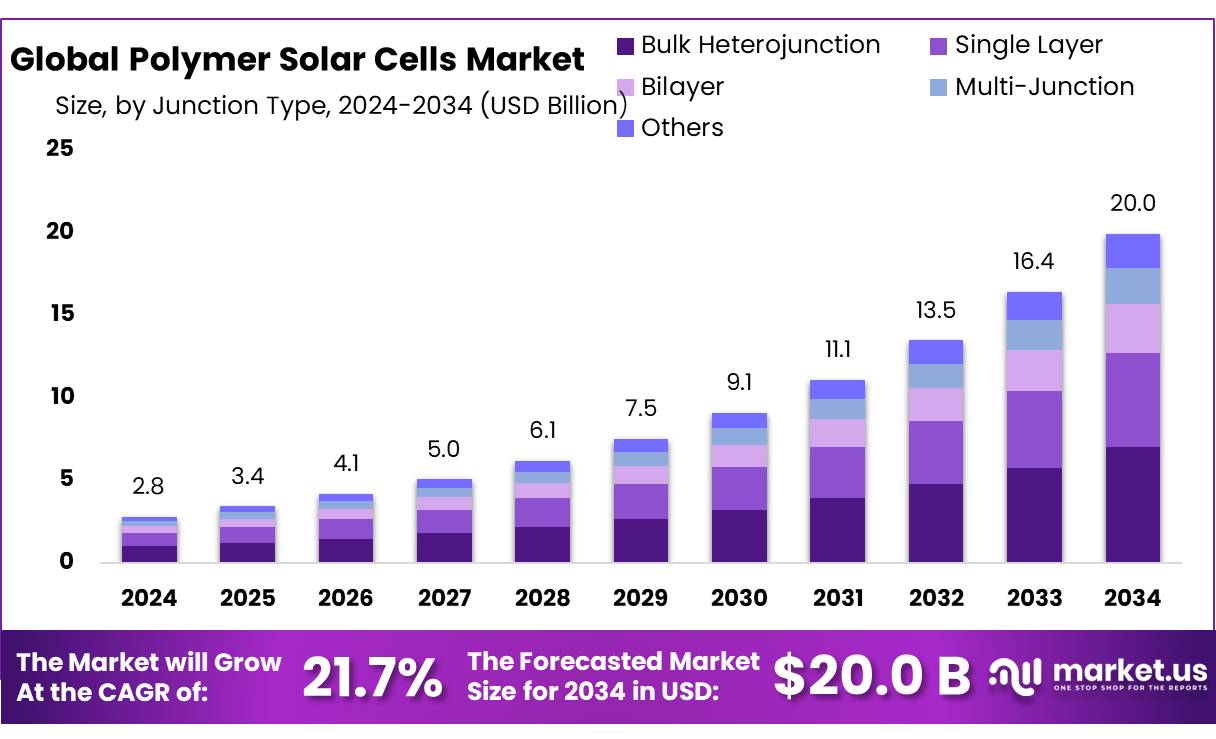
The Global Polymer Solar Cells Market size is expected to be worth around USD 20.0 Billion by 2034, from USD 2.8 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 21.7% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
Polymer solar cells (also known as organic photovoltaic cells) are ultra-thin, flexible photovoltaic devices using semiconducting polymers to convert sunlight into electricity. They typically achieve power conversion efficiencies in the range of 5–7%, with record lab efficiencies reaching roughly 6.5%. Their flexibility, low weight, and potential for low-cost, roll-to-roll manufacturing position PSCs as a disruptive alternative to traditional silicon-based PV.
Government Initiatives: Numerous national and multi-lateral efforts are catalysing PSC industry growth. Actions include building green supply chains and setting ambitious BIPV targets in Europe; Japan’s ¥157 billion subsidies to Sekisui Chemical (a leading PSC firm) to scale manufacturing capacity; and broad R&D funding programs, such as those promoted by the IEA’s 2050 roadmap that aims for PV to supply 11% of global electricity and reduce emissions by 2.3 gigatonnes CO2 annually.
Several national and regional frameworks have catalyzed deployment. For instance, the European Union’s Green Deal and Fit-for-55 strategies incentivize BIPV integration via polymer PV modules. Specific country-level programs in Germany and the Netherlands offer feed-in tariffs or tax credits for building-installed OPV systems.
In the United States, under the Inflation Reduction Act, polymer solar installations may qualify for the federal 30% Investment Tax Credit (ITC)—a substantial factor bolstering market entry. These programs have collectively reduced effective system costs by up to 20–30%, based on case studies in commercial BIPV projects.
Key Takeaways
- Polymer Solar Cells Market size is expected to be worth around USD 20.0 Billion by 2034, from USD 2.8 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 21.7%.
- Bulk Heterojunction held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 67.1% share in the global polymer solar cells market.
- Printing Technique held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 64.9% share in the polymer solar cells market.
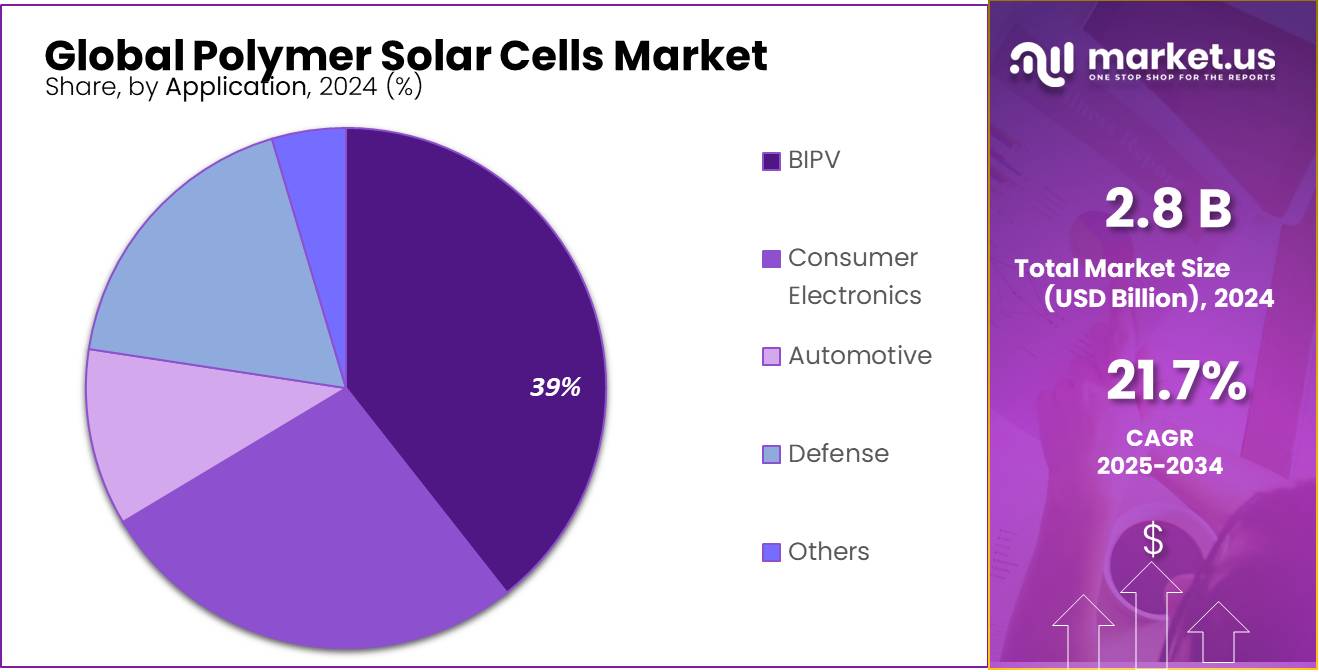
- BIPV (Building-Integrated Photovoltaics) held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 39.4% share in the polymer solar cells market.
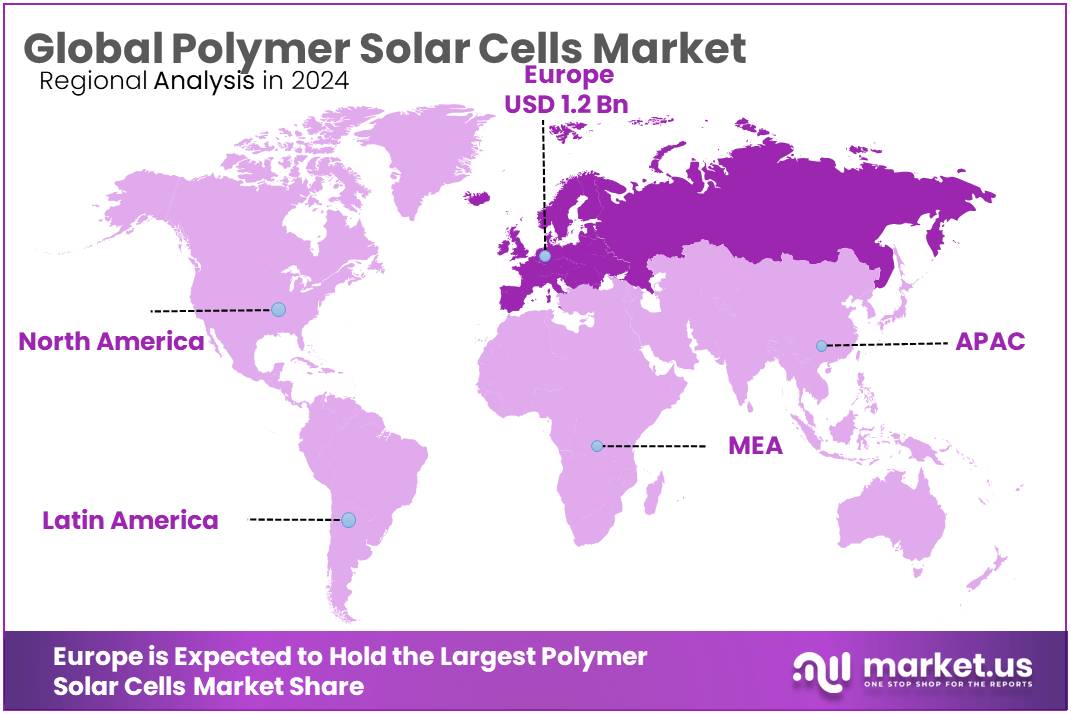
- Asia-Pacific (APAC) region is leading the global polymer solar cells market, capturing approximately 38.9% of total market share, translating to a valuation of USD 1.9 billion.
By Junction Type
Bulk Heterojunction dominates with 67.1% owing to its superior light absorption and easy processing.
In 2024, Bulk Heterojunction held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 67.1% share in the global polymer solar cells market by junction type. This strong lead is mainly due to its well-established architecture, which blends donor and acceptor materials into a single photoactive layer, allowing for better exciton dissociation and charge transport. Compared to other junction types, bulk heterojunction structures offer higher power conversion efficiencies and can be fabricated using low-cost solution-based methods, such as roll-to-roll printing and spray coating.
These processing advantages have made them highly suitable for both small-scale prototypes and large-area flexible solar modules. In 2025, this segment is expected to maintain its leadership position, supported by ongoing academic and industrial interest in optimizing material compatibility and stability. As demand rises for lightweight, bendable photovoltaic materials in electronics and building-integrated applications, bulk heterojunction technology continues to be the most commercially viable and scalable structure in polymer-based solar energy.
By Technique
Printing Technique leads with 64.9% due to its low-cost scalability and compatibility with flexible substrates.
In 2024, Printing Technique held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 64.9% share in the polymer solar cells market by technique. This prominence is largely driven by the method’s ability to support large-scale, cost-effective production using roll-to-roll and inkjet processes. These techniques allow active layers and electrodes to be deposited directly onto flexible substrates like plastic films, making the process faster and more adaptable for commercial manufacturing.
The ease of integration into lightweight and wearable solar products has also made printing techniques highly favored among developers. Looking ahead to 2025, this segment is expected to grow steadily as innovation continues in printable photovoltaic inks and multi-layer printing systems. As demand increases for portable solar panels and building-integrated photovoltaic materials, the ability of printing techniques to support mass production without expensive vacuum systems will keep it at the forefront of polymer solar cell fabrication.
By Application
BIPV dominates with 39.4% as architects favor integrated solar solutions for energy-efficient buildings.
In 2024, BIPV (Building-Integrated Photovoltaics) held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 39.4% share in the polymer solar cells market by application. This leadership is strongly tied to the growing demand for energy-efficient buildings and sustainable construction materials. Polymer solar cells are lightweight, semi-transparent, and flexible, making them ideal for integration into facades, windows, rooftops, and other architectural surfaces without compromising aesthetics.
Their compatibility with modern design trends and green building certifications has accelerated their use in both commercial and residential structures. By 2025, the BIPV segment is expected to expand further as governments enforce stricter energy regulations and offer incentives for renewable-integrated construction. With rising urbanization and interest in net-zero energy buildings, BIPV continues to be the most practical and design-friendly application for polymer solar technologies.
Key Market Segments
By Junction Type
- Bulk Heterojunction
- Single Layer
- Bilayer
- Multi-Junction
- Others
By Technique
- Printing Technique
- Coating Technique
By Application
- Bipv
- Consumer Electronics
- Automotive
- Defense
- Others
Drivers
Significance of Cost Reductions Through Policy Support
One major driving factor for the polymer solar cells market is the significant reduction in overall solar photovoltaic (PV) costs, which has been strongly influenced by proactive government initiatives. In recent years, national programs and international efforts have achieved noteworthy success in making solar energy more affordable, thereby improving the commercial viability of emerging technologies like polymer solar cells.
In 2023, global manufacturing capacity for solar PV cells nearly doubled—a clear sign of the sector’s rapid scale-up. Additionally, polysilicon production increased by about 90% and wafer output grew near 60%. These figures illustrate how targeted industrial policies and investment incentives have effectively fostered the enabling infrastructure for solar energy at large. For polymer solar cells, which typically rely on similar equipment, this creates a supportive environment for cost-effective material sourcing and component production.
Further cost pressure has been applied through specific policy programs. For instance, the U.S. Department of Energy’s SunShot 2030 initiative aims to halve the levelized cost of energy (LCOE) for utility-scale solar systems. The goal is to reach USD 0.03/kWh by 2030—an ambitious target that would position solar-generated electricity as one of the least expensive options for new power generation. Achieving such low costs for conventional PV technologies encourages parallel investments and technological innovation in polymer-based solutions that prioritize flexibility, lightweight design, and integration.
Restraints
Durability Challenges Linked to Environmental Sensitivity
One major restraining factor in the polymer solar cells market is the limited long‑term stability of these devices under real-world conditions. While polymer solar cells offer attractive benefits—such as flexibility, low cost, and lightweight structure—their sensitivity to moisture, ultraviolet (UV) radiation, and heat significantly hinders sustained performance.
A 2024 report from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) indicates that certified polymer (organic) solar cells have achieved a record efficiency of 18.2%, illustrating commendable laboratory progress. However, these cells still face a steep decline in efficiency when exposed to outdoor environments. Unprotected devices can see performance degrade notably within the first few years due to photo oxidation and thermal stresses. Conventionally, thin film PV modules such as those with amorphous silicon exhibit an average degradation rate of 0.5–1% per year, according to long-term field data. In contrast, polymer cell degradation tends to exceed these values, resulting in shorter operational lifespans.
Government support for polymer solar development generally focuses on efficiency improvements and production scale-up rather than stability enhancement. Policy frameworks, such as the U.S. Department of Energy’s Solar Performance and Efficiency program, emphasize conversion efficiency targets but do not yet include specific directives to ensure minimum module lifetimes. The absence of durability‑focused regulations creates a market gap, where investors and adopters remain cautious due to risks associated with maintenance and replacement costs.
Opportunity
Expansion through Government-Backed Flexible Solar Initiatives
A major growth opportunity for the polymer solar cells market lies in government investments focused on ultra-thin and flexible solar technologies. One strong example is in Japan, where the government has committed US $1.5 billion to support the commercialization of ultra-thin, bendable solar panels—such as perovskite and flexible polymer-based solutions—to offset land constraints and diversify energy sources.
This sizeable funding includes ¥157 billion (≈USD 1 billion) in subsidies to develop durable sealing resins and film-based architectures suitable for building façades, stadiums, airports, and urban infrastructure. The initiative is targeted at enabling these next-generation solar modules to generate energy equivalent to “20 nuclear power plants” by 2040, helping to reach approximately 50% renewable energy share in Japan’s electricity mix. While these numbers illustrate ambition and policy support, they also signal a growing opportunity for flexible polymer solar cells to be scaled for real-world deployment.
By 2027, the goal is to achieve 100 MW/year of production capacity—with plans to escalate to 1 GW/year by 2030 at Sekisui Chemical’s refurbished facilities. These capacity targets reflect a clear path for polymer solar film technology to advance commercially. The government’s direct subsidies are lowering barriers for industrial-scale manufacturing and encouraging supply chain investments in protective materials and printing infrastructure.
Trends
Surge in Government-Backed Ultra-Thin & Flexible Polymer Solar Cells
A standout trend in the polymer solar cell space is the rapid rise of ultra thin, flexible solar films, driven largely by strong government support—especially in Japan. In February 2025, Tokyo announced a USD 1.5 billion subsidy program to commercialize next generation perovskite and polymer solar film technologies. This commitment includes a ¥157 billion (~USD 1 billion) subsidy to Sekisui Chemical, supporting the move from lab-scale (30 cm width) to mass production capacity (1gigawatt by 2030).
This isn’t just an abstract goal. Sekisui’s trial units are already up and running—installed on buildings, Osaka station bus stops, and cruise terminals—showing real world rollout. The government’s backing tackles two big barriers: production scale-up and deployment adaptability. Sekisui aims to hit 100MW/year by 2027, even though initial film costs may be 3–4 times higher than traditional panels. That’s a calculated gamble—pay more now to set the stage for long-term affordability and domestic manufacturing strength.
Why does this matter for polymer solar cells globally? Japan’s goal to rival China’s solar dominance and break supply‑chain dependency signals that flexible polymer-based cells are no longer niche—they’re becoming core to national energy planning. Japan’s model also shows how policy can back innovation that’s both high-tech and human-centered: think solar window shades in urban environments rather than sprawling desert panels.
Regional Analysis
APAC leads with 38.9% share and a value of USD 1.9 billion in 2024, driven by strong policy and manufacturing strength.
The Asia-Pacific (APAC) region is leading the global polymer solar cells market, capturing approximately 38.9% of total market share, translating to a valuation of USD 1.9 billion. This regional dominance is largely driven by significant policy support, extensive research initiatives, and growing consumer demand for flexible, lightweight photovoltaic solutions. Countries like China, Japan, South Korea, and India are at the forefront, propelled by government-driven renewable energy targets and substantial investments in manufacturing infrastructure.
In particular, China is a pivotal player due to its robust solar manufacturing ecosystem and ambitious renewable energy targets, including achieving carbon neutrality by 2060. The Chinese government plans to increase solar power generation capacity significantly, promoting innovations in polymer-based solar technologies and funding extensive research.
Additionally, Japan’s recent investment of approximately USD 1.5 billion into flexible photovoltaic technologies, notably polymer solar cells, underscores its commitment to establishing energy independence and reducing reliance on conventional solar imports. Japan aims to achieve commercial-scale production of flexible solar modules exceeding 1 gigawatt by 2030, supporting widespread urban integration of polymer solar cells in buildings and infrastructure.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Tata Power Solar, a subsidiary of Tata Power, operates one of India’s largest integrated solar cell and module manufacturing facilities. In February 2025, its Tirunelveli plant with 4.3 GW capacity commenced production, initially contributing 2 GW to the domestic clean energy market and ramping to full capacity within months. The facility is equipped with advanced TOPCon and Mono PERC cell technology and is staffed by 80% women. Alongside its 682 MW module and 530 MW cell capacity in Bengaluru, Tata Power Solar strongly supports India’s energy independence goals.
Heliatek, headquartered in Dresden, Germany, specializes in ultrathin, lightweight organic photovoltaic films. With over 75 installations globally, it leads in flexible building-integrated organic PV (OPV) systems. Its flagship HeliaSol film, certified to IEC 61215 and IEC 61730 standards, offers 20 year warranties and converts around 9% of sunlight into electricity. In 2016, Heliatek achieved a 13.2% cell efficiency in laboratory conditions—a record for OPV at the time—underlining its technological leadership.
Trina Solar, a major Chinese PV manufacturer founded in 1997, is known for its vertically integrated production chain—from wafers to modules—and its strong market credibility. The company’s Vertex N series delivers up to 23.2% efficiency for utility-scale installations. In Q2 2025, it retained its BNEF Tier 1 status, confirming global trust and reliability. With offerings spanning utility, commercial, and residential sectors, Trina remains at the forefront of high-efficiency and cost-effective PV solutions.
Top Key Players in the Market
- Tata Power Solar Systems Limited
- Heliatek GmbH
- Trina Solar Limited
- Infinity PV ApS
- SolarWindow Technologies Inc.
- MORESCO Corporation
- ASCA GmbH & Co. KG
- Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE
Recent Developments
In 2024, Infinity PV ApS continued to strengthen its position as a leading equipment provider for polymer solar cell production. The Danish firm’s roll-to-roll slot-die coating technology supports precision film deposition at speeds ranging from 1.2 mm/s to 33mm/s, enabling scalable processing of organic photovoltaic layers.
In 2024, Heliatek GmbH further strengthened its position in the polymer solar cell sector by achieving IEC 61215 and 61730 certifications for its HeliaSol® solar film—making it the first flexible organic PV product certified for module durability.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 2.8 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 20.0 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 21.7% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Junction Type (Bulk Heterojunction, Single Layer, Bilayer, Multi-Junction, Others), By Technique (Printing Technique, Coating Technique), By Application (Bipv, Consumer Electronics, Automotive, Defense, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Tata Power Solar Systems Limited, Heliatek GmbH, Trina Solar Limited, Infinity PV ApS, SolarWindow Technologies Inc., MORESCO Corporation, ASCA GmbH & Co. KG, Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Polymer Solar Cells MarketPublished date: June 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Polymer Solar Cells MarketPublished date: June 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Tata Power Solar Systems Limited
- Heliatek GmbH
- Trina Solar Limited
- Infinity PV ApS
- SolarWindow Technologies Inc.
- MORESCO Corporation
- ASCA GmbH & Co. KG
- Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE










