Global Oral Controlled Release Drug Delivery Technology Market Market Analysis By Release Technology (Dissolution Controlled Release, Diffusion Controlled Release, Osmotically Controlled Release, Ion Exchange Resins, Combination Mechanism, Others), By Dosage Form (Solid Dosage Forms, Semisolid/Liquid/Suspensions) By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Nov 2025
- Report ID: 166268
- Number of Pages: 356
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
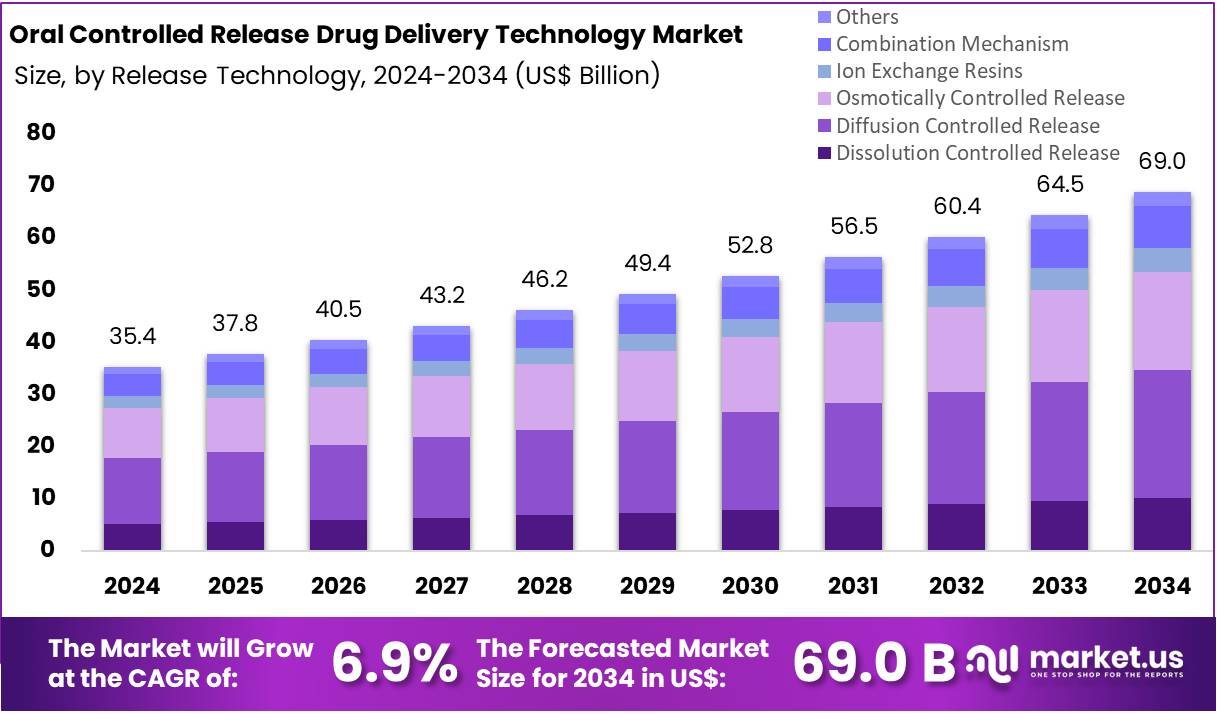
The Global Oral Controlled Release Drug Delivery Technology Market size is expected to be worth around US$ 69 Billion by 2034, from US$ 35.4 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 6.9% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 41.3% share and holding a market value of US$ 14.6 million for the year.
Oral controlled release drug delivery technologies aim to release a medication slowly over an extended period, ensuring stable drug concentrations in the body. These systems, such as tablets, capsules, and specialized coatings, offer significant benefits, including reducing dosing frequency and improving patient adherence. By maintaining consistent drug levels, they help achieve better therapeutic outcomes and enhance the quality of life for patients, especially those dealing with chronic conditions. This technology is becoming a standard choice for managing long-term health issues that require consistent medication.
The rising global burden of chronic diseases has significantly increased the need for long-term medication solutions. Noncommunicable diseases (NCDs), including heart disease, diabetes, and cancer, are now responsible for approximately 74% of all deaths worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), over 43 million deaths occurred in 2021 due to NCDs, with a large proportion of these fatalities happening in low- and middle-income countries. As the prevalence of these diseases continues to rise, the demand for efficient long-term treatment options, including oral controlled release systems, has surged. These systems are essential in maintaining stable drug levels over time, particularly in the treatment of chronic conditions that require continuous medication.
For example, the number of adults affected by diabetes has skyrocketed, with over 800 million adults now living with the condition. This number is expected to grow to 853 million by 2050, according to WHO estimates. Managing chronic diseases like diabetes demands medications that can maintain consistent blood sugar levels over an extended period. Oral controlled release products, which provide a steady drug release with less frequent dosing, are becoming a key tool in managing such long-term conditions. These systems are helping patients achieve better control over their diseases while reducing the frequency of hospital visits and improving overall quality of life.
Furthermore, studies have demonstrated that reducing the frequency of doses can significantly improve patient adherence to prescribed therapies. A meta-analysis of various chronic diseases has shown that when medication regimens are reduced from multiple doses to a once-daily schedule, patient adherence improves notably. This adherence is crucial in managing chronic diseases effectively. Oral controlled release formulations, which are designed for once-daily or even longer intervals, help address these adherence challenges and contribute to better clinical outcomes. As healthcare systems seek to improve outcomes and reduce complications from chronic conditions, the demand for controlled release oral medications is expected to continue rising.
Advancements in Oral Controlled Release Drug Delivery Technologies
Recent advancements in oral controlled release technologies are expanding the types of drugs that can benefit from these delivery systems. Traditional oral controlled release systems, such as matrix tablets, have evolved with the development of more advanced mechanisms. Gastro-retentive drug delivery systems (GRDDS) are a prime example. These systems allow drugs to remain in the stomach or upper gastrointestinal tract for extended periods while releasing the medication gradually. This technology is especially beneficial for drugs that require absorption in specific parts of the gastrointestinal tract or that need to act locally within the stomach.
Recent reviews highlight the rapid progress in the development of GRDDS, which incorporate floating mechanisms, swelling polymers, and bioadhesive materials to control the duration and location of drug release. A 2024 review emphasized that this area of research is growing rapidly due to its potential to improve the delivery of drugs with narrow absorption windows or low stability. These advancements are particularly valuable for reformulating drugs that previously needed to be taken multiple times per day, thus simplifying treatment regimens and improving patient compliance. Moreover, gastro-retentive systems enable drugs that were previously difficult to deliver orally to now be administered more effectively, expanding the range of medications that can be developed using controlled release technologies.
In addition to these advances, the emergence of “smart pills” and ingestible devices represents another significant step forward in drug delivery technology. A 2023 study reviewed several types of millimeter-scale devices that combine controlled drug release with advanced features such as sensing, wireless communication, and onboard electronics. These devices can be programmed to release drugs at specific times or in response to certain conditions within the gut. This opens up new possibilities for highly personalized and responsive drug regimens. For instance, some prototypes include micro-needles and cavities that could potentially deliver biologics or peptides, which are typically administered through injections. Though these devices are still in early-stage clinical trials, they could revolutionize the way medications are delivered in the future.
Regulatory support is a critical factor in the ongoing growth of the oral controlled release market. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has provided comprehensive guidelines for modified-release oral dosage forms, known as the SUPAC-MR guidelines. These guidelines help companies navigate the regulatory process for changes in formulation, manufacturing processes, and scale-ups while ensuring that the quality and effectiveness of the drug are maintained. This guidance reduces regulatory risks, making it easier for companies to innovate and invest in controlled release technologies. In addition, international efforts to standardize bioequivalence testing for oral dosage forms are making it easier for generic manufacturers to introduce controlled release versions of established drugs. As these regulations evolve, they create a more favorable environment for the widespread adoption of oral controlled release technologies, benefiting both originator and generic products.
In summary, oral controlled release drug delivery technology is evolving rapidly, driven by the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, advancements in drug delivery mechanisms, and supportive regulatory frameworks. The continued development of gastro-retentive systems, smart pills, and responsive polymers holds immense potential for improving patient care and treatment outcomes. With growing clinical evidence supporting the benefits of controlled release formulations, particularly in terms of patient adherence, this sector is poised for significant growth. As the demand for long-term, effective treatments continues to rise, the role of oral controlled release systems in chronic disease management will become even more critical in the years to come.
Key Takeaways
- The global oral controlled release drug delivery technology market is projected to reach about US$ 69 Billion by 2034, rising from US$ 35.4 Billion in 2024 at a 6.9% CAGR.
- Diffusion-controlled release was identified as the leading release technology in 2024, accounting for over 35.6% share within the overall oral controlled release technology segment.
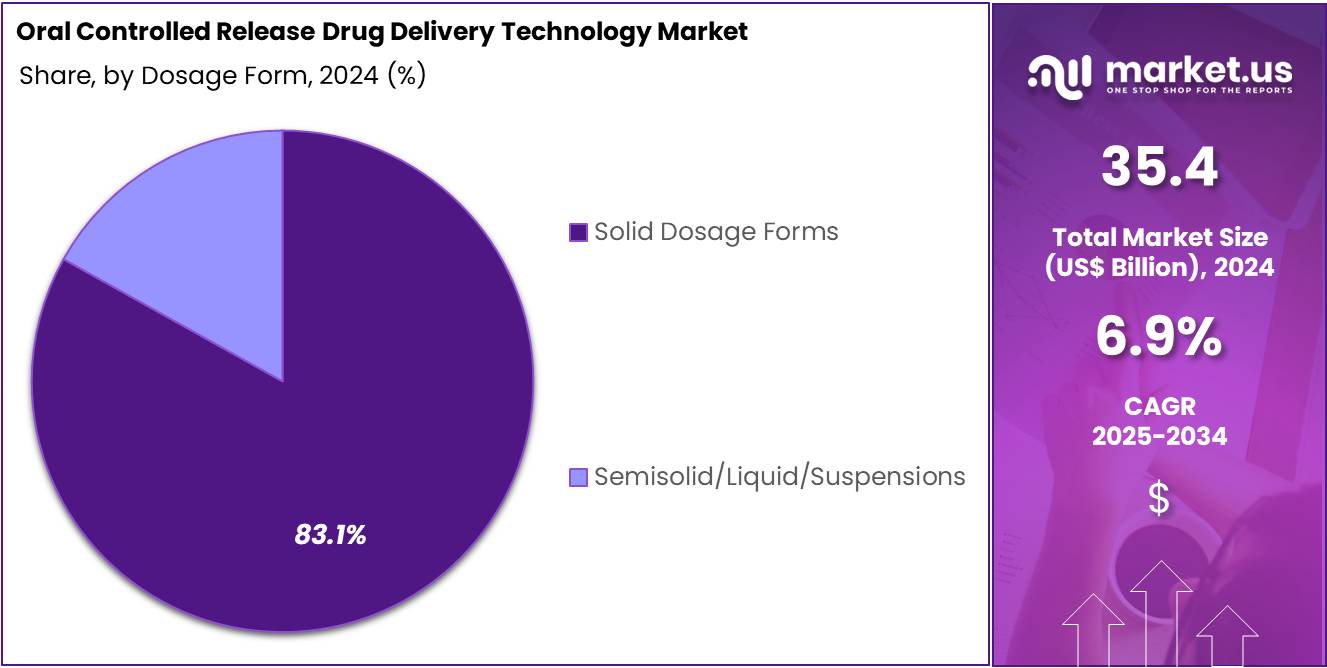
- Solid dosage forms represented the most widely adopted formulation category in 2024, securing more than 83.1% market share within the dosage form segment.
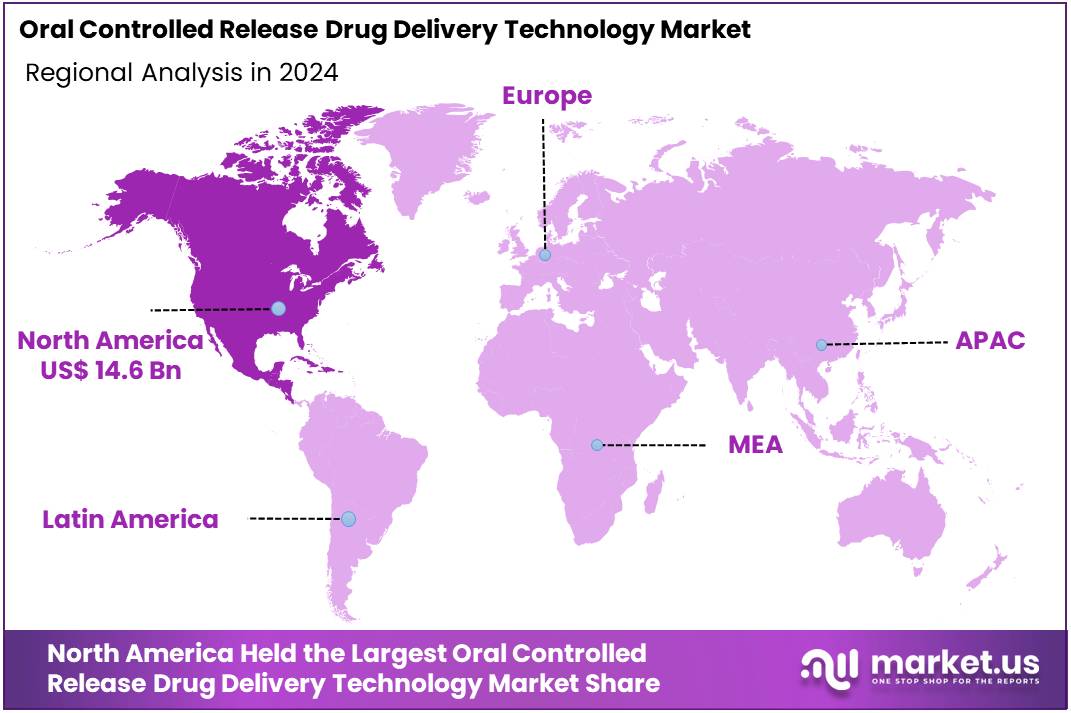
- North America emerged as the largest regional market in 2024, contributing over 41.3% share and generating approximately US$ 14.6 million in market value.
Release Technology Analysis
In 2024, the “Diffusion Controlled Release” held a dominant market position in the Release Technology Segment of the Oral Controlled Release Drug Delivery Technology Market and captured more than a 35.6% share. Its adoption was supported by predictable release profiles. The systems maintained steady plasma levels. This improved adherence. The design remained simple. Manufacturing was efficient. Broad compatibility with active ingredients strengthened demand. These factors reinforced its leadership across oral controlled release technologies.
Dissolution controlled release showed steady traction. It relied on gradual matrix erosion. This enabled consistent release. Advances in polymers supported adoption. Moisture-sensitive drugs benefited. Osmotically controlled systems also expanded. They offered high precision. Their performance was not affected by pH. This improved outcomes. Ion exchange resins gained moderate use. They helped with taste masking. They supported pediatric needs. Their stability advantages encouraged wider application. Growth across these segments remained stable.
Combination mechanisms gained attention. They merged different release processes. This created flexible profiles. Their use grew in complex therapies. Innovation in hybrid matrices supported progress. Development challenges limited speed. However, demand increased. The Others category included emerging technologies. These systems targeted specific needs. Novel excipients enabled experimentation. Adoption stayed limited. Yet interest rose. Advancements in coating methods supported future potential. These trends indicated sustained innovation across oral controlled release technologies.
Dosage Form Analysis
In 2024, the “Solid Dosage Forms” held a dominant market position in the Dosage Form Segment of the Oral Controlled Release Drug Delivery Technology Market, and captured more than a 83.1% share. This strong lead was supported by high patient acceptance. The segment benefited from simple production steps. Stable performance across therapies reinforced its growth. Rising demand for extended-release tablets also drove uptake. Consistent adoption in chronic disease treatments further strengthened its position.
Semisolid, liquid, and suspension forms held the remaining share. Their use increased in cases that required flexible dosing. These formats supported drugs with low solubility. Adoption was steady due to better formulation tools. Advances in polymer systems improved release control. Taste-masking methods enhanced patient acceptance. These dosage forms also gained traction in pediatric therapy. Their gradual expansion created new opportunities in targeted delivery applications. This trend is expected to continue with ongoing innovation.
Overall, dosage form selection was guided by patient needs, formulation goals, and therapeutic outcomes. Solid dosage formats maintained clear dominance due to predictable performance and cost advantages. Semisolid and liquid systems showed promise in specialized use cases. Their growth was shaped by research in controlled release methods. Steady improvement in excipients supported innovation. Broader adoption in complex therapies is anticipated. Market expansion will be driven by continued focus on compliance and precision in drug delivery.
Key Market Segments
By Release Technology
- Dissolution Controlled Release
- Diffusion Controlled Release
- Osmotically Controlled Release
- Ion Exchange Resins
- Combination Mechanism
- Others
By Dosage Form
- Solid Dosage Forms
- Semisolid/Liquid/Suspensions
Drivers
Rising Prevalence of Chronic Diseases Driving Demand for Oral Controlled-Release Drug Delivery Technology
The rising prevalence of non-communicable chronic diseases (NCDs) is a significant driver for the growth of oral controlled-release drug delivery technology. NCDs, including cardiovascular diseases, cancer, chronic respiratory diseases, and diabetes, are increasingly responsible for a large portion of global deaths. These diseases require long-term management and therapy, creating an expanding market for drug delivery systems. Oral controlled-release formulations help improve patient adherence by reducing the frequency of doses while maintaining therapeutic consistency, making them an essential part of chronic disease treatment.
As the global burden of chronic diseases increases, the demand for efficient drug delivery systems grows. Studies indicate that NCDs accounted for around 74% of all global deaths as of the latest data. In 2021 alone, approximately 43 million deaths were attributed to these diseases, which accounted for three-quarters of non-pandemic-related fatalities. This rising prevalence intensifies the need for long-term therapy solutions that improve patient compliance, leading to a higher demand for advanced drug delivery technologies, particularly oral controlled-release formulations.
The benefits of controlled-release technologies extend beyond mere dosage convenience. These systems reduce the frequency of administration, thus enhancing patient adherence to prescribed therapies. According to a study by the World Health Organization (WHO), the growing burden of chronic diseases is pushing the healthcare industry to seek out drug delivery systems that offer more consistent and reliable treatment over time. As such, controlled-release technologies are seen as crucial in improving therapeutic outcomes, particularly for patients suffering from chronic conditions that require sustained medication.
For instance, oral controlled-release drug formulations are designed to deliver medication gradually over an extended period. This controlled delivery not only enhances therapeutic efficacy but also minimizes side effects. With the increasing number of patients requiring long-term treatment for conditions like diabetes and cardiovascular disease, the demand for these advanced delivery systems is expected to rise. The need for consistent and convenient therapy has made oral controlled-release technologies a key focus in addressing the challenges posed by the rising prevalence of chronic diseases.
Restraints
Restraints in Oral Controlled Release Drug Delivery Technology
Oral controlled release drug delivery technology faces significant challenges that limit its consistent performance. One of the primary obstacles is the variability in gastrointestinal (GI) conditions. Factors such as pH, motility, and enzyme activity can fluctuate widely across individuals. This variability leads to inconsistent drug absorption and release rates, making it difficult to achieve reliable therapeutic effects. As a result, it becomes challenging to design systems that ensure sustained and controlled release of the drug throughout the digestive process.
The complexity of the formulation itself also contributes to these limitations. Developing novel controlled-release platforms requires advanced material science to ensure that the drug is released at the desired rate. Stringent control over release profiles is needed to achieve reproducible performance, which further complicates the formulation process. This complexity increases both the development cost and time, slowing down the overall production of such technologies.
A study published in Pharmaceutics (2023) highlights that despite the advancements in drug delivery technology, manufacturing scalability remains a critical bottleneck. The intricate processes involved in creating controlled-release formulations pose challenges to scaling up production. Additionally, obtaining regulatory approval for these complex systems adds another layer of difficulty. Manufacturers face increased scrutiny to demonstrate the technology’s consistency and safety, which can delay market entry.
For instance, according to the same Pharmaceutics study, the combination of formulation challenges, manufacturing limitations, and physiological variability makes it difficult to ensure a high level of reproducibility in oral controlled-release systems. These barriers hinder the widespread adoption of this technology, despite its potential advantages in improving drug efficacy and patient compliance. Hence, the industry’s ability to overcome these hurdles will determine the future success and market growth of oral controlled release drug delivery systems.
Opportunities
Advancements in Personalization and Smart Technology
The shift toward individualized dosing is creating a major opening for oral controlled-release drug delivery. The opportunity is driven by a clear market need for platforms that offer precision, adjustability, and patient-centric performance. Controlled-release products have traditionally followed fixed profiles, yet the rise of personalized medicine is encouraging dosage forms that adapt to patient-specific requirements. This trend is strengthening the demand for advanced oral systems capable of providing more predictable release and improved therapeutic outcomes while maintaining overall treatment convenience.
Rapid advancements in formulation science are supporting this transition. New manufacturing tools are enabling flexible designs that address limitations seen in conventional tablets. Study by Pharma Excipients in 2021 explained that 3D-printing technologies overcome the lack of precision in drug release. It was highlighted that customised oral forms can be created with tailored release patterns. For example, printing methods allow modification of geometry, internal structures, and layering, which improves control over how and when the drug is released in the patient’s body.
Emerging smart platforms are also contributing to this opportunity. According to a 2024 review cited by RROIJ, sensor-enabled and MEMS-based tablets are being developed to deliver responsive release actions. These systems integrate digital health tools to monitor adherence and track drug performance in real time. For instance, smart-pill technologies can register ingestion events and adjust release accordingly. Such innovations enhance precision, reduce dosing variability, and support personalised treatment paths for chronic and complex conditions.
Market growth is supported by the combined impact of additive manufacturing and digital integration. These two areas enable oral controlled-release systems to move beyond one-size-fits-all designs. Study findings and ongoing development efforts demonstrate that personalised tablets, adaptive release profiles, and data-enabled dosage monitoring strengthen product value. For example, advanced platforms can improve patient engagement and support better therapeutic consistency. As a result, the advancement of smart, personalised controlled-release technologies is expected to generate strong expansion prospects across the oral drug-delivery landscape.
Trends
Rising Focus on Medication Adherence Drives Adoption of Oral Controlled-Release Drug Delivery Technologies
The growing focus on medication adherence is a significant trend in chronic-disease management. Chronic conditions often require long-term treatments, and ensuring patients follow prescribed regimens is a challenge. Simplifying these regimens through fewer doses or longer-acting formulations can significantly improve adherence rates. A shift toward controlled-release oral formulations is particularly noteworthy as it directly addresses this challenge, reducing the frequency of dosing and enhancing overall patient compliance.
Studies show that a substantial number of patients fail to fully adhere to their prescribed medication regimens. For example, research indicates that more than half of patients with chronic conditions do not follow their prescribed therapy completely. This non-adherence often leads to poorer health outcomes, increasing the burden on healthcare systems. Simplified treatment options, such as long-acting formulations, are therefore seen as crucial for improving adherence.
According to a 2025 review on medication adherence, treatment regimens that reduce the number of doses required per day are key to improving persistence in chronic-disease therapies. The ability to offer fewer daily doses or extended-release versions of medications directly addresses the adherence challenge. Controlled-release oral formulations, with their smooth plasma concentration profiles and reduced dosing frequency, have emerged as a promising solution to this issue.
The trend towards enhancing adherence through simplified regimens presents a strong opportunity for the adoption of oral controlled-release technologies. This approach aligns with the growing emphasis on patient-centric care, offering a practical solution for improving medication compliance. As more chronic-disease patients benefit from such therapies, the demand for controlled-release formulations is expected to increase, driving the growth of this technology.
Regional Analysis
In 2024, North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 41.3% share and holding a market value of US$ 14.6 million for the year. This leadership was supported by strong demand for oral controlled release systems across the United States and Canada. According to the CDC, around three in four American adults have at least one chronic condition, while about 51% live with two or more. These conditions require long-term therapy, creating high preference for modified-release tablets and capsules that maintain steady drug levels.
A Study by the CDC in 2023 indicated that nearly 76% of U.S. adults were managing at least one chronic condition, and more than 51% were living with multiple conditions. For example, hypertension, diabetes, and cardiovascular disorders often require multi-year treatment. Such therapy benefits from once-daily or twice-daily controlled release formulations. These systems improve convenience and support better control of symptoms, which enhances adherence for chronic disease patients across the region.
High prescription drug use also drives market growth. According to CDC FastStats, about 49.9% of Americans used at least one prescription drug in the past 30 days during 2017–2020. About 24.7% used three or more, and 13.5% used five or more in the same period. For instance, earlier national surveys also showed that more than half of U.S. adults take at least one prescription drug monthly. This widespread use strengthens incentives to develop controlled release products that simplify complex treatment schedules.
Health spending patterns further reinforce North America’s leading position. International comparisons show that U.S. health expenditure per person reached nearly USD 13,400 in 2023, which was almost double the average in other high-income economies. OECD data also show above-average pharmaceutical spending. In such a high-investment environment, providers and manufacturers can more easily adopt value-added dosage technologies that improve outcomes, especially for chronic disease care.
The structure of the pharmaceutical industry adds extra support to market expansion. According to EFPIA, North America accounted for about 53.3% of global pharmaceutical sales in 2023, while Europe held about 22.7%. The report also noted that around 67% of sales of new medicines launched between 2018 and 2023 occurred in the United States. For instance, this concentration of launches enables faster adoption of oral controlled release systems across the region.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherland
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- New Zealand
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
The competitive landscape is shaped by major innovators with strong formulation capabilities. These companies invest in controlled-release platforms to improve dosage precision, patient convenience, and therapy adherence. Pfizer, Novartis, AstraZeneca, Merck, and Bristol-Myers Squibb continue to advance extended-release technologies within large therapeutic portfolios. Their strategies include optimization of release kinetics, expansion of once-daily dosage formats, and integration of advanced excipients. The growth of this market has been driven by sustained R&D spending, global manufacturing scale, and proven regulatory experience in complex oral formulations.
Technology-driven suppliers strengthen the value chain by providing essential polymers and advanced oral delivery platforms. Their systems enable flexible release profiles, stability enhancement, and GI-targeting benefits. Evonik, Catalent, Skyepharma, Alkermes, Adare Pharma Solutions, and Croda support innovators through specialized excipients, multiparticulate technologies, and proprietary controlled-release tablets. These organizations enhance formulation efficiency and reduce development time. Their expertise in complex solid dosage forms supports wide adoption of controlled-release solutions across therapeutic categories and global markets.
High-volume branded-generic manufacturers also contribute to market expansion. Their role has focused on delivering cost-efficient controlled-release tablets and capsules for chronic diseases. Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, and Mylan offer a broad mix of extended-release and delayed-release products. Their capabilities in matrix systems and multiparticulate designs support rapid generic entry following patent expiry. Competitive pricing and strong distribution networks have facilitated wider accessibility of controlled-release therapies, particularly in cardiovascular, neurological, and metabolic disorders.
Additional global innovators strengthen technological progress by exploring advanced delivery designs and next-generation oral formats. Companies such as GlaxoSmithKline, F. Hoffmann-La Roche, BioNTech, and Gilead Sciences invest in modified-release approaches to enhance efficacy and reduce dosing frequency. Their focus includes exposure control, GI-targeting, and improved safety margins. Emerging research on oral biologics and nucleic-acid-based therapies has introduced new opportunities for controlled-release systems. These developments are expected to support long-term innovation and sustained market growth.
Market Key Players
- Pfizer Inc.
- Novartis AG
- AstraZeneca Plc
- Merck & Co. Inc.
- Bristol‑Myers Squibb Company
- Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
- Evonik Industries AG
- Catalent Inc.
- Skyepharma Production SAS
- Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Ltd.
- Alkermes plc
- Croda International Plc
- Adare Pharma Solutions
- Mylan N.V.
- GlaxoSmithKline Plc
- F. Hoffman-La-Roche Ltd.
- BioNTech
- Gilead Sciences
Recent Developments
- In July 2024: AstraZeneca (AZ) announced the completion of its acquisition of Amolyt Pharma, a clinical-stage biotechnology company focused on rare endocrine diseases. The deal, valued at up to US$1.05 billion (with US$800 million upfront and up to US$250 million contingent on milestones), adds eneboparatide (AZP-3601), a Phase III investigational peptide therapy for hypoparathyroidism, to AZ’s pipeline. While primarily a treatment for rare diseases, this acquisition underscores AZ’s interest in advancing biologics and next-generation formulations, which may include controlled-release or enhanced oral bioavailability technologies.
- In July 2024: Pfizer announced its selection of a preferred once-daily modified-release formulation for its oral GLP-1-receptor-agonist candidate, danuglipron (PF-06882961), which is under development for obesity. The decision was based on positive pharmacokinetic data from an open-label study (NCT06153758), which confirmed the suitability of a once-daily dosing regimen. Pfizer also revealed plans to conduct further dose-optimization studies in the latter half of 2024 using the new controlled-release formulation.
- December 6, 2023: Novartis revealed that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had approved Fabhalta® (iptacopan) as the first oral monotherapy for the treatment of adults with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH). Fabhalta is a Factor B inhibitor that targets the alternative complement pathway in the immune system, offering comprehensive control over both intra- and extravascular hemolysis. In clinical trials, the treatment significantly increased hemoglobin levels by at least 2 g/dL from baseline in most patients, and nearly all participants in the APPLY-PNH trial avoided blood transfusions.
- In October 2023: Sun Pharma entered into a licensing agreement with Zydus Lifesciences Ltd. for the co-marketing of Desidustat, an innovative oral treatment for anemia associated with chronic kidney disease (CKD), in India under the brand name RYTSTAT®. Zydus had initially launched the product as Oxemia™ in 2022, and under the semi-exclusive arrangement, Sun Pharma will now market it in the region.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) US$ 35.4 Billion Forecast Revenue (2034) US$ 69 Billion CAGR (2025-2034) 6.9% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, COVID-19 Impact, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Release Technology (Dissolution Controlled Release, Diffusion Controlled Release, Osmotically Controlled Release, Ion Exchange Resins, Combination Mechanism, Others), By Dosage Form (Solid Dosage Forms, Semisolid/Liquid/Suspensions) Regional Analysis North America – The US, Canada, & Mexico; Western Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Portugal, Ireland, Austria, Switzerland, Benelux, Nordic, & Rest of Western Europe; Eastern Europe – Russia, Poland, The Czech Republic, Greece, & Rest of Eastern Europe; APAC – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia & New Zealand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, & Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Colombia, Chile, Argentina, Costa Rica, & Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – Algeria, Egypt, Israel, Kuwait, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, & Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Pfizer Inc., Novartis AG, AstraZeneca Plc, Merck & Co. Inc., Bristol‑Myers Squibb Company, Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Evonik Industries AG, Catalent Inc., Skyepharma Production SAS, Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Ltd., Alkermes plc, Croda International Plc, Adare Pharma Solutions, Mylan N.V., GlaxoSmithKline Plc, F. Hoffman-La-Roche Ltd., BioNTech, Gilead Sciences Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Oral Controlled Release Drug Delivery Technology MarketPublished date: Nov 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Oral Controlled Release Drug Delivery Technology MarketPublished date: Nov 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Pfizer Inc.
- Novartis AG
- AstraZeneca Plc
- Merck & Co. Inc.
- Bristol‑Myers Squibb Company
- Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
- Evonik Industries AG
- Catalent Inc.
- Skyepharma Production SAS
- Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Ltd.
- Alkermes plc
- Croda International Plc
- Adare Pharma Solutions
- Mylan N.V.
- GlaxoSmithKline Plc
- F. Hoffman-La-Roche Ltd.
- BioNTech
- Gilead Sciences










