Global Integrated Pest Management Market Size, Share, Analysis Report By Pest Type (Weeds, Invertebrates, Pathogens, Vertebrates), By Control Method (Biological Control, Chemical Control, Cultural Controls, Mechanical and Physical Controls, Others), By Application ( Agriculture, Commercial, Industrial, Residential, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Aug 2025
- Report ID: 156119
- Number of Pages: 300
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
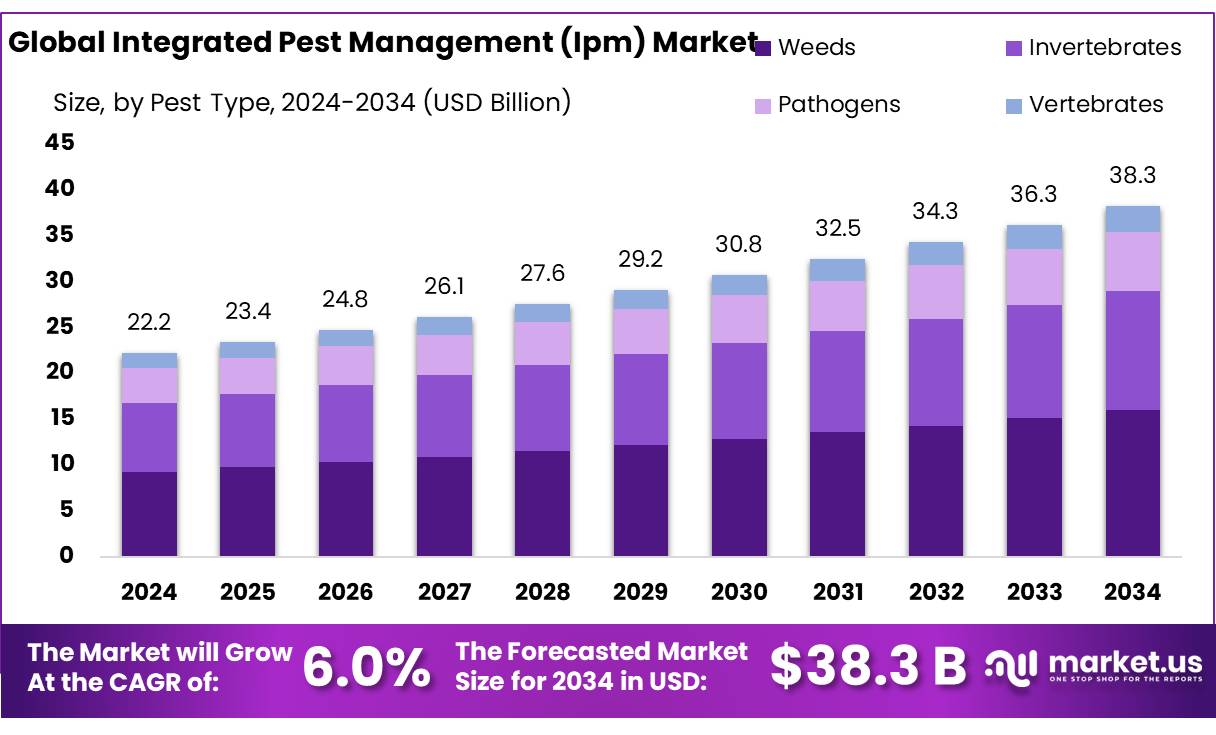
The Global Integrated Pest Management Market size is expected to be worth around USD 38.3 Billion by 2034, from USD 22.2 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 6.0% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, Asia Pacific held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 47.9% share, holding USD 85.4 Million revenue.
Integrated pest management (IPM) concentrates—microbial, botanical, pheromonal, and reduced-risk chemical formulations designed for scouting-driven, threshold-based use—are gaining prominence as growers chase efficacy with lower residues and better resistance stewardship.
The need is structural: FAO estimates up to 40% of global crop production is lost to pests and diseases each year, costing the economy over USD 220 billion, while invasive insects add at least USD 70 billion. At the same time, pesticide use in agriculture reached 3.70 million tonnes of active ingredients in 2022, up 4% year-on-year and double since 1990, underscoring the pressure to optimize inputs rather than simply apply more.
Industry dynamics reflect a pivot toward low-residue tools. In the EU, the Commission tracks progress toward non-legally binding Farm to Fork targets to cut the use and risk of chemical pesticides by 50% and the use of more hazardous pesticides by 50% by 2030; this policy signal is reshaping product portfolios and procurement standards across the value chain. Biologicals support compliance because many have short persistence and are often exempt from maximum residue limits, improving marketability of treated produce. These forces are helping IPM concentrates move from niche to program core in orchards, vegetables, and specialty crops.
On-farm practice data confirm the shift. USDA’s latest Chemical Use survey for fruit crops shows IPM fundamentals are now near-universal: 98% of planted acres were scouted for insects and mites, 98% were scouted for diseases, 70% used pesticides with different mechanisms of action to slow resistance, and 58% compared scouting data to published thresholds before treating—behaviors that favor concentrated, rotation-ready inputs.
In the U.S., the regulatory pipeline also supports IPM tools: EPA reported 390 registered biopesticide active ingredients as of 2020 and continues adding new microbial and biochemical actives through 2024–2025 (e.g., new Bacillus and Trichoderma strains), broadening the toolbox available for concentrate formulations.
Public investment further anchors demand. USDA-NIFA invested USD 19.6 million in 2023 under the Crop Protection and Pest Management (CPPM) program to develop and extend new IPM tactics and speed adoption. Separately, under Plant Protection Act Section 7721, USDA-APHIS provides up to USD 63 million annually for projects that prevent, detect, and manage plant pests and diseases—funding that drives surveillance, early warning, and targeted interventions where IPM concentrates are most effective. These programs de-risk innovation and expand extension capacity, which accelerates uptake by growers and public agencies.
Key Takeaways
- Integrated Pest Management Market size is expected to be worth around USD 38.3 Billion by 2034, from USD 22.2 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 6.0%.
- Weeds held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 41.7% share of the Integrated Pest Management (IPM) market.
- Chemical Control held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.6% share of the Integrated Pest Management (IPM) market.
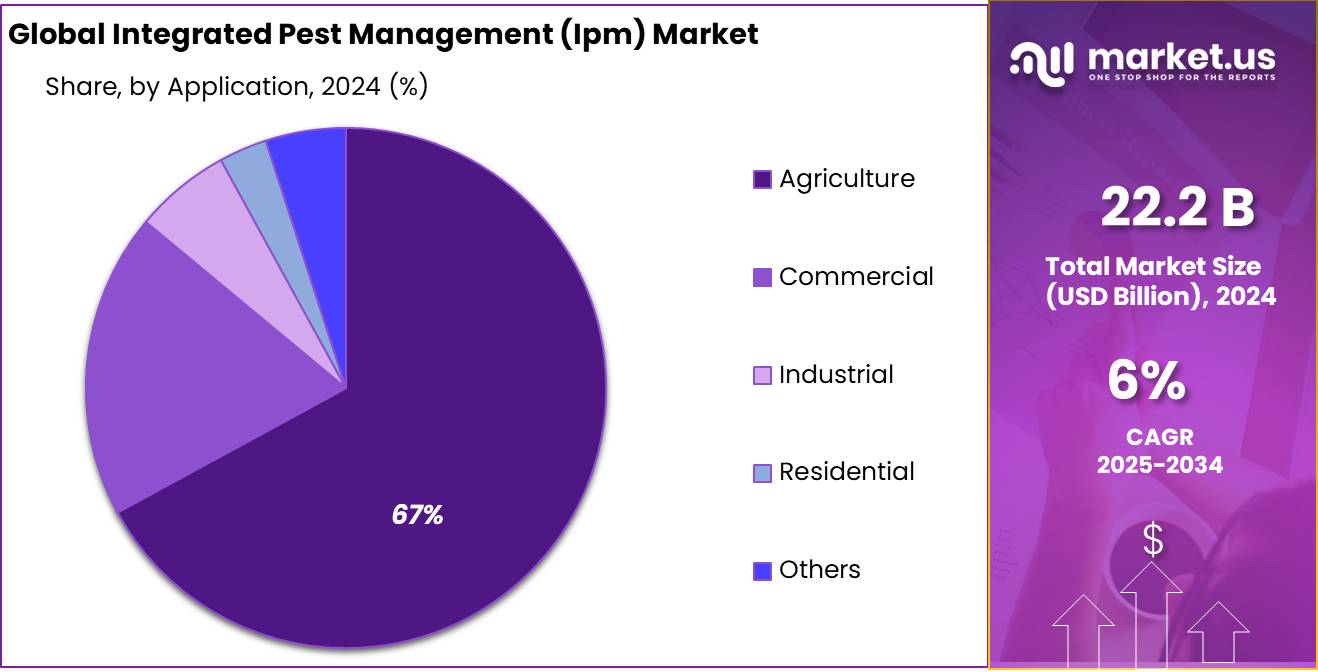
- Agriculture held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 67.2% share of the Integrated Pest Management (IPM) market.
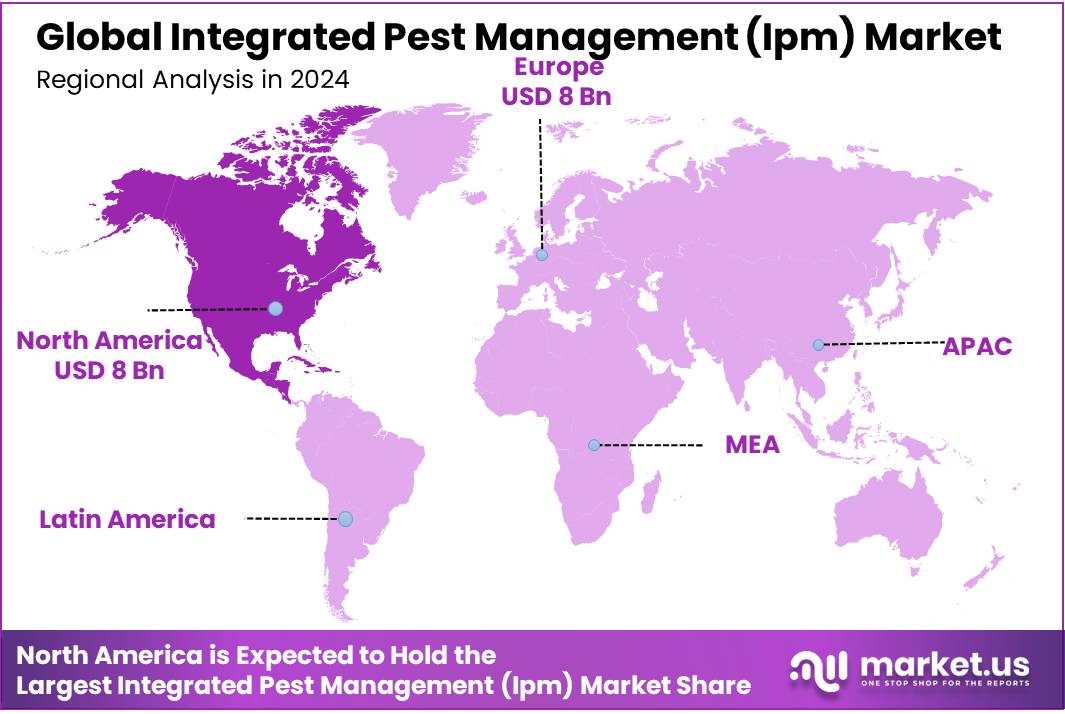
- North America held a dominant position in the Integrated Pest Management (IPM) market, capturing more than 36.2% share with a valuation of around USD 8 billion.
By Pest Type Analysis
Weeds dominate with 41.7% due to their widespread impact on crop yields
In 2024, Weeds held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 41.7% share of the Integrated Pest Management (IPM) market. This strong presence reflects the fact that weeds remain one of the most persistent and costly challenges in agriculture, often competing with crops for nutrients, water, and sunlight. Farmers across all major growing regions invest heavily in integrated solutions—ranging from herbicide concentrates to biological and cultural controls—because unchecked weed growth can cut yields by up to 30–40% in cereals and pulses.
The demand for IPM solutions targeting weeds has also grown in 2025, with adoption driven by rising pressure to reduce blanket herbicide use and comply with residue regulations. Instead of relying solely on chemical herbicides, growers are increasingly turning to IPM concentrates that integrate selective herbicide doses with crop rotation, cover cropping, and bio-herbicides. This approach helps reduce resistance build-up, which is becoming a major concern in regions like North America and Europe where herbicide-resistant weed species are spreading.
By Control Method Analysis
Chemical Control leads with 38.6% owing to its quick effectiveness and broad adoption
In 2024, Chemical Control held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.6% share of the Integrated Pest Management (IPM) market. This leading role is largely due to the continued reliance on chemical formulations for immediate and large-scale pest suppression, especially in staple crops like wheat, maize, and rice. Farmers often turn to chemical concentrates when quick results are essential, as they provide effective solutions against insects, weeds, and fungal infestations that can otherwise cause severe yield losses.
By 2025, the segment remains strong as chemical control methods continue to be integrated into wider IPM programs, where they are applied at reduced dosages and in combination with biological and cultural practices. While the regulatory push is toward lowering chemical usage, their cost-effectiveness, established supply chains, and familiarity among growers ensure their ongoing importance. For many regions, particularly in Asia and Latin America, chemical controls remain the backbone of pest management programs, while being adapted to fit into residue-compliant frameworks and resistance management strategies.
By Application Analysis
Agriculture dominates with 67.2% as farmers prioritize crop protection and yield stability
In 2024, Agriculture held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 67.2% share of the Integrated Pest Management (IPM) market. This overwhelming presence highlights how agriculture remains the primary driver of IPM adoption, as crop losses from pests continue to threaten food security worldwide. Farmers face constant pressure to balance productivity with sustainability, and IPM provides the right mix of chemical, biological, and cultural controls to protect harvests while reducing over-reliance on synthetic pesticides.
By 2025, the agricultural sector continues to strengthen its use of IPM, with rising adoption in both developed and developing regions. In Asia and Africa, where pests like fall armyworm and locusts have caused significant damage, IPM-based practices are being increasingly integrated into farming systems. Governments and extension services are providing support for training programs, subsidies for bio-inputs, and awareness campaigns to encourage farmers to shift toward integrated solutions. This makes agriculture the largest and most stable application segment for IPM concentrates.
Key Market Segments
By Pest Type
- Weeds
- Invertebrates
- Pathogens
- Vertebrates
By Control Method
- Biological Control
- Chemical Control
- Cultural Controls
- Mechanical & Physical Controls
- Others
By Application
- Agriculture
- Commercial
- Industrial
- Residential
- Others
Emerging Trends
AI-Driven Pest Detection and Management
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing Integrated Pest Management (IPM) by enabling early detection, precise monitoring, and targeted interventions. This technological advancement is particularly beneficial for small-scale farmers who may lack access to traditional pest control resources. AI-powered tools, such as mobile applications and smart sensors, allow farmers to identify pest infestations promptly and accurately, leading to timely and effective management strategies.
For instance, in Khutbav village, Maharashtra, the collaboration between the Agriculture Development Trust and Microsoft resulted in a 40% increase in crop yield and a 50% reduction in production costs through the use of AI-driven applications like Agripilot.ai. These applications provide real-time alerts on pest attacks, soil conditions, and weather forecasts, enabling farmers to make informed decisions on pesticide application and irrigation, thereby enhancing productivity and sustainability.
Furthermore, the Indian government has launched the National Pest Surveillance System (NPSS), an AI-based platform that connects farmers with experts for prompt pest identification and management advice. By uploading photos of infested crops or insects, farmers receive timely guidance on pest control measures, reducing the overuse of pesticides and promoting environmentally friendly practices.
In Andhra Pradesh, the government is implementing the Andhra Pradesh Agriculture Information Management System (APAIMS 2.0), which utilizes AI and Machine Learning to provide personalized advisories, pest and disease alerts, and digital workflows for farmers. This initiative aims to improve service transparency, efficiency, and accessibility, facilitating better pest management practices across the state.
Drivers
Growing Demand for Sustainable Agricultural Practices
One of the key driving factors behind the adoption of Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is the increasing demand for sustainable agricultural practices. With growing concerns over environmental impact, pesticide residues, and human health, there is a significant push towards minimizing the use of chemical pesticides.
According to the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), up to 40% of global crop production is lost to pests and diseases each year, costing the global economy more than USD 220 billion annually. However, conventional pesticide use, while effective in the short term, has raised concerns about environmental contamination, resistance buildup in pests, and the impact on non-target species, including beneficial insects and wildlife.
Government initiatives are playing a significant role in supporting the transition to IPM. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has emphasized the importance of IPM in its pest management strategies. The USDA’s National Institute of Food and Agriculture (NIFA) allocated USD 19.6 million in 2023 to develop and promote IPM techniques through its Crop Protection and Pest Management (CPPM) program.
This funding supports research into new IPM tactics and the development of biologically-based alternatives to traditional chemical pesticides, which is helping to drive the adoption of IPM practices across the farming sector. Additionally, USDA’s Plant Protection Act (PPA) Section 7721 provides up to USD 63 million annually to fund initiatives that prevent, detect, and manage plant pests and diseases, further strengthening the infrastructure for IPM adoption.
The European Union has also been a major advocate for sustainable pest management practices. As part of its Farm to Fork Strategy, the European Commission has set a target to reduce the use of chemical pesticides by 50% by 2030. This goal is expected to further boost the demand for IPM solutions, as farmers look for effective alternatives to chemical pesticides. With strong regulatory pressure and a market-driven demand for sustainability, IPM concentrates are becoming a crucial component of pest management programs, particularly in sensitive crop production areas like fruits, vegetables, and specialty crops.
Restraints
High Initial Costs and Limited Access to Resources
One major restraining factor for the widespread adoption of Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is the high initial cost and limited access to necessary resources, particularly for small and medium-sized farms. While IPM is a long-term, sustainable approach to pest management, it often requires substantial upfront investment in monitoring systems, training, and biological control agents, which can be financially challenging for farmers, especially those operating with tight margins.
The transition to IPM requires a significant shift from traditional pest control methods, which may initially seem more affordable, particularly for large-scale monoculture operations. For example, the adoption of biological pesticides or beneficial insects can be more costly than chemical pesticides, both in terms of the product itself and the labor needed to apply and monitor it.
In the United States, the USDA’s National Institute of Food and Agriculture (NIFA) reported that while IPM methods are cost-effective over time, the initial investments can deter adoption, especially for farmers in resource-constrained regions.
According to a study conducted by NIFA in 2021, small and mid-sized farms are less likely to adopt IPM due to these high initial costs and the need for specialized equipment for pest monitoring and control. In fact, 44% of small farms in the U.S. indicated that cost was the most significant barrier to implementing IPM practices.
Government initiatives have been instrumental in promoting IPM adoption, but funding and support are still limited. For instance, in the U.S., the USDA’s Crop Protection and Pest Management (CPPM) program allocated USD 19.6 million in 2023 to support the development of IPM tools. However, this funding is not enough to cover the widespread adoption of IPM across all farm sizes.
Moreover, in many developing countries, government subsidies for chemical pesticides still overshadow those for IPM practices, making it difficult for farmers to make the transition without financial support. The FAO has called for more comprehensive policy support to reduce the financial barriers to IPM adoption, especially for small-scale farmers.
Opportunity
Expanding Government Support for Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
A significant growth opportunity for Integrated Pest Management (IPM) lies in the increasing government support and funding aimed at enhancing sustainable agricultural practices. Governments worldwide are recognizing the importance of IPM in promoting food security, reducing environmental impact, and improving public health. This recognition is translating into substantial investments and policy initiatives that support the adoption and development of IPM strategies.
In the United States, the Department of Agriculture’s National Institute of Food and Agriculture (USDA-NIFA) has been at the forefront of supporting IPM through its Crop Protection and Pest Management (CPPM) program. In 2023, NIFA invested approximately USD 19.6 million in the CPPM program, funding projects that develop and implement IPM practices across various agricultural sectors . These projects focus on creating economically viable, ecologically sound, and socially acceptable pest management strategies that reduce reliance on chemical pesticides.
The CPPM program operates through three main areas: Applied Research and Development Program (ARDP), Extension Implementation Program (EIP), and Regional Coordination Program (RCP). The ARDP funds projects that develop new IPM tactics and technologies, the EIP supports the adoption of these practices among farmers, and the RCP enhances coordination and collaboration among stakeholders to promote IPM adoption . This comprehensive approach ensures that IPM strategies are not only developed but also effectively implemented and disseminated.
Additionally, regional IPM centers, such as the Northeastern IPM Center, receive funding from USDA-NIFA to support IPM initiatives at the regional level. For instance, the Northeastern IPM Center has been allocated approximately USD 1 million annually to coordinate IPM efforts, provide training, and distribute grants for IPM projects in the northeastern United States .
Regional Insights
North America leads with 36.20% (US$8 Bn) on scale, regulation, and precision adoption
In 2024, North America held a dominant position in the Integrated Pest Management (IPM) market, capturing more than 36.2% share with a valuation of around USD 8 billion. The region’s leadership is strongly supported by the large-scale adoption of sustainable agriculture practices across the United States and Canada. Rising concerns over the environmental and health impacts of chemical pesticides have encouraged growers to shift toward integrated methods that combine biological control, cultural practices, and precision monitoring technologies.
According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), nearly 55% of major crop producers in the U.S. report adopting at least one IPM strategy, demonstrating a steady shift in pest management practices.
Government initiatives also play a key role in strengthening North America’s position. Programs such as the USDA’s Integrated Pest Management Centers provide funding and research support to expand IPM practices in key crops including maize, soybeans, fruits, and vegetables. In Canada, regulatory frameworks are increasingly aligned with environmental sustainability targets, encouraging farmers to cut reliance on synthetic pesticides and adopt eco-friendly biological solutions. Furthermore, the region benefits from a well-established agri-biotech industry that offers advanced biopesticides, pheromone traps, and digital pest monitoring systems, further boosting adoption levels.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
FMC Corporation is a global leader in crop protection solutions and plays an active role in Integrated Pest Management (IPM). The company develops insecticides, herbicides, and fungicides while expanding its biological portfolio to align with sustainable farming practices. FMC invests heavily in precision agriculture, digital tools, and reduced-dose formulations that fit IPM strategies. Its partnerships with growers worldwide focus on balancing productivity with environmental safety, making it a key innovator driving IPM adoption in major agricultural markets.
Oxitec specializes in biotechnology-driven pest control, particularly through its genetically engineered insects designed to reduce pest populations without broad chemical spraying. Its “Friendly™” mosquito and crop pest programs have been deployed in several countries, offering targeted solutions that integrate smoothly into IPM strategies. By limiting the reproduction of harmful pests, Oxitec provides environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional pesticides. The company’s work positions it as a pioneer in bio-based IPM, helping address resistance issues and supporting sustainable farming systems.
BASF SE is a global chemical giant with a strong agricultural solutions division that contributes to IPM. The company’s portfolio includes crop protection products, seed treatments, and biological controls. BASF invests in research to combine digital farming platforms with pest management, offering farmers data-driven decision support alongside advanced chemistries. Its focus on resistance management and residue reduction has made its IPM-compatible products central to sustainable agriculture. With a presence in over 100 countries, BASF is a vital player in modern IPM systems.
Top Key Players Outlook
- FMC Corporation
- Oxitec
- BASF SE
- Hercon Environmenta
- Bayer Crop Science AG
- ADAMA Ltd.
- Rentokil Initial plc
- Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd.
- AgBiTech
Recent Industry Developments
FMC Corporation has long been a thoughtful player in Integrated Pest Management (IPM), blending innovation with practicality in its approach to sustainable crop protection. In 2024, FMC reported revenue of about US $4.25 billion, reflecting a modest 5% decline from the previous year.
Bayer Crop Science AG spent 2024 pushing Integrated Pest Management (IPM) that blends smart chemistry, biologicals, and digital tools. The division managed a tough year with Crop Science sales down 2.0% in 2024, yet kept investing where growers see value.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 22.2 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 38.3 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 6.0% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Pest Type (Weeds, Invertebrates, Pathogens, Vertebrates), By Control Method (Biological Control, Chemical Control, Cultural Controls, Mechanical and Physical Controls, Others), By Application ( Agriculture, Commercial, Industrial, Residential, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape FMC Corporation, Oxitec, BASF SE, Hercon Environmenta, Bayer Crop Science AG, ADAMA Ltd., Rentokil Initial plc, Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd., AgBiTech Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Integrated Pest Management MarketPublished date: Aug 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Integrated Pest Management MarketPublished date: Aug 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- FMC Corporation
- Oxitec
- BASF SE
- Hercon Environmenta
- Bayer Crop Science AG
- ADAMA Ltd.
- Rentokil Initial plc
- Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd.
- AgBiTech










