Global Healthcare IT Outsourcing Market Analysis By Type [Clinical IT Outsourcing (Electronic Health Records (EHR) Systems, Hospital Information Systems (HIS), Clinical Trial Management Systems (CTMS), Health Information Exchange (HIE), Patient Engagement and Monitoring Systems, Telehealth, Healthcare Analytics and Management, Regulatory Compliance and Reporting, Others), Non-Clinical IT Outsourcing (Claims Processing, Billing and Coding, Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Fraud Detection and Prevention, Business Process Outsourcing (BPO), Supply Chain Management, Revenue Cycle Management (RCM), Network Management, System Integration Services, Data Center Operations, Cloud Computing Services, Others)], By End-User (Healthcare Providers, Healthcare Payers, Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology Companies, Medical Device Companies) By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Aug 2025
- Report ID: 156293
- Number of Pages: 383
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
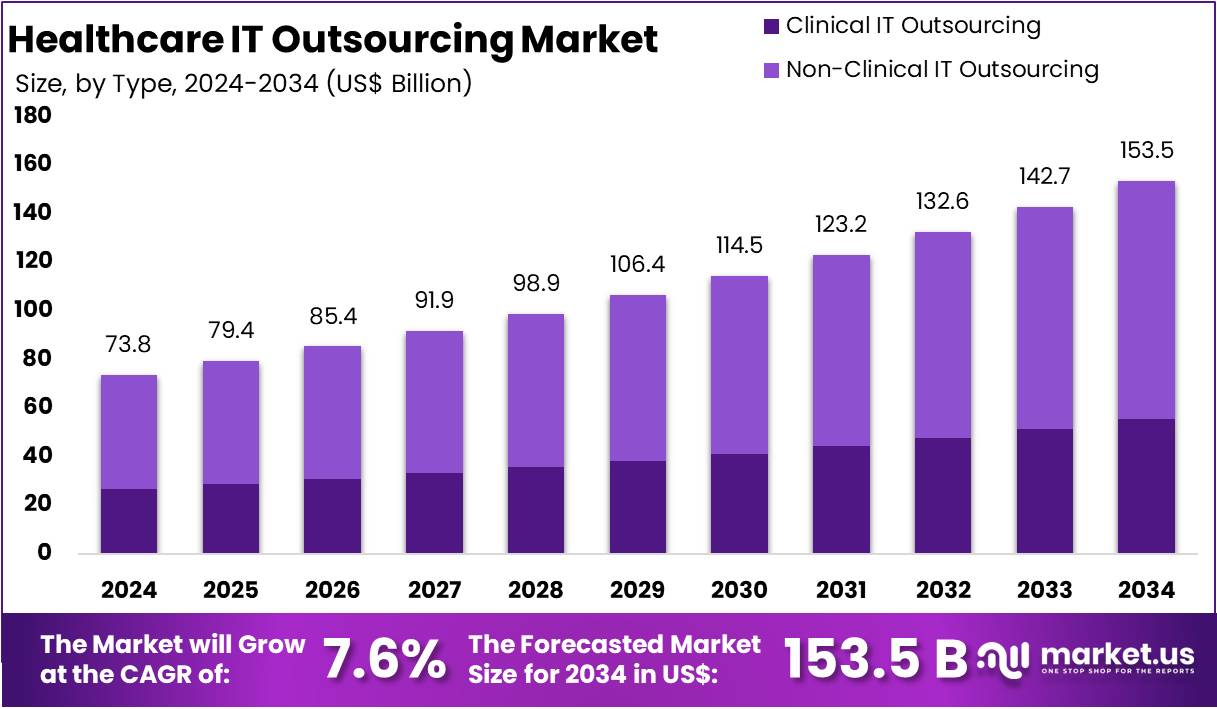
The Global Healthcare IT Outsourcing Market Size is expected to be worth around US$ 153.3 Billion by 2034, from US$ 73.8 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 7.6% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 39.5% share and holds US$ 39.5 Billion market value for the year.
Market Demand Drivers
Healthcare IT outsourcing is the delegation of IT activities to external providers. Scopes include EHR implementation and support, RCM and claims processing, application development, help desk, hosting, cybersecurity, interoperability, analytics, and telehealth. It is adopted to reduce cost, access specialized skills, and improve service levels. Budgets are shifted from capital to operating expense under SLAs and compliance controls. For example, vendor-managed services are used to accelerate digital programs while maintaining auditability.
The market denotes demand and supply for these services among providers, payers, and life-science firms. Segmentation is by service line, delivery model, end user, and geography. Growth is driven by digital transformation, interoperability mandates, cyber-risk management, cloud migration, and telehealth. Restraints include data-privacy concerns and vendor lock-in. According to industry assessments, nearshore and offshore models are favored for scale, while onshore partners are retained for regulated workloads and complex integrations.
Public policy is placing digital health at the center of care. According to WHO, more than 129 countries have adopted national digital health strategies. The agenda has been extended and operationalized. These commitments generate steady program budgets and multi-year build plans. For instance, ministries and payers are using framework contracts to deliver identity, consent, and data-exchange capabilities with external partners, creating resilient, recurring outsourcing demand across regions and care settings.
Electronic health record coverage has reached scale in major markets. In the United States, 96% of non-federal acute care hospitals and 78% of office-based physicians had adopted certified EHRs by 2021. By 2023, 70% of hospitals were exchanging information across all four exchange domains. Study by HHS/ONC indicates expanding integration, upgrade, and support workloads. These volumes are routinely handled through outsourced implementation teams and managed-service operations to ensure uptime, compliance, and performance.
Interoperability networks are expanding nationally. Under TEFCA, 10 Qualified Health Information Networks now operate, with more than 9,200 organizations exchanging under the framework. On the payer side, API mandates are widening. CMS finalized the Interoperability and Prior Authorization Rule in January 2024. Impacted payers must implement HL7 FHIR APIs for patient access, provider access, and payer-to-payer exchange. These specifications and reporting duties are commonly delivered with external engineering support and testing partners.
Utilization, Risk Landscape, Workforce, and Policy Programs
Virtual care has preserved remote workflows that depend on cloud and EHR integration. Medicare data show 14.83 million telehealth users in 2020, 10.25 million in 2021, 8.50 million in 2022, 6.97 million in 2023, and 6.73 million in 2024. The share of eligible users with at least one telehealth service was 48% in 2020 and 25% in both 2023 and 2024. Operations and security for these channels are outsourced to ensure scale, resilience, and user experience.
Cyber risk has risen sharply, shifting spend toward managed security. ENISA reports that 45% of analyzed EU health-sector incidents in 2024 were ransomware and 28% were data breaches. In the United States, OCR received 626 reports of large breaches in 2022 affecting about 41.7 million people. The 2024 Change Healthcare incident has been reported to impact about 190 million individuals. For example, 24/7 monitoring, hardening, and incident-response services are being procured through specialized MSSPs.
Staffing constraints reinforce outsourcing. WHO estimates a projected global shortfall of about 11.1 million health workers by 2030, even as the total workforce exceeds 70 million. According to workforce studies, providers are using external vendors to automate workflows, maintain compliance, and run platforms without adding permanent headcount. Managed services embed standardized playbooks and metrics. For instance, application maintenance and data-platform operations are shifted to partners to stabilize costs and reduce vacancy risk.
Large public programs are creating concrete implementation work. The European Health Data Space regulation entered into force in March 2025, requiring new connectors, consent services, and governance tools. In England, the NHS App surpassed 34 million users; December 2024 saw 4.9 million repeat prescription orders and 17.4 million record views. In India, ABDM reported 73.98 crore ABHA numbers and 49.06 crore linked records by February 2025—roughly 740 million IDs and 491 million records—driving identity, exchange, and registry services.
International evidence shows digital use has become routine. An OECD review notes the average number of teleconsultations per patient more than doubled from 2019 to 2021. Only 15 of 27 surveyed countries had a single national EHR; most rely on multiple platforms. This fragmentation sustains integration, migration, and API work, often contracted out. In summary, EHR scale, interoperability targets, durable telehealth, rising cyber incidents, workforce shortages, and flagship national programs indicate structural, policy-led growth across healthcare IT outsourcing.
Key Takeaways
- The global healthcare IT outsourcing market is projected to grow from US$ 73.8 Billion in 2024 to US$ 153.3 Billion by 2034.
- This market expansion reflects a steady CAGR of 7.6% between 2025 and 2034, driven by rising digital transformation and cost-efficiency demands.
- In 2024, the non-clinical IT outsourcing segment dominated the type category, capturing more than 63.9% of the total market share.
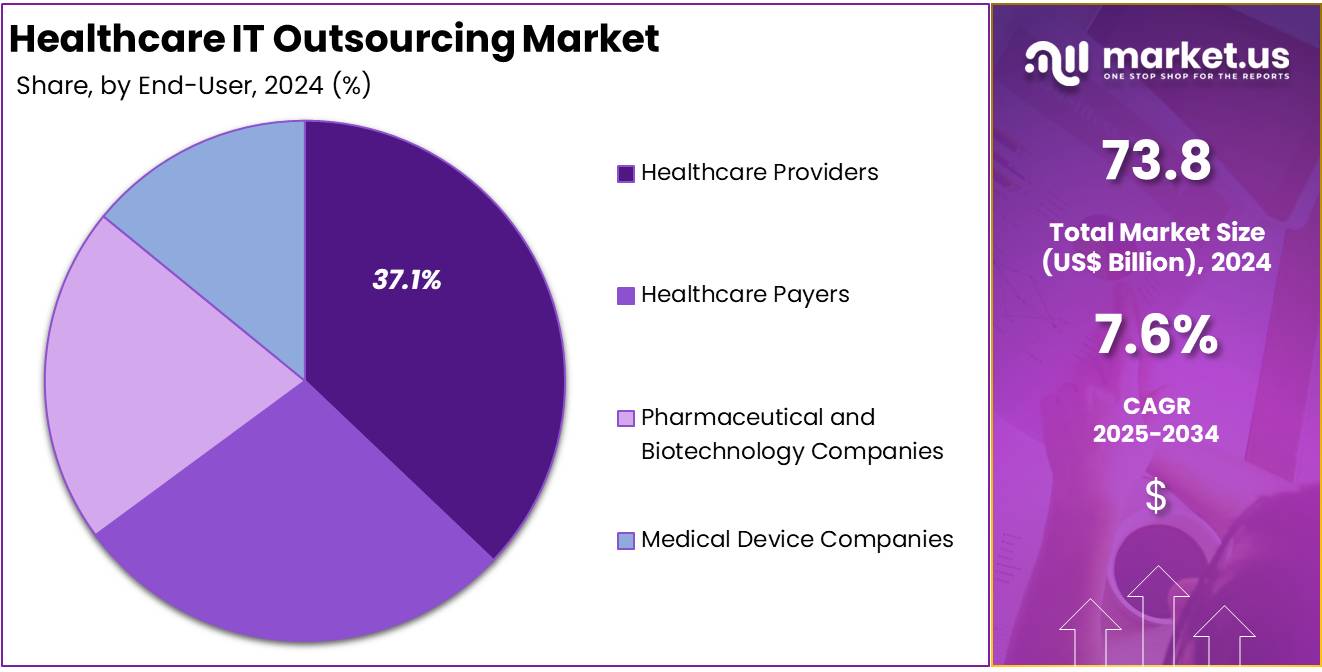
- Among end-users, healthcare providers led the market in 2024, accounting for over 37.1% of the overall share within the sector.
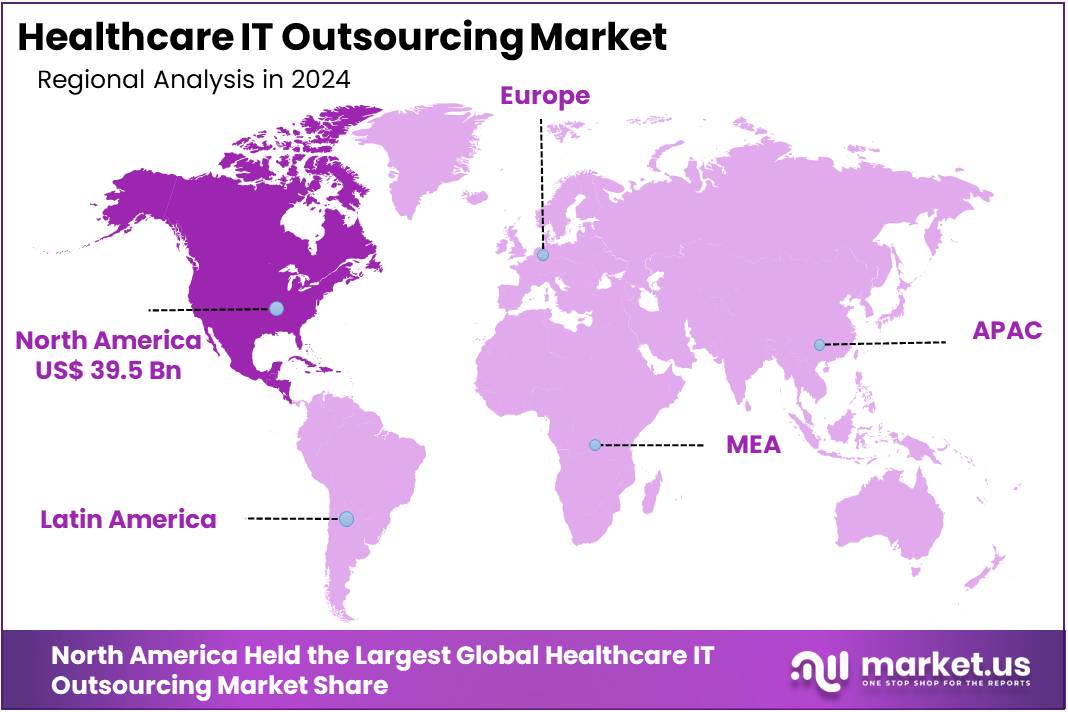
- North America remained the leading region in 2024, contributing over 39.5% share, equivalent to a market value of US$ 39.5 Billion.
Type Analysis
In 2024, the Non-Clinical IT Outsourcing Section held a dominant market position in the Type Segment of Healthcare IT Outsourcing Market, and captured more than a 63.9% share. This growth is mainly driven by the rising demand for administrative efficiency and cost reduction. Hospitals and healthcare providers are increasingly outsourcing billing, coding, claims processing, and revenue cycle management. These services allow organizations to focus on patient care, while external vendors manage the financial and operational aspects with improved accuracy and speed.
The Clinical IT Outsourcing section, though smaller in comparison, is witnessing strong growth. Electronic Health Records (EHR), hospital information systems, and telehealth platforms are in high demand. Rising digital transformation in healthcare is fueling this segment. Patient engagement tools and health information exchanges are also expanding due to the focus on better care coordination and patient outcomes. Regulatory compliance and reporting services are becoming vital as governments tighten data privacy and healthcare regulations.
Non-Clinical IT Outsourcing is expected to maintain its lead in the coming years. The need for advanced fraud detection, business process outsourcing, and cloud computing services is accelerating. Network management and system integration are also critical to handle large healthcare datasets. Meanwhile, Clinical IT Outsourcing will continue its upward trajectory with innovations in analytics, monitoring systems, and telemedicine. Together, both segments highlight the growing reliance of healthcare institutions on outsourcing partners to streamline operations and enhance service delivery.
End-User Analysis
In 2024, the Healthcare Providers held a dominant market position in the End-User Segment of the Healthcare IT Outsourcing Market, and captured more than a 37.1% share. Hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic centers are outsourcing IT services to cut costs and improve efficiency. The need for advanced electronic health records, telehealth platforms, and cloud data management drives this adoption. Rising patient volumes and complex clinical workflows make outsourcing a cost-effective option for providers.
Healthcare Payers also represent a strong growth segment. Insurance companies and other payer organizations rely on IT outsourcing to handle claims processing, fraud detection, and regulatory compliance. Increasing demand for digital payment platforms and automated claim adjudication adds momentum. Outsourcing helps them reduce operational expenses while ensuring data security and accuracy in policy management.
Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology Companies are investing in IT outsourcing for research support, clinical trial management, and supply chain optimization. With rising drug discovery costs, outsourcing IT functions improves flexibility and speeds up time-to-market. Medical Device Companies are also leveraging outsourcing to manage regulatory documentation, product lifecycle management, and cybersecurity needs. This shift ensures compliance with global standards and enhances innovation in connected healthcare devices.
Key Market Segments
By Type
- Clinical IT Outsourcing
- Electronic Health Records (EHR) Systems
- Hospital Information Systems (HIS)
- Clinical Trial Management Systems (CTMS)
- Health Information Exchange (HIE)
- Patient Engagement and Monitoring Systems
- Telehealth
- Healthcare Analytics and Management
- Regulatory Compliance and Reporting
- Others
- Non-Clinical IT Outsourcing
- Claims Processing
- Billing and Coding
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- Fraud Detection and Prevention
- Business Process Outsourcing (BPO)
- Supply Chain Management
- Revenue Cycle Management (RCM)
- Network Management
- System Integration Services
- Data Center Operations
- Cloud Computing Services
- Others
By End-User
- Healthcare Providers
- Healthcare Payers
- Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology Companies
- Medical Device Companies
Drivers
Remote Patient Monitoring Adoption as a Key Driver for Healthcare IT Outsourcing
remote patient monitoring (RPM) and digital transformation needs have emerged as a strong driver for healthcare IT outsourcing. Healthcare providers face rising costs and operational pressure to improve efficiency. According to industry insights, outsourcing IT services for RPM, EHR management, and telehealth infrastructure enables adoption of advanced digital capabilities without building expensive in-house systems. For example, the need to manage AI-driven RPM platforms and cloud infrastructure is pushing hospitals to partner with specialized providers who deliver scalable and compliant solutions.
Physician adoption of digital care tools further accelerates this outsourcing trend. A study by the American Medical Association highlighted that 30% of U.S. physicians were using remote monitoring devices in 2022, while nearly 80% reported using tele-visits, compared to only 14% in 2016. This rapid uptake reflects growing enthusiasm for technology-enabled care. For instance, physicians increasingly rely on outsourced platforms that handle device integration, secure data exchange, and workflow management, ensuring seamless patient engagement and compliance.
Medicare data also illustrates the scale of RPM adoption. According to CMS, over 570,000 Medicare enrollees received RPM services in 2022, with payments exceeding $300 million, a more than 20× increase from 2019. The average payment per enrollee also doubled to $545, while one in four enrollees was monitored for over nine months. These metrics highlight growing demand for outsourced solutions. For example, managed service providers help organizations handle longitudinal monitoring, complex billing requirements, and secure patient data management at scale.
Regulatory and operational requirements make outsourcing even more critical. CMS clarified in the CY-2024 rulemaking that certain RPM and RTM codes must meet the “16 readings in 30 days” threshold. Study data also show that 94% of Medicare RPM users were chronic disease patients, but 43% lacked at least one required component like education, device supply, or treatment management. For instance, outsourcing ensures device logistics, onboarding, data completeness, and clinical escalation are standardized, enabling providers to close gaps and deliver compliant, high-quality care.
Restraints
Data security and integration challenges
In healthcare IT outsourcing, data security and integration challenges act as major restraints. Healthcare data is highly sensitive, and outsourcing IT functions increases exposure to cyberattacks and breaches. For instance, in 2024, there were 725 large healthcare breaches reported, exposing about 275 million records, and 81.2% of these were hacking incidents. Around 30% of breaches occurred at business associates, highlighting the vulnerability of outsourced supply chains. Such risks significantly restrict market adoption and delay outsourcing decisions.
The financial impact of breaches further strengthens this restraint. According to IBM, the average cost of a healthcare data breach reached USD 10.10 million in 2022 and USD 9.77 million in 2024, the highest across all industries. Third-party breaches are identified as cost-amplifying factors, making outsourcing riskier. For example, the Change Healthcare incident alone affected around 190 million individuals, demonstrating concentration risk when critical services are outsourced. These high costs raise insurance, risk premiums, and compliance expenses for healthcare organizations.
Regulatory and Compliance Burden
Regulatory exposure adds another layer of restraint for outsourcing healthcare IT services. According to the Office for Civil Rights (OCR), HIPAA enforcement reports show that corrective actions often include revising business associate agreements and strengthening risk analysis for vendors. In Europe, GDPR enforcement also remains strict. For instance, the French DPA fined Dedalus Biologie €1.5 million in 2022 for a health-data breach, while CEGEDIM SANTÉ was fined €800k in 2024 for unlawful processing of health data. These cases show vendors face penalties, which also transfer to healthcare providers.
Integration complexity and uneven interoperability also hinder outsourcing growth. A study by the ONC revealed that while 70% of U.S. non-federal acute-care hospitals engaged in all four interoperability domains in 2023, only 42% reported that clinicians routinely used outside information at the point of care. Moreover, only 16–17% of hospitals shared summaries with most long-term or behavioral-health providers (NCBI). A 2024 national survey further showed that 57% of digital health firms rely on mixed APIs, with 47% citing high access fees as a barrier. These gaps make vendor integration costly and slow.
Opportunities
Leveraging Big Data And Analytics For Advanced Healthcare Insights
In the Healthcare IT Outsourcing market, the growing adoption of big data and analytics is creating a strong opportunity. Providers are increasingly outsourcing analytics to external vendors for predictive modeling, population health insights, and real-time care delivery optimization. According to a HIMSS-Medscape report (Dec 2024), 86% of health systems already use AI, and 60% value it for pattern detection beyond human ability. This creates demand for outsourced data pipelines, model operations, and validation services that transform vast datasets into actionable intelligence.
The supply of healthcare data has also expanded rapidly, driven by API and FHIR readiness. For instance, the ONC’s Hospital IT Survey (2022) revealed that nine in ten U.S. hospitals used APIs for patient access, and about two-thirds reported using FHIR APIs—up 12 percentage points year-over-year. This shift highlights a step-change in data availability, where external vendors are required to engineer, map, and maintain API systems that enable secure and scalable data sharing across health ecosystems.
Infrastructure for interoperability has matured further, opening doors for outsourced solutions. In 2024, the Trusted Exchange Framework and Common Agreement (TEFCA) moved into execution, with seven organizations designated as Qualified Health Information Networks (QHINs). These QHINs enable large-scale, multi-network data exchange. However, building connectivity and establishing data governance remain complex tasks. As a result, providers and payers are increasingly depending on outsourcing partners to integrate multi-source datasets, manage compliance, and ensure secure interoperability across national healthcare systems.
Policy developments are also fueling this outsourcing opportunity. For example, the CMS finalized its Interoperability & Prior Authorization Rule (Jan 2024), requiring payers to implement Patient, Provider, and Payer-to-Payer FHIR APIs, with phased compliance set for 2026–2027. The regulation also mandates strict prior-authorization response times—72 hours for urgent and 7 days for standard cases. Meeting these requirements demands outsourced capacity for API engineering, real-time monitoring, and advanced data management. Thus, regulatory mandates further accelerate the reliance on external IT partners in healthcare.
Trends
Rise Of Ai-Powered Healthcare And Interoperability Technologies
The rise of AI-powered healthcare is transforming the healthcare IT outsourcing landscape. Providers are increasingly adopting artificial intelligence to improve predictive diagnostics, streamline workflows, and automate administrative processes. These advancements reduce costs and enhance efficiency for healthcare organizations. AI also supports early disease detection and personalized treatment planning, making it a key driver for outsourcing services. As healthcare systems face rising demand, AI integration in outsourced solutions ensures faster decision-making, improved clinical outcomes, and a stronger focus on patient-centered care.
Big data analytics is further accelerating this transformation by enabling healthcare organizations to process large volumes of clinical and operational information. Outsourced analytics services provide predictive modeling and insights into patient populations, resource allocation, and care management. These solutions allow providers to achieve greater accuracy in diagnosis and treatment while optimizing operational performance. By leveraging external expertise, healthcare organizations reduce the burden of managing complex analytics tools internally. This trend positions outsourcing vendors as critical partners in driving healthcare intelligence and innovation.
At the same time, interoperability technologies are becoming central to modern outsourcing. Digital platforms powered by blockchain and secure APIs are fostering seamless data exchange across healthcare networks. These tools ensure safe clinical data sharing while maintaining regulatory compliance. Interoperability also supports virtual care models and cross-border collaboration, strengthening the role of outsourcing in global healthcare. By combining AI, analytics, and blockchain, outsourcing is evolving into a hub for high-value, smart healthcare services. This positions providers to deliver efficient, connected, and future-ready healthcare systems.
Regional Analysis
In 2024, North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 39.5% share and holds US$ 39.5 Billion market value for the year. The region’s strong base of advanced healthcare infrastructure has driven this dominance. A growing demand for cost-effective IT solutions, coupled with rapid digitalization in hospitals and clinics, has further boosted outsourcing adoption. The presence of skilled IT professionals and well-established service providers also supported steady market growth across the region.
The increasing burden of chronic diseases has intensified the need for efficient healthcare delivery. Outsourcing IT functions such as electronic health records (EHR), cloud hosting, and revenue cycle management has helped providers reduce costs. Healthcare organizations in North America are also under pressure to comply with strict data security regulations. This has made outsourcing to specialized vendors an attractive option. As a result, healthcare facilities are able to streamline operations and focus on patient care.
Government initiatives in the United States and Canada to promote digital healthcare adoption have also contributed. The widespread use of telemedicine, mobile health applications, and AI-based platforms has created strong outsourcing opportunities. With high healthcare spending and continuous innovation, North America is expected to retain its lead in the global Healthcare IT Outsourcing market. The combination of regulatory compliance, technology adoption, and demand for scalable solutions ensures long-term regional dominance.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherland
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- New Zealand
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
The Healthcare IT Outsourcing (HITO) market is characterized by the presence of global leaders with diversified capabilities and strong investments in next-generation technologies. Accenture plc stands out as a top-tier, end-to-end partner with a broad portfolio across payers, providers, life sciences, and public health. Its $3 billion multi-year Data & AI investment and global delivery scale reinforce its positioning. The firm’s strength lies in managing complex transformation overlays, integrating clinical platforms, and rapidly scaling GenAI with enterprise-level governance.
Cognizant Technology Solutions maintains a strong presence in payer and life sciences outsourcing, underpinned by deep client relationships with top global pharmaceutical firms. With 2024 revenues nearing $19.7 billion, the company demonstrates significant delivery capacity. Its $1 billion GenAI investment and partnerships with Microsoft and Google Cloud further enhance competitiveness. Cognizant is recognized for payer platform modernization, digital member experience, and life sciences operations, making it a preferred partner for regulated workloads and hyperscaler-enabled delivery in healthcare environments.
IBM Corporation leverages its hybrid cloud and watsonx AI ecosystem to deliver advisory-to-run services with an emphasis on governance, interoperability, and security. Its co-innovation initiatives, such as the AI solution with Roche for glucose prediction, highlight applied AI strengths in clinical use cases. IBM’s Granite open-source models provide enterprise flexibility, while its consulting arm strengthens healthcare transformation projects. The company’s clear differentiation is its focus on cyber resiliency and secure AI adoption, which align with the needs of regulated healthcare clients.
Infosys and Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) provide competitive options for cost-efficient, large-scale healthcare outsourcing. Infosys, through its Topaz AI-first stack, advances automation and digital modernization with a proven cloud and managed services posture. TCS, meanwhile, is recognized for leadership in provider digital services, scaling patient-centric engagement, and global data/AI platforms. Together, these firms complement market leaders by offering structured, cost-optimized frameworks and multi-year managed services. This competitive landscape ensures robust growth opportunities for healthcare enterprises seeking digital transformation and operational resilience.
Market Key Players
- Accenture Plc
- Cognizant Technology Solutions
- IBM Corporation
- Infosys Limited
- Tata Consultancy Services Ltd.
- Wipro Ltd.
- McKesson Corporation
- Siemens Healthineers
- Optum Inc.
- Allscripts Healthcare Solutions
- Dell Technologies Inc.
- Xerox Corporation
Recent Developments
- In December 2024: Siemens Healthineers concluded the acquisition of the Advanced Accelerator Applications (AAA) Molecular Imaging business from Novartis. This strategic acquisition expanded its network of PET radiopharmaceutical manufacturing and distribution across Europe, adding 13 new sites in France, Spain, Portugal, Italy, and Germany. The move complements the existing PETNET Solutions network, bolstering Siemens Healthineers’ capabilities in diagnostic radiopharmaceutical supply and supporting oncology, cardiology, and neurology imaging services. This acquisition likely enhances Siemens Healthineers’ ability to offer outsourced solutions in molecular diagnostics and imaging. The addition of European production and distribution infrastructure strengthens its outsourcing capacity in radiopharmaceutical services, improving turnaround times and geographic coverage.
- In February 2024: Optum signed a 10‑year agreement with Allina Health, under which Optum would assume responsibility for Allina’s information technology (IT) systems and billing operations. The strategic collaboration aimed to enhance Allina Health’s administrative efficiency by leveraging Optum’s advanced technology infrastructure, including artificial intelligence (AI) and automation, within back‑office functions.
- In June 2023: McKesson unveiled Foster & Thrive™, a unified private-label brand of over-the-counter (OTC) health and wellness products. This initiative consolidated products previously offered under its Health Mart® and Sunmark® brands. The consolidation aimed to increase production efficiencies and expand product availability, thereby addressing growing patient and pharmacy demand under a streamlined, quality-oriented portfolio. The launch leverages McKesson’s nearly two centuries of supply chain infrastructure to deliver private-label OTC solutions that meet both pharmacist expectations and consumer demand, particularly amid rising interest in cost-effective, “store-brand” alternatives to national OTC products.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) US$ 73.8 Billion Forecast Revenue (2034) US$ 153.5 Billion CAGR (2025-2034) 7.6% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, COVID-19 Impact, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Type [Clinical IT Outsourcing (Electronic Health Records (EHR) Systems, Hospital Information Systems (HIS), Clinical Trial Management Systems (CTMS), Health Information Exchange (HIE), Patient Engagement and Monitoring Systems, Telehealth, Healthcare Analytics and Management, Regulatory Compliance and Reporting, Others), Non-Clinical IT Outsourcing (Claims Processing, Billing and Coding, Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Fraud Detection and Prevention, Business Process Outsourcing (BPO), Supply Chain Management, Revenue Cycle Management (RCM), Network Management, System Integration Services, Data Center Operations, Cloud Computing Services, Others)], By End-User (Healthcare Providers, Healthcare Payers, Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology Companies, Medical Device Companies) Regional Analysis North America – The US, Canada, & Mexico; Western Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Portugal, Ireland, Austria, Switzerland, Benelux, Nordic, & Rest of Western Europe; Eastern Europe – Russia, Poland, The Czech Republic, Greece, & Rest of Eastern Europe; APAC – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia & New Zealand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, & Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Colombia, Chile, Argentina, Costa Rica, & Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – Algeria, Egypt, Israel, Kuwait, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, & Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Accenture Plc, Cognizant Technology Solutions, IBM Corporation, Infosys Limited, Tata Consultancy Services Ltd., Wipro Ltd., McKesson Corporation, Siemens Healthineers, Optum Inc., Allscripts Healthcare Solutions, Dell Technologies Inc., Xerox Corporation Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Healthcare IT Outsourcing MarketPublished date: Aug 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Healthcare IT Outsourcing MarketPublished date: Aug 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Accenture Plc
- Cognizant Technology Solutions
- IBM Corporation
- Infosys Limited
- Tata Consultancy Services Ltd.
- Wipro Ltd.
- McKesson Corporation
- Siemens Healthineers
- Optum Inc.
- Allscripts Healthcare Solutions
- Dell Technologies Inc.
- Xerox Corporation










