Global UPS Battery Market Size, Share, Growth Analysis By Battery (Lead Acid, Li-ion, Nickel Cadmium, Others), By Application (Residential, Commercial, Data Centers, Industrial) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Nov 2025
- Report ID: 168329
- Number of Pages: 204
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
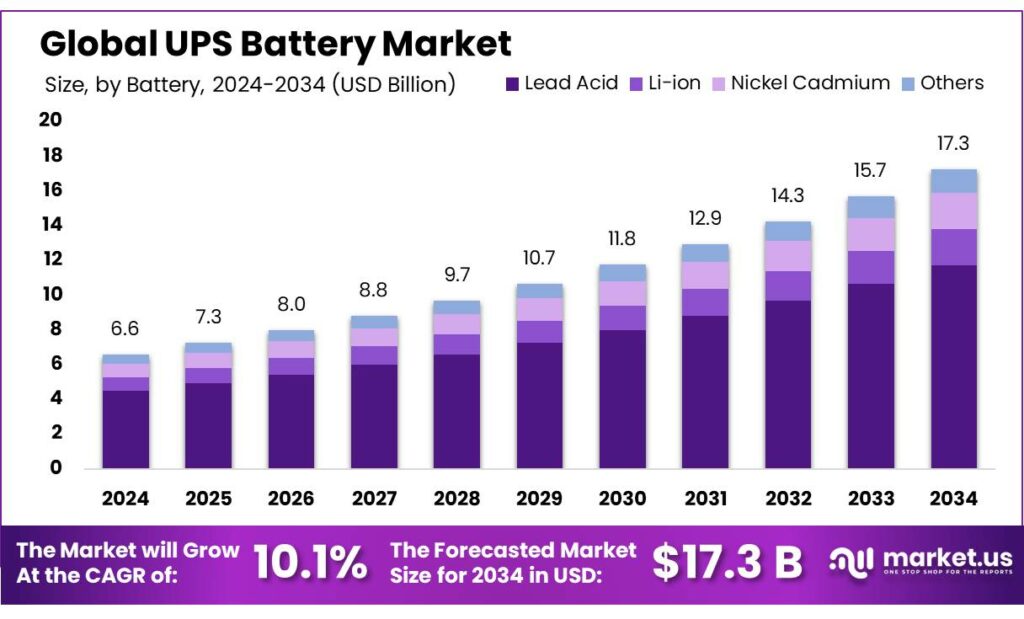
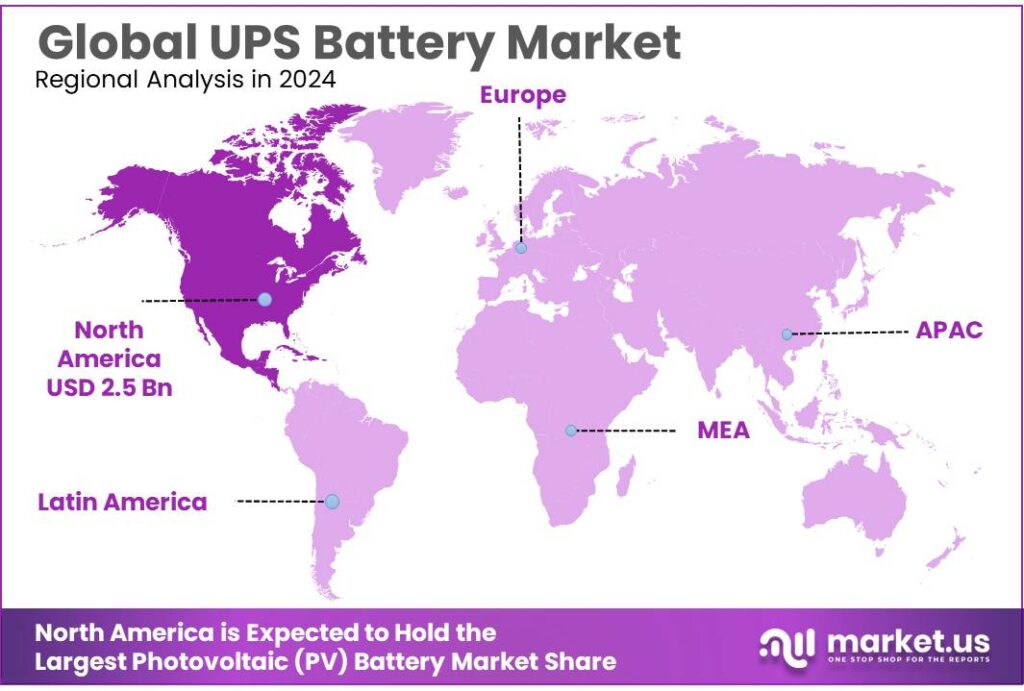
The Global UPS Battery Market size is expected to be worth around USD 17.3 Billion by 2034, from USD 6.6 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 10.1% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, Asia Pacific held a dominan market position, capturing more than a 38.9% share, holding USD 2.5 Billion revenue.
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) batteries sit at the heart of digital resilience, keeping IT, healthcare, industrial and commercial systems running when the grid fails. Their importance is rising as electricity use and digital workloads climb. The International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates that data centres consumed about 415 TWh of electricity in 2024, around 1.5% of global electricity demand, after growing roughly 12% per year over the last five years. This scale of critical load means any interruption now carries much higher financial and operational risk than a decade ago.
Industrial buyers increasingly treat UPS batteries as strategic infrastructure because power quality events remain common and costly. The U.S. Energy Information Administration reports that American electricity customers experienced about 5.5 hours of power interruptions on average in 2022. For data centres, the Uptime Institute finds that 54% of operators said their most recent significant outage cost more than USD 100,000, and 20% reported losses above USD 1 million.
A major structural driver is the twin expansion of electrification and renewables. Globally, electricity consumption rose by around 1,080 TWh in 2024, nearly double the annual average increase seen over the past decade. At the same time, renewable sources already supply 29.9% of global electricity, totalling 8,928 TWh in 2023. Variability from solar and wind makes on-site UPS batteries more attractive in hospitals, semiconductor fabs, cold storage, and telecom hubs that cannot tolerate disturbances when local grids are stressed.
Policy and investment trends further support long-term UPS battery demand. IRENA notes that renewables delivered 92.5% of global power capacity additions in 2024, lifting their share of installed power capacity from 43.0% to 46.4% in a single year. In its 1.5°C pathway, renewable energy’s share in the global energy mix would rise from 16% in 2020 to 77% by 2050, with a twelve-fold increase in renewable electricity capacity versus 2020 levels. Governments backing this transition with grid-modernisation and data-centre policies indirectly expand the installed base of UPS systems that stabilise behind-the-meter power.
Battery deployment itself is accelerating under government and utility programs. REN21 notes that global battery storage capacity grew 120% in 2023 to about 55.7 GW, with China surging 250% year-on-year to 27.1 GW. The IEA adds that battery storage in the power sector was the fastest-growing commercially available energy technology in 2023, with around 42 GW of new capacity added across grid-scale, behind-the-meter, and off-grid systems. Although much of this capacity serves grid applications, it builds supply chains, standards, and cost curves that also benefit UPS-specific batteries.
Key Takeaways
- UPS Battery Market size is expected to be worth around USD 17.3 Billion by 2034, from USD 6.6 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 10.1%
- Lead Acid held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 67.9% share of the UPS battery market due to its established reliability and cost efficiency.
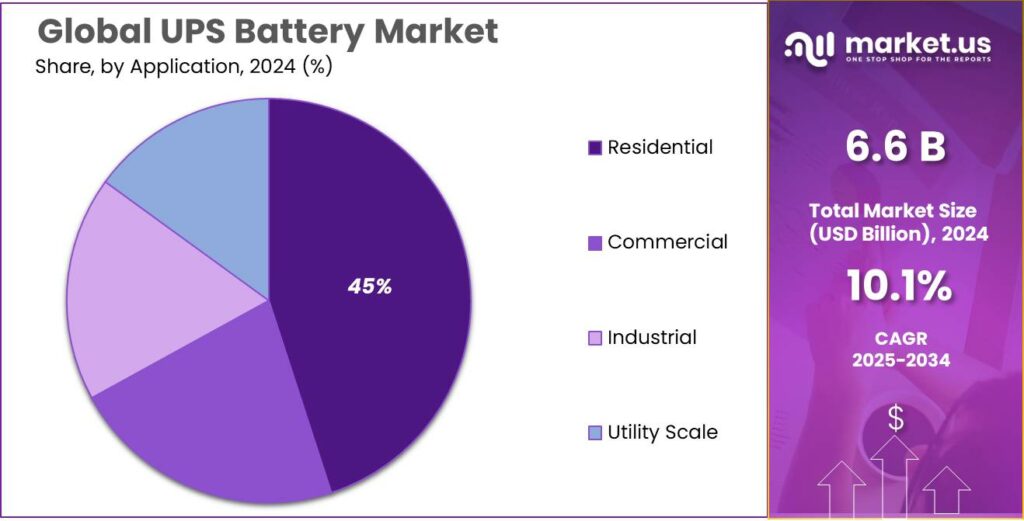
- Commercial held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.8% share.
- Asia Pacific region held a dominant position in the UPS battery market, accounting for 38.9% share, with market valuation reaching USD 2.5 billion.
By Battery Analysis
Lead Acid Batteries dominate UPS market with 67.9% share in 2024
In 2024, Lead Acid held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 67.9% share of the UPS battery market due to its established reliability and cost efficiency. These batteries have remained the preferred choice for many small to medium-sized enterprises, data centres, and industrial applications because of their long service life, proven safety record, and ease of maintenance. Over the year, the deployment of lead-acid batteries grew steadily as businesses sought dependable backup power solutions, particularly in regions with frequent grid instability or where capital investment for newer lithium-ion systems was constrained.
By Application Analysis
Commercial applications lead UPS battery market with 38.8% share in 2024
In 2024, Commercial held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.8% share of the UPS battery market as businesses increasingly prioritized uninterrupted power for their operations. This segment includes offices, retail establishments, hospitals, and small to medium-sized enterprises, where even brief power outages can disrupt services, cause financial losses, and impact customer satisfaction. The adoption of UPS batteries in commercial setups was driven by the growing reliance on digital systems, IT infrastructure, and sensitive equipment that require continuous power supply.
Key Market Segments
By Battery
- Lead Acid
- Li-ion
- Nickel Cadmium
- Others
By Application
- Residential
- Commercial
- Data Centers
- Industrial
Emerging Trends
Rising Demand from Food Cold-Chains Highlights a New Trend for UPS Batteries
A major recent trend shaping the demand for UPS batteries comes from rapid expansion of food cold-chain infrastructure worldwide — and growing awareness that reliable backup power is no longer optional for food safety and loss prevention. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) estimates that 14% of global food output — valued at about USD 400 billion annually — is lost between harvest and retail, largely due to inadequate storage, transport conditions and unreliable electricity supply.
As governments and private players invest in expanding cold-storage, processing facilities and refrigerated transport networks, there is a rising need for continuous, stable power. Indeed, a recent joint FAO/un-environment report highlights that lack of effective refrigeration is responsible for loss of approximately 526 million tonnes of food per year globally — nearly 12% of total food production.
This trend — of scaling up “sustainable cold-chains” — is increasingly backed by public-policy efforts. Many developing countries are now pushing to extend cold-chain networks to rural and peri-urban areas to reduce post-harvest losses and improve food security.
Beyond basic backup, this trend also encourages adoption of more advanced UPS battery technologies — such as lithium-ion and modular systems — which offer longer lifetimes, greater energy density and reduced maintenance. These features appeal especially where cold-chain uptime is critical to avoid spoilage and food loss.
Drivers
Expansion of Cold Chain Infrastructure and Food Safety Requirements Driving UPS Battery Demand
One major driving factor for UPS battery demand is the rapid expansion of cold chain and food processing infrastructure, where uninterrupted power is critical to avoid spoilage, safety risks, and economic losses. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), around 14% of global food produced is lost before reaching retail, with inadequate cold storage and unreliable power supply being key contributors in developing and emerging economies.
Electricity reliability is especially critical for temperature-controlled storage of meat, dairy, seafood, fruits, and vaccines. The International Institute of Refrigeration (IIR), working closely with FAO, estimates that more than 526 million tonnes of food depend on cold chains in developing regions, yet only about 40% of required refrigerated capacity is currently installed. This gap forces food processors and warehouses to rely heavily on UPS batteries to protect refrigeration systems during power fluctuations.
Government-led food security programs further strengthen this driver. In India, the Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MoFPI) approved cold chain infrastructure projects worth over INR 2,400 crore under PMKSY schemes to reduce post-harvest losses and stabilize farmer incomes. These facilities mandate backup power systems to qualify for subsidies, directly stimulating industrial UPS battery installations.
Food safety regulations also raise the stakes. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) highlights that cold storage failures during power outages significantly increase microbial growth risks, especially for ready-to-eat foods. Even a temperature deviation of 2–3°C for a few hours can make certain perishables unsafe, pushing operators toward zero-interruption power setups supported by UPS batteries.
Restraints
High Cost and Maintenance Complexity of UPS Batteries Limiting Adoption in Food Facilities
One major restraining factor for UPS battery adoption in the food industry is the high upfront cost and ongoing maintenance burden, especially for cold storage and food processing facilities operating on thin margins. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) notes that small and mid-sized food enterprises account for over 90% of food businesses globally, many of which struggle to invest in capital-intensive infrastructure like industrial UPS systems.
Cold chain operations are already energy intensive, and adding UPS batteries significantly raises capital expenditure. The International Institute of Refrigeration (IIR) reports that refrigeration and cold chain systems consume about 17% of global electricity usage. When UPS batteries are included to protect these systems, initial power redundancy costs can rise by 20–30%, making adoption harder for cost-sensitive operators.
Battery maintenance and replacement further complicate decision-making. Lead-acid batteries, still widely used in food warehouses, typically require replacement every 3–5 years, while lithium-ion alternatives offer longer life but at higher upfront cost. The World Bank highlights that limited technical skills and poor maintenance practices cause premature battery failures in food storage infrastructure across developing regions, increasing lifecycle costs rather than reducing them.
Despite government incentives for food security, affordability remains a real barrier. FAO data shows that food losses due to infrastructure gaps still cost the global economy about USD 400 billion annually, yet many operators cannot access financing for resilient power systems. Until battery costs decline further or targeted subsidies expand, high upfront and maintenance costs will continue to restrain wider UPS battery adoption in the food sector.
Opportunity
Sustainable Food Cold Chains Create a Strong Growth Runway for UPS Batteries
A powerful growth opportunity for UPS batteries lies in sustainable food cold chains. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) estimates that about 14% of the world’s food, worth roughly USD 400 billion each year, is lost between post-harvest and retail. Much of this loss is linked to weak storage, unreliable power, and temperature excursions—exactly the problems that robust UPS systems are built to prevent.
The lack of effective refrigeration alone leads to the loss of around 526 million tonnes of food annually, equivalent to roughly 12% of global food production, according to a joint FAO/UN Environment/IIR analysis. These figures immediately translate into a technical opportunity: every new cold store, pack-house, or refrigerated warehouse that aims to cut these losses needs stable backup power. UPS batteries can protect compressors, control systems, and monitoring equipment during voltage dips and outages, keeping the cold chain unbroken.
Governments are now framing cold-chain reliability as a food-security and climate issue, not just an infrastructure upgrade. FAO and UNFCCC point out that food loss and waste account for 8–10% of global greenhouse gas emissions, nearly five times aviation’s emissions. Policies that fund cold-chain efficiency and emission cuts—such as national food-loss reduction strategies and climate-aligned agricultural programs—implicitly create demand for long-life, energy-efficient UPS batteries that can integrate with renewables and smart controls.
FAO projects that feeding the world in 2050 will require about a 70% increase in food production compared with 2005/07 levels. Building this extra capacity without fixing power-reliability gaps would simply magnify losses. That is why many donor-backed cold-chain and agro-logistics programs now bundle investments in refrigeration, monitoring, and power backup together. For UPS battery suppliers, this creates a long-term pipeline of projects—from rural pack-houses to large export hubs—where reliable backup power is no longer optional but a basic design requirement.
Regional Insights
Asia Pacific dominates UPS battery market with 38.9% share valued at USD 2.5 billion in 2024
In 2024, the Asia Pacific region held a dominant position in the UPS battery market, accounting for 38.9% share, with market valuation reaching USD 2.5 billion. The strong presence of this region is driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and the expansion of data centres across countries such as China, India, Japan, and South Korea. Increasing adoption of digital infrastructure, telecommunication networks, and cloud computing services has significantly amplified the demand for reliable backup power systems in commercial, industrial, and IT sectors.
China, being the largest contributor within the region, witnessed significant investments in energy storage and UPS battery systems for both industrial and commercial applications. India followed closely, where growing electrification projects and government initiatives promoting energy resilience further fueled the market. Small and medium enterprises in Southeast Asia also adopted UPS batteries extensively to mitigate risks associated with frequent power interruptions, thereby strengthening regional demand.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Schneider Electric is recognised for integrated UPS systems and battery solutions tailored to data centres, IT rooms and commercial facilities. Products are offered under the APC and Schneider brands and include modular UPS, external battery packs and runtime extensions that support both lead-acid and lithium-ion chemistries. Services for monitoring, lifecycle management and retrofit are provided to improve uptime and reduce total cost of ownership. Emphasis is placed on scalable deployments and software-enabled management for distributed infrastructures.
Vertiv is presented as a specialist in critical power and thermal technologies, offering Liebert UPS platforms and high-density lithium-ion battery systems designed for colocation, hyperscale and enterprise data centres. The company’s offerings are complemented by UPS and battery services, including replacement, testing and maintenance programs aimed at maximising asset life and resilience. Solutions are optimised for modern data centre architectures and distributed edge deployments.
Emerson’s Liebert heritage underpins a wide array of UPS products and battery integration services that are targeted at industrial, healthcare and data centre customers. Emphasis is placed on engineered solutions that balance efficiency and reliability, with a portfolio covering online double-conversion UPS, DC-UPS variants and service contracts for preventive maintenance and rapid battery replacement to limit downtime. Product and service channels support global installations and retrofit projects.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Schneider Electric
- Eaton Corporation
- Vertiv Group Corp.
- Emerson Electric Co.
- Delta Electronics, Inc.
- Exide Industries Limited
- GS Yuasa International Ltd.
- East Penn Manufacturing Company
- EnerSys
- Vision Group
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024 Schneider Electric’s activity in the UPS battery sector was anchored by its APC brand and integrated UPS offerings, where product sales for energy management and data-centre solutions supported strong financials; Revenue (FY 2024): €38.2 billion, Q4 2024 revenue: €10,669 million, Adjusted EBITA margin (2024): 18.6%, Profit for 2024: €4,439 million.
In 2024 Emerson reported net sales of $17,492 million and adjusted earnings per share of $5.49, supported by strong cash generation with operating cash flow of $3,317 million; these financials enabled continued investment in service networks and critical-power offerings that include its uninterruptible power systems and battery integrations.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 6.6 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 17.3 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 10.1% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Battery (Lead Acid, Li-ion, Nickel Cadmium, Others), By Application (Residential, Commercial, Data Centers, Industrial) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Schneider Electric, Eaton Corporation, Vertiv Group Corp., Emerson Electric Co., Delta Electronics, Inc., Exide Industries Limited, GS Yuasa International Ltd., East Penn Manufacturing Company, EnerSys, Vision Group Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Schneider Electric
- Eaton Corporation
- Vertiv Group Corp.
- Emerson Electric Co.
- Delta Electronics, Inc.
- Exide Industries Limited
- GS Yuasa International Ltd.
- East Penn Manufacturing Company
- EnerSys
- Vision Group










