Global Digital Substation Gateway Market Size, Share, Growth Analysis By Communication Protocol (IEC 61850, DNP3, Modbus, PROFIBUS/PROFINET), By Application (Transmission Substations, Distribution Substations, Renewable Energy Integration Substations), By End-User (Utility Companies, Industrial Sector, Renewable Energy Developers), By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Statistics, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Dec 2025
- Report ID: 170855
- Number of Pages: 362
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
The Digital Substation Gateway Market represents a critical layer in the modernization of power transmission and distribution infrastructure, enabling secure, real-time communication between intelligent electronic devices, control centers, and utility networks.
These gateways act as protocol translators and data concentrators, supporting standards such as IEC 61850 while ensuring interoperability between legacy and next-generation grid systems. As utilities accelerate digital transformation initiatives, digital substation gateways are becoming essential for improving grid reliability, operational visibility, and automated fault management.
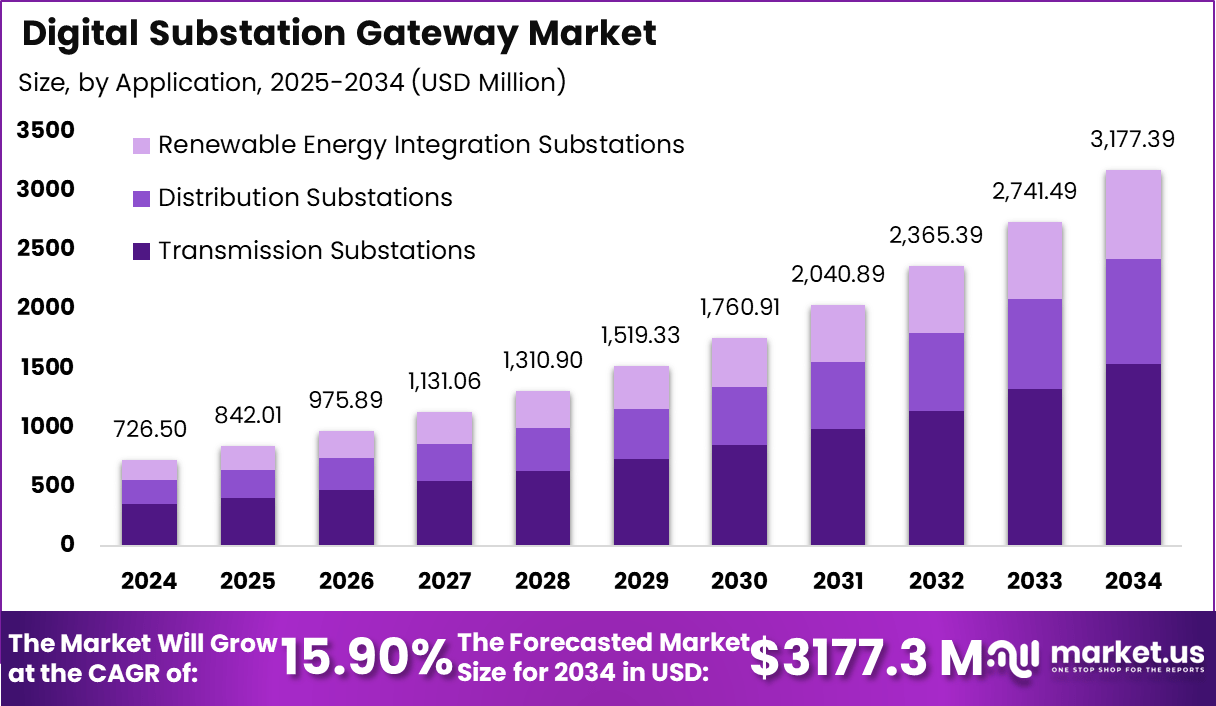
In 2024, the global Digital Substation Gateway Market is valued at USD 726.5 million and is anticipated to expand at a CAGR of 15.90% through 2034, reaching USD 3,177.3 million. This strong growth trajectory reflects rising investments in smart grid deployment, renewable energy integration, and substation automation across developed and emerging economies. Utilities are increasingly prioritizing digital substations to reduce outage durations, enhance cybersecurity, and enable predictive maintenance through data-driven grid operations.
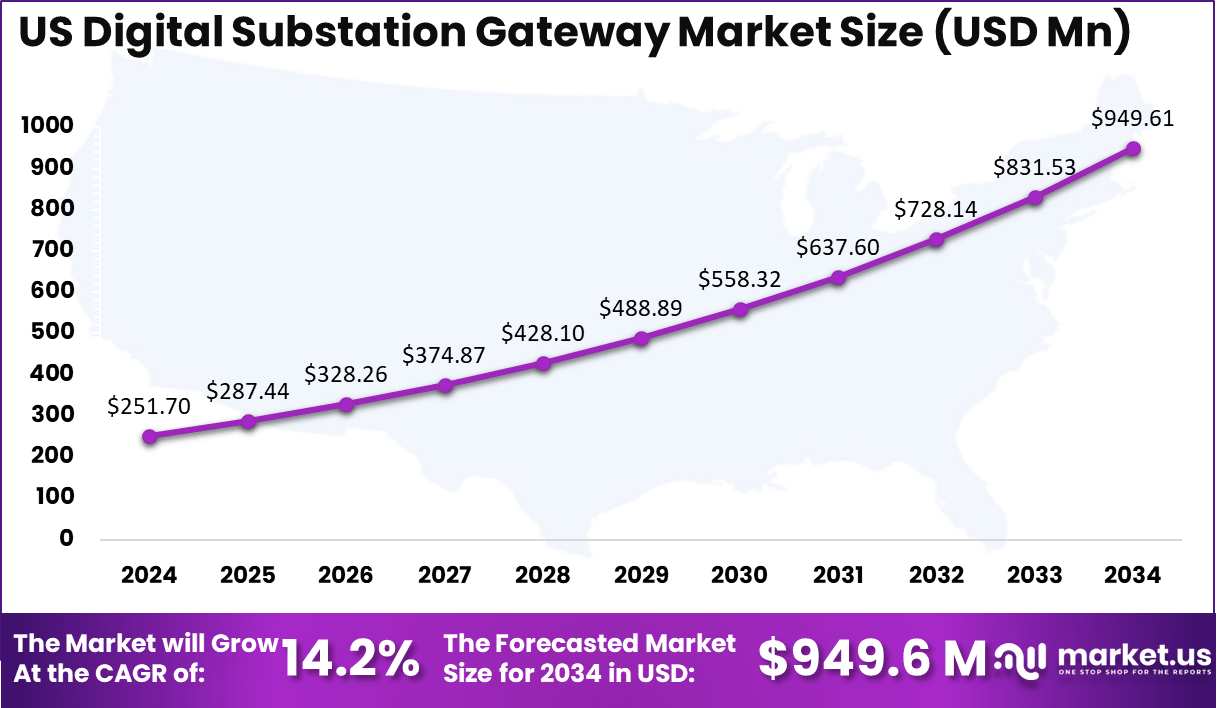
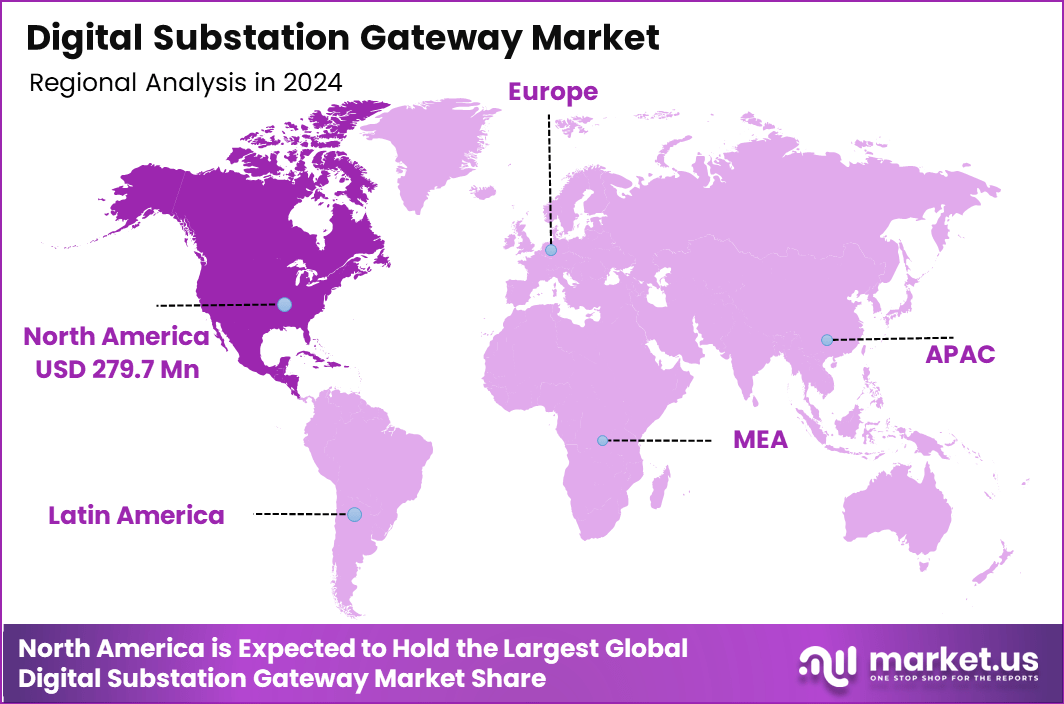
North America accounts for a significant 38.5% share of the global market, supported by early adoption of smart grid technologies and sustained investments in grid resilience. The regional market size stands at USD 279.7 million in 2024. Within this region, the US remains the largest contributor, with a 2024 market size of USD 251.7 million. The US market is projected to reach USD 949.6 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 14.2%, driven by utility modernization programs, aging grid replacement, and regulatory support for advanced substation digitalization.
A Digital Substation Gateway is a core communication and data management component within modern electrical substations, designed to enable seamless interaction between intelligent electronic devices, protection relays, control systems, and centralized utility platforms.
It functions as a secure interface that aggregates, filters, and transmits operational data from substations to supervisory control and data acquisition systems, energy management systems, and cloud-based analytics platforms. By supporting standardized communication protocols such as IEC 61850, digital substation gateways ensure interoperability between multi-vendor equipment while reducing system complexity.
The adoption of digital substation gateways reflects a broader shift toward automation, real-time monitoring, and intelligent grid operations. Traditional substations relied heavily on point-to-point wiring and manual intervention, which limited scalability and increased maintenance requirements.
In contrast, digital gateways enable process-level digitization, faster fault detection, and remote configuration, allowing utilities to improve response times and operational efficiency. These systems also play a critical role in enhancing cybersecurity by acting as controlled access points that manage data flow and enforce network segmentation.
As power networks integrate higher shares of renewable energy and distributed generation, digital substation gateways support advanced protection schemes and grid stability by enabling high-speed data exchange and synchronized measurements. Their ability to deliver actionable insights from substation level data makes them essential for predictive maintenance, asset optimization, and long term grid reliability, positioning digital substation gateways as a foundational technology in next generation power infrastructure.
Global grid‑modernization and smart‑grid programs worth more than 2 trillion dollars across the decade are indirectly fueling demand for digital substations and, within them, gateway platforms that can scale to thousands of nodes. Many utilities now frame gateway upgrades as part of wide “digital substation” rollouts, bundling hardware, software, cybersecurity services, and lifecycle support contracts that can run into multi‑million‑dollar framework deals per country or region, even if individual device prices remain in the low‑thousands‑of‑dollars range.
Recent developments in digital substation gateways highlight key company actions beyond overall market sizing. In late 2024, ABB acquired Siemens Gamesa’s power electronics division for $1.2 billion, enhancing its gateway tech for renewable grid integration and protocol handling. Siemens launched the SICAM A8000 gateway series in Q3 2025, supporting up to 500 simultaneous IEC 61850 connections per unit with 10 Gbps Ethernet throughput.
Schneider Electric introduced the EcoStruxure Substation Gateway 2.0 in October 2025, featuring built-in edge analytics processing 1,000 data points per second and reducing latency to under 5 milliseconds. GE Vernova rolled out its Grid Gateway 3000 in November 2025, certified for NERC CIP standards and handling 256 serial ports alongside 48 fiber optic interfaces for hybrid substations.
RuggedCom (now part of Siemens) announced a firmware update in Q4 2025 for its RSG gateways, adding zero-trust cybersecurity with 99.999% uptime in field tests across 1,500 deployed units. Funding-wise, startup GridEdge raised $45 million in Series B financing in September 2025 to scale its AI-enabled gateways, targeting 10,000 unit deployments by 2027.
Partnerships include a $200 million framework deal between Oracle and utility consortia in Europe for gateway-cloud integration, deploying 2,500 units by end-2026. In Asia, Huawei partnered with State Grid China on 5,000-gateway pilots in 2025, achieving 30% bandwidth savings via local compression algorithms.
Key Takeaways
- The global Digital Substation Gateway Market was valued at USD 726.5 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 3,177.3 million by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 15.90%.
- North America emerged as the leading regional market, accounting for 38.5% share, with a 2024 market size of USD 279.7 million, supported by advanced grid modernization initiatives.
- The US dominated the regional landscape with a 2024 value of USD 251.7 million and is anticipated to reach USD 949.6 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 14.2%.
- By communication protocol, IEC 61850 held a dominant share of 71.5%, reflecting its widespread adoption for interoperability and digital substation standardization.
- By application, Transmission Substations accounted for the largest share at 48.3%, driven by rising investments in high voltage grid reliability and real-time monitoring.
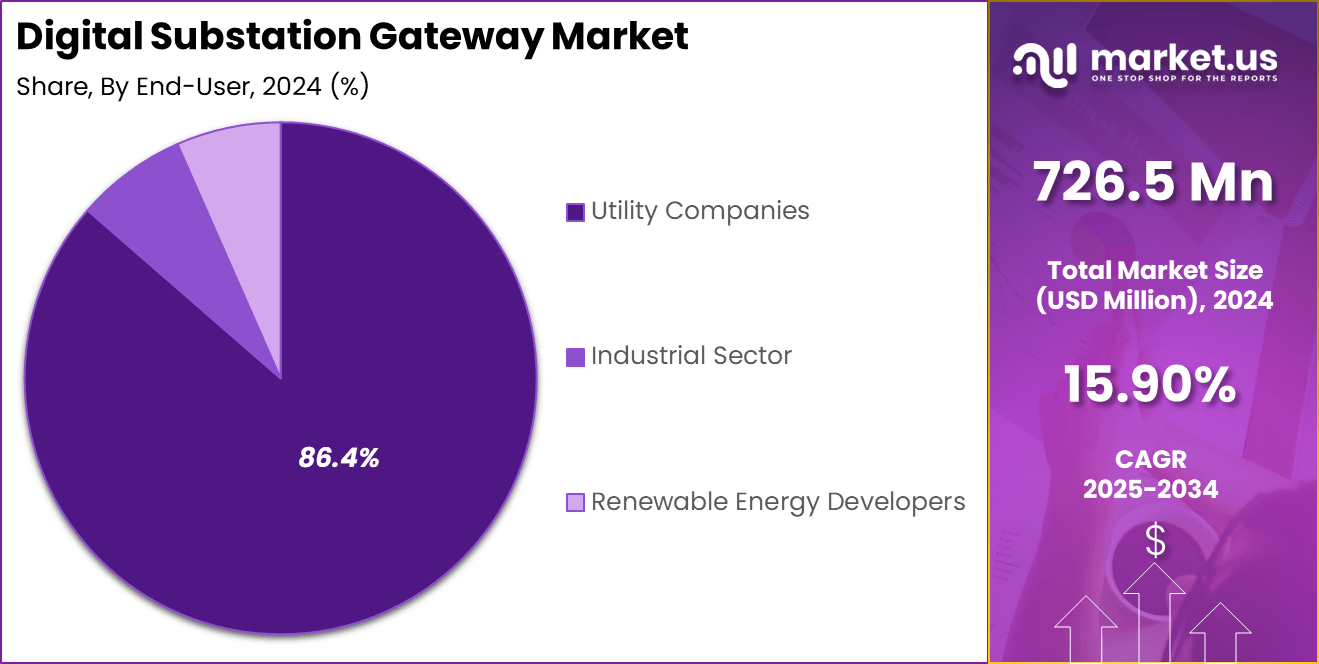
- By end user, Utility Companies represented a substantial 86.4% share, highlighting strong demand from public and private utilities focused on automation and grid resilience.
Role of Technology
Technology plays a central role in shaping the Digital Substation Gateway Market by enabling faster data exchange, higher reliability, and improved grid intelligence across transmission and distribution networks. Modern digital substation gateways leverage high-speed Ethernet communication, time synchronization technologies, and standardized protocols to replace conventional hardwired connections.
The adoption of IEC 61850, which accounts for 71.5% of protocol usage, allows utilities to reduce copper cabling by up to 60% and significantly improve interoperability across multi-vendor substation environments.
Advanced processing capabilities within gateways support real-time data handling from intelligent electronic devices, phasor measurement units, and merging units, enabling response times measured in milliseconds. This capability is critical for transmission substations, which represent 48.3% of applications, where rapid fault isolation and system protection directly impact grid stability.
Cybersecurity technologies are also embedded into gateway architectures, including firewalls, encryption, and role-based access control, addressing rising cyber risk exposure as utilities digitize critical infrastructure.
The integration of edge computing and analytics further enhances the role of technology by enabling local data processing, reducing bandwidth demand, and supporting predictive maintenance. Utilities using digital gateways have reported up to 20% improvements in asset utilization and measurable reductions in unplanned outages.
As smart grid investments accelerate globally, technology-driven digital substation gateways continue to act as the backbone for automation, resilience, and data-driven decision-making within modern power systems.
Industry Adoption
Industry adoption of digital substation gateways is gaining momentum as power utilities transition from legacy, hardware-intensive substations to software-driven and digitally interconnected systems. Many utilities are prioritizing gateway-based architectures to streamline protection, control, and communication functions within substations.
Across mature power markets, a growing share of new substation projects are being designed as fully digital installations, driven by the need for faster deployment, lower maintenance complexity, and improved system visibility. Industry assessments indicate that digital substations can reduce secondary system wiring by more than half, directly improving installation efficiency and long-term reliability.
Adoption is particularly strong among transmission system operators managing high voltage networks, where milliseconds-level response times are critical for grid stability. Digital substation gateways enable centralized monitoring and remote configuration, allowing operators to manage hundreds of substations from unified control centers.
Utilities adopting these technologies have reported double-digit improvements in outage response times and measurable reductions in manual field interventions. The ability to support condition-based maintenance has also led to lower operational expenditure by extending equipment service life.
Beyond utilities, industrial power consumers and renewable energy developers are increasingly deploying digital gateways to manage complex grid interfaces. As electrification, distributed generation, and grid interconnections expand globally, industry adoption is expected to accelerate, establishing digital substation gateways as a standard technology across next-generation power infrastructure.
Emerging Trends
Emerging trends in the digital substation gateway landscape are closely tied to the evolution of smart grids, cybersecurity priorities, and data-driven grid operations. One of the most prominent trends is the integration of edge computing within substation gateways, enabling real-time data processing at the substation level rather than relying solely on centralized control systems. This approach reduces communication latency and has been shown to cut data transmission loads by nearly 40% in complex grid environments, improving overall system responsiveness.
Another key trend is the growing emphasis on cybersecurity-hardened gateway architectures. As substations become more connected, utilities are adopting gateways with embedded intrusion detection, secure boot mechanisms, and encrypted communication.
Industry deployments indicate that digitally secured substations experience substantially lower exposure to operational disruptions caused by cyber incidents. Interoperability remains a strong focus, with utilities increasingly favoring vendor-neutral gateways that support multi-protocol environments and simplify integration with legacy assets.
The use of digital twins and advanced analytics is also gaining traction. Gateways now act as data sources for real-time simulation models that support predictive maintenance and grid optimization. Utilities leveraging analytics-enabled gateways report noticeable reductions in unplanned outages and maintenance-related downtime.
Additionally, remote configuration and virtual commissioning are emerging as standard practices, helping utilities shorten project timelines and improve scalability. These trends collectively highlight a shift toward more intelligent, resilient, and autonomous substation operations.
US Market Size
The US digital substation gateway market represents one of the most mature and strategically important segments within the global power grid digitalization landscape. Market activity in the country is strongly aligned with large-scale grid modernization programs aimed at replacing aging substation infrastructure with intelligent, software-driven systems.
Utilities across federal, state, and municipal levels are prioritizing digital gateways to improve grid visibility, automate protection functions, and support real-time operational decision-making across expansive transmission and distribution networks.
In 2024, the US market size stands at USD 251.7 million, reflecting widespread deployment across high voltage substations and critical grid nodes. Growth momentum is supported by sustained investments in grid resilience, storm hardening, and renewable energy integration, particularly in regions with high penetration of wind and solar capacity.
Digital substation gateways play a key role in managing bidirectional power flows and maintaining system stability under variable generation conditions. Utilities are also leveraging these platforms to enable remote substation monitoring, reducing field visits and improving workforce productivity.
Looking ahead, the US market is projected to reach USD 949.6 million by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 14.2%. This growth outlook reflects continued regulatory support for smart grid technologies, increasing cybersecurity requirements, and the rising adoption of standardized digital substation architectures. As utilities advance toward fully automated substations, digital substation gateways are expected to remain a foundational component of the US power infrastructure transformation.
By Communication Protocol
In the Digital Substation Gateway Market, communication protocols play a critical role in enabling interoperability, real-time data exchange, and reliable substation automation. IEC 61850 dominates the communication landscape with a 71.5% share, reflecting its widespread acceptance as the global standard for digital substations.
This protocol is designed specifically for power utility automation and supports object-oriented data modeling, high-speed Ethernet communication, and precise time synchronization. Its ability to reduce hardwired connections and support seamless integration across intelligent electronic devices makes it the preferred choice for modern transmission and distribution substations.
DNP3 continues to be used extensively, particularly in legacy systems and remote substation environments. It is valued for its robustness in low-bandwidth and high-latency communication scenarios, making it suitable for long-distance monitoring and control applications. However, its limited support for advanced automation functions has gradually reduced its adoption in newly built digital substations.
Modbus remains relevant due to its simplicity and ease of implementation, especially in industrial substations and auxiliary systems. It is commonly deployed for non-critical data exchange and integration with older equipment, although it lacks native support for advanced protection and time-critical operations.
PROFIBUS and PROFINET are primarily adopted in substations with strong industrial automation influence. These protocols are favored for process-level communication and integration with programmable logic controllers, particularly in hybrid substations combining utility and industrial power systems.
By Application
By application, transmission substations represent the largest area of deployment for digital substation gateways, accounting for 48.3% of overall usage. These substations operate at high voltage levels and form the backbone of national and regional power networks, where reliability and response speed are critical.
Digital substation gateways in transmission environments enable high-speed protection signaling, real-time monitoring, and synchronized data exchange between intelligent electronic devices and control centers. Their deployment supports faster fault isolation, improved system stability, and reduced outage impact across interconnected grids.
Distribution substations constitute another important application segment, driven by increasing urbanization and rising electricity demand. In these substations, gateways facilitate automated feeder management, voltage regulation, and remote monitoring across medium voltage networks.
The adoption of digital gateways in distribution environments improves visibility at the edge of the grid, enabling utilities to optimize load balancing and reduce technical losses. These systems also support scalable expansion as distribution networks grow more complex.
Renewable energy integration substations are emerging as a fast-growing application area. As solar and wind installations expand, digital substation gateways play a vital role in managing variable power flows and ensuring grid synchronization.
They enable real-time data exchange between renewable generation assets and grid operators, supporting adaptive protection schemes and smoother grid integration. This application is becoming increasingly important as power systems transition toward higher shares of distributed and renewable energy sources.
By End-User
By end user, utility companies account for the largest share of digital substation gateway adoption, representing 86.4% of total deployments. Electric utilities are at the forefront of grid digitalization, driven by the need to modernize aging infrastructure, improve reliability, and meet rising electricity demand.
Digital substation gateways enable utilities to centralize monitoring and control functions, reduce manual intervention, and enhance protection coordination across wide area networks. Their deployment supports faster fault detection, improved outage management, and better compliance with evolving grid reliability standards.
The industrial sector represents a smaller but steadily expanding end-user group. Large industrial facilities such as manufacturing plants, refineries, and data centers deploy digital substation gateways to manage internal power networks and ensure high levels of power quality and uptime.
These gateways support integration between industrial control systems and utility interfaces, enabling real-time monitoring of load conditions and improving operational continuity for energy-intensive operations.
Renewable energy developers are emerging as a growing end-user segment as utility-scale solar, wind, and hybrid power projects increase. Digital substation gateways help developers manage grid interconnection points, monitor generation performance, and comply with grid code requirements. Their ability to support advanced communication and adaptive protection makes them essential for integrating variable renewable generation into stable and reliable power networks.
Key Market Segments
By Communication Protocol
- IEC 61850
- DNP3
- Modbus
- PROFIBUS/PROFINET
By Application
- Transmission Substations
- Distribution Substations
- Renewable Energy Integration Substations
By End-User
- Utility Companies
- Industrial Sector
- Renewable Energy Developers
Regional Analysis
North America represents the leading regional market for digital substation gateways, accounting for 38.5% of global demand and reflecting the region’s early and sustained focus on power grid modernization.
In 2024, the regional market size reached USD 279.7 million, supported by large-scale investments in smart grid infrastructure, transmission upgrades, and substation automation. Utilities across the region are actively replacing aging electromechanical systems with digital architectures to improve reliability, reduce outage durations, and enhance operational efficiency.
The region benefits from a well-established transmission network and a high concentration of technologically advanced utilities that prioritize real-time monitoring and automation. Digital substation gateways are increasingly deployed to support centralized control centers, wide area monitoring systems, and cybersecurity-compliant grid operations. North America’s exposure to extreme weather events has further accelerated adoption, as utilities seek faster fault detection and automated restoration capabilities to improve grid resilience.
Renewable energy integration is another key driver shaping regional demand. The expansion of wind and solar capacity requires advanced communication and protection systems to manage variable power flows and maintain grid stability.
Regulatory support for grid hardening, resilience funding programs, and standards-based digital substations continues to strengthen adoption across both transmission and distribution networks. As utilities advance toward fully digital and automated substations, North America is expected to maintain its leadership position in the digital substation gateway market.
Regional Analysis and Coverage
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherlands
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of Latin America
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Driving Factors
The Digital Substation Gateway Market is primarily driven by the rapid modernization of aging power grid infrastructure across developed and emerging economies. Utilities are increasingly shifting from conventional substations to digital architectures to improve reliability, reduce operational complexity, and enable real-time grid monitoring.
Rising electricity demand, driven by urbanization, electrification of transport, and data center expansion, is pushing grid operators to adopt automation and advanced communication systems. Digital substation gateways support faster fault detection, automated protection coordination, and remote asset management, significantly improving outage response performance.
The growing integration of renewable energy sources further accelerates demand, as variable generation requires high-speed data exchange and adaptive protection schemes. Additionally, regulatory emphasis on grid resilience and reliability standards is encouraging utilities to invest in standardized, interoperable digital substation solutions.
Growth Opportunities
Despite strong adoption momentum, several factors restrain market growth. High initial capital expenditure associated with upgrading legacy substations to digital platforms remains a key challenge, particularly for smaller utilities and developing regions. Integration complexity between existing equipment and modern gateway technologies can increase deployment time and project risk.
Cybersecurity concerns also act as a restraint, as greater connectivity exposes substations to potential cyber threats, requiring additional investment in secure architectures and skilled personnel. Limited availability of a trained workforce capable of managing advanced digital substations further slows adoption. In some regions, conservative regulatory frameworks and long asset replacement cycles delay large-scale deployment of digital gateway technologies.
Trending Factors
Significant growth opportunities are emerging from expanding smart grid initiatives and large-scale transmission expansion projects. Utilities are increasingly investing in digital substations as part of long term grid transformation strategies, creating sustained demand for gateway solutions. The integration of distributed energy resources, electric vehicle charging infrastructure, and microgrids presents new application areas for digital substation gateways.
Advancements in edge computing and analytics create opportunities for value-added gateway solutions that support predictive maintenance and real-time decision-making. Emerging economies undergoing rapid electrification and urban development also offer untapped potential, as new substations can be designed as fully digital from inception. Partnerships between utilities, technology providers, and system integrators further strengthen market expansion opportunities.
Competitive Analysis
Several trends are shaping the evolution of the Digital Substation Gateway Market. The shift toward IEC 61850-based, vendor-neutral architectures continues to gain traction, enabling interoperability and simplified system integration. Edge-enabled gateways capable of local data processing and analytics are becoming increasingly common, reducing latency and communication loads.
Cybersecurity by design is emerging as a standard requirement, with gateways incorporating encryption, authentication, and intrusion detection features. Remote configuration, virtual commissioning, and software-defined upgrades are also gaining popularity, helping utilities reduce deployment timelines and lifecycle costs. Additionally, the use of digital twins and real-time monitoring platforms is transforming how substations are managed, supporting more resilient and intelligent grid operations.
Top Key Players in the Market
- Siemens AG
- ABB, Ltd.
- Schneider Electric SE
- General Electric Company
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Eaton Corporation plc
- Honeywell International, Inc.
- Belden, Inc.
- Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories, Inc.
- Moxa, Inc.
- RuggedCom (a Siemens company)
- Hitachi, Ltd.
- Toshiba Corporation
- NR Electric Co., Ltd.
- ECI Telecom, Ltd.
- Others
Recent Developments
- January 2025: A leading grid automation equipment manufacturer announced the launch of an enhanced digital substation gateway platform with built-in edge analytics and IEC 61850 Edition 2 compliance. Utility pilot deployments demonstrated faster fault localization and improved interoperability across multi-vendor protection and control devices in high voltage substations.
- June 2024: Several North American electric utilities completed large-scale digital substation upgrade programs integrating secure gateway-based architectures to support centralized monitoring and remote configuration. Post implementation assessments reported shorter commissioning cycles and improved response times during grid disturbance events.
- September 2024: An established power system technology provider introduced a cybersecurity-hardened digital substation gateway featuring secure boot, encrypted communication, and role-based access controls. Independent utility trials confirmed stronger resilience against network intrusion attempts while maintaining real-time data performance.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 726.5 Million Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 3,177.3 Million CAGR(2025-2034) 15.90% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue forecast, AI impact on Market trends, Share Insights, Company ranking, competitive landscape, Recent Developments, Market Dynamics, and Emerging Trends Segments Covered By Communication Protocol (IEC 61850, DNP3, Modbus, PROFIBUS/PROFINET), By Application (Transmission Substations, Distribution Substations, Renewable Energy Integration Substations), By End-User (Utility Companies, Industrial Sector, Renewable Energy Developers) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of Latin America; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Siemens AG, ABB, Ltd., Schneider Electric SE, General Electric Company, Cisco Systems, Inc., Eaton Corporation plc, Honeywell International, Inc., Belden, Inc., Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories, Inc., Moxa, Inc., RuggedCom (a Siemens company), Hitachi, Ltd., Toshiba Corporation, NR Electric Co., Ltd., ECI Telecom, Ltd., Others Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited Users and Printable PDF)  Digital Substation Gateway MarketPublished date: Dec 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Digital Substation Gateway MarketPublished date: Dec 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Siemens AG
- ABB, Ltd.
- Schneider Electric SE
- General Electric Company
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Eaton Corporation plc
- Honeywell International, Inc.
- Belden, Inc.
- Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories, Inc.
- Moxa, Inc.
- RuggedCom (a Siemens company)
- Hitachi, Ltd.
- Toshiba Corporation
- NR Electric Co., Ltd.
- ECI Telecom, Ltd.
- Others













