China Autonomous Crane Market Size, Share, Industry Analysis Report By Crane Type (Tower Cranes, Mobile Cranes, Overhead Cranes), By End-Use Industry (Construction, Energy, Manufacturing, Logistics & Warehousing, Others), By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Nov 2025
- Report ID: 166033
- Number of Pages: 348
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
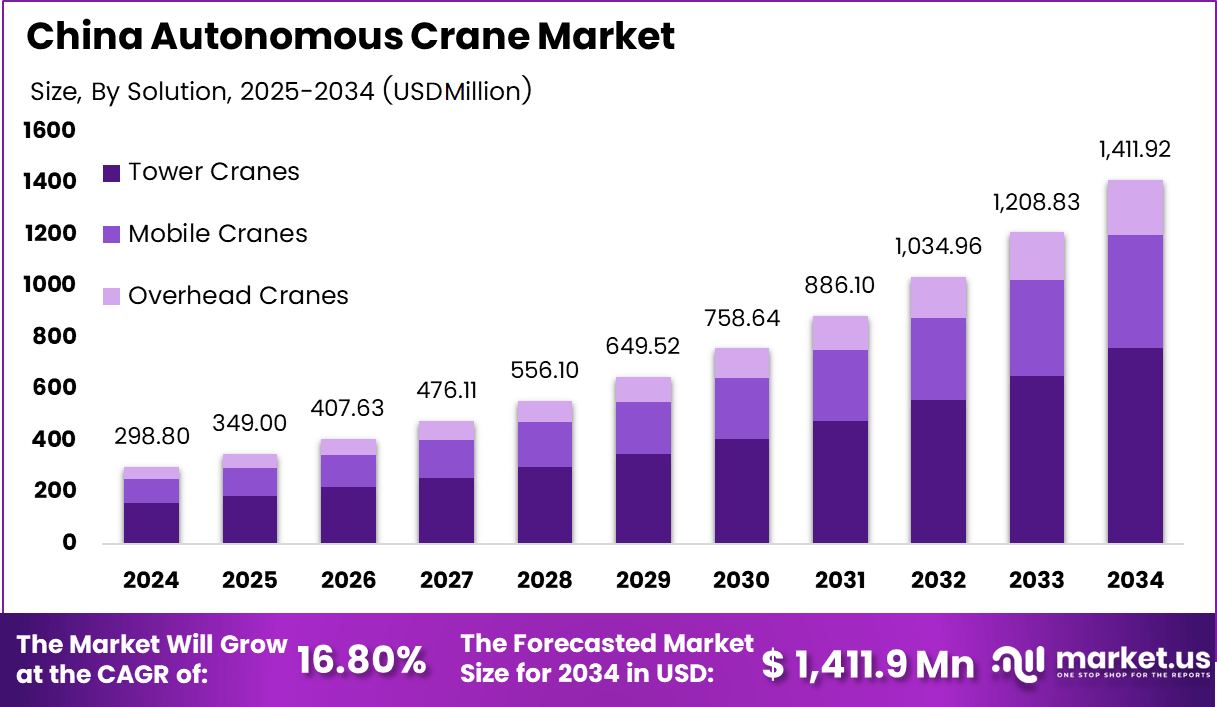
China’s autonomous crane market size stands at USD 298.8 million in 2024 and is expected to grow steadily at a CAGR of 16.8% through 2034, reaching USD 1,411.9 million by the end of the forecast by 2034.
China’s autonomous crane market is entering a strong growth phase, supported by rapid construction activity, manufacturing automation, and expanding warehousing needs across the country. Tower cranes remain the dominant solution due to their extensive use in high-rise construction and large infrastructure projects, while mobile and overhead cranes continue to gain traction with the shift toward flexible, automated material-handling systems.
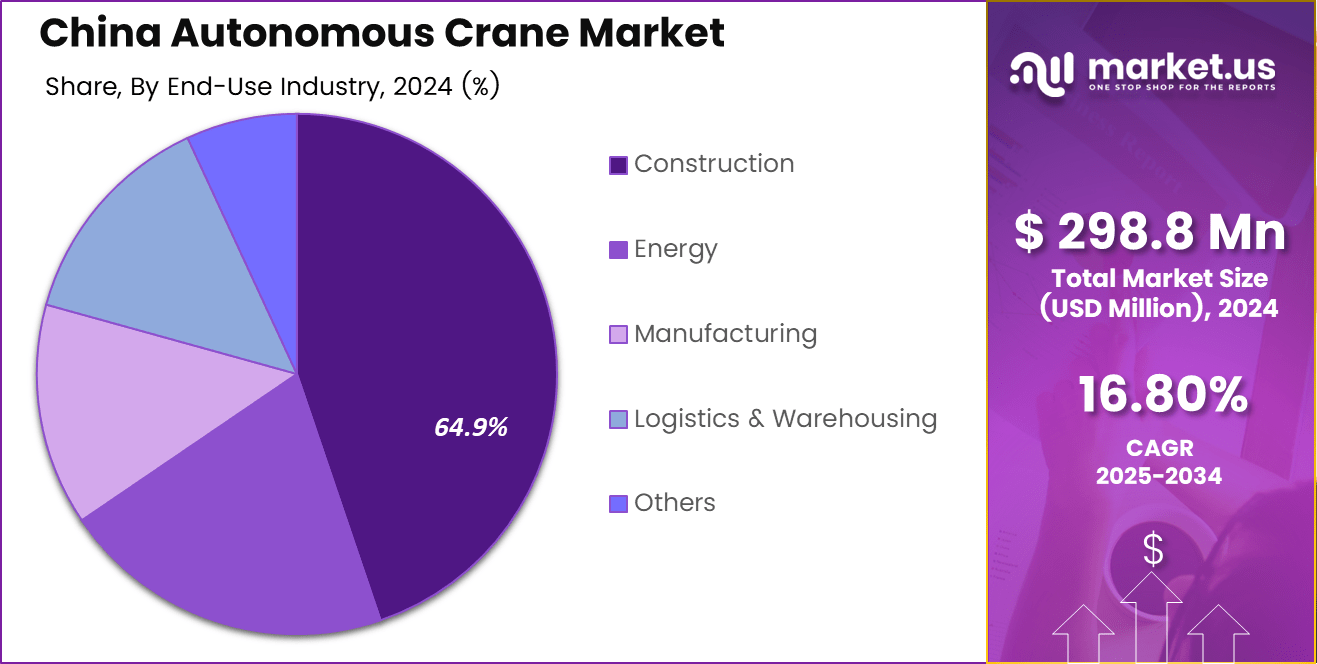
The end-use landscape is strongly led by the construction sector, holding 64.9% of the market share in 2024, reflecting China’s continued investment in smart construction and urban development. Manufacturing, logistics, warehousing, and energy sectors also contribute significantly as industries adopt autonomous lifting systems to reduce labor dependence, improve safety, and enhance operational efficiency. The combined rise of digitalization, AI-based crane navigation, and China’s push for intelligent industrial equipment further strengthens the market outlook over the next decade.
Key Takeaways
- The Chinese autonomous crane market is growing from USD 298.8 million in 2024 to USD 1,411.9 million by 2034, driven by rapid automation across construction and industrial sectors.
- Tower cranes dominate the market with a 53.8% share in 2024, supported by China’s extensive high-rise construction and infrastructure development.
- Construction leads all end-use industries with a 64.9% share, reflecting heavy investment in smart construction technologies and large-scale urban development projects.
- Manufacturing and logistics & warehousing account for a growing share as factories and distribution centers shift toward automated material-handling systems.
Analysts Viewpoint
The Chinese autonomous crane market is entering a transformative growth phase as the country accelerates digital construction, industrial automation, and smart logistics infrastructure. Analysts observe that the dominance of tower cranes, holding 53.8% share, reflects China’s sustained investment in high-rise and mega-infrastructure projects, where automation enhances safety and operational precision. The construction sector’s leading 64.9% share further reinforces this trend, driven by strong government-backed urban development and smart city initiatives.
Demand is also expanding in manufacturing and logistics, where autonomous cranes reduce labor dependency and improve throughput in large industrial and warehousing facilities. Mobile and overhead cranes are gaining traction as factories upgrade to intelligent, sensor-based lifting systems aligned with Industry 4.0 adoption. Over the next decade, the market is expected to benefit from advances in AI-guided navigation, real-time monitoring, and autonomous fleet coordination, positioning China as a hub for next-generation crane technologies.
Emerging Trends
China is witnessing a rapid shift toward smart and automated lifting systems as industries adopt digital construction practices and intelligent manufacturing. One major trend is the integration of AI, computer vision, and LiDAR-based sensing into autonomous cranes to enhance precision, safety, and real-time decision-making.
Construction companies are gradually shifting to fully automated tower cranes that can operate with minimal human intervention, reducing accident risks on high-rise sites. Another notable trend is the rise of autonomous mobile cranes in logistics hubs and manufacturing plants, driven by the growth of e-commerce and large-scale warehouse automation.
Remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and IoT-enabled crane management platforms are also emerging as operators prioritize efficiency and equipment lifecycle optimization. China’s strong push for smart factories and digital infrastructure accelerates the adoption of these technologies across multiple sectors.
Growth Factors
Growth in China’s autonomous crane market is strongly supported by large-scale infrastructure expansion and continuous investment in urban development projects. The predominance of tower cranes, along with high demand from the construction segment, reflects the increasing dependency on automated material-handling equipment to improve site productivity.
Rising labor shortages and stricter safety regulations encourage companies to shift toward autonomous systems that reduce manual operations and enhance accuracy. In manufacturing and warehousing, the rise of automation, fueled by Industry 4.0 initiatives, accelerates the deployment of autonomous cranes to manage high-volume, repetitive lifting tasks. Additionally, advancements in AI, robotics, and sensor technologies improve performance reliability, making autonomous cranes a cost-efficient long-term solution.
By Crane Type
Tower cranes hold the leading position with a 53.8% share, reflecting their extensive use in China’s high-rise construction and mega infrastructure projects, where automation improves precision and site safety. Mobile cranes rank next as industries adopt flexible autonomous lifting systems for ports, logistics hubs, and industrial sites that require mobility and rapid deployment. Overhead cranes form the third segment, gaining traction in manufacturing plants and warehousing facilities where automated material handling, repetitive lifting tasks, and seamless integration with smart factory systems are increasingly essential.
By End-Use Industry
Construction dominates the Chinese autonomous crane market with a 64.9% share, driven by continuous high-rise development, large infrastructure projects, and China’s adoption of smart construction practices that rely on automated lifting for accuracy, safety, and faster project execution. Manufacturing stands as the next major segment, supported by extensive factory automation and Industry 4.0 upgrades that require autonomous overhead and mobile cranes for precise, repetitive material handling.
Logistics and warehousing follow closely, benefiting from China’s rapidly expanding e-commerce ecosystem, where automated cranes improve throughput and reduce labor dependency in large distribution hubs. The energy sector accounts for a steady share as power plants, renewable energy sites, and utility projects integrate autonomous cranes for heavy component installation and maintenance tasks.
The other category represents emerging applications across industrial parks, mining sites, and large public infrastructure facilities, gradually transitioning toward intelligent material-handling equipment.
Key Market Segments
By Crane Type
- Tower Cranes
- Mobile Cranes
- Overhead Cranes
By End-Use Industry
- Construction
- Energy
- Manufacturing
- Logistics & Warehousing
- Others
Driver Analysis
Construction & Industrial Automation Growth
China’s autonomous crane market grows strongly because construction companies and factories now prefer automated lifting for better safety and faster work. Large infrastructure projects, high-rise buildings, and modern industrial parks rely on cranes that operate with higher accuracy and fewer human errors. For instance, automated tower cranes help reduce site accidents and improve coordination in crowded construction zones.
Industries also move toward automation to overcome labor shortages and rising wage costs. Autonomous cranes support continuous operations, making them useful in busy manufacturing units and logistics centers. As China expands smart factories and digital construction, the demand for automated crane solutions continues to rise.
Restraint Analysis
High Cost & Complex Technology
One major restraint is the high upfront cost of autonomous cranes, which are more expensive than traditional models. Smaller construction firms and mid-sized manufacturers find it difficult to invest in these systems, especially when budgets are tight. The need for advanced sensors, software, and trained teams adds to the total installation and operating cost.
Technical complexity is another limitation because autonomous cranes require skilled operators who understand digital interfaces and smart control systems. Many regions still lack trained technicians, making adoption slower. These cost and skill barriers together delay mass deployment across China.
Opportunity Analysis
Upgrading Existing Crane Fleets
A strong opportunity lies in the retrofitting of older cranes with autonomous modules. Many construction and industrial companies prefer upgrading their existing equipment rather than buying entirely new cranes. For instance, converting a traditional crane with automation kits offers improved safety and efficiency at a lower cost.
This upgrade pathway helps companies modernize without interrupting operations. As more businesses see successful results from retrofitted cranes, demand is likely to grow. This creates a large long-term opportunity because China has one of the world’s biggest existing crane fleets.
Challenge Analysis
Skilled Workforce & Regulatory Uncertainty
The biggest challenge is the shortage of skilled technicians who can operate and maintain autonomous cranes. These systems use advanced software, sensors, and AI features that require specialized training. Companies struggle to find staff who can handle troubleshooting, programming, or predictive maintenance tasks.
Regulatory clarity is also a challenge. Different regions follow different safety standards, and rules for autonomous equipment are still evolving. For instance, questions about certification, liability, and autonomous operation guidelines often slow down approvals. This mix of skill gaps and regulatory uncertainty remains a major obstacle for consistent market growth.
Top 5 Use Cases
- Port container handling: Used in major Chinese ports for automated container loading, stacking, and unloading to improve turnaround time and reduce labor reliance.
- Smart manufacturing facilities: Deployed for precise material transfer and assembly-line logistics in advanced factories to enhance productivity and reduce manual errors.
- High-rise construction: Autonomous tower cranes support stable heavy lifting, automated load-path planning, and safer operations during vertical construction projects.
- Mining and bulk material handling: Utilized for ore loading, waste removal, and bulk transfers in harsh mining environments, reducing worker exposure to risks.
- Warehouse and logistics automation: Employed in large distribution centers for pallet movement, racking, and inventory flow optimization through AI-driven routing and continuous operations.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
- Strong demand driven by China’s large construction and infrastructure pipeline, especially high-rise and mega-project developments.
- Advanced autonomous features such as AI navigation, sensors, and remote monitoring improve safety, accuracy, and site productivity.
- Rapid digitalisation in manufacturing and logistics supports wider use of autonomous cranes for automated material handling.
- An established domestic manufacturing ecosystem enables competitive pricing and widespread availability of crane equipment.
Weaknesses
- High upfront investment for autonomous cranes limits adoption among smaller contractors and mid-tier industrial users.
- Need for specialised software, calibration, and technical expertise increases operational complexity.
- Limited availability of skilled technicians in many regions slows maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Slower adoption outside major industrial and metropolitan zones due to uneven technological readiness.
Opportunities
- Growing demand for retrofit autonomy kits that upgrade legacy crane fleets at lower cost than full replacement.
- Expansion of smart factories and automated warehouses creates new use-cases for autonomous mobile and overhead cranes.
- Increasing integration with digital platforms such as BIM systems, digital twins, and predictive maintenance tools.
- Potential to expand into overseas infrastructure and industrial projects aligned with China’s construction initiatives.
Threats
- Skills shortage and inconsistent training across regions create operational risks for autonomous crane deployment.
- Regulatory uncertainties around autonomous equipment certification and safety compliance may delay approvals.
- Rising competition from domestic and international technology suppliers may pressure margins.
- Dependence on advanced electronics and sensors exposes manufacturers to supply chain disruptions.
Key Players Analysis
The China autonomous crane market is shaped by a mix of strong domestic manufacturers and selective players, each driving technology adoption in different ways. Zoomlion holds a leading position with its expanding crane portfolio and smart-factory initiatives that support automated lifting systems. The company’s focus on digital controls and high-capacity cranes places it in a strong spot as construction projects demand safer and more precise operations.
XCMG also plays a major role through its large manufacturing base, wide crane range and strong customer network, giving it the scale needed to integrate autonomy across multiple crane categories. Sany contributes through its diverse construction machinery lineup and ongoing investment in intelligent equipment platforms. Among international players, Liebherr maintains a solid reputation in China by supplying advanced systems, high-reliability components and automation-ready cranes. Together, these companies push the market toward safer, more efficient and technology-driven crane operations across construction, manufacturing and logistics.
Top Key Players in the Market
- ZPMC
- XCMG
- Zoomlion Heavy Industry
- Sany Heavy Industry
- Inovance Technology
- Liebherr (China)
- Manitowoc Cranes China
- Konecranes China
- Terex China
- Tadano China
Recent Developments
- November 2024: Manitowoc Company, Inc. announced the launch of the new Potain MCT 2205 top-slewing tower crane — part of its Asia range — increase in capacity and addressing larger scale construction requirements at the bauma China 2024 exhibition.
- April 2025: At bauma 2025 in Munich, Zoomlion showcased over 20 featured products including cranes with 5G remote control, AI-based monitoring, modular localisation for Europe, and announced further expansion of its German factory phase II — reinforcing its intelligent, green crane strategy.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 298.8 Million Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 2.35 Million CAGR(2025-2034) 16.80% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue forecast, AI impact on Market trends, Share Insights, Company ranking, competitive landscape, Recent Developments, Market Dynamics, and Emerging Trends Segments Covered By Crane Type (Tower Cranes, Mobile Cranes, Overhead Cranes), By End-Use Industry (Construction, Energy, Manufacturing, Logistics & Warehousing, Others) Competitive Landscape ZPMC, XCMG, Zoomlion Heavy Industry, Sany Heavy Industry, Inovance Technology, Liebherr (China), Manitowoc Cranes China, Konecranes China, Terex China, Tadano China Customization Scope Customization for segments will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited Users and Printable PDF)  China Autonomous Crane MarketPublished date: Nov 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
China Autonomous Crane MarketPublished date: Nov 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- ZPMC
- XCMG
- Zoomlion Heavy Industry
- Sany Heavy Industry
- Inovance Technology
- Liebherr (China)
- Manitowoc Cranes China
- Konecranes China
- Terex China
- Tadano China










