Global Capability Centers Market By Function / Capability (Information Technology (IT) and Digital Services, Engineering / ER&D, Business Process Management (BPM), Knowledge Process Outsourcing (KPO)), By Engagement Model (Captive (Self-Build)/In-house, Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT), Hybrid Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT)), By Organization Size (Large Enterprises, Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)), By Industry Vertical (Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI), Telecom and IT, Healthcare and Life Sciences, Manufacturing, Automotive and Industrial, Retail and Consumer Goods, Other Industry Verticals), By Regional Analysis, Global Trends and Opportunity, Future Outlook By 2025-2034
- Published date: Dec. 2025
- Report ID: 171056
- Number of Pages: 261
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
- Report Overview
- Top Market Takeaways
- Function / Capability Analysis
- Engagement Model Analysis
- Organization Size Analysis
- Industry Vertical Analysis
- Key Reasons for Adoption
- Key Benefits
- Key Usage
- Emerging Trends
- Growth Factors
- Key Market Segments
- Regional Analysis
- Opportunities & Threats
- Competitive Analysis
- Future Outlook
- Recent Developments
- Report Scope
Report Overview
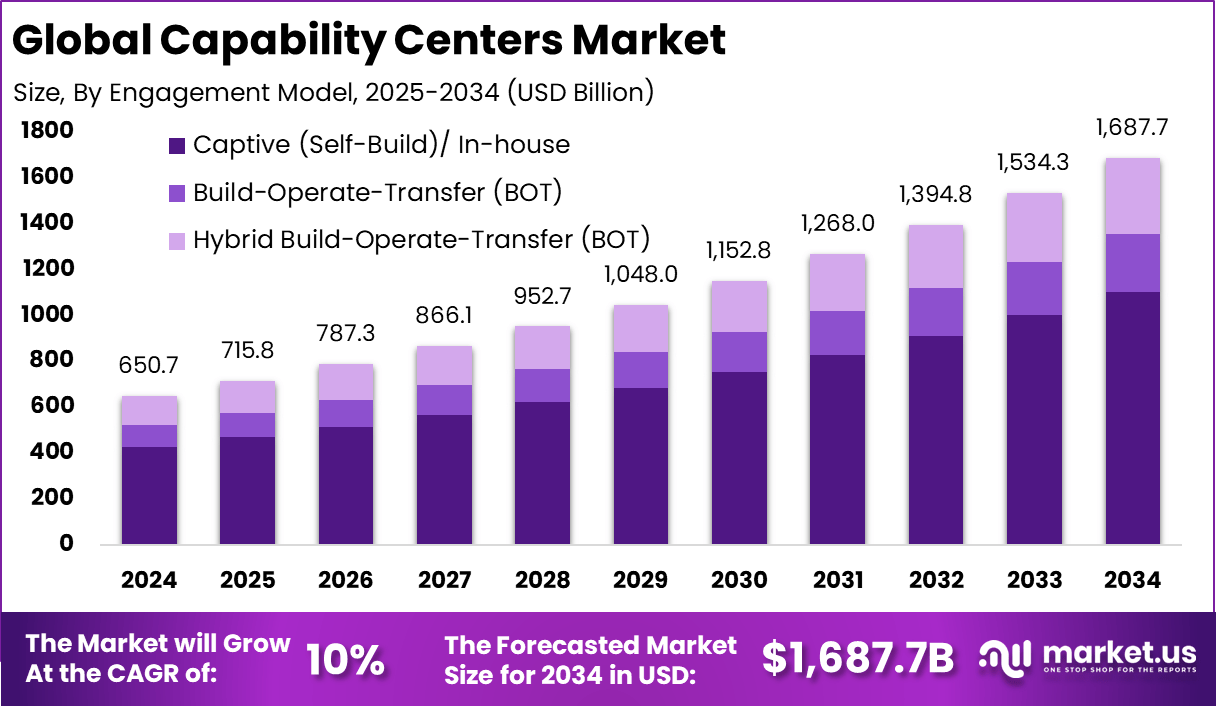
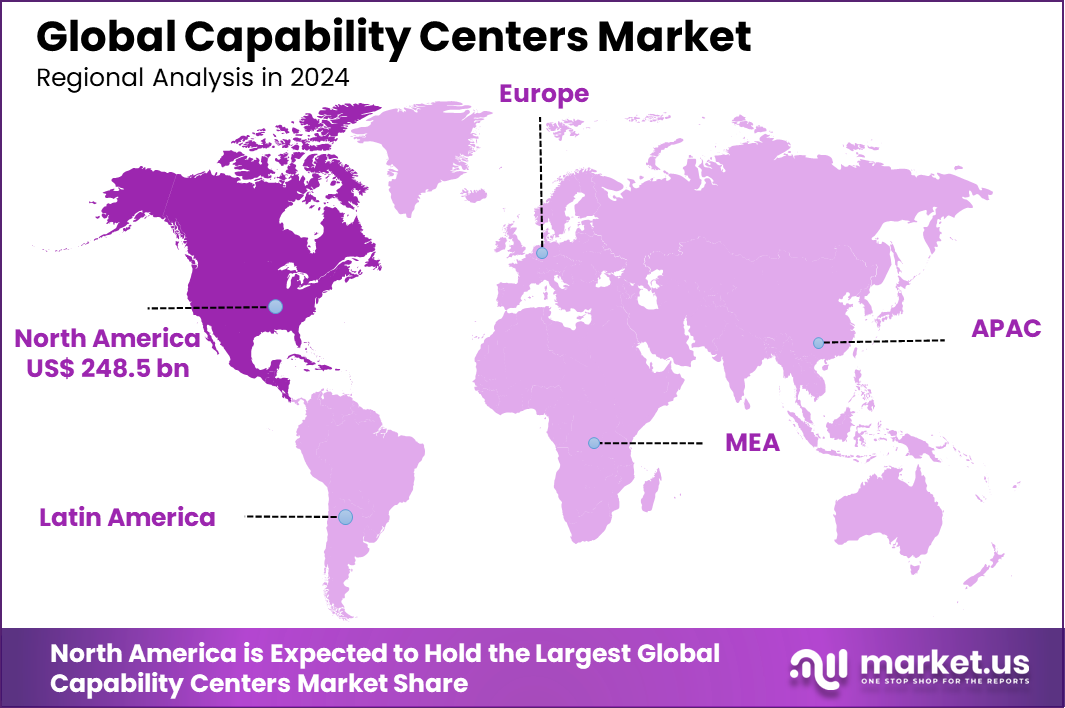
The Global Capability Centers Market generated USD 650.7 billion in 2024 and is predicted to register growth from USD 715.8 billion in 2025 to about USD 1,87.7 billion by 2034, recording a CAGR of 10% throughout the forecast span. In 2024, North America held a dominan market position, capturing more than a 38.2% share, holding USD 248.56 Billion revenue.
The capability centers market refers to centralized units established by organizations to deliver specialized skills, processes, and services at scale. These centers support functions such as information technology, finance, analytics, engineering, customer operations, and research activities. Companies use capability centers to improve efficiency, consistency, and operational control. The market has evolved as organizations seek structured models to support global operations.
Demand for capability centers is increasing among multinational enterprises. Companies seek scalable models to support growth without increasing complexity. Capability centers offer predictable service levels across functions. This makes them attractive for long-term planning. Demand is also growing from organizations undergoing digital transformation. Centralized expertise helps manage technology upgrades and process changes.
Top Market Takeaways
- By function or capability, information technology and digital services accounted for 45.7% of the capability centers market, as companies set up centers for software development and cloud services.
- By engagement model, captive or in-house centers held 65% share, chosen by firms for full control over operations and data.
- By organization size, large enterprises captured 72.5%, using centers to handle complex global IT needs and cost savings.
- By industry vertical, banking, financial services, and insurance led with 38.4%, setting up centers for secure tech support and compliance.
- North America had 38.2% of the global market, with the U.S. at USD 279.03 billion in 2025 and growing at a CAGR of 8.4%.
Function / Capability Analysis
Information technology and digital services account for 45.7%, showing that capability centers are primarily focused on core IT functions. These centers support software development, infrastructure management, cybersecurity, and digital transformation initiatives. Organizations rely on IT-focused capability centers to maintain operational continuity. Digital services also enable faster innovation cycles.
The dominance of this function is driven by growing dependence on technology across business operations. Enterprises centralize IT capabilities to improve efficiency and reduce costs. Digital service teams support cloud adoption and system modernization. This makes IT capability centers a strategic asset.
Engagement Model Analysis
Captive and in-house models hold 65.4%, reflecting strong preference for internal ownership of capability centers. Organizations choose this model to maintain full control over processes, data, and talent. In-house centers align closely with corporate goals. This model supports long-term capability building.
Adoption of captive centers is driven by security and compliance needs. Enterprises prefer internal teams for sensitive operations and intellectual property protection. In-house models also support stronger cultural alignment. These factors sustain high adoption levels.
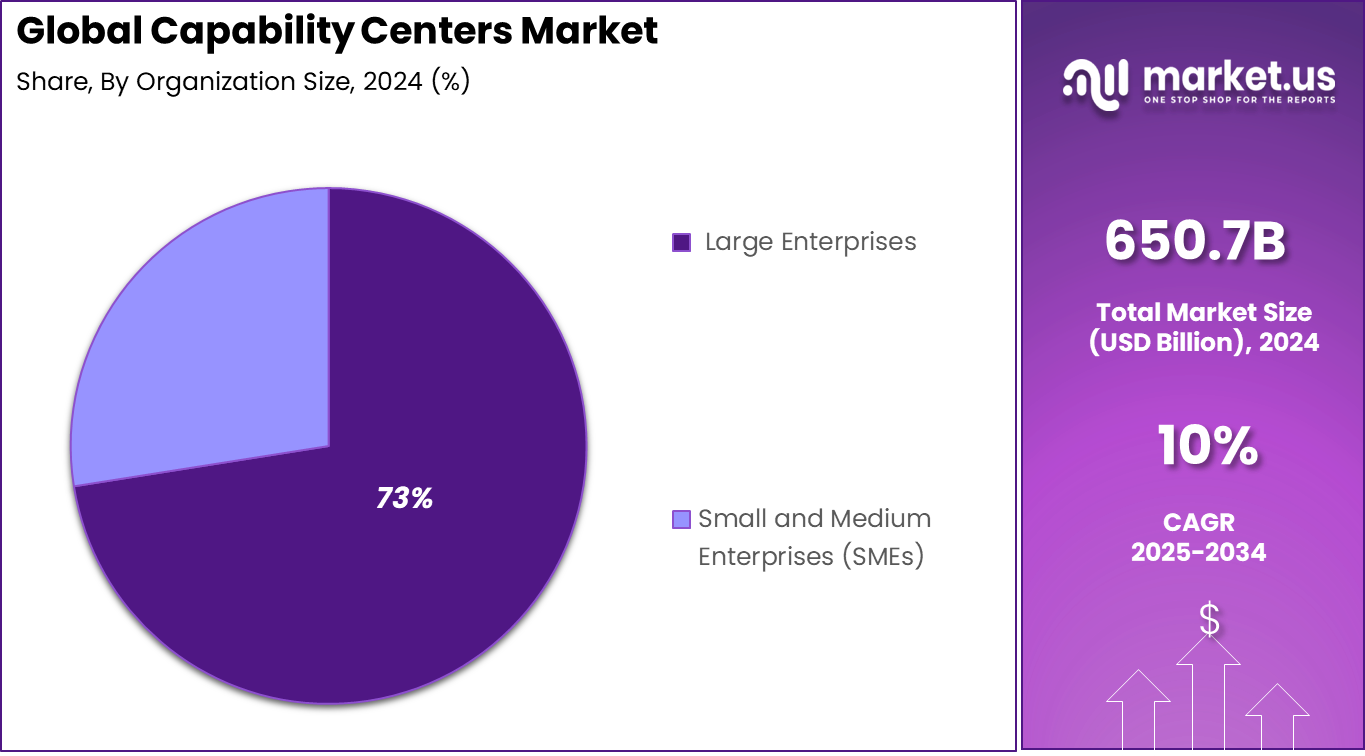
Organization Size Analysis
The Large enterprises represent 72.5%, highlighting their dominant role in the capability centers market. These organizations operate at scale and require dedicated teams to manage complex functions. Capability centers help standardize processes across regions. They also support centralized governance.
Adoption among large enterprises is supported by higher budgets and global operations. Centralized centers improve coordination and cost efficiency. Large organizations use capability centers to support growth strategies. This continues to drive demand.
Industry Vertical Analysis
The BFSI sector holds 38.4%, making it the leading industry vertical for capability centers. Financial institutions use these centers to support IT operations, analytics, compliance, and customer services. High transaction volumes require stable and secure systems. Capability centers help manage these needs.
Growth in BFSI adoption is driven by regulatory requirements and digital banking expansion. Institutions rely on centralized teams for risk management and process control. Capability centers support operational resilience. This makes them critical for BFSI organizations.
Key Reasons for Adoption
Advanced digital tools are increasingly adopted within capability centers. Cloud platforms support centralized operations and collaboration. Automation tools improve process efficiency and accuracy. These technologies enable scalable service delivery. Data analytics and workflow management systems are also widely adopted. They help monitor performance and resource utilization.
Real-time reporting improves decision making. Technology adoption enhances operational transparency. One key reason for adoption is improved control over critical business processes. Capability centers operate under enterprise governance frameworks.
This ensures compliance and consistency. Organizations benefit from predictable outcomes. Another reason is knowledge retention and capability building. Internal centers allow organizations to develop long-term expertise. Skills remain within the enterprise rather than external vendors. This supports strategic resilience.
Key Benefits
- Better alignment between business goals and operational execution is achieved through direct ownership
- Higher productivity is supported by dedicated teams with deep domain knowledge
- Improved data security and regulatory compliance are maintained within controlled environments
- Long term cost optimization is realized through stable talent models and reduced vendor dependency
- Stronger innovation culture is developed through continuous learning and internal collaboration
Key Usage
- Information technology development, maintenance, and digital transformation programs
- Data analytics, artificial intelligence, and business intelligence operations
- Finance, accounting, and risk management support functions
- Customer experience management and process optimization activities
- Research, product engineering, and innovation support across business units
Emerging Trends
Key Trend Description AI ML Centers Boom Global capability centers are expanding AI and data science teams to support smart and digital products. Tier Two City Spread New centers are opening in cities like Pune and Hyderabad to access fresh and skilled talent. Cloud Native Focus Organizations adopt cloud native tools to enable faster and more flexible work from any location. Startup Like Speed GCCs operate with startup style agility, local leadership, and independent innovation models. Green ESG Push Sustainability goals and eco friendly technologies are integrated into daily operations. Growth Factors
Key Factors Description Talent Pool Deep India offers a large base of skilled professionals across technology and AI domains. Cost Savings High Operating costs remain significantly lower compared to the U.S. and European markets. Government Boost Supportive policies encourage the expansion of global capability centers nationwide. Digital Shift Need Enterprises increase demand for AI and cloud solutions to drive business transformation. Job Growth Fast Rapid expansion of GCCs contributes strongly to employment generation and economic growth. Key Market Segments
By Function / Capability
- Information Technology (IT) and Digital Services
- Engineering / ER&D
- Business Process Management (BPM)
- Knowledge Process Outsourcing (KPO)
By Engagement Model
- Captive (Self-Build)/ In-house
- Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT)
- Hybrid Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT)
By Organization Size
- Large Enterprises
- Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
By Industry Vertical
- Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI)
- Telecom and IT
- Healthcare and Life Sciences
- Manufacturing, Automotive and Industrial
- Retail and Consumer Goods
- Other Industry Verticals
Regional Analysis
North America held a 38.2% share of the Capability Centers Market, reflecting the region’s strong enterprise adoption of global and regional capability centers. The market growth has been supported by the presence of large multinational corporations that continue to centralize critical functions such as IT services, digital transformation, analytics, finance, and customer operations.
Capability centers in North America are increasingly positioned as strategic hubs rather than cost centers, with a strong focus on innovation, automation, and advanced analytics. The region benefits from a mature business environment, strong governance frameworks, and high demand for skilled professionals.
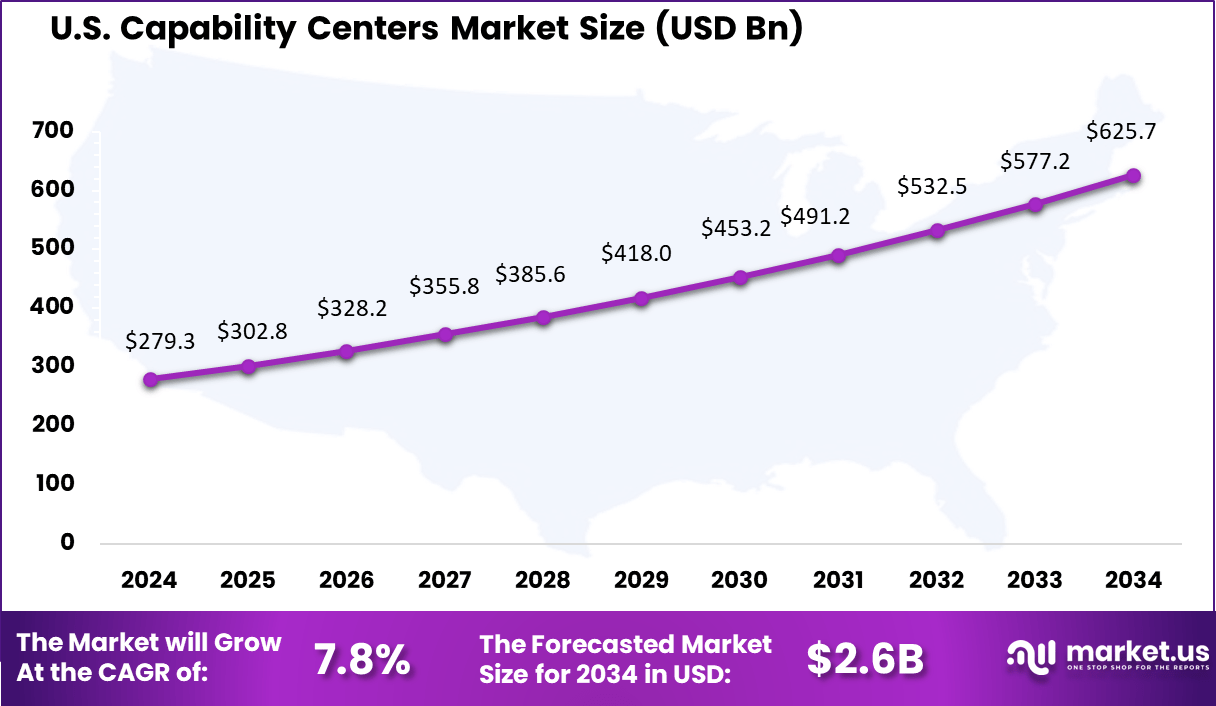
The U.S. Capability Centers Market was valued at USD 279.03 Bn and is expanding at a CAGR of 8.4%, indicating sustained investment by large enterprises. The U.S. market has been shaped by strong demand from sectors such as BFSI, technology, healthcare, retail, and manufacturing.
Companies are increasingly using capability centers to support digital product development, cybersecurity, risk management, and enterprise transformation initiatives. The availability of advanced infrastructure and a strong innovation ecosystem continues to support market expansion.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherlands
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Opportunities & Threats
The Capability Centers market continues to create strong opportunities as enterprises look to build long term internal expertise and reduce reliance on external vendors. Organizations are increasingly using these centers to support digital transformation, data analytics, cloud operations, and advanced engineering functions. The rising focus on cost efficiency, process control, and faster innovation cycles is supporting steady expansion of capability centers across multiple industries.
Additional opportunities are emerging from the growing adoption of automation, artificial intelligence, and advanced analytics within capability centers. These technologies allow enterprises to improve productivity, standardize processes, and deliver higher value outcomes to global business units. Expanding operations in emerging talent hubs is also supporting access to skilled professionals at competitive costs, which further strengthens the business case for capability centers.
One of the major threats facing the Capability Centers market is increasing competition for skilled talent, especially in areas such as digital engineering, cybersecurity, and data science. High attrition rates and rising wage pressures can affect operational stability and increase long term costs for enterprises running large centers. Another key threat comes from changing regulatory and compliance requirements across different regions.
Competitive Analysis
Accenture, IBM, Tata Consultancy Services, Infosys, Wipro, and HCL Technologies lead the capability centers market by helping global enterprises set up and scale global capability centers for technology, analytics, and business operations. Their services cover center design, talent sourcing, digital transformation, and governance models. These companies focus on operational efficiency, access to skilled talent, and long term value creation.
Tech Mahindra, Cognizant, Capgemini, DXC Technology, Deloitte, EY, PwC, and EPAM Systems strengthen the market with consulting led capability center services. Their offerings support advanced engineering, cloud, AI, and industry specific operations. These providers emphasize agile delivery, domain expertise, and integration with global business strategies. Increasing adoption of hybrid delivery models and nearshore centers supports wider market growth.
ANSR Consulting, Zensar Technologies, LTTS, Globant, Luxoft, Nagarro, Persistent Systems, UST Global, Mindtree, Virtusa, and other players expand the landscape with flexible and niche focused capability center solutions. Their services cater to digital native firms and mid sized enterprises. These companies focus on speed of setup, scalability, and specialized skills. Growing enterprise focus on resilience and distributed operations continues to drive steady expansion of the capability centers market.
Top Key Players in the Market
- Accenture plc
- IBM Corporation
- Tata Consultancy Services Limited
- Infosys Limited
- Wipro Limited
- HCL Technologies Limited
- Tech Mahindra Limited
- Cognizant Technology Solutions Corporation
- Capgemini SE
- DXC Technology Company
- ANSR Consulting Inc.
- Zensar Technologies Limited
- Larsen and Toubro Technology Services Limited
- Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu Limited
- Ernst and Young Global Limited
- PricewaterhouseCoopers International Limited
- EPAM Systems Inc.
- Globant S.A.
- Luxoft Holding Inc.
- Nagarro SE
- Persistent Systems Limited
- UST Global Inc.
- Mindtree Limited
- Virtusa Corporation
- Others
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the Capability Centers market is expected to remain positive as global companies look to centralize expertise and improve operational efficiency. These centers are being used to support core functions such as technology, analytics, finance, engineering, and customer operations across multiple regions.
Growing demand for skilled talent, cost control, and standardized processes is supporting wider adoption. Over time, capability centers are expected to move beyond cost focused roles and take on higher value activities, including innovation, digital transformation, and strategic decision support.
Opportunities lie in
- Expansion of advanced digital skills: Centers can focus on areas such as AI, data analytics, and automation to support enterprise wide transformation.
- Support for global business scalability: Centralized teams can help organizations expand into new markets with consistent processes and governance.
- Shift toward innovation and R&D roles: Capability centers can act as hubs for product development, process improvement, and experimentation.
Recent Developments
- September, 2025 – Accenture was named a Leader in ISG’s Provider Lens Global Capability Center Services 2025 report, with its GCC transformation services emphasizing AI-led innovation, talent upskilling and lean operations across India hubs.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 650.7 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 1,687.7 Bn CAGR(2025-2034) 10% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue forecast, AI impact on Market trends, Share Insights, Company ranking, competitive landscape, Recent Developments, Market Dynamics and Emerging Trends Segments Covered By Function / Capability (Information Technology (IT) and Digital Services, Engineering / ER&D, Business Process Management (BPM), Knowledge Process Outsourcing (KPO)), By Organization Size (Large Enterprises, Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)), By Industry Vertical (Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI), Other Industry Verticals) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of Latin America; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Accenture plc, IBM Corporation, Tata Consultancy Services Limited, Infosys Limited, Wipro Limited, HCL Technologies Limited, Tech Mahindra Limited, Cognizant Technology Solutions Corporation, Capgemini SE, DXC Technology Company, ANSR Consulting Inc., Zensar Technologies Limited, Larsen and Toubro Technology Services Limited, Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu Limited, Ernst and Young Global Limited, PricewaterhouseCoopers International Limited, EPAM Systems Inc., Globant S.A., Luxoft Holding Inc., Nagarro SE, Persistent Systems Limited, UST Global Inc., Mindtree Limited, Virtusa Corporation, Others Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three license to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Accenture plc
- IBM Corporation
- Tata Consultancy Services Limited
- Infosys Limited
- Wipro Limited
- HCL Technologies Limited
- Tech Mahindra Limited
- Cognizant Technology Solutions Corporation
- Capgemini SE
- DXC Technology Company
- ANSR Consulting Inc.
- Zensar Technologies Limited
- Larsen and Toubro Technology Services Limited
- Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu Limited
- Ernst and Young Global Limited
- PricewaterhouseCoopers International Limited
- EPAM Systems Inc.
- Globant S.A.
- Luxoft Holding Inc.
- Nagarro SE
- Persistent Systems Limited
- UST Global Inc.
- Mindtree Limited
- Virtusa Corporation
- Others










